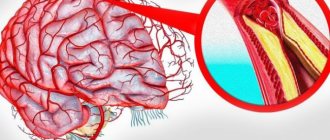
The vascular system of the head and neck includes vital arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the brain, facial muscles, oral structures and eyes. The blood supply network also includes veins that return oxygen-deprived blood to the heart and lungs. Brain tissue is considered metabolically active because it uses about 20% of the total oxygen and glucose entering the body daily. Any disruption of blood flow to the brain very quickly leads to a decrease in mental function, loss of consciousness, and with prolonged ischemia, death.
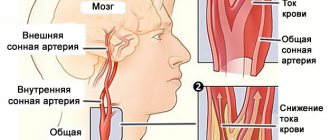
The vessels of the head and neck that supply blood to the brain are represented by paired structures:
- left and right vertebrates;
- left and right common carotid arteries.
The vertebral arteries pass through the transverse foramina of the cervical vertebrae. Along their course, they give off several meningeal, muscular and vertebral branches to various structures. The vessels enter the skull through the foramen magnum and connect at its base. From there they supply blood to the hindbrain structures, including the brainstem, cerebellum and medulla oblongata. It is the occipital regions that are responsible for the functions of breathing, regulating blood circulation and heartbeat.
The vertebral arteries arise from the subclavian arteries, located in the chest below the collarbones, where the neck muscles attach. Therefore, their condition depends on posture and the condition of the cervical spine.
The anatomy of the vessels of the neck has its own peculiarities, since the vertebral and internal carotid arteries are not separate formations. The vessels connect in the cerebral arterial circle, which is located at the base of the skull. The Circle of Willis ensures that the brain is supplied with blood even if one of the main arteries is blocked.
The left and right carotid arteries are divided into two branches:
- the internal carotid arteries pass into the skull through openings where at the base of the brain they branch into the left and right anterior and middle cerebral arteries, which supply blood to the corresponding areas;
- The external carotid artery divides into the superior thyroid, ascending pharyngeal, lingual, facial, occipital, posterior auricular, maxillary and superficial temporal arteries, which provide blood flow to the skin, muscles and organs. Most of them supply the head and face with oxygen, but only the superior thyroid and ascending pharyngeal structures in the neck.
Three pairs of large veins return blood from the tissues of the head and neck to the heart. The vertebral veins descend through the transverse foramina of the cervical vertebrae, providing drainage from the spinal cord, vertebrae and neck muscles. Superficial structures on the outside of the skull are drained by the external jugular veins. The outflow of blood from the brain is maintained by venous sinuses in the dura mater, which unite into the jugular veins between the occipital and temporal bones. A spasm of the neck muscles can disrupt the outflow of venous blood, causing headaches.
Symptoms and treatment of vascular diseases of the neck and head
Most often, the vessels of the head and neck are affected due to the development of atherosclerosis.
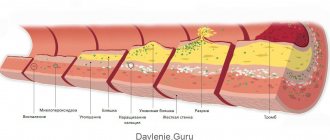
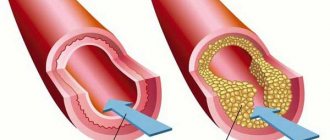
This is the name for a disease in which “bad” cholesterol is deposited on the walls of arteries and veins and atherosclerotic plaques form. They interfere with normal blood flow and the saturation of tissues and organs with oxygen and nutrients. There are non-stenotic and stenotic atherosclerosis. In the first case, cholesterol deposits are observed along the wall of the vessel, which does not cause significant narrowing. With the stenotic type of the disease, atherosclerotic plaques grow in breadth, causing not only vasoconstriction, but also excessive thrombus formation. Risk factors for the development of atherosclerosis and diseases of the arteries and veins:
- Middle and old age (depending on the specific pathology).
- Overweight and obesity.
- Physical inactivity is a lack of physical activity.
- Smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Poor diet with excessive amounts of animal fats, lack of protein, etc.
Some other diseases can provoke the deposition of cholesterol on the walls of blood vessels: arterial hypertension, especially complicated by periodic crises, diabetes mellitus, autonomic dysfunction syndrome and metabolic disorders. Heredity is also an important factor.
Various pathologies of the vessels of the neck and head can provoke completely opposite symptoms. For example, with the same vegetative-vascular dystonia, a person may suffer from hyperactivity and nervousness or, conversely, from weakness, drowsiness and fainting. Therefore, only a qualified specialist can make a correct diagnosis and determine the cause of the disease. The main symptoms of vascular pathologies of the neck and head include:
Dizziness and headache. Feeling of heaviness or squeezing in the head. Throbbing sensation in temples. Drowsiness, fatigue, or vice versa, hyperactivity and irritability. Intolerance to even feasible physical activity. Unreasonable fainting. Mood swings. Numbness in the arms or legs. Loss of vision. Forgetfulness, problems with memory and attention, and in the future - with thinking. Change in gait to shuffling or mincing. Serious dysfunction of the brain, as a result of which the patient cannot coordinate his movements, bowel movements and urination. Progressive dementia.
