The question of whether a brain tumor can be treated is acute for those who have been diagnosed with it. Brain cancer is a serious disease, the causes of which are still not fully understood. It is most common in women and appears in adulthood. The main physiological symptoms are associated with increased intracranial pressure and the impact of the cancer on other organs. The patient often feels dizzy, loses orientation and balance. Severe headaches appear in the first half of the day and towards night. Painful sensations are accompanied by vomiting, most often before the first meal, as well as spontaneous urges throughout the day.
Diagnosis before treatment for brain cancer
Diagnostic methods for detecting brain cancer include:
- An examination by a doctor, during which the patient performs a series of tasks. The health worker will be able to determine from them violations in the coordination and motor skills of the applicant. A neurologist must check the tendon reflex. In addition, a complete medical history is collected.
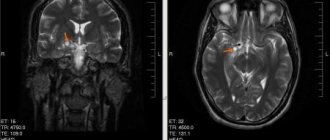
- MRI with contrast helps to detect the presence of a tumor at an early stage, view the location and prescribe timely treatment.
- A biopsy of brain tissue can reveal not only the presence of a tumor, but also the stage of the cancer. But a biopsy is not always possible due to the difficult-to-reach location of the tumor.
- X-rays also rely on the injection of a contrast agent into the brain. The images can reveal the appearance of a tumor by the displayed vessels.
Diagnostics
The first stage of diagnosing the disease is a consultation with a neurologist. The doctor examines the motor function of the eyes, hearing, tendon reflexes, the level of sensitivity of the skin and sense of smell, coordination of movements, muscle tone, balance. If there is a suspicion of the presence of a neoplasm, instrumental diagnostic measures are prescribed.
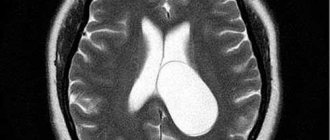
Magnetic resonance imaging
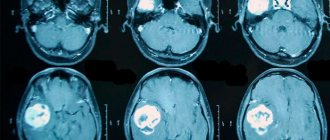
Magnetic resonance imaging is the most reliable method for detecting brain tumors. The appearance of the neoplasm in the image is presented in the form of a three-dimensional image and in the thinnest section. At the initial stage of development of the disease, the formation in the picture appears in the form of edema.
The diagnostic measure is capable of identifying even a small neoplasm, as well as a formation whose location is near the bone or brain stem.
CT scan
Computed tomography is a less informative method. Using CT, you can determine the exact location of the tumor, as well as accompanying symptoms, such as hematoma and swelling.
Computed tomography is one of the main studies necessary to detect a brain tumor
Positron emission tomography (PET)
Radioactive labeled sugar is delivered to the brain area, which makes it possible to determine the state and activity of the brain: the absorption of glucose by pathological cells occurs faster than normal cells. Using PET, cancer cells are detected at any stage of pathological development.
Laboratory diagnostics
One of the most effective diagnostic measures carried out in the laboratory is a blood test for tumor markers. There are specific tumor markers, the presence of which can accurately determine the type of tumor.
A biopsy is also performed - the collection of biological material from the neoplasm, which is then subjected to microscopic examination. This allows you to determine the malignancy or benignity of the pathology. The study also provides answers about the type of tumor and its structure.
Average lifespan of patients with brain cancer
To assess the patient’s physical condition and the development of oncology, doctors use the concept of “five-year survival rate.” In this case, all patients with this diagnosis are assessed, regardless of the course of treatment and therapy. With successful therapy, patients will live much more than five years, but most of them will have to undergo ongoing medical examinations and procedures.
According to experts, the survival rate for various types of brain is 35%. In patients with malignant cancer, this percentage does not exceed 5%.
How successful can treatment be for stage 3 cancer?
Before starting treatment for stage 3 cancer, a person is usually interested in what results he can expect: is it possible to cure the disease, or is the goal of therapy only to reduce symptoms? If it is impossible to finally defeat the disease, is it possible to prolong life, and if so, by how much?
All these questions cannot be answered unambiguously. Because different types of cancer have different clinical course and different prognosis. Even tumors of the same organ often differ in the degree of aggressiveness. In addition, stage 3 is a very loose concept. In many oncological diseases, substages A, B, C, and often A1, A2, etc. are distinguished.
