Wernicke encephalopathy is a form of alcohol-induced brain damage. With this pathology, a clinical picture of neurological ataxic disorders develops. Along with them, symptoms of memory loss and cognitive function progress. This acute neuropsychiatric disorder is called the disease. Below we will tell you how the disease develops.
Broca's and Wernicke's areas
It is generally accepted that alcohol damage to the central nervous system is manifested by impaired motor functions. The nerve cells of the cerebellum are especially sensitive to alcohol. But sometimes chronic drinking leads to degradation of the cortex. Broca's and Wernicke's areas are affected. What are these departments responsible for?
Broca's center is located in the posterior part of the inferior frontal gyrus. This area regulates speech motor skills. When it is damaged, motor aphasia is formed: the patient cannot speak or read. At the same time, he perfectly perceives information that is conveyed to him orally. Broca's center controls the movements of the muscles of the tongue, face, pharynx and jaws.
Wernicke's area is located in the posterior part of the superior temporal gyrus. Neurons in this area convert sound information into words and sentences. Patients with encephalopathy cease to understand simple speech.
What is Wernicke's encephalopathy
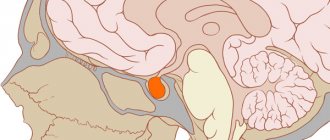
Wernicke encephalopathy (or acute hemorrhagic polyoencephalitis Gaye-Wernicke) is a disease localized in the brain. It occurs as a consequence of a lack of vitamin B1 (thiamine) and mainly has a negative effect on the activity of the midbrain, cerebellum and thalamus .
The impact on these essential components of brain structures contributes to disruption of the central nervous system (CNS), which manifests itself in the appearance of hallucinations, states of confusion, delusions and other symptoms.
Syndromes
Neuropsychiatric disorder develops as a result of several factors. First of all, this is the effect of alcohol. An acute condition develops due to ethyl alcohol intoxication. It is short-term and can be reversible. With chronic use, similar disorders appear, but they do not progress as quickly. With this form, the changes are irreversible.
Similar symptoms develop with vitamin B1 hypovitaminosis. This disorder occurs when there are problems with the digestive tract. For example, during resection of large volumes of intestine when removing tumors.
Other factors that provoke hypovitaminosis B1:
- Toxicosis of pregnant women;
- Prolonged uncontrollable vomiting;
- Helminthic lesions;
- Active form of malignant neoplasms;
- Hemodialysis;
- AIDS.
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome
Korsakoff psychosis develops in the last stage of alcoholic illness. It is associated with long-term memory loss. And with Wernicke encephalopathy, the loss of function is short-term.
When a combination of diseases occurs, Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome is formed. With it, the patient experiences two types of amnesia. He does not remember either present events or past ones. The cause of the disease is said to be chronic alcoholism combined with lack of nutrition. In rare cases, it is preceded by trauma.
Fact! When large doses of vitamin B1 are administered, patients recover the loss only partially.
ICD 10
In the international classification of diseases, Korsakov psychosis goes under the following code:
| F10 | Mental and behavioral disorders associated with alcohol use |
If alcohol is not recognized as the result of the disease, but there are eating disorders and nutritional deficiency of thiamine, then the code is as follows:
| F04 | Organic amnestic syndrome not associated with alcohol consumption |
Danger
If Gaye-Wernicke Syndrome is not treated promptly, it can lead to the following negative consequences:
- changes in human behavior and functioning;
- inability to restore brain function;
- amnesia or partial memory loss;
- drowsiness;
- loss of consciousness;
- constant heartburn;
- schizophrenia;
- brain tumor;
- complete atrophy of brain activity.
If not treated promptly, coma and then death may occur.
Gaye-Wernicke syndrome
This concept is synonymous with Wernicke encephalopathy. The author described the disease in 1881. The first name is acute hemorrhagic polioencephalitis. The disease affects the hypothalamus and midbrain. The cause of the disease is vitamin B1 deficiency.
