What is the expansion of the subarachnoid space
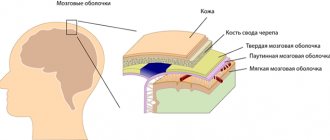
The human brain is surrounded by three protective membranes - hard, arachnoid and soft. The latter is directly adjacent to the medulla and provides its nutrition. The arachnoid membrane is connected to other membranes of the brain using connective tissue membranes. In areas where there are no membranes, there are cisterns.
With concomitant expansion of the subarachnoid space, arachnoiditis should be taken immediately.
The inflammatory process rapidly spreads to the brain tissue.The disease can lead to disability, serious visual impairment, hydrocephalus, and seizures.
Neurologist, reflexologist, hirudotherapist
Kislitsyna Ekaterina Nikolaevna
10 years of experience
Cerebrospinal fluid circulates in the 4 ventricles of the brain (third, fourth and two lateral) and the subarachnoid space. Liquor performs the functions of feeding neurons, removing metabolic products, and mechanically protecting the brain.
The normal amount of cerebrospinal fluid in children is 80-120 ml, in adults 120-160 ml. It is updated 3-5 times per day. The rate of circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid is affected by the position of the body, the intensity of the heartbeat and breathing.
The expansion of the subarachnoid space occurs due to difficulty in the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. Fluid accumulates in the subarachnoid spaces, dilating the ventricles of the brain. The mechanisms of development of the disorder are different: the tumor mechanically blocks the paths for the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, inflammation provokes increased production of cerebrospinal fluid. Intracranial pressure may increase.
Treatment and consequences of dilated subarachnoid space in newborns
The method and principle of treating this disease takes quite a long time and is strictly individual.
To a large extent, everything depends on the nature of the disease, its level of severity, and complications. Primarily by doctors specializing in neurology, neurology - normalization of circulation is restored, the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid in the supracerebral region, intracranial pressure is normalized, as well as suppression, with laboratory confirmation, of identified infections through the use of a number of complex anti-inflammatory drugs, medications that improve and restore metabolism of tissues and cells of the central nervous system.
If necessary, in complex neurotherapy, the doctor can prescribe a number of physioneurological outpatient procedures that will minimize the symptoms of the diagnosed disease and speed up the long-awaited recovery process.
Symptoms of the disease
The expansion of the subarachnoid space in an adult has characteristic signs:
- paralysis of the laryngeal muscles responsible for articulation and, as a result, speech impairment;
- loss of sonority ;
- difficulty swallowing;
- disturbances of visual and auditory perception;
- severe pain in the head, especially in the morning;
- nausea and vomiting accompanying headache;
- dizziness;
- drowsiness or sleep disturbances;
- dementia;
- impairment ;
- hallucinations;
- walking disorders - the patient is able to imitate walking movements in a lying position, but when standing up, walking is difficult, the gait is uncertain, shuffling;
- increased fatigue.
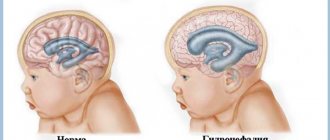
In young children, there is an abnormal enlargement of the skull as a result of developed hydrocephalus. Earlier symptoms are:
- increased sensitivity to sound and light stimuli;
- excessive regurgitation;
- unequal pupil size;
- strabismus;
- problems ;
- slowly overgrowing fontanel;
- swelling of the fontanel;
- restless behavior due to changing weather;
- tremor of the chin and limbs.
The intensity of symptoms depends on the causes of the disease and the severity. In the absence of adequate and timely treatment, expansion of the subarachnoid space in infants is dangerous due to the possible development of hydrocephalus.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
This disease leads to a lag in motor development, the appearance of seizures, paralysis, and intellectual impairment. The effects of hydrocephalus can last a lifetime.
Symptoms
Painful symptoms during liquorodynamic headaches are bursting and dull in nature, intensifying with overexertion, movement, and taking a vertical position. Any uncomfortable position of the body can provoke painful sensations, which are accompanied by vomiting and loss of consciousness. The course of pain is monotonous.