Thus, the prognosis for stage 3 cancer for an individual patient can be very variable. But we can give average figures from medical statistics to understand how aggressive a particular type of cancer is. Some tumors, if detected at stage 3, are successfully treated, others are highly likely to lead to the death of a person within the first year after diagnosis.
Most stage 3 cancers are locally advanced cancers. For this form of the disease, the five-year survival rate is as follows:
- breast cancer - 85%;
- cervix - 56%;
- endometrium - 70%;
- ovaries - 75%;
- prostate - 100%;
- intestines - 71%;
- gallbladder - 26%;
- pancreas - 12%;
- nasopharynx - 70%;
- adrenal glands - 56%;
- melanoma - 64%.
The most dangerous tumors that are practically not treated at stage 3: cancer of the pancreas, liver, biliary tract and gallbladder, glioblastoma. At the same time, some neoplasms are much less aggressive. It is possible to cure or significantly prolong life for prostate, breast, and colon cancer.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation with an oncologist now
Brain cancer treatment
Effective treatment of brain cancer requires the participation of doctors of various specializations. The therapist, oncologist, radiologist, neurologist interact, and the participation of a neurosurgeon and rehabilitation specialist is also necessary. The whole process begins with a diagnosis in the therapist’s office, and after the appointment, an examination by other specialists and examinations are already scheduled.
The plan of treatment procedures directly depends on the patient’s age group. There are three of them:
- junior (up to 19 years old);
- average (yes 55 years);
- older.
When planning a course of treatment, great importance is given to the type and location of the tumor, as well as the general physical condition of the patient.
Radiation therapy, surgery, and radiotherapy are used to treat a brain tumor. Removing a cancerous tumor through surgery is the most reliable method of treatment. But the difficult-to-reach location of the tumor sometimes makes it impossible to perform surgery. Also, surgical intervention is not used at the third and fourth stages of the disease. Firstly, this carries great risks for the patient’s health, and secondly, it is ineffective, since by this period the cancer cells have already affected vital organs and sections of the brain, and it is impossible to completely remove the tumor.
Symptomatic treatment
The following groups of medications significantly alleviate the patient’s condition, but do not eliminate the main cause of the disease. Glucocortecosteroids help reduce cerebral symptoms. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs help relieve pain. Narcotic analgesics are used for severe pain, vomiting and psychomotor agitation.
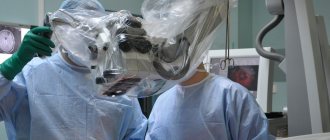
Surgery
This is the most effective way to treat cancer. The neurosurgeon excises the tumor through healthy tissue. It all depends on the location and stage of the tumor. In practice, the operation is effective only at stage 1. At subsequent stages of the disease, treatment tactics are different. In particular, radiation therapy is used.
Radiation therapy
Such therapy is necessary to stop the growth of pathological cells. It is also carried out before and after surgery.
Chemotherapy
Typically, this treatment is prescribed when the tumor is at the last stage and is inoperable. The dose and type of specific drugs for each patient are calculated individually.
Treatment with surgery
Surgical removal of a brain tumor is a reliable and effective method of treating cancer in the early stages. It is most effective for benign tumors. But there is great danger in brain surgery, and the surgeon cannot remove part of the tissue closest to the tumor in order to prevent relapse and spread of cancer cells.
Psychosomatics of a brain tumor
Surgical interventions for brain diseases must be carried out with maximum precision. The slightest mistake and a millimeter of damaged tissue can cost the patient his life. In severe, late stages of the disease, surgery is ineffective. Pathological processes are already spreading, and it is simply impossible to remove parts of the infected cells. Palliative therapy helps reduce the pressure that a cancerous tumor puts on nearby organs and tissues. After the operation, the patient undergoes a course of drug treatment and chemotherapy, which stops the brain tumor; whether he is treated or not cannot be answered unequivocally.
In the first and second stages of a benign tumor, the symptoms of brain cancer are completely eliminated. This suggests that if detected early, the prognosis for the patient will be more than favorable. If the operation is complicated by the difficult-to-reach location of the tumor, then a more accurate study will be required that will determine the location of the tumor. To classify the stage of cancer, your doctor will take a biopsy of your brain tissue.