The following manifestations of the disease are characteristic: memory loss and loss of skin sensitivity. The scientific work describes a triad of classic symptoms: ophthalmoplegia, ataxia and confusion. But observations show that it occurs only in a third of patients.
ICD 10
The medical history contains the following code:
| E51.2 | Wernicke's encephalopathy |
FACT! Karl Wernicke is a neurologist, author of numerous scientific works. In addition to the disease, a syndrome is named after him. When the temporoparietal region is damaged, sensory aphasia and agraphia are formed, sensitivity and motor activity of one lower limb disappear. Pick-Wernicke syndrome was described at the end of the 19th century.
Pathogenesis
Gaia-Wernicke encephalopathy is characterized by acute damage to the hypothalamus, brain stem and cerebellum. The development of the pathology mechanism is based on a decrease in the number of nerve cells and destruction of myelin in the white matter.
The damage extends to the substances of those parts of the brain that are located in the 4th ventricle, near the 3rd ventricle and the Sylvian aqueduct - the channel connecting these parts. In acute cases, pinpoint hemorrhages are diagnosed. In chronic cases - atrophy of the mastoid bodies.
Despite the fact that the disease mainly accompanies chronic alcoholism, the syndrome can develop due to vitamin deficiency and exhaustion after prolonged fasting, continuous vomiting, malignant tumors and other factors. Also, with this pathological condition, vascular-dystrophic changes occur.
Vitamin B1 deficiency reduces glucose processing by neurons and damages mitochondria. Excessive accumulation of glutamate due to decreased activity of the enzyme alpha-ketoglutar dehydrogenase due to lack of energy has neurotoxic effects.
Not only people who abuse alcoholic beverages or have a lack of thiamine in their bodies can develop this disease. There are a number of other factors that can provoke pathology, so Wernicke encephalopathy develops in the following conditions:
- malnutrition;
- avitaminosis;
- tumors;
- prolonged fasting;
- poisoning with medications that contain digitalis extract;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- pregnancy.
Vitamin B1 serves as a cofactor for several enzymes, including transketolase, pyruvate dehydrogenase, and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. With vitamin B1 deficiency, glucose utilization by neurons is reduced and mitochondria are damaged. The accumulation of glutamate as a result of decreased activity of alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase due to energy deficiency has a neurotoxic effect.
As a result, there is a decrease in the number of neurons, demyelination and gliosis of the periventricular gray matter. The areas most commonly involved are the medial hypothalamus, which is thought to cause amnesia, damage to the mammillary bodies, the cerebellar vermis, and the nuclei of the III, VI, and VIII cranial nerves.
The acute form of alcoholic encephalopathy usually occurs in men aged 35-45 years. There is also a chronic form of alcoholic encephalopathy - Korsakoff psychosis. All forms of encephalopathies are characterized by a pre-illness period of varying degrees of duration: from several weeks to a year or more; it is shortest in the hyperacute form - 2-3 weeks.
This period is characterized by the development of asthenia with a predominance of adynamia, loss of appetite up to complete anorexia, and aversion to fatty and protein-containing foods. A fairly common symptom is vomiting, mainly in the morning. Heartburn, belching, abdominal pain, and unstable stools are often observed.
Physical exhaustion increases. Sleep disturbances are typical for the prodrome state - difficulty falling asleep, shallow superficial sleep with vivid nightmares, frequent awakenings, early waking up. There may be a distorted sleep-wake cycle: drowsiness during the day and insomnia at night. More often, sensations of chills or heat occur, which are accompanied by sweating, palpitations, pain in the heart, and a feeling of shortness of breath, usually at night. In various areas of the body, usually in the limbs, skin sensitivity is impaired, and cramps are observed in the muscles of the calves, fingers or toes.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The disease manifests itself in acute and chronic forms. And if the first option is quite easy to diagnose, then the subacute or chronic types of the disease often proceed smoothly. Without the necessary treatment, irreversible changes occur in the brain. A person’s personality is lost, and the outcome of the disease is often death.