Symptoms of hypertension
Pain syndromes in the head with high blood pressure are intense. The appearance of pain in the depths of the head is characteristic. In such a condition, the rate of increase in liquorodynamic disorder is important: acute hydrocephalus always causes intense attacks. The following symptoms may appear:
- increased pain when sneezing and coughing;
- dizziness;
- decreased heart rate;
- loss of appetite.
Symptoms of hypotension
In conditions caused by a decrease in cerebrospinal fluid pressure, the pain is localized in the crown area, has moderate strength, but a long duration. The patient finds relief in lying down with his head down. It is also possible that:
- attacks of pain when coughing and sharp turns of the head;
- pulsating sensations in the intracranial arteries.
Reasons for expansion
In infants, the disorder occurs due to congenital malformations, birth injuries, brain tumors, and infectious diseases. In some cases, the subarachnoid space and ventricles return to normal by the age of two years. However, pathology requires constant monitoring by specialists who can determine the further prognosis of the disease and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
In adults, expansion of the subarachnoid space occurs as a consequence of a stroke, vascular pathologies, head or spinal injuries, infectious and colds, and tumor cell degeneration. Meningitis, encephalitis, ventriculitis, tuberculosis, inflammation of the sinuses are diseases that affect the brain and can cause disruption of the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
The disease may indicate concomitant leptomeningitis or arachnoiditis - inflammatory processes in the tissues of the soft and arachnoid membranes of the brain. Long-term exposure to toxic substances, such as alcohol, arsenic, and lead, can cause inflammation.
Explanation of terms: subarachnoid space, convexital and cerebrospinal fluid, fissures
The subarachnoid space (SAS) exists in all people. It is located between the soft and arachnoid (arachnoid) membranes of the brain. Its purpose is the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, that is, cerebrospinal fluid. Therefore, it is also called the liquor space. Liquor and membranes protect the brain from traumatic damage, deliver necessary microelements and biologically active substances, and remove tissue metabolic products.
Expansion of SAP occurs when a lot of cerebrospinal fluid is formed or its outflow is difficult. Since the brain is placed in a limited cavity of the cranium, as the volume of fluid increases, its structures are subject to compression. Depending on the type of disease, there is general (uniform) expansion and local expansion. In turn, the latter can cover the frontal, parietal lobes, and convexital surfaces (as all convex parts of the cerebral hemispheres are called).
When describing a tomogram, there is such a thing as a subarachnoid fissure. The sheets of the meninges diverge above the recess of the gyrus and connect above its surface. These spaces are called slits. When they expand, a fairly large amount of liquid accumulates in them.
It should be noted that the concept of expanding SAP is only a conclusion obtained from X-ray, ultrasound or tomographic diagnostics. To determine its cause, a study of symptoms, a history of complaints, and a neurological examination are carried out.
We recommend reading the article about subarachnoid hemorrhage. From it you will learn about the causes of traumatic and non-traumatic hemorrhage, symptoms and pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment, and possible complications. And here is more information about cerebral arachnoiditis.
Diagnostics
An accurate diagnosis can be made after a comprehensive examination. To study the state of brain structures, the following methods are used:
- Computed tomography is a method for diagnosing pathologies of the brain and central nervous system using x-rays. It is highly informative and accurate. The disadvantages of the method are high cost and health risks from irradiation. Although the x-ray dose is much lower than permissible, the method is contraindicated for pregnant women.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is one of the most effective diagnostic methods; it allows you to obtain a layer-by-layer picture of each part of the brain. MRI with contrast is used to examine the condition of the vessels of the head and determine disturbances in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. Before the procedure begins, the patient is given a contrast agent intravenously. The disadvantages of the method are the high cost and the presence of contraindications: MRI is not performed if the patient has metal implants or a pacemaker.
- Cisternography is a type of X-ray diagnostic examination used in combination with CT to study the flow of cerebrospinal fluid. Requires injection of air or contrast agent.
The patient is prescribed a general and biochemical blood test, urine and cerebrospinal fluid tests. To collect cerebrospinal fluid and measure intracranial pressure, a lumbar puncture is performed - a puncture of the spinal cord membranes at the lumbar level.
When examining the cerebrospinal fluid, the concentration of protein and glucose, the number and structure of cells are determined, and a bacterioscopy of a Gram-stained fixed drop is performed. Additionally, an examination of the fundus is performed. If tumor cell degeneration is suspected, a biopsy is performed.