Tissue damage during surgery can cause irreversible consequences in the body. To prevent negative manifestations, the method of meteoric radiosurgery is used. This is a high-precision surgical intervention based on the radiation of gamma rays or X-ray irradiation in high doses. Is it possible to cure a brain tumor without consequences? This effect allows you to destroy cancer. Healthy brain tissue is hardly affected or is damaged with minimal, insignificant effect. This technique can also be applied depending on the location of the tumor and the stage of its development. Such treatment minimizes the risk of injury from surgery and complications, and also reduces rehabilitation after the intervention.
Before the operation, doctors carry out drug therapy, which consists of:
- Anticonvulsants. They are used in the second and subsequent stages of cancer, and save from epileptic seizures.
- Steroid anti-inflammatory drugs. Reduce the pressure of the neoplasm on neighboring tissues. The most commonly used drug is descamethasone, a proven and reliable remedy.
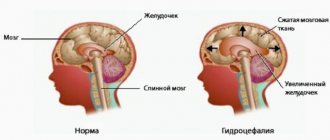
To reduce increased intracranial pressure, shunting can be used, during which excess cerebrospinal fluid is removed through a catheter.
Treatment approaches
The treatment plan is selected individually, taking into account the histological type of the tumor, its size and the general condition of the patient. Treatment consists of conventional methods (surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy), symptomatic medications, and modern targeted medications.
Surgical
If the tumor is located in an anatomically accessible location, and the procedure for its removal does not cause irreversible neurological damage, the first stage is neurosurgery. It is carried out to maximize the removal of tumor masses, reduce compression of the brain, eliminate edema and intracranial hypertension. The material obtained during the operation is used for histological and molecular studies to select the next therapeutic steps.
Radical interventions involve complete excision of the tumor, and in palliative neurosurgery the maximum amount of pathological tissue is removed to improve the patient’s condition.
For cerebral formations, classical operations are performed using surgical microscopes, as well as modern variants of stereotactic surgery, if the size of the pathology allows such treatment.
For metastatic lesions in the brain that have arisen against the background of oncopathology of another localization, surgery is prescribed in the presence of no more than 3 neoplasms. The diffuse process of metastasis and the involvement of vital centers are contraindications to neurosurgical intervention. These patients may undergo bypass surgery to reduce symptoms.
Chemotherapy
This type of treatment is most often performed for high-grade astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, neuronal and embryonal neoplasms. In the treatment of patients with brain oncology, 3 modes of administration of chemotherapy drugs are used:
- Neoadjuvant. Cytostatics are prescribed in the preoperative period to reduce the volume of tumor cells and transform the formation into a resectable form.
- Adjuvant. The use of medications in the postoperative period to destroy remaining malignant cells and prevent relapse of the disease.
- Independent. In case of inoperable brain cancer, chemotherapy drugs are prescribed as the only method of treatment, or in combination with targeted agents.
The selection of chemotherapy drugs is based on histological analysis of biopsies or resected tumor material. For treatment, temozolomide, vincristine, irinotecan, cisplatin, etoposide, and methotrexate are used.
In the treatment of brain cancer, there is a problem of drug resistance. To overcome it, the principle of polychemotherapy is used - the simultaneous administration of several medications with different mechanisms of action. Another way to improve response to treatment is direct delivery of chemotherapy drugs via the intrathecal or intraventricular route.
The response to chemotherapy is assessed after completion of the course:
- complete regression - disappearance of the tumor;
- partial regression - reduction in the volume of pathological tissues by more than 50%;
- stabilization - reduction in the size of education to less than 50%;
- progression - tumor enlargement by 25% or more.
Radiotherapy
Radiation begins 2-8 weeks after surgery. If the patient has contraindications to surgery, radiation therapy is the leading method of treatment, along with polychemotherapy. It can be performed even without obtaining biopsy results (if it is impossible to take a biopsy due to the complex anatomical location). Another indication for radiation treatment is recurrence of a primary cerebral tumor.
Radiotherapy has a number of contraindications:
- location of atypical cells in the brain stem, hypothalamus and vital subcortical structures;
- presence of cerebral edema or dislocation syndrome;
- intracranial hemorrhage;
- active purulent-inflammatory foci;
- incurable condition of the patient;
- acute psychosis, inability to control the patient’s behavior.