Carl Wernicke described four classic signs of the disease: nystagmus, ataxia, ophthalmoplegia and confusion. In modern society they are rarely observed (all together). Most often, neurologists see the following clinical picture: disorientation, dizziness and apathy, drowsiness against the background of problems with memory and concentration.
Such a blurred picture does not allow doctors to make a diagnosis or begin treatment on time. Typically, Wernicke encephalopathy is diagnosed based on an MRI scan or during an autopsy. Most often, objective data for the disease are discovered as an accidental finding.
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome
What disorders appear in the subacute form of the disease?
- Short-term and long-term memory is lost;
- There is confusion;
- The patient is drowsy and apathetic;
- The gait is unsteady and uncertain;
- Atypical mobility of the eyeballs.
The patient reproduces recent events extremely poorly. When talking about the past, he recalls certain moments. The amnesiac fragments are conjectured or fantasized. There is inattention and inability to concentrate. Often prone to repetitive actions (asking the same question, reading a magazine several times).
MRI
The diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture and tomogram results. Encephalopathy is confirmed by decreased thiamine levels and erythrocyte transketolase activity. So what changes appear on an MRI?
Scanning is carried out in T2W and Flair modes. In this case, multiple symmetrical hyperintense accumulations of substance are detected. Their localization: thalamus, mammillary bodies, quadrigeminal plate. Atypical zones of change can also be identified. For example, asymmetric lesions occur in the medulla oblongata, subcortical nuclei and pons, cerebellum and corpus callosum.
CT
The results of computed tomography do not allow an accurate diagnosis. Based on its results, only indirect signs of destruction of the brain matter can be determined. Areas of reduced intensity are identified at the level of the aqueduct and ventricles, as well as in the thalamus. Such findings require clarification on CT.
Fact! Ultrasound is not performed for Wernicke encephalopathy.
Alcoholic encephalopathy of the brain: diagnosis, prognosis
Today, alcoholism is not just a disease of an individual, it is a social problem of the entire society as a whole.
Medical research has proven that there is a relationship between an irresistible craving for alcohol and various neuropsychiatric pathologies.
Alcohol toxic encephalopathy is one of the most common and very dangerous phenomena that leads to irreversible processes in the brain.
Concept and classification
Many people have only a vague idea of what alcoholic encephalopathy is. In medical terminology, this phenomenon is characterized as alcoholic psychosis, which occurs in an extremely severe form.
The disease is characterized by poisoning and death of brain cells due to systematic alcohol consumption. As a rule, it combines several diseases, which are united by a single clinical picture, symptoms and etiology.
According to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), alcoholic encephalopathy belongs to class 6 out of 10.
In addition to pathological changes occurring in the brain, the disease is characterized by severe exhaustion of the body, intoxication with alcohol metabolism products (liver cirrhosis, hepatitis, etc.), deficiency of vitamins and microelements, and oxidative stress.
Alcoholic encephalopathy of the brain is often diagnosed in people who abuse alcohol substitutes. It is these people who most often end up in medical institutions with various poisonings, delirium tremens (delirium tremens) and other mental disorders, as well as diseases of internal organs caused by alcohol.
Alcoholic encephalopathy has two forms of the disease - acute and chronic. Other types are much less common, and the reasons for their appearance are usually attributed to the abuse of certain varieties of wine.
The acute alcoholic stage includes Gaye-Wernicke syndrome (Wernicke encephalopathy), which affects representatives of the stronger sex in adulthood (from 35 to 45 years), but sometimes cases are diagnosed when young people also suffer from it.
Let's look at each stage in detail.
Acute encephalopathy (Haye-Wernicke syndrome)
If we talk about the time frame of the stage, then it is individual for each patient. For some it lasts several weeks, for others it lasts for months. But in any case, the acute stage is characterized by a sharp deterioration in health.
A person experiences a number of disorders of both a nervous and somatic nature, as well as the development of some diseases characteristic of chronic alcoholics (pancreatitis, hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver).