Also, a neurologist examines the patient’s medical history, conducts an examination and makes a conclusion based on all the data.
Features of brain examination in children
CT and MRI are considered the most effective modern diagnostic methods, however, their use is undesirable for young children. It is difficult for a child under one year of age to lie still for a long time. Therefore, in cases where there is still a need to resort to CT or MRI, children are given anesthesia.
To detect expansion of the subarachnoid space in children, the following is used:
- Neurosonography is an ultrasound examination of brain structures. To conduct the examination, the child must have a non-ossified fontanel. The procedure is safe, takes no more than 15 minutes, can be performed repeatedly, and does not require special preparation. A sonologist interprets the results.
- Echoencephalography is a method of examining the brain using ultrasound, used in children with already overgrown fontanelles and in adults. Can be carried out in one- and two-dimensional modes. Allows you to determine the damage to the brain and its displacement relative to the bones of the skull under the pressure of cerebrospinal fluid. Does not require preliminary preparation and is not harmful to health. The disadvantage of the method is its low accuracy.
To prevent brain damage due to birth injuries, hypoxia, and infectious diseases, neurosonography is performed in maternity hospitals. Pediatricians also monitor the growth of the skull in children - this simple procedure allows them to detect hydrocephalus.
What it is
Externally, the brain is reliably protected from external influences by the bones of the skull. Cerebrospinal fluid is responsible for its internal protection: it prevents injury to the organ on the inner surface of the skull, ensures the maintenance of optimal intracranial pressure and regulates the internal state of the water-electrolyte environment.
In addition, cerebrospinal fluid is responsible for metabolic processes between blood and brain matter and removes the products of its metabolism.
Thus, cerebrospinal fluid plays a secondary, but no less significant role in the functioning of all brain structures. Therefore, any disturbances in its composition or deviations in concentration inside the skull immediately affect a person’s well-being.
The production of cerebrospinal fluid occurs in the ventricles of the brain through the epithelium lining them inside. From there, the fluid is delivered through the cerebrospinal fluid pathways to the outer surface of the organ, where it is collected in tanks, washes it and is absorbed through the venous sinuses and granulations of the arachnoid membrane.
The expansion of the external cerebrospinal fluid spaces of the brain in adults is characterized by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid on the surface of the organ. This disease is called external hydrocephalus. It manifests itself in the expansion of the external brain cavities and deformation of brain tissue due to their compression.
The following external liquor spaces of the brain are prone to such changes:
- Tanks (located in the subarachnoid space in the areas of divergence of the arachnoid and pia mater);
- Subarachnoid fissures (located under the arachnoid membrane).
The accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in them leads to an increase in intracranial pressure and the appearance of signs of hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome. It manifests itself in neurological abnormalities: convulsions, cephalgia, deterioration of hearing and vision, and in especially severe cases – paresis, paralysis, and decreased mental abilities. These manifestations are caused by increased pressure on neurons and their dysfunction.
Causes of pathology with uniform and local
In order for SAP to expand, an excess amount of cerebrospinal fluid is needed. This occurs for one of the following reasons or a combination of them:
- increased education (uniform expansion);
- malabsorption due to inflammation, swelling (there are usually local and uneven changes);
- obstructions to outflow - tumor, cyst, hemorrhage (both local and general disturbances occur depending on the level of blockage of the cerebrospinal fluid circulation);
These pathological mechanisms can arise during the period of intrauterine development. In this case, the baby is born with hydrocephalus (water on the brain).
Hydrocephalus
The factors of this pathology are:
- malformations (closure of outflow holes, narrowing of the Sylvian aqueduct, defect in the structure of the SAP);
- anomalies in the structure of the skull, its connection with the spine;
- trauma during childbirth;
- infectious diseases of the mother - syphilitic, toxoplasma, cytomegalovirus, rubella.
Older children and adults suffer from hydrocephalus for the following reasons:
- inflammation of the brain tissue (encephalitis) or membranes (meningitis, arachnoiditis);
- skull injuries, concussions;
- hemorrhage – ventricular, intracerebral with transition to the ventricles;
- cyst or tumor of the brain.