The size of the irradiation zone is selected taking into account the diameter and number of tumor foci and the degree of malignancy of the cells. Several types of radiation therapy are used: 2-dimensional conventional (2DRTC), 3-dimensional conformal (3DCRT), intraoperative (IORT), image-guided (IGRT).
For highly malignant gliomas, simultaneous chemotherapy and radiation therapy are prescribed. In such a situation, irradiation is carried out in a hypofractionated or classical mode, supplemented with the drug temozolomide in a standard dosage.
New directions of therapy
Modern methods are used for cerebral neoplasms:
- Bevacizumab . A monoclonal antibody to vascular endothelial growth factor reduces tumor vascularization and inhibits its growth. Used in the treatment of cancer of 3-4 degrees of malignancy. It is most effective when used in combination with temozolomide and irinotecan.
- Larotrectinib . A universal drug that is used regardless of the type of pathology, if it contains NTRK proteins, which indicate the presence of a TRK gene mutation.
- CAR T cell therapy . This approach uses the patient's own T cells, which are isolated from the blood, modified, and injected into the patient's body. This increases the ability of cells to destroy tumor tissue. A combination of CAR T and immune checkpoint inhibitors is being considered in the future.
Recently, a personalized vaccine for immunotherapy of patients with glioblastoma multiforme was developed in Belgium. It is based on the activation of the macrophage immune system to destroy pathological tissue. Studies show that its use can stabilize the condition or reduce the growth of the tumor.
Symptomatic treatment
The following medications are used simultaneously with a course of specific therapy:
- corticosteroid hormones to eliminate cerebral edema;
- centrally acting antiemetics;
- narcotic and non-narcotic analgesics;
- tranquilizers, mood stabilizers and other groups of psychotropic drugs;
- preparations of digestive enzymes to prevent cachexia;
- antibacterial and antiviral agents for infectious complications of treatment;
- immunomodulators for correction of iatrogenic immunosuppression;
- ready-made concentrates for enteral nutrition or medicinal mixtures for parenteral administration of nutrients.
To improve the quality of life, patients are prescribed comprehensive rehabilitation. Classes with speech therapists, tutors, and psychologists are needed to restore cognitive function, stabilize the emotional background, and eliminate depressive disorders that arise against the background of a serious illness. Specially selected exercise therapy, mechanotherapy, and exercises in the pool help eliminate residual disorders of motor activity and coordination.
Dispensary observation
After achieving remission, the patient is prescribed an individual examination plan with an oncologist to monitor the situation, assess the neurological status and timely detect relapses. The standard frequency of examination in the first 2 years after cancer treatment is once every 3 months, then once every six months for another 2 years, and if the condition is satisfactory, they switch to annual preventive visits.
During a medical examination, a complex of laboratory and instrumental studies is carried out:
- clinical blood test;
- biochemical blood test with liver tests;
- MRI of the brain.
If the patient experiences alarming symptoms: headaches, sensory or motor impairment, behavioral disorders, he is prescribed an emergency examination. In this case, a set of neuroimaging methods is performed to exclude or confirm relapse of oncology.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy in the treatment of brain tumors is necessary in the following cases: the patient cannot undergo surgery for health reasons or to prevent relapse after surgery. Chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system, pathologies in combination with surgery can cause irreparable harm to health. Surgery will not produce results in the later stages of the disease, and it can also be dangerous. The only effective method remains radiation therapy. This technique helps prevent the oncological process after removal of a cancerous tumor.
For each patient, the radiation dose is prescribed by the doctor individually. The impact on the tumor is carried out locally so that as little as possible of the radiation affects the tissues adjacent to the tumor. When prescribing radiation therapy, the specialist takes into account the size of the tumor, stage and location.
There are two types of such treatment:
- Brachytherapy. The technique is intended for patients undergoing inpatient treatment. Special substances are injected into the tumor to act on it from the inside. The dose of the radioactive isotope is precisely calculated to affect only the neoplasm and leave healthy cells unharmed.