Wernicke encephalopathy has the following symptoms:
- weakness, arrhythmia, shortness of breath even with minor physical exertion;
- poor appetite and, as a result, weight loss;
- nausea, vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- strong heartbeat, headaches;
- trembling of limbs, uncoordinated movements;
- swelling, blue discoloration of the skin on the arms and legs;
- burning in the chest;
- psychological abnormalities manifested in depression, fear, anxiety, hallucinations;
- severe speech impairment (the person cannot speak);
- insomnia or sleep disturbances accompanied by nightmares;
- delirium tremens;
- decreased muscle tone;
- fever, hyperthermia, sweating, peeling of the skin (in some cases, the formation of bedsores).
Gaye-Wernicke encephalopathy is characterized by a rather striking symptom - a person’s lack of satisfaction from drinking alcohol.
A patient with an acute alcoholic form must receive immediate medical attention, otherwise he will develop a syndrome of depression of consciousness - stupor, stupor, coma. Even if a person manages to survive, the prognosis is unfavorable: in most cases it is dementia.
Chronic stage of encephalopathy
Korsakov's psychosis is also called polyneuritic. Characterized by fixation or retrograde amnesia, disorientation in space, time and place.
A person loses the ability to move, cannot speak, he experiences muscle atrophy, polyneuritis of the extremities, and skin sensitivity decreases.
Sometimes the patient experiences confabulation - false memories of events that did not happen in his life.
Another form of the chronic stage of encephalopathy is alcoholic pseudoparalysis. Diagnosed much less frequently than Korsakoff psychosis.
The signs are in many ways similar to Korsakoff psychosis, but not so pronounced:
- manic and delusional states, partial or complete memory loss;
- trembling of limbs, impaired facial expressions.
If the patient’s treatment was carried out correctly and in a timely manner, then the above mental pathologies disappear, leaving no consequences, in contrast to the acute stage of encephalopathy, which in most cases leads to irreversible consequences, disability and death.
Diagnostic measures
Toxic encephalopathy in alcoholism, which is characterized by multidirectional symptoms, is dangerous because it can easily be confused with certain diseases: schizophrenia, delirium tremens, acute psychoses (non-alcoholic etiology), brain tumors, as well as an acute form of vitamin deficiency that developed as a result of anorexia.
That is why the decisive factor in the fight against alcoholic encephalopathy is collecting anamnesis and studying the medical history. These actions will allow the specialist to make correct assumptions about what exactly led to such a clinical picture.
The doctor clarifies when exactly the disease began and the drinks the patient consumed.
If consciousness is not impaired, the doctor talks directly with the patient, but if he has depression of consciousness, then relatives or people who were in close proximity to the victim are interviewed.
Additional diagnostic measures - ultrasound, MRI, CT.
Diagnostic measures must be carried out as early as possible, otherwise the patient may experience heart failure, cerebral edema and other irreversible phenomena, including death.
Providing first aid
If alcoholic encephalopathy is suspected, a person should immediately call an ambulance. Before the medical team arrives, you need to cover the patient with a blanket to keep the body warm. At the same time, it is necessary to ensure that the person does not choke on vomit - unfortunately, such cases occur in medical practice.
If the patient falls into a coma, then all that remains is to trust the doctors, since this state can only be recovered with the help of medications and appropriate procedures. It should be noted that such a condition is a powerful stress, so it is unlikely to happen without consequences for all organs and systems of the body.
What methods are used to treat
There is no single treatment regimen for alcoholic encephalopathy; it all depends on the form of the disease and the patient’s condition. The requirement for successful treatment is a complete abstinence from alcohol. Treatment is continuous and long-term. Its duration ranges from several weeks to months.
Treatment of alcoholic encephalopathy includes the following steps:
- removal of alcohol metabolism products from the body (detoxification);
- formation of persistent gag reflexes to the smell and taste of alcohol (conditioned reflex therapy);
- elimination of cravings for strong drinks (sensitization);
- psychotherapy (individual and group);
- hypnotherapy.
If a patient has Wernicke encephalopathy, they require immediate medical attention.