Signs of vascular diseases of the head and neck are arranged in order of occurrence. At first, a person may not be bothered by any symptoms at all, he feels well and does not notice jumps in blood pressure or oxygen starvation of the brain. However, over time, the disease progresses and quickly causes deterioration.
Main pathologies of blood vessels of the neck and head
The blood supply to the brain is maintained by only two pairs of main arteries. Problems with the vessels of the neck cause cerebral circulation disorders - acute and chronic. With a decrease in blood flow, cells begin to experience oxygen starvation and disruption of metabolic processes. The main pathologies of the vessels of the neck and head include:
- Ischemic strokes are caused by a blockage of the arteries by a blood clot or embolus. Most often, the carotid and vertebral arteries are partially blocked, but the reduced blood supply leads to cell starvation, disruption of signal conduction and dysfunction of ischemic areas. Completely bloodless tissues die in five minutes, but a penumbra forms around them - a zone with impaired energy metabolism. These cells remain active for another three hours.
- Hemorrhagic stroke is provoked by hypertension, rupture of an aneurysm or vascular malformation, and occurs as a complication of anticoagulant therapy. Intracerebral hemorrhage occurs directly into the brain tissue with the formation of a blood clot - a hematoma. Depending on its size, the risk of cerebral edema and increased intracranial pressure increases.
- The carotid arteries are most often blocked by accumulations of lipids and cholesterol, which leads to atherosclerosis. Severe blockage of the lumen is called carotid stenosis. Narrowing of the arteries leads to transient ischemic attacks - micro-strokes.
- Cerebral aneurysms are a weakening of the vascular wall, leading to its swelling. Typically, protrusions develop at the site of branching of the vessel. Aneurysms can result from birth defects, high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, and head injuries.
- Arteriovenous malformations are tangles of abnormal or poorly formed vessels (veins and arteries) with an increased bleeding rate. Changes in blood vessels occur in various parts of the body. The arteries of the brain suffer during embryonic development or after traumatic brain injury. Malformations can compress brain tissue, causing seizures and headaches. Sometimes they rupture, causing intracerebral or subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Abnormalities of the vascular ring - the circle of Willis - lead to various symptoms due to asymmetric blood supply to the brain. Sometimes, due to underdevelopment of the arteries, the formation becomes incomplete. The areas supplied by the posterior cerebral artery and the visual cortex suffer, migraines develop, and fatigue appears.
Carotid arteries
The carotid arteries are most often affected by atherosclerosis, a progressive vascular disease. The pathology is characterized by the accumulation of fatty deposits along the inner layer of the arteries, which leads to the formation of plaques. The plaque is made up of smooth muscle cells, fatty substances, cholesterol, calcium and cellular waste. The thickening in the wall narrows the arteries and reduces blood flow to the brain.
How is the diagnosis confirmed?
The main method for diagnosing narrowing of the carotid and basilar arteries is CT angiography. This method allows you to study a three-dimensional image of the blood vessels under study and evaluate the strength and characteristics of blood flow. Unlike conventional angiography, computed tomography eliminates the risk of complications from surgical interventions associated with the introduction of contrast (with CT angiography, the solution is injected into the femoral vein). Significant contraindications for this study are allergies to iodine and iodine-containing drugs, high obesity, pregnancy, severe forms of tachycardia or other heart diseases. The use of CT angiography is contraindicated in cases of decompensated diabetes mellitus, as well as acute renal or heart failure.
CT angiography
If there are such contraindications, CT angiography can be replaced by the following types of diagnostics (usually in combination):
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and head (using Doppler ultrasound);
- magnetic resonance scanning;
- determination of blood cholesterol levels and study of blood lipid balance;
- instrumental examination of the arterial pulse (used quite rarely).
Ultrasound of neck vessels
An ECG is also used to identify provoking factors and assess the functioning of the heart muscle.
Methods for diagnosing the condition of blood vessels
All people who often experience stress, headaches, or tension in the neck need to have their blood vessels checked. The doctor will send you for an instrumental examination only if there are persistent symptoms: visual impairment, complaints of dizziness and tinnitus, numbness in the hands.
Most vascular problems are detected using imaging techniques:
- Cerebral angiography, or X-ray with contrast, involves injecting a substance through a catheter under the guidance of a fluoroscope and then taking X-ray images.
- Carotid duplex is an ultrasound examination of the arteries, identifying plaques, blood clots and assessing the level of blood flow in the carotid arteries. Non-invasive and fast diagnostic method.
