Features of concussion in children under 2 years of age
According to statistics, 9 out of 10 children with TBI are diagnosed with a concussion. The reason for this is that in children under two years of age the head is larger and heavier, and the coordination of the body does not allow it to react in a timely manner to a fall, so in infancy the child’s head is the first to suffer.
The harder the impact, the greater the likelihood of a concussion, despite the fact that the bones of the baby’s skull are strong, and the cerebrospinal fluid prevents the brain cells from colliding with the tissues of the skull.
Reference. Liquor is a fluid that circulates in the anatomical spaces of the spinal cord and brain.
In children under one year of age, the fontanel has not yet closed and with a sharp blow, it can easily become dislodged, which will lead to serious health problems in the future. You may also be interested in the reasons for the appearance of balls on the scalp in children.
Signs of a concussion in a child under 1 year of age
Most children begin to speak by age two and are able to express emotions, which helps parents understand whether their child is sick or not. Family members may notice uncharacteristic signs of behavior in a young child:
- Loss of orientation in space.
- Loss of coordination.
- Lethargy.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Pale skin tone on the face and body.
- Bad, restless sleep.
- Sudden loss of appetite.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Abdominal pain.
- Headaches (“rumbling in the head”).
- Loss of concentration.
Attentive parents who notice these symptoms should immediately consult a doctor. In newborn infants, the first symptoms are very vague as they are often similar to other disorders.
After an injury, you should pay attention to the following symptoms:
- Restless crying.
- Decreased appetite, even to the point of absence.
- Frequent regurgitation.
- Enlargement or displacement of the fontanel.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Restless sleep or lack thereof.
Attention! The first symptoms of TBI can appear both in the first hours after injury and within 24 hours. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition and well-being of the child during this period.
What should parents do?
At the first stage, parents should carefully monitor the child. Any change in his behavior should be interpreted in favor of the presence of injury. In this matter, it is better to be safe than to waste time. If symptoms appear, you should immediately call an ambulance. You should not take your child to the emergency room on your own, since there is absolutely no way for you to diagnose the exact type of injury at home without the appropriate medical education and equipment.
The baby needs to be picked up, face turned towards you on the right side, and carried like this until the doctor arrives. It is advisable that the baby's legs and arms are bent at the joints, this can alleviate his condition if cramps suddenly begin. The side position in mother's arms will not allow the baby to choke on vomit if he starts to feel sick. Until the doctor arrives, it is better not to let the child eat or drink, and also do not give any medications.
If a child wants to sleep, let him sleep; there is no need to wake him up, as is done with older children. Describe the symptoms found to the doctor, show the location of the impact, the height from which the child fell, indicate at what time it happened and how long has passed since the fall.
The child will be taken to the hospital, where he will undergo an ultrasound of the brain, and, if necessary, an EEG, radiography and MRI. An examination by a neurologist will be performed, and an ophthalmologist will perform an ophthalmoscopy to examine the condition of the fundus.
It is recommended to stay in the hospital for several days. Doctors need this to make sure there are no other injuries other than a concussion. Then you can continue recovery at home - the child is shown rest, bed rest, and the absence of sharp light and sound stimuli. Games should be calm, daily massage should be temporarily canceled.
The mother must ensure that the doctor’s recommendations regarding taking the prescribed medications are followed. Usually, infants are recommended sedatives to make it easier to fall asleep, vitamins and nootropic drugs that improve cerebral circulation.
You will learn more about concussion in infants from the following video.
medical reviewer, psychosomatics specialist, mother of 4 children
Source of the article: https://o-krohe.ru/bolezni/mozg/simptomy-i-priznaki-sotryaseniya/
The first symptoms in a baby
- Strong restless crying, with short-term cessation of breathing.
- Paleness of not only the skin, but also the mucous membranes. Often due to lack of blood flow, bluish lips and areas of skin may appear.
- Regurgitation, body temperature can rise to 38 degrees.
Excessive crying and elevated body temperature are the main indicators of traumatic brain injury. Infants are often left with bruises and contusions after injury , but due to the elastic skull, severe injuries are unlikely.
Much more dangerous signs of a concussion in a child under 1 year of age, requiring immediate hospitalization, are:
- Swelling, displacement, curvature of the fontanel.
- Decreased or absent reflexes.
- Impaired motor function of the eye - rolling of the eyes (or eyes), squint, drooping eyelid.
- Complete lack of appetite.
If parents do not consult a doctor in time, a concussion carries a number of complications:
- Strabismus.
- Developmental delay (or even mental retardation).
- The child will suffer from headaches.
- Hyperkinesis is uncontrolled movements of body parts.
- Vegetative-vascular disorders.
Treatment
Treatment of concussion in infants must be carried out exclusively in the hospital under the supervision of qualified specialists. At an early age, the baby still has very fragile health, so during therapy there should always be an experienced doctor next to him who knows exactly how to recognize certain complications and what measures need to be taken to prevent them.
During treatment, the child should be completely at rest. Since during this period the baby’s body reacts sharply to bright light rays and loud sound vibrations, it must be protected from such external factors. It is also important that only the mother and medical staff are near the child; an excessive number of strangers can negatively affect the overall well-being. It is necessary to reduce the child’s motor activity as much as possible and protect him from everything that may affect his emotional state.
