Atherosclerosis is called the silent killer. For a long time the disease is asymptomatic. Drugs for the treatment of atherosclerosis help slow down the course of the pathology, and most importantly, prevent the development of complications: coronary heart disease, brain disease, myocardial infarction, stroke, gangrene of the legs.
Features of drug therapy
Treatment of atherosclerosis with drugs should be selected individually, based on the results of diagnostic measures. The choice of medications, dosage and duration of treatment should be made by a doctor.
Drugs for the treatment of atherosclerosis can achieve the following effects:
- Reducing the severity of symptoms;
- Normalization of the level of “bad” cholesterol in the bloodstream;
- Preventing the penetration of lipids into the vascular wall;
- Normalization of fat metabolism;
- Improving the general condition of vascular endothelial cells;
- Stabilization of atherosclerotic plaques;
- Normalization of blood flow in the body.
However, self-therapy can only aggravate the pathological process, as a result, patients will have to seek help from a surgeon or resuscitator.
Classification of drugs for the treatment of atherosclerosis:
- Statins or reductase inhibitors;
- Fibrates or fibric acid derivatives;
- Nicotinate group;
- Bile acid sequestrants or anion exchange resins;
- Products based on amega-3-triglycerides;
- Herbal medicines;
- Other drugs.
It is necessary to consider each of the listed groups in more detail.
Statins
Drugs for the treatment of atherosclerosis can block the enzyme that regulates synthesis processes
cholesterol by hepatocytes. Regular use of statins reduces the flow of cholesterol into the walls of blood vessels and helps reduce the lipid core in existing plaques. As a result, the vascular endothelium is stabilized, and the risk of developing blood clots due to plaque rupture is reduced.
Medicines from the group of statins for atherosclerosis are prescribed in the following cases:
- Exceeding the normal level of cholesterol in the bloodstream. Therapy is carried out against the background of diet therapy;
- To prevent the development of cardiovascular pathologies in people at risk (smokers, a history of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, genetic predisposition);
- To prevent complications of atherosclerotic vascular lesions: heart attack, angina, stroke;
- All patients who have had a heart attack, stroke, or have a history of unstable angina.
Simvastatin (can be replaced by Vabadin, Simvacor, Vasilip, Simvacard, Zocor, Vasostat, Simvatin), Lovastatin and Pravastatin are natural drugs for atherosclerosis, which are created based on the waste products of certain fungi. Fluvastatin, Atorvastatin (replaced by Atorvasterol, Amvastan, Liprimar, Livostor, Torvazin, Torvacard, Tulip) and Rosuvastatin (analogue drugs: Klivas, Rozart, Rozulip, Crestor, Rosucard) are synthetic drugs.
What medicine is good for treating atherosclerosis? New generation medications (Rosuvastatin and Atorvastatin) have a pronounced lipid-lowering effect. Therefore, these tablets for atherosclerosis normalize cholesterol levels even in patients who are not sensitive to other medications.
Statins not only effectively reduce lipid levels in the bloodstream, but also have the following effects:
- Improves the condition of the vascular endothelium;
- Anti-inflammatory effect;
- Reduce cell adhesion;
- Dissolves cholesterol stones;
- Reduce platelet aggregation (sticking process);
- Reduce proliferation of smooth muscle cells;
- Reduce cholesterol levels in bile;
- Prevention of Alzheimer's disease, osteoporosis, oncopathologies, vascular dementia.
It is important to remember that in some cases, taking statins leads to disruption of the synthesis of vitamin K. As a result, calcium begins to be deposited in atherosclerotic plaques, which causes fragility of blood vessels, impairs blood flow, and can lead to a heart attack.
Heavy metals will destroy the circulatory system
When a necessary element does not enter the cell, its place is automatically taken by an antagonist metal and, unfortunately, more often these are toxic and heavy metals (lead, cadmium, arsenic, etc.), which are so rich in our environment - air, water, food , household chemicals, cosmetics, medicines. Deficiency of microelements and accumulation of toxic metals (microelement imbalance) provokes the development of cardiovascular pathology, accompanies their chronic forms and aggravates their severity.
Lead causes the development of atherosclerosis, hypertension, vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels), and damage to capillary vessels. The body's reaction to lead poisoning can be so strong that blood pressure rises to the highest levels and anemia develops; endocrine disorders, resulting in arrhythmia, sinus bradycardia, tachycardia, vasoneurosis.