- Computed tomography visualizes the condition of bone tissue, blood, and brain well, and is used in the diagnosis of hemorrhagic strokes. CT angiography allows you to evaluate the condition of the vessels of the brain and neck instead of an invasive angiogram.
- Doppler ultrasound allows you to examine superficial and deep vessels and veins. Ultrasound is used to evaluate the carotid arteries.
- An electroencephalogram involves placing electrodes on the scalp to evaluate brain waves in different areas.
- A lumbar puncture is an invasive diagnostic test that involves removing a sample of cerebrospinal fluid from the space around the spinal cord with a long needle. Used when detecting bleeding caused by a cerebral hemorrhage.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is the production of three-dimensional images of body structures using magnetic fields and computer technology. MRI is commonly used to visualize the brainstem and posterior regions of the brain to evaluate transient ischemic attacks.
- A magnetic resonance angiogram is a non-invasive test that evaluates the health of the arteries in the head and neck. The scan is aimed at identifying aneurysms, stenosis and atherosclerotic plaques.
If the cause of the symptoms is not identified, the MRI shows the norm in relation to the vessels and vertebrae, then the patient is sent for treatment of psychosomatic diseases. A neurologist prescribes antidepressants for adults, and valerian for children.
Sometimes they send you for a massage, which needs to be done carefully. Spasmed muscles react to manual stimulation by repeated contraction, which is why relapses in the form of dizziness and increased blood pressure are possible
Symptoms and diagnosis of cholesterol plaque clearance
Vascular atherosclerosis is a dangerous disease that has the status of cardiovascular pathology. The disorder is typical for older people whose bodies experience hardening of the arterial walls and connective tissues. Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using ultrasound, digital angiography and CTA.
The process of plaque formation narrows the lumens of the tubular organ, bringing the functioning of the internal organs to a critical point.
Symptoms of the disease:
- severe headaches and dizziness, tinnitus,
- heart pain, angina attacks,
- increased blood pressure,
- deterioration of speech, vision and hearing,
- fast fatiguability,
- memory loss,
- numbness of human limbs,
- irritability,
- impaired coordination of movements.
Prevention measures
To prevent spasm of blood vessels in the neck and brain, you must:
- Control emotions, monitor the state of the nervous system, preventing it from overstraining.
- Completely give up bad habits, spend at least 2 hours outdoors every day, follow a daily routine, toughen up, and don’t forget about relaxation.
- Establish a sleep schedule - the body should rest at least 8 hours a day.
- Adjust your diet: give up unhealthy foods, give preference to raw vegetables, fruits, berries, herbs (especially parsley), garlic, carrots, cabbage, and green tea as a drink. All of the products listed will help blood vessels maintain their elasticity.
- Drinking black tea, coffee, fatty and smoked foods is not permissible. Pickles and spicy foods should be consumed in limited quantities.
- Hardening methods such as taking a contrast shower or dousing your feet first with cool and then cold water will help strengthen the vascular system.
Thus, if a spasm of the cervical vessels occurs, you can try to help yourself, but only for temporary relief. In conditions caused by serious disorders in the body, only a doctor should carry out further diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
Diagnostics
If symptoms of stenosis of the veins (arteries) of the head and neck appear, you should consult a neurologist. Modern research methods used in medicine make it possible to diagnose even minor stenosis of the vessels of the head and neck. Methods to identify problems with the veins and arteries that transport blood to the brain include:
- Ultrasound examination: makes it possible to evaluate the vessels of the head and neck both outside and inside the skull. The examination itself does not cause any discomfort or pain to the patient.
- Duplex scanning: an ultrasound mode that allows you to examine not only the blood vessels of the brain, but also the tissues that surround them. This procedure can also be used to evaluate blood flow parameters.
- Angiography: a contrast agent is injected into the human vascular bed, after which X-ray images of the examined arteries are taken.
- Computed tomography: a tomograph allows you to see a layer-by-layer image of the structures of the brain, as well as assess the condition of its arteries and veins. The data is processed using special programs.
- Magnetic resonance imaging: thanks to this method, it is possible to see a three-dimensional image of the structures and blood vessels of the brain.
After conducting all the necessary research and studying the symptoms, the doctor diagnoses the patient and prescribes treatment.
A person with vascular stenosis of the head and neck requires lifelong maintenance therapy. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of stenosis, as well as the disease that provoked the dysfunction of blood vessels. If the cause of vascular narrowing is atherosclerosis, the person is prescribed:
- Statins (Actalipid, Vasilip): drugs that lower blood cholesterol levels and also destroy atherosclerotic plaques.
- Instead of statins, fibrates, for example, Miscleron, can be prescribed.
