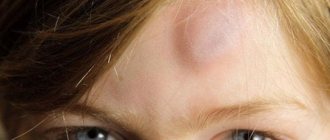
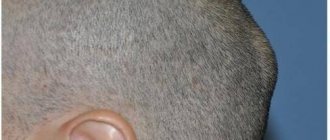
There is no need to worry too much if you notice a lump or ball on the back of your head. Most of them, as a rule, do not pose any danger. However, it is recommended to visit a doctor after the appearance of such a formation, especially if it causes concern, in order to establish a correct diagnosis.
Painful balls or bumps on the back of the head that appear suddenly within a day or two can be caused by infection or injury. If the formation was caused by an infection, the area around it will be red and warm to the touch. You can always consult a doctor for advice. A lump in the neck or back of the head most often represents:
- Injury. You may, for example, hit something and unconsciously not notice it or soon forget it
- Enlarged lymph nodes . Usually indicates that you have an infection.
- Skin tumors are harmless soft and less often hard growths on the skin that are a cosmetic defect.
- Cysts are fluid-filled bumps that may go away on their own. They usually do not require any medical treatment.
But there are other reasons, which are discussed in more detail below.
Causes
If a lump under the skin in the back of the head causes pain, then it is difficult not to notice it and not think about it. People can sometimes live with painless growths for years, paying attention to them only occasionally, for example, when combing, styling their hair or cutting their hair. Moreover, often the same reason may be accompanied by unpleasant sensations, or may not physically bother you at all.
Main reasons include:
Lipoma
Lipoma (fat)
This is a tumor that mainly consists of fat cells. It is a capsule that usually feels like a soft and mobile lump. The reasons for its occurrence are unknown, although it is believed that they may be genetic.
Symptoms include:
- A small bump that may become larger over time
- Feels like a soft and doughy ball
- Pain may occur if it continues to grow
Atheroma
Atheroma
This is a small cyst that appears when the sebaceous gland is blocked. They are usually harmless. However, it is important to have a doctor examine these growths, especially when they begin to change in appearance, size, or shape.
Symptoms of atheroma include:
- They may ooze, leaving a dry crust over time.
- The scalp is flaky in this area
- Sometimes they may encyst and turn into hard lumps
- May become inflamed, painful, swollen and red
Hair (follicular) cyst
Pilar cyst
This is a type of cyst that forms in the area of the hair follicles. It is a type of the above-mentioned atheroma, along with an epidermal cyst.
The pilar cyst is filled with keratin, which helps your hair grow. These lesions mainly affect the scalp, but can also be found in any other part of the body where hair grows.
May develop into cancer in rare cases. Therefore, many doctors prefer to remove them to be on the safe side.
Symptoms include:
- Presence of a hard lump on the back of the head
- Pain
- Inflammation
Ingrown hairs
Lumps due to ingrown hairs
The cause of the appearance of a hard ball may simply be an ingrown hair. These growths can appear after shaving, cutting or damage to the hair as a result of the cut hair continuing to grow inside your skin next to the follicle.
The problem is common among people who regularly shave their hair, in this case the back of their head. Ingrown hairs should be examined for signs of infection, which can cause them to grow to the size of a noticeable bump. Common symptoms of its presence include:
- Edema
- Redness
- Painful bump that looks like a pimple
Gout
Tophi with gout on the head most often form on the auricle.
But there are also atypical cases involving other areas of the head and neck (source) This disease is characterized by an increase in the level of uric acid in the blood. This is a form of arthritis that also causes joint pain. Uric acid forms crystals, which then accumulate in your body.
Clusters of such crystals are called tophi or gouty nodes. They can form in areas such as the head, fingers, joints, and also on the earlobes. Tophi are known to be extremely painful, but the pain usually goes away when the level of uric acid in the blood begins to decrease.
Common symptoms include:
- Joint pain
- Swelling and redness in the affected area
- Fever
- Problems walking
Keloid acne
The condition is also called papillary dermatitis. But the term “keloid acne” is not entirely correct, since it is not acne, but a severe form of folliculitis. Moreover, histologically the lesions are not keloid scars. They form almost exclusively on the back of the head, and are found only in black men who serve in the army and shave the back of their heads. For example, in the USA, this is a massive problem for African-American military personnel, so even protocols have been developed to prevent it. In the early stages, keloid acne can be treated well, but in advanced stages the prognosis is not so favorable.