Typically, the treatment period lasts no more than a month; in some cases, if a mild concussion is diagnosed, the doctor may send the child and mother home to undergo treatment on their own. But for this you need to write a receipt. When self-treating at home, it is very important to follow all prescriptions and recommendations of the attending physician.
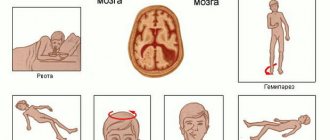
Signs of head injuries by age and their complications
Let's look at how to understand that an infant or a child aged 2 years has suffered a concussion after a fall.
In an infant during the first 20 weeks
How does a concussion manifest in an infant in the first months of life? Signs:
Prolonged crying after injury and after a while.- Regurgitation of more than 25 ml of breast milk or formula, more than twice at one meal.
- Vomit.
- Noticeable swelling of the fontanel.
- Pallor.
- Bluishness (the baby’s lips and skin may take on a light blue tint) due to lack of oxygen.
- Your heart rate may slow down significantly.
At this stage, vomiting and regurgitation are the main symptoms. It is difficult to lull the baby to sleep; the baby may refuse to eat and the sucking reflex may be impaired.
Important! If after receiving an injury the baby immediately loses consciousness, you must immediately call an ambulance.
If you do not provide help, you may encounter a number of complications in the future:
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Developmental retardation (inhibition in motor and speech development).
- Increased sensitivity to various infections.
- In a particularly severe form, hydrocephalus may develop.
In a baby from 6 to 9 months
At this age from six months to 8 or 9 months, the symptoms are very similar , but you should pay attention to:
- Pain when lifting, difficulty supporting the head on your own.
- Uncontrollable crying with temporary delay (swallowing) of air.
- Intermittent sleep.
- Not typical activity for a child.
- Uncontrolled body movements, most often on one side.
- The size of the pupils - if the pupils are of different sizes, this is a sign that the brain is damaged and urgent hospitalization is necessary.
In babies from 9 to 12 months
Signs of a concussion in an infant over 9 months of age and in a one-year-old baby:
- Increased heart rate from 140 beats and above.
- A sharp increase or decrease in pressure.
- Lack of appetite.
- Tearfulness.
- Cold extremities.
- Excessive salivation.
At this age, after an injury, it is necessary to measure the pulse every 20 minutes and note the dynamics .
It is necessary to check the fontanel and the site of the bruise, carefully monitor the child’s condition and well-being. At this age, a concussion carries the same consequences as mentioned above, but epilepsy, seizures and tics can also develop.
How to determine after 1 year?
Let's consider the signs of TBI in a one-year-old child and under the age of 2 years.
- Head pain and dizziness.
- Temporary blindness.
- Noise in ears.
- Temporary disorientation.
- Whims, bad mood.
In addition to these complications, the following may also occur:
- Meteor dependence.
- Depression and frequent mood swings.
- Some people find it difficult to manage their emotions.
- Loss of appetite leads to lack of body weight, as well as a lack of vitamins.
- Frequent fatigue, lethargy, weakness.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Frequent headaches, dizziness.
- Memory and speech disorders.
- Motor and movement function is impaired.
Children over the age of one year often experience increased sweating, weakness and a rapid pulse.
Reference. With a brain injury, a child immediately loses orientation in space, the ability to concentrate and fixate his gaze.
Diagnostics
Correct and accurate diagnosis of brain damage in an infant can only be carried out in a medical facility. The examination is carried out by a pediatric neurologist and traumatologist.
Diagnosis of a concussion in an infant is performed in 3 stages:
- The doctor evaluates the baby’s motor activity and reflexes.
- Afterwards, using an ophthalmoscope, intraocular pressure is determined. The eyeballs are also examined for the presence of neurological symptoms. If, when directed towards the light, the pupils of the eyes do not constrict, this indicates that the child has a concussion. After hitting the head, the baby may experience strabismus, which also indicates a serious brain injury.
- Final data are obtained after neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain through the fontanel). It allows you to get an accurate picture of the contents of the baby’s skull. For children whose skull bones are more developed and thicker, this method is not used, because it is not possible to obtain an accurate picture.
TBIs are divided into 3 degrees of severity
Lightweight
These are minor injuries that are not particularly dangerous. Most often, your health improves after 20-30 minutes.
- In newborns and infants: loss of consciousness is not observed, symptoms are visible in the first 15-20 minutes. Characteristics of TBI are increased body temperature, vomiting and regurgitation. After this time, the babies return to normal and calm down.
- In children from one to two years: a short-term loss of consciousness may occur;
- headache;
- nausea;
- Noticeable damage may appear (bruises, contusions, nosebleeds, etc.).
Average
In newborns and infants: the pulse may slow down or speed up; you should check every 15 minutes. Restless crying, vomiting, disorientation and loss of coordination lasting more than 25 minutes.- In children aged one to two years, loss of consciousness, disorientation in space, inability to give a clear answer, “rumbling” in the head, a feeling of weakness, nausea, the gaze cannot concentrate on a specific object, absent-mindedness, inhibited reaction.
Heavy
- In newborns and infants: severe crying;
- loss of appetite;
- lack of coordination (on the one hand);
- pallor;
- sometimes blueness of the skin;
- possible shortness of breath;
- displacement, curvature, depression of the fontanel;
- vomit;
- sleep disturbance.
- blurred vision;
temporary blindness;
Coordination and regulation in space are impaired, a feeling of squeezing of the head and slurred, meaningless speech may appear.