- Vasodilators: relieve spasm, thereby expanding the lumens of veins and arteries.
If stenosis of the vessels of the head and neck is caused by osteochondrosis, it is enough to limit treatment to taking antispasmodics, for example, No-shpa and Papaverine. For hypertension, complex treatment is indicated, aimed at normalizing blood pressure and improving the functioning of blood vessels. To relieve symptoms, tranquilizers (Phenazepam) and anti-headache drugs (Ibuprofen) are indicated.
Treatment of the disease also includes taking vitamins (C, A, E), selenium and iodine-containing drugs. People with vascular stenosis of the head and neck should spend more time in the fresh air and exercise moderately. The diet includes vegetables, fruits, berries, cereals, sea fish, lean meat and dairy products, as well as nuts and dried fruits. It is recommended to limit foods high in cholesterol and fat, fast food and processed foods. Avoid drinking coffee, alcohol and energy drinks
It is important to pay attention to hardening: contrast showers, dousing with cold water, etc.
As for traditional medicine, their use should be previously agreed with a doctor. To eliminate problems with the vessels of the head and neck, products are used, which include:
People suffering from vascular spasm of the head and neck should be regularly observed by a neurologist and follow his recommendations.
Everything is so beautifully described, I went to a bunch of neurologists, had an MRI of the head of the neck, had a stenosis of the neck vessels done, an EEG, took a bunch of medications, took about 30 IVs, showed a narrowing of the right vertebral artery, no medications help, neurologists all around are charlatans who are grandmothers current sucks, free medicine generally smokes on the sidelines. In general, I don’t even know what to do, who to turn to! (((
try taking trental tablets, it helped me a lot
Regarding the treatment once and for all, I also can’t find it, but I know a secret, I have a narrowing of both the right and left arteries, I take picamilon (it dilates blood vessels) 1 ton per day, aspirin 1 tablet per day (dilutes blood clots) and drink St. John's wort (both as a sedative and good for the kidneys) no coffee, chocolate, alcohol, and especially cigarettes, they constrict blood vessels and I drink it for 2 months if I like, and in 2 years my blood pressure has never risen and there have been no seizures
Symptoms and signs of obstructed venous outflow
The first clinical symptoms of impaired venous outflow with cervical osteochondrosis appear 2-3 months after the onset of development of pathological changes in the vascular bed. In this case, a developed clinical picture is already present and the venous vessels are quite deformed. It is recommended to visit a doctor earlier. Therefore, it is important to know the first signs of obstructed venous outflow, which can occur literally 2-3 days after the development of the disorder.
These symptoms of obstructed venous outflow include a feeling of fullness in the back of the head and temples in the first hours after waking up. These pains are dull and indistinct in nature and may be accompanied by an attack of nausea, lack of appetite, general weakness and weakness. If such manifestations appear, it is necessary to consult a vertebrologist as soon as possible.
In the future, as the disease develops, symptoms of obstructed venous outflow of the head may manifest themselves in the form of:
- regularly occurring obsessive noise in the ears (this can be the splashing of waves, the sound of the surf, humming, buzzing, etc.);
- decreased hearing and visual acuity on the affected side or symmetrically with prolapse of the vena cava;
- gradual development of problems with falling asleep and insomnia, accompanied by obsessive thoughts at night and a feeling of enormous fatigue in the morning;
- development of depressed mood, sometimes with suicidal thoughts;
- decreased mental performance, memory, ability to concentrate;
- high degree of dependence on meteorological conditions and magnetic storms;
- bluish tint of the skin in the neck, collar area and face;
- pronounced swelling of the face and infraorbital areas in the morning;
- a dull, pressing headache in the back of the head and temples (may occur in the morning, after an emotional shock, heavy physical activity or prolonged tension in the neck muscles);
- dizziness, which at first are orthostatic in nature (when standing up suddenly), then turn into a constantly present state of lightheadedness, often leading to fainting.
With prolonged obstruction of the venous outflow of blood from the structures of the brain, muscle weakness and partial numbness of the upper extremities develop. Problems with memory, ability to perform mental work, concentration, etc. quickly begin. Neuroses and psychoses may develop, and the patient's mood is constantly depressed. Approximately 20% of patients develop a syndrome of persistent increased intracranial pressure over time. This condition can lead to regular epileptic seizures.
Treatment
A diagnosis of cerebral and neck vascular stenosis means that the patient will need treatment throughout his life. Therapy should be aimed at eliminating the clinical picture of spasm, the direct cause of vascular dysfunction. It is carried out using several methods.
Medications
The choice of medication is determined by the cause of the development of the pathology. If vascular spasm was caused by atherosclerosis, the treatment program includes the following groups of drugs:
- statins lower cholesterol levels and have a destructive effect on atherosclerotic plaques;
- Vasodilators help relieve spasms by widening the spaces in the arteries and veins.
