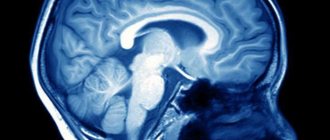
Ventriculomegaly is a pathology that affects the ventricles of the brain. The function of these parts of the organs is to maintain intracranial pressure and ensure normal blood circulation to the human cerebral cortex.
Most often, the disease occurs in unborn babies, less often in children of preschool and school age. Ventriculomegaly in adults develops in exceptional cases, since the disease is congenital.
Let's take a closer look at what ventriculomegaly is, the causes of its occurrence and how it is treated.
Causes and prerequisites for the development of ventriculomegaly in the fetus
According to medical research, ventriculomegaly of the lateral ventricles occurs due to the following reasons:
- Hereditary prerequisites. If any of the child’s close relatives (mother, father, siblings/cousins) suffered from a similar disease, the likelihood of its occurrence in the newborn increases to 25% compared to a baby in whom no one in the family had such a disease;
- Ventriculomegaly in the fetus often develops as a side disease along with another disease, such as Down syndrome;
- Pathology is provoked by intrauterine infections, as a result of which the ventricles of the brain enlarge.
General concept of the disease
Ventriculomegaly in the fetus is a pathology characterized by an increase in the size of the cerebral ventricles.
Such a change can cause damage to the central and autonomic nervous system, heart and blood vessels. Normally, any person, including a developing fetus, has 4 cerebral ventricles in the brain. Two of them (lateral ones - first and second) are located in the white matter of the brain.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=upload
Using the interventricular foramen, the lateral ventricles are connected to the third. It, in turn, has an anatomical connection with the fourth ventricle located in the bottom of the rhomboid fossa.
The entire ventricular system of the brain performs one of the most important functions - it synthesizes cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which then collects in the fourth ventricle and from there enters the subarachnoid space.
If there are certain disturbances in the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, then part of it accumulates in the ventricles and causes their expansion, that is, ventriculomegaly. Normally, the size of the ventricles should not be more than 10 mm.
According to statistics, the frequency of ventriculomegaly in the fetus is 0.6%. The pathology is usually diagnosed between 17 and 34 weeks of pregnancy using an ultrasound scan. In case of pathology, fetal death at the time of birth or in utero cannot be ruled out.
Pathology is sometimes detected in adults when performing a computed tomography scan. However, in such cases, ventricular enlargement is normal and does not require treatment.
The course of fetal ventriculomegaly in pregnant women after 35 years
Ventriculomegaly in the fetus most often develops if the child’s mother is over 35 years old. This happens for the following reasons:
- The risk of genetic disorders (for example, Down syndrome) increases;
- Intrauterine infections occur more often;
- A pregnant woman over 35 years of age is susceptible to complications while bearing a child.
Thus, if the mother is under 35 years old, ventriculomegaly in the child occurs only in exceptional cases.
Why is ventriculomegaly dangerous?
Ventriculomegaly in a child can lead to the development of serious disorders in the functioning of the central nervous system and brain. In an isolated form, when the deviation is observed on its own, the prognosis is usually favorable.
Ventriculomegaly, the causes of which are genetic disorders, is often combined with abnormalities in mental development. In particularly severe cases, the child may not be viable. It is important not to skip an ultrasound during pregnancy, when it is already possible to detect many developmental disorders, in particular, ventriculomegaly. What is dangerous about this situation is that by starting the process, you can miss precious time.
Ventriculomegaly, caused by prolonged exposure to infection on the fetus, hypoxia during gestation or childbirth can cause consequences from various kinds of psychoneurological disorders to severe forms of cerebral palsy. Such consequences of ventriculomegaly are difficult to treat. It has its effect, but requires a huge amount of time and effort from doctors and parents.
Diagnosis of lateroventriculoasymmetry of the brain
Ultrasound procedure of a child’s brain
Depending on the age of the patient, various methods for diagnosing pathology are used:
- The disease can be detected in the fetus starting from the 17th week of pregnancy. For diagnosis, the doctor performs an ultrasound of the mother’s abdominal cavity;
- Ventriculomegaly in an infant is confirmed after an ultrasound of the head;
- To diagnose an adult, an MRI of the brain is prescribed.
All procedures are aimed at examining the ventricles of the brain and identifying lateroventriculoasymmetry (violation of ventricular symmetry).
Diagnosis of the disease
Ventriculomegaly is diagnosed during pregnancy (from 17 to 33 weeks) using ultrasound and spectral karyotyping of the fetus. Perinatal examinations should include studies of all anatomical structures of the fetus, especially the ventricular system of the brain.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, a transverse scan of the fetal head is performed to determine the threshold value of the lateral ventricles of the brain. Ventriculomegaly is defined as ventricle size greater than 10 mm.