Therapy includes taking vitamins B1, B6, PP (3 times a day, dosage is determined by the doctor), magnesium sulfate, nootropic drugs (if there are disorders of the brain).
In some cases, therapeutic measures may be required, the purpose of which is to normalize intracranial pressure. Treatment similar to severe forms of delirium tremens and psychological support are used.
Therapy for Korsakoff psychosis includes fortification (taking vital vitamins B, C, P, K). An appropriate diet is mandatory. Measures are taken to cleanse the blood of toxins and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Alcoholic pseudoparalysis should be treated with the same methods as Korsakoff psychosis. Drugs to support liver function and medications aimed at eliminating pain are also added here.
Connection to a ventilator, hemodialysis, parenteral nutrition, that is, the use of life support systems is advisable in severe cases. Furosedin is used to prevent the appearance of brain tumors.
Particular importance is given to the rehabilitation process, since there is a high risk of irreversible changes in the body and severe complications: impaired cardiovascular activity, the occurrence of brain tumors, paralysis of the limbs, dementia, and others.
If we talk about the effectiveness of traditional methods for alcoholic encephalopathy, then they are advisable at the acute stage. They can be used, but only in combination with the main treatment and after consulting a specialist. Self-medication is dangerous and can complicate the situation.
To create a lasting effect of aversion to alcohol and support the body during the rehabilitation period, you can use thyme, sea buckthorn, and wormwood.
Forecasts and preventive measures
It is difficult to predict what consequences alcoholic encephalopathies will have; it all depends on the timing of the disease, the frequency of alcohol consumption (mostly surrogates), the patient’s environment, and heredity.
In advanced cases, the risk of disability, both physical and mental, is very high due to disruption of the activity of all organs and systems.
Prevention measures include identifying alcoholism in the early stages and voluntary cessation of alcoholic beverages of any strength, support from loved ones, a healthy lifestyle, a balanced diet, and reasonable sports training.
Source: https://GolovaUm.ru/zabolevaniya/alkogolnaya-entsefalopatiya-gaje-vernike.html
Treatment
Timely therapy in the early stages of the disease leads to complete regression of symptoms. If thiamine drugs are prescribed late or their dosage is insufficient, then changes in the brain remain forever. The worst outcome is mortality. It continues to remain high even at the present stage of development of medicine.
Wernicke encephalopathy is an emergency condition. Vitamin B1 is used to treat it. It is also called thiamine. Traditionally, doses of at least 100 mg per day are prescribed. In this case, the method of drug administration is parenteral. Unfortunately, there is no single treatment plan for the disease.
Some authors suggest using infusion of thiamine in a dose of at least 500 mg 2-3 times a day for the treatment of the acute phase. This therapy is carried out for 2-3 days. Next, you can go to 200 mg per day.
First aid
When a patient is admitted to a hospital, the patient must be examined by a neurologist. If, based on the medical history (pregnancy with toxicosis, nutritional deficiency, alcohol consumption) and the clinic, the specialist suspects an acute illness, then an MRI scan is immediately performed. Only on the basis of this study is a diagnosis made.
Clinical guidelines
- In case of Wernicke's disease, it is worth diagnosing the “alcoholic” and “non-alcoholic” forms. Even MRI scans reveal different changes in the first and second groups of individuals;
- Differential diagnosis is carried out: with hemorrhagic fevers, atypical course of Jacob's disease, influenza A virus, venous thrombosis, encephalopathy due to high doses of methylprednisolone;
- The “alcoholic” form often occurs gradually. It does not have an acute onset and does not respond to therapy. In addition, the outcome of such an illness is Korsakoff psychosis;
- There are many atypical variants of the course of the disease.