Patients with diagnosed vascular stenosis, which developed against the background of cervical osteochondrosis, can limit treatment with antispasmodics. Spasms resulting from hypertension should be treated comprehensively. Therapy should normalize blood pressure and improve the functioning of blood vessels.
Be sure to take vitamins, iodine-containing medications, and selenium. Moderate exercise and regular walks in the fresh air help saturate the body with oxygen. Foods containing fats and cholesterol should be excluded from the diet.
Traditional methods
Today, therapy for vascular pathologies is carried out not only with pharmaceuticals. They are often supplemented with infusions of medicinal herbs.
Important!
Treatment and prevention of vascular pathologies of the head and neck with folk remedies must be previously agreed with the attending physician.
To strengthen blood vessels, using elecampane root tincture is effective. It is drunk several times a day, 30 drops dissolved in 0.5 glasses of water. Dried fruit salad helps improve blood circulation. To prepare it, raisins, figs, prunes, walnuts and dried apricots are ground in equal proportions. The mixture is stored in the refrigerator in an airtight container. You should consume 1 tbsp. l.
In folk medicine, tinctures based on garlic and lemon are actively used to treat blood vessels. Recipe example. Peel 1 kg of garlic and pass through a meat grinder. The resulting mass is transferred to a 3-liter jar. The remaining space in the container is filled with water and closed with a lid. Leave to infuse for 10 days in a cool and dark place, stirring from time to time. The resulting infusion is filtered and diluted with juice obtained from 1 kg of lemons. Take 1 tbsp. l. To avoid damaging the gastric mucosa, it is better to do this after eating.
Diet
In the treatment of vascular pathologies of the neck and head, not only the use of medications is important. Proper nutrition helps restore lost functions. The daily diet of patients is based on the following rules:
- Complete exclusion of fatty, spicy, smoked, pickled dishes, fast food.
- Limited consumption of refined sugar, coffee, mayonnaise, yeast dough, chocolate.
- The amount of salt should be minimal.
- It is better to use vegetable oil for cooking.
Patients should eat plenty of seasonal fruits, vegetables, berries, and seafood. Also shown are low-fat varieties of fish, all kinds of cereals, herbs, honey, fresh juices.
Important!
If you strictly follow the diet recommended by your doctor, you can achieve lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Surgical methods
If the patient seeks medical help late, medications and diet do not provide the desired therapeutic effect. Therefore, a decision is made to use radical methods. Some of them:
- Carotid endarterectomy. It involves cutting the damaged artery to remove the plaque.
- Angioplasty. A catheter is inserted into the cavity of the vessel, which expands the problem areas. Increased pressure pushes through the cholesterol plug.
- Stenting. The walls of the arteries are strengthened with a wire frame.
Symptoms of various vascular diseases of the head and neck
There are many known diseases of blood vessels in medical practice. Each of them has its own clinical picture. But the final diagnosis is made only by a specialist based on the results of the examination. Signs common to all diseases:
- sudden attacks of dizziness, which are accompanied by loss of coordination and fainting;
- pain that is localized in the back of the head is the main symptom of stenosis;
- state of lethargy, fatigue or, on the contrary, increased irritability;
- limited physical activity;
- problems with memory, concentration, signs of dementia;
- feeling of heaviness in the head.
Important!
Cause for concern - these signs are observed regularly.
Atherosclerosis
The most common cause of violations. The disease develops against the background of the formation of atheromatous plaques on the inner surface of the arteries. If left untreated, the connective tissue gradually grows, making it difficult to fully supply the brain with blood. Signs of atherosclerosis are most often observed in people over 50-60 years of age.
The condition occurs against the background of regular intake of fatty foods, physical inactivity, and metabolic disorders. Bad habits are also important - smoking, drinking alcohol.
Spasms
The condition is accompanied by a narrowing of the lumen between the walls of capillaries and blood vessels. This can be observed against the background of vasospasm - intense reflex muscle contraction. The reason for this may be the following conditions:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- disturbances in the functioning of the heart;
- kidney and thyroid dysfunction.
Provoking factors also include regular hypothermia, overwork, and lack of sleep. Among the congenital pathologies that can cause stenosis are:
- underdevelopment of neck vessels;
- bone formations on the vertebrae.
Hypertension
The main characteristic is high blood pressure. The stenosis that occurs against this background leads to the fact that the vessels lose their elastic qualities. Pathology can cause spasms, paralysis, decreased or even loss of sensation in the limbs.
Advice!
The clinical picture is observed extremely rarely. Therefore, hypertensive patients should regularly measure their blood pressure. If three times the results may exceed 140 mmHg. Art., you should consult a doctor.