Attached tick or Lyme disease
After the bite of an infected tick, a small papule appears, around which redness spreads more and more every day - this is the beginning of Lyme disease.
Ticks usually live on bushes and trees and react to your breathing. This parasite can fall from a branch and attach itself to the back of the head. You may not even feel anything until you accidentally feel a lump on the back of your head, which is a blood-filled tick.
The tick can also transmit Lyme disease, one of the first symptoms of which is sometimes the formation of a small nodule (papule), although not always. Its appearance usually takes about three days from the moment of the bite. Other symptoms of this serious infection include:
- Headache
- Fever
- Nausea
- Joint pain
- Rash at the site of the bite
Diagnosis of the disease
Often, the clinical picture alone is sufficient to make a diagnosis and determine a treatment regimen. In some cases, the use of additional diagnostic techniques is still required. In particular, they are necessary to clarify the nature of the tumor and exclude its malignant nature.
To determine the nature of the lump, you may need to undergo the following procedures:
- general blood and urine tests - aimed at identifying an infectious or inflammatory process;
- blood biochemistry - allows you to identify problems with metabolism and suspect oncology;
- the use of tumor markers is an informative method for detecting cancer;
- X-ray or CT scan of the skull - help assess the condition of the bones of the skull, exclude their fractures, the presence of cracks;
- Ultrasound – aimed at studying the structure of the lump, its composition and the depth of penetration into the tissue;
- histology – studies the cellular structure of the biomaterial, which allows you to quickly make a diagnosis;
- A biopsy is another way to examine tissue for cancer.
Based on the diagnostic results, the optimal treatment method is selected. If necessary, the procedures are repeated several times, which makes it possible to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment.
Painful lump on the back of the head
There are several different reasons why painful lumps may form under the skin on the back of your head. This may be inflammation of the lymph nodes or enlargement of the salivary glands, as well as atheroma or lipoma, which sometimes begin to hurt.
An inflamed lymph node is one of the causes of painful lumps
The reasons associated with enlarged lymphatic nodes or salivary glands can be as minor as an allergic reaction or quite serious, such as oral cancer.
The reason why the lymph nodes in the cervical region are inflamed may be bacteria. But there are also cases when viruses are to blame, which can be a symptom of the following diseases:
- Rubella
- Herpes
- AIDS
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Viral pharyngitis
Additional causes that may contribute to swelling in this area include:
- Allergic reactions
- Hodgkin's lymphoma
- Allergy to medications
- Oral cancer
- Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas
- Food allergies
- Leukemia
- Thyroid disease
A soft skin formation that appears on the back of the head may be an atheroma or a lipoma. Although most often they are not painful, this can change over time. A medical examination is mandatory to determine the correct diagnosis.
A lump on the back of the head can also be painful or not, depending on whether it is benign or malignant. The actual cause can only be determined through a medical examination.
You can always try to use proven home remedies to get rid of bumps that are not dangerous to your health. However, it is important that the doctor conduct a preliminary examination of this formation.
Which doctor should I contact?
Absolutely any new formation that can be detected at the back of the head is a harmless superficial bump or the first sign of a dangerous disease. To avoid deterioration of well-being and more serious health problems, it is recommended to show the “ball” to the doctor. Examination and diagnosis of such pathologies is carried out by a therapist, ENT specialist, surgeon, allergist, dermatologist or oncologist.
Lump on the back of the neck
The appearance of a lump in this area can also be a sign of malignancy or infection. The lump on the back of the neck can be soft and tender or, on the contrary, hard and tough. It can originate just under the skin or much deeper.
Many tissues, organs and muscles are located near the back of your head and neck. They include:
- Arteries and veins
- Neck muscles
- Cervical vertebrae
- The lymph nodes
- Salivary glands
Enlarged lymph nodes are considered the main cause of the appearance of balls and bumps on the back of the neck. Lymph nodes are made up of cells that help your body fight infections and also prevent cancer cells from spreading. These protective organs enlarge when you are sick to help your body fight infections.
Additional causes of swollen lymph nodes may include:
- Pharyngitis
- Sinus infection
- Dental infections
- Ear infections
Lump on the back of the head behind the ear
There are a number of different reasons for the appearance of balls and lumps behind the ear. They also tend to come in a variety of shapes. Lumps in this area may be harmless, while others are a sign that something serious is going on in your body.