Drugs
Etiotropic treatment is the administration of vitamin B1. Preferably high dosages and parenteral route of administration are required. But additionally, agents are prescribed that inhibit the destruction of myelin fibers.
| Thiamine (B1) | On the first day up to 1 g, then reduce the daily norm to 100-200 mg. |
| Administration of colloids and crystalloids | Substances replenish the volume of the bloodstream, reduce the concentration of toxins, bind and remove these molecules through the kidneys |
| Magnesium replacement therapy | Dose 2 mEq/kg; carried out taking into account kidney function |
| Sedation (benzadiazepines) | Sibazon for anxious and violent behavior |
| Alpha Choline Preparations | Restores the functioning of neuron mitochondria |
Complications
Unfortunately, patients with acute encephalopathy often cannot be cured. What complications appear after an illness:
- Korsakov psychosis. Characterized by memory loss and resistant to thiamine therapy. Observed in the alcoholic form of the disease;
- Death occurs when therapy is delayed or the diagnosis is not established. Wernicke's disease is most often discovered at autopsy.
Prevention
The risk group includes people suffering from chronic alcoholism, malabsorption syndrome, pregnant women with toxicosis, vegans, raw foodists, people on diets, patients with late stage AIDS. Also at risk are individuals who have a genetic defect that does not allow them to fully absorb thiamine.
Such individuals require vitamin B1 supplementation. Patients with chronic alcoholism require a course of injection therapy once every six months. And of course, you should stop taking ethyl alcohol and monitor the course of concomitant diseases.
Therapy methods
This disease is classified as an emergency condition. If even a few symptoms are detected, the patient requires urgent hospitalization.
Without proper and timely treatment, coma and further death may occur.
The essence of general treatment is to replenish the water balance in the body, correct electrolyte imbalances, replenish thiamine deficiency, and return the patient to a normal diet.
For this, the following drugs are prescribed:
- thiamine - administered intravenously or intramuscularly at a dose of 100 mg, the course of treatment is at least 5 days;
- magnesium sulfate - injections are carried out every 6-8 hours at a dose of 1-2 g;
- magnesium oxide - administered orally at a dose of 400-800 mg once a day;
- complex of vitamins B2, B6;
- ascorbic and nicotinic acid;
- anabolic steroid;
- glucose - must be administered intravenously after the administration of thiamine, otherwise, if glucose is used incorrectly, the condition can quickly worsen.
Taking thiamine in this dosage continues until the patient completely transitions to a normal diet. In addition to the above medications, the patient is prescribed a course of multivitamins. Along with this, constant monitoring of the functioning of the cardiovascular system is carried out.
A prerequisite for successful therapy is complete abstinence from drinking alcoholic beverages.
This syndrome is treated only in hospitalization; self-medication is strictly prohibited. In a clinical setting, the patient undergoes a course of thiamine therapy; At the first stages of treatment, vitamin B1 is administered intravenously, then gradually switches to injections into the muscles.
Since most often the patient suffers from general vitamin deficiency, in addition to introducing thiamine into the body, the doctor prescribes complex therapy, including the administration of vitamins C, PP and group B.
In addition, treatment involves taking psychotropic drugs (mainly Barbambil and Seduxen are used), which is carried out strictly under the supervision of a doctor.
Complex therapy involves the use of nootropic drugs and drugs that stabilize metabolism and support the normal functioning of the cardiovascular system.
In pregnant women
A rare extragenital pathology is Wernicke encephalopathy in pregnant women. It occurs in 1% of cases. But it poses a significant threat to both the mother and the fetus. What signs indicate pathology? Who most often develops the disease? Is it possible to perform MRI in the early stages?
Pathogenesis
In severe toxicosis in combination with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, decompensation of the gastrointestinal tract occurs. Pregnant women suffer from vomiting, which occurs more than 20 times a day.
Patients are exhausted, dehydrated, and the smell of acetone is often detected from the mouth. Against the background of loss of fluid and electrolytes, a decrease in the level of vitamins B1 and B12 is observed. In this regard, the clinical picture of encephalopathy develops.
Fact! If suspected, the patient undergoes an MRI. Pregnancy is not a contraindication.
Symptoms
How does the disease occur during pregnancy?