Cervical hernia
The condition is accompanied by rupture of the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc and release of the nucleus. The clinical picture is formed by the following phenomena:
- pain in the upper spine, which intensifies due to changes in head position;
- numbness, tingling in the hands;
- muscle weakness;
- headaches, coordination problems.
The symptoms of a hernia are the most striking. Therefore, detection of pathology occurs in the early stages. Especially when compared with other vascular diseases.
Osteochondrosis
Dystrophic changes in intervertebral discs in the cervical region. The damage also extends to the vertebrae, soft and cartilaginous tissues. It can lead to the development of a hernia, which in medicine is called intervertebral protrusion.
Osteochondrosis is caused by a number of factors. For example, cervical injuries, lack of physical activity. Also, holding the neck in an uncomfortable position for a long time, hereditary predisposition, prolonged mental stress.
Clinical manifestations
First of all, the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are expressed in aching pain, localized in the neck and radiating to the upper limbs and shoulders. Their “faithful companions” are the following clinical manifestations:
- headache;
- increased pain when trying to turn or tilt your head;
- muscle spasms;
- restriction of physical activity.
If compression of the nerve roots is observed, the following symptoms can be added to the above:
- shooting, cutting pain in the neck;
- feeling of weakness in the arm or hands;
- numbness of the skin of the upper extremities;
- cervical scoliosis, curvature in the cervical spine;
- decreased reflexes.
With the development of vertebral artery syndrome, which can occur as a reaction to irritation of its sympathetic plexus, the following symptoms are observed:
- dizziness;
- throbbing, burning headache;
- floaters and colored spots before the eyes.
Treatment: drugs, surgery and recommendations
Drug treatment of carotid artery stenosis can be quite effective, but only if the course is uncomplicated and there are no other diseases.
Drugs
Depending on the degree of narrowing, the following drugs may be included in the treatment regimen:
microcirculation correctors (“Actovegin”, “Trental”);
"Actovegin"
- neuroprotective drugs (“Pantogam”);
- vasodilators with antihistamine action (“Cinnarizine”);
- statins for correcting cholesterol levels and cholesterol load (“Atorvastatin”).
"Atorvastatin"
Treatment also includes correction of the underlying disease, against which the narrowing of the blood vessels in the neck and head occurred. For example, for osteochondrosis, drugs from the group of NSAIDs, chondroprotectors, and centrally acting muscle relaxants are additionally prescribed. If there are intervertebral hernias that compress the blood vessels of the cervical spine, they are reduced (surgically).
Ischemic stroke, cerebral hemorrhage
Clinical guidelines
To achieve and maintain positive dynamics, it is also important for the patient to follow the clinical recommendations of specialists on lifestyle and diet. It is necessary to exclude from the diet all foods containing large amounts of fats and carcinogens (smoked meats, lard, sausages, etc.)
etc.), as well as alcoholic beverages and hot spices. About 30% of the daily food intake should be vegetables and fruits. This group also includes berries and greens: their consumption improves the viscosity and fluidity of the blood and enriches the diet with essential vitamins and minerals.
If the patient suffers from tobacco addiction, you should contact a specialist who will prescribe complex therapy and help cope with the addiction
At the same time, it is important to understand that the craving for smoking is very difficult to correct, so observation by a narcologist is not enough: in most cases, patients also need the help of a psychologist or psychotherapist
You need to stop smoking
Obese people should control their body weight, as excess weight is one of the main factors in the development of atherosclerosis and other vascular pathologies.
Clinical recommendations for the treatment of vascular insufficiency caused by pathological narrowing of the neck vessels also include the following points:
- control of psycho-emotional state;
- providing adequate physical activity appropriate to age and level of fitness;
- selection of anatomical sleeping accessories;
- regular walks (necessary to prevent hypoxia).
Regular walks are very important
Experts also call therapeutic exercises as one of the main measures for complex treatment of stenosis. Sets of special exercises for the cervical spine help eliminate muscle spasms, increase the flow of blood and lymph in the vessels, improve metabolic processes in the intervertebral discs of the neck, reducing the risk of dystrophic changes and degeneration of neighboring vertebrae.
Gymnastics for the cervical spine
Surgery
One of the most effective and safe methods of treatment for narrowing of the vessels of the cervical spine is stenting. The essence of the operation is to install a special metal stent in the form of an elongated tubular plate, which expands the internal lumen of the affected artery and restores its capacity. The speed of recovery depends on the individual characteristics of the patient and is about 3-10 days. In some cases, the patient is discharged home the very next day with recommendations to follow a gentle regimen and to attend a follow-up appointment with a surgeon and neurologist after 10 days.