- External radiation therapy. The course lasts several weeks with a break of 2 days. During treatment, the patient receives a large dose of radiation, which gradually kills the tumor.
Chemotherapy cannot be considered a panacea for cancer. Therefore, the question: whether brain cancer can be cured remains open. Despite its effectiveness, such an effect almost never excludes a negative impact on other human organs. When drawing up an individual course of treatment, the doctor also prescribes medications. These can be antibiotics, antimetabolites, drugs of the alkylating group. Irradiation is carried out intermittently, during which a specialist can examine the progress of treatment. The main danger of chemotherapy is the effect on the circulatory system and digestive tract.
Radiation therapy for brain tumors
Signs at different stages
Most cancers are characterized by a long asymptomatic course and a gradual onset. At the same time, the manifestations of primary and metastatic neoplasms are identical, and they can be differentiated only with detailed laboratory and instrumental diagnostics. Symptoms of brain tumors in men and women do not have clinically significant differences.
Early stage brain cancer
The first manifestation of the disease in most patients is focal neurological symptoms, and headaches and cerebral disorders occur at later stages.
Early focal symptoms include:
- when the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex is damaged, sloppiness and lack of initiative develop, the person loses interest in work, hobbies, communication with family and friends;
- involvement of the parietal lobe in the process is manifested by local disturbances in skin sensitivity, writing and reading, inability to find a specific place (geographical agnosia), failure to recognize familiar objects when palpating them (agnosia);
- pathology in the temporal cortex is manifested by loss of the ability to understand spoken language and music, tinnitus and auditory hallucinations;
- damage to the nervous structures of the occipital lobe is manifested by loss of visual fields, inability to recognize the faces of friends, visual illusions such as micropsia or macropsia;
- cerebellar tumors are manifested by unsteadiness of gait, clumsiness and sweeping movements, problems with fine motor skills, and inability to perform the finger-nose test;
- neoplasms in the structures of the limbic system are accompanied by memory impairment, a decrease or pathological change in the emotional background, loss of smell, and deterioration in learning abilities.
An important manifestation of cancer pathology is headache. In most cases, it is diffuse in nature and clinically resembles a tension headache, so patients tend to ignore it and self-medicate with analgesics for a long time.
Headache as a sign of cancer has distinctive features:
- the most severe pain occurs in the morning;
- the localization and nature of sensations may change;
- occurs more often in children and young patients;
- accompanied by dizziness. nausea and vomiting.
In the early stages of cerebral tumors, general symptoms may occur that indicate cancer intoxication. These include increased fatigue, nonspecific pain in bones and muscles, pale skin and shortness of breath during exercise. Against the background of decreased immunity, a person becomes susceptible to viral, bacterial and fungal infections.
Late stage of oncopathology
If the pathology is not diagnosed in time, it begins to increase in size, squeezing surrounding tissues or growing into them. This is manifested by intracranial hypertension, and with the rapid growth of the tumor, mass effect and dislocation syndrome are possible. In this case, the medulla oblongata and cerebellum are wedged into the foramen magnum, and vital centers suffer.
In later stages, symptoms of a brain tumor include painful, paroxysmal or constant headaches. These are deep and intense sensations that sometimes become bursting. General cerebral signs are supplemented by cerebral vomiting, which is not associated with food and does not have typical precursors. There is also double vision, episodes of visual impairment, and depression of consciousness.
As the pathology progresses, specific symptoms arise that help establish the type and location of the pathology:
- Diseases in the frontal cortex are characterized by memory impairment, decreased concentration, and deterioration of mental performance. Epileptiform Jacksonian seizures occur, and primitive reflexes characteristic of the newborn period return.
- Oncopathology of the temporal lobe is characterized by the phenomena of depersonalization (alienation of one’s body, thoughts and actions), severe emotional disorders and behavioral disorders, and complex multimodal hallucinations.
- Acoustic neuroma causes causeless hearing loss and periodic tinnitus. Damage to the labyrinth structures causes episodes of dizziness, coordination and balance disorders.
- When oncopathology is localized in the posterior cranial fossa, patients experience irritability, gait disturbances, ataxia, and repeated painful vomiting.
- For lesions of the supratentorial region, convulsions, paralysis and paresis of half the body, speech, vision and hearing disorders are typical.