Cadmium poisons the liver, affects the blood vessels of the kidneys (renal failure), its accumulation in the kidneys of a smoker can increase 1000 times, causing urolithiasis.
Arsenic acts on the blood in the same way as parasitic poisons or transfusion of incompatible blood, causing vascular damage and intravascular hemolysis. Complications of arsenic intoxication can be a decrease in the pumping function of the heart (cardiogenic shock), acute renal failure, and liver poisoning.
Heavy metals are forced out of cells with the introduction of selenium, zinc, and silicon.
Fibrates
This group of drugs for atherosclerosis includes fibric acid derivatives. Fibrates accelerate the utilization of fats by activating lipoprotein lipase.
Regular use of drugs leads to an increase in the rate of lipid oxidation, normalization of glucose metabolism, vascular nutrition, and prevents the rupture of cholesterol plaques.
According to the modern classification, there are 4 generations of fibrates:
- Clofibrate. The drug is practically not used in the treatment of atherosclerosis;
- Gemfibrozil and Bezafibrate;
- Fenofibrate and Ciprofibrate;
- Improved form of Fenofibrate.
Medicines for atherosclerosis from the group of fibrates are prescribed for:
- Increased levels of triglycerides in the bloodstream with normal total cholesterol;
- Excess body weight;
- Development of mixed hyperlipidemia, if taking statins is impossible;
- Metabolic syndrome;
- The patient has a history of gout;
- Development of diabetic retinopathy.
- Contraindications for the use of fibrates are:
- Individual hypersensitivity to any ingredient of the drug;
- Severe pathologies of the liver and kidneys;
- Development of calculous cholecystitis;
- Simultaneous use with hepatotoxic medications;
- Development of photosensitivity;
- Acute or chronic inflammatory process in the pancreas.
"Atorvastatin"
The product reduces the level of low-density cholesterol in the patient's blood and maintains the presence of good cholesterol. These tablets are available in 20, 30 and 40 mg forms. The medicine is prescribed to older people whose metabolism has deteriorated, as well as to people who have a hereditary form of hypercholesterolemia. The course of treatment lasts about four weeks. First, a small dosage is prescribed, which is gradually increased. For severe liver diseases, this drug is completely contraindicated. It should also be used with caution if you have diseases of the gallbladder and the gastrointestinal tract in general. After injuries, infections, operations and other similar situations, it is better not to use this medication.
Nicotinate group
Niacin, nicotinic acid, Enduracin are drugs used in the treatment of atherosclerosis. They are able to reduce triglyceride and cholesterol levels by increasing the concentration of “good” lipoproteins in the bloodstream.
Medicines based on nicotinic acid are affordable. They should be taken after a meal with water. To achieve a therapeutic effect, up to 3 g of nicotinates per day are prescribed.
This dosage can lead to the development of the following negative symptoms:
- Feeling hot;
- Development of pain in the epigastric region;
- Headache;
- Liver dysfunction.
Taking Enduracin, due to the slow release of nicotinic acid, minimizes the possibility of side effects.
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptom of ischemic disease is pain.
Acute severe pain in the head, which is very difficult to relieve with medications. At this point, blockage of the arteries occurs. A person cannot cope without emergency medical care.
The pain syndrome occurs against the background of a drop in blood pressure.
Due to the disruption of blood flow to the internal organs, their functioning occurs. As a result: bloating, nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting.
Bile acid sequestrants
In the presence of intolerance to statins, Cholestyramine and Colestipol are used to treat atherosclerosis. The action of the drugs is based on the binding of bile acids, which ensure the absorption of fats in the digestive tract. As a result, lipid levels in the bloodstream are normalized.
With regular use of medications in this group, many patients report impaired absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and medications. Therefore, sequestrants should be taken 4 hours before meals and medications or 1 hour later. It is recommended to take the medicine with juice or soup to drown out the unpleasant taste.
The therapeutic effect of tablets for atherosclerosis develops after 3-5 weeks.
With long-term use of drugs, the following side effects develop:
- Increased bleeding;
- Indigestion;
- Decreased folate levels.
Combined products
If there are contraindications for combination drugs, an alternative replacement should be selected.