Surgery
Video - Carotid artery stenosis
The blood vessels of the neck are one of the most important arteries in the human body, as they carry blood directly to the brain. Narrowing of blood vessels in the cervical spine is a dangerous pathology, which doctors recognize as one of the main factors determining the risk of ischemic stroke. It is necessary to treat the disease at the initial stage, when the effectiveness of drug correction reaches 70-90%. In the absence of positive dynamics within 6 months, the use of surgical methods is indicated.
Choose among the best clinics based on reviews and the best price and make an appointment
Show all Moscow clinics
Show all Moscow specialists
Vessels of the head and neck: symptoms, treatment of the disease
· You will need to read: 7 minutes
Unexpected attacks of headaches, dizziness, and ringing in the ears are familiar to almost every adult.
Some experience forgetfulness when, for example, they have difficulty remembering an important date, the place where the keys were left, etc.
Some attribute this to overwork, others jokingly say that they are developing multiple sclerosis. Often the cause of these symptoms is stenosis of the head and neck vessels caused by poor circulation.
Mechanism of occurrence
Through vessels and veins, blood supplies oxygen and useful elements to all tissues and cells, ensuring the normal functioning of organs.
Deformation, slagging, and accumulation of cholesterol plaques narrow the arteries that supply brain cells with blood. As a result, the elasticity of the walls and the patency of blood vessels are lost.
With spasms of the vessels of the head, as a result of prolonged and active contraction, the space between their walls decreases. In people prone to a sharp increase or decrease in blood pressure, a hypertensive reaction is observed at this time. Atherosclerotic plaques, which cause disruption of blood flow in the vessels of the brain, thoracic and cervical region, are formed as follows:
- An unbalanced diet with a lot of fatty and spicy foods increases the level of bad cholesterol (LDL) in the blood.
- The vascular walls lose their natural flexibility, microcracks appear on them and are filled with small cholesterol plaques.
- Platelets, small platelets of blood that promote blood clotting, adhere to the formed plaques. A blood clot forms, leading to complete blockage of the vessel.
Neck stenosis generally begins with a narrowing of the left or right carotid artery.
Stages of the disease
Disease of the blood vessels of the neck and brain usually occurs in a chronic or acute form. Without proper treatment, the acute form can lead to ischemic stroke or cerebral hemorrhage, which is usually fatal.
The chronic form of stenosis develops gradually. First, increased fatigue occurs, then unbearable headaches are noted. At times the patient experiences dizziness and suffers from forgetfulness. Chronic vascular atherosclerosis can develop over several years.
Experts conditionally divide the disease into three stages:
- The first stage is considered mild. It goes away without visible symptoms, since many people attribute a slight decrease in performance, headaches and irritability to fatigue, sudden changes in weather, and stress.
- The second stage, when the vessels of the neck and head narrow, is accompanied by disruption of the functioning of the genitourinary and musculoskeletal systems. The person’s gait noticeably changes (he begins to shuffle and step his feet while walking). Limbs may go numb and there may be a false urge to urinate. The patient becomes overly irritable, his mood often changes, which causes misunderstandings and groundless quarrels. The occurrence of these symptoms is a serious reason to go to the hospital.
- When the blood vessels in the head narrow at the last stage, dysfunction of the brain is clearly manifested. The patient loses coordination and begins to move slowly, as if feeling his way. Over time, a person loses the ability to move independently and stand on his feet. Vision rapidly declines, speech becomes slurred, and signs of dementia appear.
Types of cleaning blood vessels of the head and neck
It is difficult to get rid of cholesterol plaques in the vessels of the neck. Harmful formations are easier to prevent. The factors that provoke the development of the disease are completely eliminated. Heredity, bad habits, poor activity and poor nutrition are the main reasons for the formation of atherosclerosis.
Timely reduction of the level of harmful cholesterol is the basis for the restoration of the body. The treatment method is selected by the doctor individually.
Qualified doctors believe the recovery process should be comprehensive and orderly:
- drug treatment. Medicines lower cholesterol levels
- blood filtration. The connecting fluid is filtered, eliminating LDL particles,
- strict adherence to the diet. A balanced diet affects the quality of metabolism, reduces the concentration of harmful structures in the plasma,
- folk remedies. Medicines allow you to improve the functioning of systems and saturate cells with necessary elements, eliminating harmful formations,
- elimination of harmful factors. Quit tobacco/vodka, increase activity.
The method of extracorporeal hemocorrection will help remove cholesterol plaques in the vessels of the head and neck. The procedure should be carried out in a hospital setting (7-10 sessions). Blood is taken from the patient, passed through the device, cleansing it of harmful elements, and poured back into the patient’s body. The regimen is effective in combination with other treatment options for atherosclerosis (including to strengthen the immune system).