A bump on the back of the head behind the ear can often be caused by swollen lymph nodes. They are an essential part of the immune system, acting as a biological filter and usually enlarge when an infection enters the body.
Enlarged lymph nodes should return to normal on their own after treatment of the underlying disease. Ear or skin infections are the main reason for their enlargement. It is recommended to consult a doctor if the formation does not go away for more than fourteen days or if additional symptoms appear.
Other causes of a lump in the back of the ear include:
- Acne
Pimples behind the ear can occur when pores or hair follicles become clogged. Although it is rare, the possibility that acne can appear behind the ears cannot be ruled out.
- Infections
Infections that can cause swelling in the throat can also cause a lump. Mononucleosis is one of the main diseases, which is accompanied by inflammation of the lymph nodes behind the ears, and the throat also swells.
- Abscesses and cysts
Abscesses (boils) and cysts are very similar in that they are both fluid-filled structures. The distinguishing factor is that an abscess is filled with pus, while a cyst most often is not. Abscesses can develop due to an infection or foreign body in the ear.
- Atheromas
They are also known as epidermoid cysts. Atheromas are known to form from clogged sebaceous glands and are the most common type of skin cyst. Atheroma can also appear in rare cases behind the ear.
- Mastoiditis
There are mastoid processes of the temporal bone, which are located directly in the area behind the ears. An ear infection can spread to this bone in some cases. The result will be swelling and a lump behind the ear.
A bite of an insect
Insect activity, as a rule, increases in the spring and summer, and very often their bites do not pose any particular danger. However, some insects inflict very painful bites, accompanied by the formation of a small bump or pimples in one area or another of the head.
The scalp at the site of the bite is very itchy, swollen and red. Typically, swelling caused by an insect bite may subside within a few days.
Lump on the back of the head and headache
These bumps may appear due to an injury you recently suffered. They can also form due to a torn or strained muscle tendon. Symptoms of this:
- Swelling near the neck
- Sensitive areas on the neck and back of the head
- Pain in the shoulders, neck and upper back
- Neck muscle stiffness
Additionally, growing osteomas (abnormal hard bone growths) may also be associated with headaches.
Lump on the back of the head made of hard tissue
Some hard lumps may appear on the back of the head and remain there for several months or even years. Those that form in this area are usually inactive. Although they are benign in many cases, they can also be malignant.
If you notice a hard lump under the skin on your head that is not a regular bruise, it was not soft before and does not go away over time, then it may be:
- Osteoma is a benign bone tumor that is known to occur in this area
- A dermoid cyst is a rare tumor consisting simultaneously of various hard tissues, among which hard tissues may predominate. It can be diagnosed in a child. It is usually benign and does not hurt, although it can become infected.
Osteoma is a hard formation of bone tissue.
It is very important to consult a doctor to establish the correct diagnosis. Surgery may be necessary, depending on the cause and the problems created.
Treatment
Treatment of neoplasms is only surgical. Drug therapy is prescribed to relieve symptoms, prepare for surgery and recover after surgery.
Typically, drug treatment is symptomatic. The same applies to traditional medicine methods. This point is especially important, because in achieving therapeutic goals, many use truly barbaric methods of getting rid of pathology, which is absolutely forbidden to do.
A few weeks before the proposed manipulation, diagnostics and general clinical research methods (ECG, echocardiography, blood tests, urine tests) are carried out. Consult with an anesthesiologist to select adequate anesthesia and medications for emergency cases.
On the eve of the operation, it is better to be in the hospital and monitor your blood pressure. If there is severe anxiety, doctors may prescribe sedatives.
The last meal should be no later than 20.00 the previous evening. In the morning it is permissible to drink some water. Adequate nutrition can provoke severe vomiting and severe intoxication after the administration of anesthesia.
Removal of cranial osteoma of any location is usually carried out using the direct cavity method:
- To do this, the skin along with living tissue is cut through, the affected bone is released, the tumor is drilled out and removed within healthy tissue.
- Instead of the void, a titanium mesh or the patient’s own bone material is installed.
- Afterwards the wound is treated, sutured and re-treated.
If the tumor is localized in the frontal sinus or sinuses, you can try access through the nasal cavity using endoscopic equipment. However, such methods are suitable for tiny osteomas.
Minimally invasive manipulations also include radiofrequency vaporization under the control of a computed tomograph.
To achieve high aesthetic results, the incision can be made in the scalp, then the scar tissue will not be visible after the patient’s final recovery.