Brain tumor is one of the causes of hydrocephalus and expansion of the subarachnoid space
A special form of the disease is atrophy (reduced volume) of the brain and filling of the formed spaces with fluid. Such changes are typical for elderly patients against the background of atherosclerosis, malignant hypertension, complications of diabetes with widespread arterial damage (macroangiopathy).
Features of the deviation and possible reasons for its development
The human brain is a very complex organ; like the heart, it is forced to constantly work. In this active mode, it requires optimal nutrition and blood supply to function properly. So that in the future you understand what we are talking about, the human brain consists of three membranes:
- arachnoid;
- hard;
- soft.
The space between the arachnoid and pia mater is called the subarachnoid space. The arachnoid membrane itself surrounds the brain and is covered with endometrium on top. It communicates with the other two tissues using subarachnoid connections - membranes. The choroid subarachnoid plexuses form the ventricular system of the brain and spinal cord, consisting of 4 reservoirs. It is in these reservoirs that cerebrospinal fluid circulates.
Subarachnoid spaces, as mentioned above, are cavities in the brain that are filled with a special liquid called cerebrospinal fluid. The cavity filled with fluid serves the function of nourishing and protecting the brain. Liquor is an optimal environment for the exchange of useful substances between the blood and the organ itself - the brain; it also carries nutrients to the nerve cells and ventricles of the brain. The end products of brain tissue metabolism are isolated and removed in the cerebrospinal fluid. Liquor constantly circulates in the brain cavities, its movement determines the contraction of the heart, body position, breathing, and even the movement of the epithelium on the choroid plexuses. Under normal conditions, the amount of fluid in the subarachnoid space should remain no more than 140 ml.
As a rule, the diagnosis of dilation of subarachnoid convexital spaces does not apply to adults, but is given to young children and, in particular, infants. This could occur due to birth trauma or abnormalities in brain development. If such a phenomenon has occurred, then the baby is prescribed an ultrasound scan of the brain; it is this diagnostic method in children that determines the deviation of the subarachnoid convexital spaces.
Expansion rates
The expansion of the subarachnoid space occurs in three degrees:
- moderate - increase from 1 to 2 mm;
- medium - increase from 3 to 4 mm;
- heavy from 4 mm.
The expansion of the cerebrospinal fluid spaces occurs in proportion to the growth of the newborn’s head and the swelling of the fontanelle.
Article on the topic: What are the most common spinal diseases and how are they treated?
The course and outcome of the disease depends on timely seeking medical help and initiation of treatment. If the treatment is chosen correctly, then the changes in the ventricles remain almost within normal limits.
Diagnostic methods and goals
The disease can be diagnosed only after a comprehensive examination and laboratory tests. After receiving the results of magnetic resonance or computed tomography, blood biochemistry results, ultrasound examination of the cerebral hemispheres, assessment of the patient’s symptoms and behavior, the neurologist will establish the final diagnosis, the extent of the disease and prescribe medication.
Basic diagnostic methods:
- Neurosonography . It lasts no more than fifteen minutes and is carried out using an ultrasonic sensor through an open fontanel on the newborn’s head. The study can be carried out quite often, without negative consequences for the child. As a rule, neurosonography is performed on all newborns in the maternity hospital to identify pathologies in brain development at the initial stage. A neurologist or pediatrician interprets the examination data. Only by comparing symptoms and examination data can a doctor make a diagnosis.
- Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are very expensive research methods and are carried out when serious abnormalities are detected. As a rule, for newborns it is enough to conduct neurosonography through the fontanel, but adults already need more serious diagnostic methods. Today these are the most reliable and accurate methods for studying the human body. MRI allows you to see a layer-by-layer image of the desired area of the brain. Examination of infants is very problematic, as it requires complete fixation and immobility, which is very problematic for small children. If a baby needs this type of examination, it is carried out under anesthesia.
- Cisternography is used to determine the direction of cerebrospinal fluid and clarify the type of hydrocephalus.
- Angiography is an examination method in which contrast is injected into the artery and abnormalities in the patency of blood vessels are detected.
- Neuropsychological examination - examination and questioning of the patient, collecting all tests and studies together to identify disorders in the functioning and functioning of the brain.
Article on the topic: Spironolactone - instructions for use, indications and price