Medications
You can clean the vessels of the head with a slight level of contamination of the vessels using high-quality medications. Medicines are prescribed by a qualified doctor. You need to buy them at the pharmacy.
Effective means include:
- Statin substances. The mechanism of action of the drugs is based on enzymatic, receptor, exogenous effects. Structural elements influence the synthesis of cholesterol and inhibit the process of its absorption.
- Fibrates. The medicine is relevant for patients with elevated triglyceride levels. The substance activates an enzyme that metabolizes fats. The inflammatory process subsides, and the blood vessel returns to normal.
- Ion exchange resins. “Colestipol” and “Cholestyrin” affect the absorption of bile acids in the intestines and the interaction of the liver with blood lipids.
- "Probucol" drug increases the concentration of protein structures.
- "Ezetimibe" medication optimizes the absorption process of fats (cholesterol type) in the organ.
- "Omega-3" substance affects the degree of lipid metabolism in the body. The drug approach affects the condition of the liver.
Doctors say that when taking tablets or giving injections, the active substances are absorbed by 65%. Some items may not reach their destination. Using a dropper gives a quick and long-lasting effect. The headache goes away.
An effective and efficient option for placing an IV is the following scheme:
- “Cavinton” is a herbal remedy that comprehensively cleanses the arteries and restores blood flow to the neck/head,
- “xanthinol Nicotinate” medicine actively dilates blood vessels (including the carotid artery), having a beneficial effect on blood circulation,
- "Eufillin" substance inhibits platelet aggregation, reduces blood pressure,
- "Mexidol" drug has an effect on optimizing blood circulation,
- nootropics. The products stimulate mental activity and have a membrane-stabilizing effect.
We recommend reading
- Rules for cleaning leg blood vessels from cholesterol
- Folk remedies for cleaning blood vessels in the legs
- Cleansing blood from cholesterol plaques
Folk remedies
Cleaning the blood vessels of the head and neck with folk remedies at home is based on a balanced diet, systematic use of tinctures and medicinal decoctions. Herbalists recommend cleaning blood vessels in the summer and autumn. Effective herbal preparations:
- A collection of rose hips + eleutherococcus + burdock root + cudweed + kidney mint. The components are mixed in equal parts, 500 ml of boiling water is poured. The liquid is infused for 30 minutes and filtered. Reception is carried out 3 times a day. The folk method is widespread,
- St. John's wort + chamomile + birch bud + immortelle (all 2 tablespoons). The mixture is filled with 0.5 liters of boiling water and infused in a thermos for 10-12 hours. After passing through a strainer, the broth is diluted with 1 teaspoon of honey. Reception is carried out in the morning and evening,
- In 1 liter of boiling water, dilute 5 tablespoons of coniferous tree needles, rose hips, 2 tbsp. l. onion peels. Leave the broth in the container overnight. The liquid is drunk for 3 months, 500 ml.
- 2 tbsp. flax seed, pour 250 ml of boiling water. After cooling, the healing tea should be drunk for 4 months.
Products are offered from nutmeg (200 g of product + vodka) and meadow clover (1 glass of flowers + 500 g of vodka). The drugs are infused for 2 weeks and taken 1 tsp. 6 weeks. The use of lemon is effective, strengthening the walls of blood vessels and ensuring the outflow of lymph. In a meat grinder, the citrus is mixed with the peel and stirred with 2 tablespoons of honey.
Onions and garlic release healing juice. The liquid is mixed with honey and taken 1 tbsp. spoon daily (garlic drink).
A mixture of nuts and dried apricots in equal proportions. Eat the dish 20 minutes before meals. Blood-vascular channels are cleaned and dangerous particles are removed.
What information is missing from the article?
- Detailed review of medications
- More practical treatments
- Innovative developments in this area
- Qualified expert opinion
Diet and breathing practices
Diet in the treatment of atherosclerosis is an integral part of therapy. 30% of cholesterol enters the human body with food. Scientists have confirmed that a balanced diet helps reduce lipid levels. Avoid fatty foods (sour cream, lard, meat and butter). Cottage cheese, egg yolks, and any caviar are undesirable.
Focus nutrition on:
- vegetables, fresh fruits. Foods rich in fiber activate the immune system,
- low fat dairy products,
- nuts The fruits have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the heart muscle and are a preventative against atherosclerosis,
- fresh juices, still water, green tea. Fluids thin the blood.
Breathing to cleanse the vessels of the head has its own technique. Gymnastics is carried out according to the following scheme: short inhalation through the nose - holding the breath - exhaling through the mouth.
For the elasticity of blood vessels, a deep breath (3-5 seconds) with breath holding is suitable. The lips are pulled out with a tube and air is slowly released. Repeat the procedure about 5-6 times. After gymnastics, my head and neck stop hurting.