- Uncontrollable vomiting;
- Duration from 4 to 12 weeks;
- Exhaustion;
- Ketone smell;
- Sleep disorders;
- Nightmares;
- Hallucinations;
- Delusional thoughts;
- Confusion;
- Lethargy, apathy;
- Unsteadiness when walking;
- Memory impairment.
Nystagmus and neurological strabismus may appear.
Treatment
As a rule, a serious condition requires active treatment of the mother. Therefore, pregnancy is often recommended to be terminated. High doses of thiamine are prescribed. Active infusion therapy is carried out. With the help of solutions, doctors compensate for the loss of fluid and electrolytes (K, Ca, Na, Mg).
With timely treatment and early diagnosis, the prognosis for a woman is favorable. Rarely, residual neurological changes such as decreased sensitivity occur.
Wernicke encephalopathy is a severe psychoneurological disorder. Timely diagnosis and adequate therapy provide the opportunity for complete recovery. However, against the background of alcoholic illness, the pathology often occurs hidden. The symptoms are erased, and it is impossible to diagnose the disease. Avoiding ethyl alcohol and taking vitamin complexes is the best prevention of the disease.
Causes of pathology
A pronounced deficiency of thiamine in the body can occur for various reasons, however, in any case, this deficiency will affect metabolic processes and enzymatic regulation of brain tissue.
While glucose levels rapidly drop, the enzyme glutamate begins to accumulate in the body, which is responsible for the activity of receptors on cerebral neurons and is a catalyst for related reactions. An increase in the amount of glutamate provokes an increased influx of Calcium cations.
An excessive amount of ions of this element activates the action of many enzymes that begin to attack neurons. Cells that are weak due to low glucose intake are destroyed and not restored, which greatly affects the functioning of the brain and the functioning of the nervous system as a whole.
Thiamine deficiency can be caused by various reasons. Below is a list of factors that provoke the appearance of Wernicke encephalopathy:
- long-term alcohol abuse (average duration – up to 20 years);
- malabsorption (vitamin B1 is not absorbed while passing through the gastrointestinal tract);
- eating disorders associated with prolonged fasting (most often with anorexia nervosa or strict religious fasts);
- prolonged, almost continuous vomiting during pregnancy;
- grueling sports;
- metabolic disorders;
- helminthiasis;
- HIV AIDS;
- states of severe poisoning with digitalis preparations;
- the presence of a malignant neoplasm;
- prolonged diarrhea and vomiting.
Despite the number of possibilities listed above for getting this syndrome, the most common of them is alcoholism. Moreover, it has been noted that women, due to the characteristics of their body, are much more likely to become victims of this disease, and the average duration of their alcohol abuse is 5 years.
On the one hand, a lack of thiamine inhibits the process of removing glucose from the body. This leads to damage to the mitochondria, which supply cells with energy. On the other hand, the presence of thiamine is necessary in the body for enzymes to perform their functions. Otherwise, glutamate accumulates, which has a toxic effect on nerve cells. As a result, neurons contract, the speed of nerve impulses decreases, Wernicke encephalopathy develops, which can occur:
- in acute form;
- in chronic
There are a number of factors that can provoke pathology:
- avitaminosis;
- prolonged fasting;
- incessant vomiting during pregnancy;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- oncological tumors;
- poisoning of the body with medications that include digitalis extract;
- metabolic disease;
- AIDS;
- hemodialysis;
- helminthic poisoning.
Forecast
Wernicke encephalopathy is a very dangerous disease, since in approximately half of cases it ends in death for patients . The high mortality rate is explained by critical destructive processes in the body, as well as the exacerbation of all chronic diseases with Gaye-Wernicke encephalopathy.
If the damage to brain tissue turns out to be insignificant, then mental abilities gradually return, however, patients often communicate at very late stages, when the degradation has become irreversible.
After discharge from the hospital, a person who has suffered Wernicke encephalopathy must forget about drinking alcohol forever, otherwise the disease may return to a weakened body.
Wernicke encephalopathy is a serious disease with severe destructive manifestations. At the first suspicion of this syndrome, you should immediately consult a doctor, since every minute of delay can affect the patient’s entire future life.