A drug for atherosclerosis of combined action not only normalizes lipid levels in the body, but also reduces blood pressure. Before use, medications used in treatment are analyzed for safety. If there are contraindications, an alternative replacement should be selected. The main combination drugs include:
- Azi-Ator;
- Caduet;
- Duplecore;
- Ineji;
- Biperine.
Omega-3 triglycerides
Atherosclerosis can be cured using drugs containing omega-3 triglycerides: Vitrum-cardio, AngiNorm, Fish oil, Omacor, Eikonol. They have the following effects:
- Hypolipidemic. Effectively normalize the level of “harmful” lipids in the bloodstream and fat metabolism;
- Immunomodulatory. Increases the body's defenses;
- Anticoagulant. Prevents the development of blood clots;
- Antiplatelet. Reduce the intensity of platelet aggregation;
- Anti-inflammatory.
The drugs are widely used for the treatment and prevention of atherosclerosis, prevention of heart attack and stroke.
However, omega-3 triglycerides are not recommended for the following conditions:
- Active tuberculosis;
- Hemophilia;
- Inflammatory processes in the pancreas, gall bladder;
- Acute and chronic pathologies of the liver and kidneys;
- Sarcoidosis;
- Dehydration of the body;
- Increased levels of vitamin D and calcium in the body.
Causes
Sclerosis of the cerebral vessels with its characteristic symptoms can be provoked by diseases that give rise to the accumulation of such deposits in the blood. The provocateurs of negative processes are:
- heredity;
- blood pressure disorders;
- disruptions in the endocrine system (thyroid, pancreas);
- obesity;
- bad habits (smoking and alcohol);
- abuse of animal products;
- physical inactivity;
- heart diseases;
- dysfunction of the hemostasis system, causing increased blood coagulation;
- damage to the body by viruses;
- infectious pathologies that cause weakening of the walls of blood vessels;
- inflammatory reaction with prolonged fever.
Herbal remedies
The following can effectively reduce cholesterol levels in the bloodstream: Ravisol, which is a combination drug, and pumpkin seed oil. The latter is widely used in the treatment of hyperlipidemia types IIa and IIb, and the prevention of atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels. The oil has a pronounced lipid-lowering effect due to vitamin E and saturated fatty acids included in its composition.
Ravisol is a tincture of horse chestnut seeds, mistletoe shoots and leaves, horsetail and periwinkle herbs, Japanese Sophora and hawthorn fruits, and clover flowers. Herbal ingredients help normalize the level of triglycerides and cholesterol in the bloodstream, have a diuretic and antiplatelet effect.
The medicine helps alleviate the course of atherosclerosis (subject to complex treatment of the pathology).
The drug is prescribed 5 ml three times a day before meals. Before use, shake the bottle, then dilute the required amount of tincture in boiled water. The duration of therapy should not exceed 10 days.
Ravisol is contraindicated in the following situations:
- Presence of pathologies of the kidneys, liver, history of hypotension;
- Hypersensitivity to any component of the combination product.
During treatment, the simultaneous use of Ravisol with cardiac glycosides, sedatives, hypnotics, antiarrhythmics, and antihypertensive drugs should be avoided.
The medicine is well tolerated, but the following adverse reactions may rarely occur:
- Tachycardia;
- Hypotension;
- The appearance of nausea and vomiting;
- Abnormal stool;
- Epigastric pain;
- Pain when urinating;
- The appearance of an allergic rash, which is accompanied by severe itching;
- Feeling hot.
Diagnostics
Before choosing a treatment tactic, the doctor prescribes an examination. The following methods are used for this:
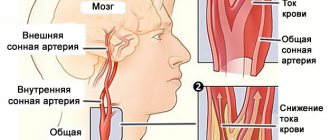
- Vascular ultrasound. The procedure identifies problems with blood supply to the neck and head. Through this event, the patient's condition is determined.
- Additionally, duplex examination is used, which has 2 modes. This is two-dimensional, the task of which is to study all the vessels approaching the head, as well as transcranial, which allows you to examine the vessels inside the skull.
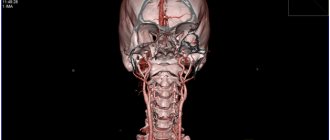
- Vascular angiography is a manipulation involving the introduction of a contrast agent into the vessels, which appears on the images. Based on the rate of filling with this liquid, the specialist makes a conclusion about the state of the vascular system of the head.