Severity of ventriculomegaly of the lateral ventricles
Doctors distinguish three degrees of severity of pathology:
- First: an increase in the ventricles of the brain to 11-12 mm. Patients are diagnosed with “ventriculodilation” - a slight expansion of the ventricles of the brain in newborns and preschool children;
- Second: enlargement of the ventricles up to 15 mm. Against this background, asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain and impaired blood flow to the affected areas are often observed;
- Third: enlargement of the ventricles up to 20 mm. At this stage, irreversible changes occur in the structure of the brain.
In addition, the child may be diagnosed with “borderline ventriculomegaly,” which means an increase in the lateral ventricles by no more than 9 mm.
Ventriculomegaly 1st degree
At the first stage of development of the disease, there are no pronounced symptoms. Only a neurologist can detect it after diagnosis. Most parents notice that the child becomes excitable and irritable. Unfortunately, no other symptoms appear.
Moderate ventriculomegaly
The second stage of the disease is also called “moderate ventriculomegaly.” As a rule, it is combined with other ailments, for example, ventriculomegaly and agenesis of the corpus callosum often occur together. Also in this case, lateroventriculoasymmetry of the brain (asymmetry of the ventricles) occurs. The following symptoms are also observed:
- Periodic convulsions, similar to epileptic seizures;
- Increase in head size;
- The presence of bulging veins on the forehead;
- Slow physical development;
- Mental retardation.
Severe ventriculomegaly
In addition to abnormal expansion of the ventricles of the brain, the following symptoms are present:
- Increased intracranial pressure due to the asymmetric shape of the ventricles;
- Recurrent headaches;
- Speech disorders.
Additional diseases are often added to the pathology: cerebral palsy, Down syndrome or hydrocephalus.
Classification
Ventriculomegaly of the lateral ventricles is classified by type, cause, course and location.
Due to the occurrence:
- idiopathic, when the cause of the pathological process has not been identified and all indicators in the pregnant woman are normal;
- symptomatic - a woman suffered from an infectious disease during pregnancy, abused alcoholic beverages, or suffered severe stress.
Type:
- right-sided;
- isolated – has a favorable prognosis, recovery occurs in 80% of cases;
- asymmetric – with a severe course, the prognosis for recovery is low.
According to the severity of ventriculomegaly in newborns and preschool children, it is:
- mild degree, when the ventricles are small in size - up to 12 millimeters, the child becomes irritable and easily excited;
- moderate degree, when the ventricles increase to 15 millimeters - an asymmetric anomaly and a change in blood flow in the area of the disturbance are observed;
- severe - the ventricles increase to 20 millimeters, which leads to irreversible consequences in the structure of the brain;
According to the location of ventriculomegaly, it can be:
- with lateral dilatation of the ventricles (left and posterior);
- pathological changes affect the third ventricle (in the front, on the forehead);
- changes in the fourth ventricle (in the occipital part, in the cerebellum and medulla oblongata).
Moderate ventriculomegaly is a borderline condition when the size of the ventricles is 10–15 millimeters, which is a high risk, since there is a high probability of developing a pathological process. Such cases are monitored and constantly checked to eliminate the risk of further growth.
Treatment of ventriculomegaly in the fetus
The disease is most often congenital, so it can be detected even before the birth of the child. To do this, the expectant mother undergoes an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, based on the results of which the degree of pathology is determined. In the third degree, the woman is offered an abortion, since the risk of miscarriage is high.
In other cases, doctors begin searching for the cause of the pathology:
- A woman must be tested for infectious diseases;
- The fetus is checked for the presence of congenital pathologies (cerebral palsy, Down syndrome, etc.);
- If no abnormalities are found, the pregnant woman is prescribed potassium tablets. It saturates the fetus with oxygen, which improves its condition.
With ventriculomegaly in the fetus, the consequences depend on the promptness of treatment at the stage of pregnancy.
Diagnostics
Ventriculomegaly is detected during a routine ultrasound examination between 17 and 30 weeks. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to observe the process over time, and for this, repeated diagnostics are prescribed. After a few weeks, if the suspicions are confirmed, the patient is referred to a geneticist for consultation.
Additional genetic studies are carried out, karyotyping is prescribed, which will help to clarify the structure of the anomaly and the composition of the chromosomes.
Additionally, the patient undergoes a blood test to determine the presence or absence of an infection that could affect the deviation of intrauterine development.
The fetus or newborn is checked for congenital abnormalities.
A magnetic resonance thermogram of the child is performed, and if a mild or moderate degree is detected, then neurosonography is performed to track the process over time.
If no abnormalities are detected, therapy is prescribed in the form of potassium tablets, which will replenish the cells with the missing oxygen.
If a severe pathology is detected, the pregnancy is terminated, and in the case of a mild to moderate degree, therapeutic measures are used.
Treatment of ventriculomegaly in a newborn
With a mild degree of pathology, no therapy is prescribed: the mother only needs to carefully monitor the child’s condition and, at the slightest deviation from the norm, contact a neurologist.