A typical manifestation of cerebral oncopathology is convulsive seizures, which occur both during the manifestation of the disease and in its later stages. This symptom often develops with supratentorial neoplasms. Convulsions are preceded by an aura, by the nature of which the doctor assumes the topic of the lesion.
With cerebral damage, patients develop polymorphic mental disorders. They manifest themselves as visual, auditory and olfactory hallucinations, episodes of confusion, and persistent affective disorders.
If a patient develops a metastatic tumor, its manifestations overlap with the clinical picture of the primary malignant neoplasm. This makes diagnosis difficult, since against the background of a general serious condition, a person does not distinguish signs specific to cerebral damage.
Endoscopic treatment
Endoscopy is less dangerous than other neurosurgical interventions in the brain, although it is also an operation. This is due to the use of modern medical equipment, which allows for minimal incisions. In a routine operation, doctors perform a brain trepanation, opening the skull. This is not only dangerous to human life, but also prolongs the patient’s rehabilitation period. So can brain cancer be cured safely? Endoscopic treatment is carried out without serious consequences for the brain, minimizing possible damage to blood vessels, cells, and tissues - this is a fundamental part of a safe operation.
Endoscopy is used in the treatment of children with hydrocephalus. An effective method is also for pituitary adenoma, when special instruments are inserted into the patient through the nose without damaging the skull. In addition, endoscopic therapy is used for cyst removal and traumatic brain injuries.
You need to know the enemy by sight
What is a brain tumor, cancer, head oncology? This is a terrible disease that affects the main organ - the brain, the head or its individual parts. A broken arm or leg can be healed. A diseased internal organ can be cured or, in extreme cases, transplantation can come to the rescue. People can live with one kidney, without a spleen, with an artificial heart, but none of them can live without a brain. It is he who is the most important organ. Thanks to him, a person remains himself, moves, breathes, talks, thinks, remembers his past, can plan the future, works in the present. A brain tumor, with its very appearance, erases your entire life, takes away memories, fills existence with pain, fear, and hopelessness. In fact, with further progression, the neoplasm in the head turns the patient into a motionless doll, and, in the language of modern times, into a vegetable.
Naturally, having heard such a diagnosis, the patient begins to prepare in advance for the worst, says goodbye to loved ones, acquaintances, and relatives. He surrenders to the mercy of the disease - mistake No. 1. The patient immediately asks the question why he became the victim of an unfair fate, completely ignoring the reasons why the tumor appeared. This is mistake number 2. To fight, first of all, you need to know your enemy.
A malignant tumor is the result of sudden, uncontrolled cell division. Every day hundreds of small particles are born in the body. They live, mature, die - the natural process through which a person exists. Malignant cells are common, but the immune system prevents them from growing in the body by destroying them. But one day, under the influence of viruses and infections, the immune system weakens and protective barriers fall sharply. During such periods, people feel a loss of strength and often get sick. This is why vitamins, rest, and fruits are so necessary. Malignant cells begin to grow sharply, and certain factors also help them:
- radiation exposure;
- bad ecology;
- preservatives, chemicals, carcinogens;
- GMO products;
- living near power lines;
- constant stress, depression, nervous breakdowns, negative environment;
- heredity;
- bad habits.
Such reasons cause particles to “go crazy.” The body is unable to cope with division, and the process of neoplasm growth begins. Gradually, aggressive cells invade neighboring tissues, destroying them; all signs point to a tumor. Tumors exhibit the following symptoms:
- Weight loss.
- Headache, intensifying at night in the morning.
- Attacks of loss of consciousness, paralysis of individual organs of the body.
- Insomnia or, conversely, a constant desire to sleep.
- Numbness of some areas of the skin and body.
- Distortion of the mouth, eyes, eyelids.
- Constant fatigue, depression, nervousness, phobias.
- Hallucinations: sound, olfactory, auditory, visions.
- The vestibular system is severely disturbed: the gait changes, the orientation in space is lost.
- Deterioration of vision, loss of vision, cloudy veil before the eyes, the effect of floaters.
- Changes in memory: some fragments fall out, elementary names of things, names, events are forgotten. Formation of false memories.
- Nausea during painful attacks.
- Manifestation of aggression and inappropriate behavior.