- Magnetic resonance angiography is the most accurate method for diagnosing capillaries. The procedure is carried out through the introduction of a contrast substance, or without it.
The patient is also prescribed laboratory diagnostics, which includes:
- general and biochemical analysis of blood fluid;
- determination of blood sugar concentration;
- lipid analysis.
Based on diagnostic measures, the doctor determines how to treat cerebral vascular sclerosis.
Other drugs
If the patient has pronounced symptoms of atherosclerotic vascular lesions of the lower extremities, then, along with lipid-lowering drugs, it is necessary to take drugs from the following groups:
- Angioprotectors (Pentoxifylline, Trental, Persantine, Curantil). The drugs normalize the delivery of nutrients to the tissues of the lower extremities and improve metabolic processes. As a result, the severity of pain decreases;
- Antiplatelet agents. Preparations based on acetylsalicylic acid prevent the formation of blood clots and thin the blood;
- Beta blockers (Nebivolol, Atenolol, Metoprolol). The drugs have a pronounced hypotensive effect;
- ACE inhibitors (Captopril, Sinopril, Lisiropril). They have a cardioprotective effect, reduce the load on the myocardium and blood pressure;
- Hypoglycemic agents. Allows you to control blood sugar levels.
Classification
Depending on the root cause and degree of damage, 2 forms of vascular sclerosis are classified:
- progressive;
- cerebral.
To effectively eliminate cerebral vascular sclerosis, adequate treatment must begin as early as possible. Pathology can have 3 degrees of damage:
- initial;
- average;
- heavy.
initial stage
Warning symptoms:
- noise in ears;
- constant lethargy;
- fatigue;
- slight dizziness;
- drowsiness;
- memory lapses;
- high excitability;
- minor headaches.
Most often, at the initial stage of lesions, 90% of patients experience headaches of varying degrees of intensity (pressing, bursting, throbbing). Such discomfort bothers a person at any time of the day and often interferes with normal sleep. With increased mental and physical stress, these symptoms worsen.
Second stage
If the process is not stopped, the pathology becomes more serious. Because of the problem, the intellect suffers, which is expressed in poor memory and inability to concentrate. In this phase, the patient begins to forget even basic professional skills. Added to these manifestations are:
- coordination problems;
- speech loss of varying severity;
- irritability.
To prevent such an effect, it is important to promptly notice any deviations in the natural state and urgently get rid of the disease.
Third
This is the most complex degree of vascular damage. The patient receives partial and complete incapacity, disability. This is due to the fact that patients:
- they don’t remember a lot;
- cannot take care of themselves;
- unable to read, speak.
Prevention of atherosclerosis
The following drugs are available for the prevention of atherosclerosis:
- Antiplatelet agents. Medicines prevent the aggregation of platelets and endothelial cells, therefore they are widely used to prevent thrombosis;
- Statins. The drugs inhibit the production of cholesterol in the liver, therefore they are widely used to treat and prevent the development of atherosclerosis;
- Bile acid sequestrants. Widely used to prevent disease in individuals who cannot tolerate statins.
During the treatment of atherosclerosis, it is necessary to strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations. Medicines will help alleviate the patient’s condition, but for effective therapy it will be necessary to adjust lifestyle, normalize nutrition, and introduce regular moderate physical activity. Only complex treatment will help eliminate the symptoms of atherosclerosis and slow down the pathological process.
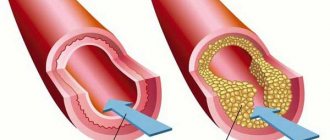
Cholesterol - friend or foe?
Cholesterol is an organic compound, a natural fatty (lipophilic) alcohol that is found in all cells of the body. Cholesterol is involved in the formation and protection of cell membranes, and is also necessary for the production of vitamin D, steroid hormones (cortisol, estrogen, testosterone, etc.), bile acids, as well as the normal functioning of the immune and nervous systems. Thus, the body needs cholesterol. The function of delivering cholesterol to all organs is performed by transporter proteins - lipoproteins. All we know good about cholesterol is that it binds to high-density lipoprotein (HDL). Cholesterol, when combined with low-density lipoproteins (LDL), is poorly soluble and tends to precipitate. This “bad” cholesterol is the enemy of blood vessels.