The second stage is treated with medication: the child is prescribed drugs that accelerate processes in the brain:
- Vitamin B tablets;
- Diuretics are drugs that remove excess fluid from the body;
- Medicines to improve blood circulation.
To enhance the effect, it is recommended to walk with your child in the fresh air more often and perform minimal physical exercise with him.
Surgery
The third degree of pathology is treated surgically, since taking medications will not give any results. The asymmetric shape of the ventricles is corrected by performing ventriculo-peritoneal shunting.
This is an operation during which shunts are installed to remove excess fluid. After surgery, children recover quite quickly: insomnia disappears and appetite returns.
Treatment
In infants, with the expansion of the gastrointestinal tract, the hemodynamics of blood vessels and anterior cerebral arteries are disrupted during the first 2-3 weeks of life, and the pH of the blood shifts to the acidic side. The child's body compensates for these phenomena. If compensatory mechanisms fail by the end of 4 weeks of life, Diacarb is prescribed.
A diuretic belongs to the group of diuretic drugs that are prescribed for epileptic seizures and disruptions in the dynamics of the cerebrospinal fluid. The drug is prescribed with caution, monitoring kidney function, as it has a nephrotoxic effect. Diacarb can increase blood oxidation.
Infants are prescribed antihypoxants to eliminate oxygen deficiency. Saturation of the brain with O2 improves the functionality of the central nervous system.
B vitamins have a positive effect on the immature nervous system, normalize metabolic processes at the cellular level, and synthesize hemoglobin. If the expansion of the gallbladder is caused by an infection, the woman is prescribed antibiotics.
Neurosurgical treatment is indicated for children if the disease progresses to hydrocephalus, when a large amount of fluid accumulates in the brain. If the condition of the fetus during gestation is extremely serious, there is a high probability of incompatibility with life, it is recommended not to give birth.
Causes and symptoms of pathology
Ventriculomegaly in the fetus can develop as an independent pathology. But it can also occur in combination with other developmental anomalies.
The ventricles of the brain, which normally have a width of 10 mm, with ventriculomegaly can reach 20 mm or more.
The main causes of the anomaly are considered to be chromosomal changes in the body of a pregnant woman. Such disorders occur in approximately 18% of women with pathologies of pregnancy.
Ventriculomegaly can occur due to trauma sustained by the pregnant woman, infectious diseases, obstructive hydrocephalus, hemorrhage and genetic predisposition.
The presence of other anomalies in fetal development accelerates and intensifies the development of pathology. At the same time, a single development of ventriculomegaly reduces the severity of its consequences.
The risk of developing brain diseases with ventriculomegaly is determined by the attending physician based on the characteristics of the enlargement of the ventricles.
Experts have established a pattern of increasing incidence of the disease in the fetus in the age category of pregnant women who have passed the 35-year mark.
The disease can be diagnosed without any problems during an intrauterine ultrasound procedure. But a specialist may miss the pathology if the deviation is small (a mild form of ventriculomegaly, not combined with any other diseases).
If a child is born with this deviation, then it is necessary to carefully monitor the progress of its development. The baby requires specialist advice in the following cases:
- he later sat down and walked (in comparison with his peers);
- the child is silent at a time when it is time to babble and try to pronounce sounds;
- experiences headaches and seizures;
- with a large head size (the difference between the volume of the skull and the baby’s chest exceeds 3 centimeters).
Sometimes the diagnosis is made to children with existing delays in motor and speech development. But as such, ventriculomegaly is absent. Subsequently, such children easily catch up with their peers in development and, of course, we are not talking about any neurological type deviations.
In adults, ventricular asymmetry rarely causes symptoms. However, in some cases, this anomaly can cause the following symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- feeling of heaviness and fullness of the head;
- apathy;
- feeling of anxiety.
In addition to these symptoms, the picture of the disease can be supplemented by symptoms of diseases that caused ventricular asymmetry.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcopyright
Such symptoms include cerebellar disorders, paresis, cognitive impairment or sensory disorders.
In infants, symptoms depend on the severity of the pathology. In addition to general discomfort, symptoms such as throwing back the head, regurgitation, increased head size and others may occur.
Symptoms of the pathology also include strabismus, refusal to breastfeed, frequent crying, anxiety, tremors, and decreased muscle tone.
However, quite often the pathology does not cause characteristic symptoms and can only be detected after an ultrasound scan.
The disease can be diagnosed without any problems during an intrauterine ultrasound procedure. But a specialist may miss the pathology if the deviation is small (a mild form of ventriculomegaly, not combined with any other diseases).
Sometimes the diagnosis is made to children with existing delays in motor and speech development. But as such, ventriculomegaly is absent. Subsequently, such children easily catch up with their peers in development and, of course, we are not talking about any neurological type deviations.