- Intracranial pressure is sharply increased.
Most of the moments can be attributed to everyday fatigue, which is present in almost every working person. That is why many people ignore the first important symptoms of the disease, preferring to be treated with painkillers and sedatives. Poor vision is improved with lenses and glasses; hallucinations and memory loss are treated with sedative herbs. Meanwhile, vital minutes are running out, and the disease is seizing new territories.
How to treat brain cancer?
One of the most dangerous diseases is brain cancer. The possibility of normal processing of incoming and outgoing information depends on the nerve endings between the hemispheres. Thus, during treatment there is always a risk of negative effects on healthy organs. The slightest mistake or deviation can cause amnesia, decreased or loss of intelligence, paralysis and other disorders.
The high risk forces neurosurgeons and other specialists to look for ways to cure the disease and develop new treatment methods that are safer for the patient. Japanese scientists have made great progress in this research. Their innovative technique is based on the use of atomic hydrogen. Medical care in Japan and the development of modern technologies are at a high level, each remedy or method of treatment undergoes the strictest control.
Alternative treatment methods are not uncommon in Japan. But we are not talking about folk remedies. Specialists from this country are trying to show that everything ingenious is simple; a person’s life resource is capable of helping in the treatment of the most dangerous diseases.
Research into the effects of atomic hydrogen on human cells and organs for the treatment of various diseases began 10 years ago. At this time, a positive trend is also observed when affecting cancer tumors. It is worth noting that the speed of such treatment is much lower than with traditional surgery, but much safer. Researchers were able to establish that after a 5-month course of regular procedures, the tumor significantly decreases in size and subsequently completely disappears. This is clearly demonstrated in X-ray images of cancer patients.
Interestingly, the innovative technology is based on Soviet research, in which they tried to cure viral or bacterial diseases by heating the body to 42 degrees. In this state, the so-called heat shock protein is released, which can help identify the tumor. Then the study was closed due to the high risk of protein damage in the body. The Japanese, in this technique, decided to use not only heated water, but atomic hydrogen. With the help of the interaction of active hydrogen particles, artificially created hyperthermia occurs without consequences for the human body. An undoubted advantage is the possibility of performing the procedure for older people, because most of the patients are of retirement age.
Modern medicine has advanced in the treatment of cancer, but the effectiveness of any technique depends on the timely detection of the disease. But a complete recovery and the answer to the question: can brain cancer be cured cannot be given by any specialist.
Removal of a brain tumor: consequences
Any surgical intervention is accompanied by poor health after it. As a rule, patients complain of dizziness and confusion. These symptoms are episodic, appearing and disappearing on their own.
The development of potential side effects depends on factors such as:
- type of operation
- tumor localization
- neurological status of the patient before surgery
- general health of the patient
- complete or partial removal of the tumor was performed
- whether healthy tissue was damaged during the operation.
The main possible undesirable consequences include the following:
- development of bleeding (intra- or postoperative), which is accompanied by neurological changes
- the occurrence of pain - to relieve it, specialists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe analgesics of the latest generation
- development of edema in the incision area (disappears after 2-4 days)
- wound infection - to prevent the development of this complication, patients are prescribed antibacterial drugs
- swelling of brain tissue: relieved by taking corticosteroids, one of which is dexamethasone, a hormonal drug that has an immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, antiallergic and membrane-stabilizing effect. Dexamethasone for brain tumors is used as a decongestant drug that helps reduce intracranial pressure;
- development of neurological disorders that prevent the restoration of normal neurological function;
- the occurrence of seizures and convulsive syndrome, which can be prevented by taking anticonvulsants;
- thrombus formation - to reduce the risk of blood clots, specialists at the Yusupov Hospital recommend changing the patient’s body position in the postoperative period and developing special exercises for the legs. In addition, the patient must stop smoking;
- hydrocephalus – if this complication occurs, the patient needs endoscopic ventriculostomy, drainage installation, and shunting;
- leakage of cerebrospinal fluid through the incision made for the operation - another surgical intervention is performed to restore the flow of cerebrospinal fluid;
- divergence of the edges of the staples installed to fasten the edges of the postoperative wound - to prevent this complication, the patient must refrain from physical activity for one to one and a half months after surgery.