Formations of the scalp - this article will tell you about the types of neoplasms that arise in the scalp area.
The scalp is exposed to various external influences. In the course of our life, we constantly experience the effects of various chemicals, exposure to ultraviolet rays on the street or in a solarium. In any case, the variety of allergens and irritants greatly affects the scalp. The consequences can be dire. Neoplasms may occur.
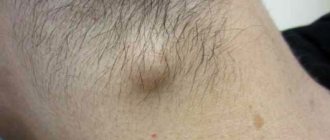
Scalp formations
What to do if warts appear on your head?
The likelihood that warts will disappear on their own in the near future is very low.
They do not go away even under the influence of mysterious spells, medicinal herbs or other methods that the boundless human imagination can come up with.
Perhaps the warts really are regressing.
But this can happen only in a few years, or even decades.
At the same time, they bother most people.
Even if the wart is overgrown with hair and is not visible, in any case it interferes with cutting and combing.
She is easily injured.
It may bleed, and sometimes the resulting wound festeres.
The wart should be removed.
This procedure does not cause pain, takes a few minutes and allows you to forget about the problem once and for all.
If a person does not see a doctor and is not treated, the wart may increase in size.
This does not pose a direct threat to health.
But subsequent removal requires treatment of a larger area of the head.
There is a higher risk that a scar will appear and hair in this area will no longer grow.
Therefore, it is better to remove a wart on the head earlier, while it is still small.
Symptoms
You can understand what atheroma looks like from the photo, but we will also describe the characteristic symptoms of this disease. If the tumor is localized on the head, then most often (in 70% of cases) multiple tumors are diagnosed; only in 30% of cases are single formations found. With multiple formations in 10 percent of patients, their number may exceed ten pieces.
If we talk about what atheroma is, then in most cases it is manifested by the following symptoms:
- this is a superficially located mobile tumor;
- the main symptoms are a painless, densely elastic formation;
- the skin over the tumor is unchanged;
However, sometimes the formation can become inflamed, in which case the symptoms are supplemented by the following signs:
Surgitron device: principle of operation and areas of application of the radioknife
- the skin over the tumor turns red;
- if there is rapid growth of a festering tumor, the skin over it ulcerates.
Quite often, in the central part of the bulge on the skin, you can notice an enlarged, clogged sebaceous duct. Sometimes there is a long course of the disease, when the tumor does not change for many years. Its gradual growth or abscess is often noted. There are also cysts that communicate with the surface of the skin through a small hole. Whitish or yellowish thick masses that smell unpleasantly are periodically separated from it.
Attention! It is important to differentiate the disease from other soft tissue tumors, for example, dermoid cysts, fibromas, lipomas, osteomas.
A dangerous complication of atheromas is their suppuration. In this case, pain, swelling occurs, the swelling increases, and the skin turns red. If treatment is not carried out, the suppuration may break out on its own. At the same time, sebum-like and purulent fetid contents are released. When the infection spreads to surrounding tissues, phlegmon develops, so antibiotic therapy is performed. In case of suppuration, an urgent surgical operation is indicated, which consists of opening the abscess and installing drainage. In this case, the cosmetic effect will be worse, since no suture is applied. In addition, it is not possible to completely remove the capsule, so the disease may recur.
Warts on the head: is conservative treatment possible?
Conservative treatment of warts on the head is possible, although it is not always effective.
Are used:
- applications of lactic salicylic collodion
- 40% salicylic patch
The use of these techniques is difficult given the location of the wart.
Most people have hair on their heads.
Therefore, applying the patch can be very painful, and also ruins your hairstyle.
Treatment with drugs is also difficult.
They wet the hair.
With a lot of hair, an adequate dose does not always reach the goal.
Therefore, conservative measures to combat warts of the scalp are often ineffective.
It is much easier to remove them using physical methods in one procedure.
Advantages of this approach:
- one-time procedure
- no spread of warts to adjacent areas of skin
- minimal risk of relapse
- 100% effective (after removal, the wart will definitely disappear, which cannot be said about conservative treatment or chemical coagulation)
Curettage is sometimes used under local anesthesia.
Causes and provoking factors
Oncological diseases today still remain poorly studied . But some of the causes that can cause scalp cancer include:
- influence of harmful substances: nicotine, arsenic, carcinogen;
- radiation exposure;
- decreased immunity;
- heredity;
- exposure to high temperatures or ultraviolet radiation;
- chronic dermatitis and other skin diseases;
- use of hormonal or immunostimulating drugs;
- influence of direct electromagnetic current.
Provoking factors:
- Skin type – people with very fair skin who spend a lot of time under the scorching sun are most likely to get sick.
- Large volume of moles on the head. Especially if they are frequently exposed to injury.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine apparatus.
- Long-term injury to the same area of skin.
- Paget's or Bowen's disease.
Attention! Most often, skin cancer under the hair occurs when moles are damaged by combing.
Is it painful to remove warts?
Removing warts using cryodestruction is painful.
Painful sensations are observed both during the period of removal and after it, when an inflammatory reaction is formed.
If electrocoagulation or laser is used, there is no pain.
Because anesthesia is used.
When a wart is located on the scalp, topical anesthesia is usually used.
A cream containing prilocaine and lidocaine is applied to the skin.
After a few minutes, skin sensitivity disappears.
The doctor can remove the wart, and the patient does not feel anything during the procedure.
After its completion, when the anesthesia wears off, there is no pain either.
Lip cancer
Up to 95% of lip cancer cases occur in men; the typical location of the tumor is the lower lip. From a histological point of view, malignant tumors of the lip are usually squamous cell carcinoma. It is most often preceded by precancerous conditions - chronic fissures, limited hyperkeratosis, warty precancer, etc.
Lip cancer at different stages of development is characterized by local changes in the form of depression or painful erosion covered with crusts. Over time, lip cancer covers an increasingly larger area and can ulcerate. Due to its location, lip cancer is easily recognized in the early stages and therefore responds well to treatment.
Treatment of brain tumors at the Yusupov Hospital
Treatment of brain tumors at the Yusupov Hospital Oncology Center is carried out using the most advanced non-surgical techniques:
- stereotactic radiosurgery – which allows you to remove small tumors in one session;
- radiation therapy using the latest generation installations, the latest linear accelerators and systems that ensure maximum safety and effectiveness of therapy, etc.
If surgical treatment is unavoidable, it is performed by the best specialists who masterfully master all the technologies and methods of interventional neuroradiology and modern neurosurgery. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital Oncology Center make every effort to use gentle, minimally invasive methods and operations with transnasal access, which do not require an incision in the skull.
Thanks to the innovative equipment of the oncology center, doctors have the opportunity to perform high-quality diagnostics and carry out effective treatment of brain tumors using non-surgical or minimally invasive methods.
In parallel with neurosurgeons, neurologists, oncologists, and radiologists take part in the treatment of patients with brain tumors. The patient is provided with supportive therapy and qualified psychological support.
You can make an appointment with an oncologist at the oncology clinic and find out the conditions of hospitalization by calling the Yusupov Hospital or online on the website from the coordinating doctor.
Classification of brain tumors by occurrence
There are different types of brain tumors in adults, which are classified according to certain criteria.
First of all, all brain tumors are divided into primary and secondary.
A primary tumor (for example, primary CNS lymphoma) is formed by the brain tissue itself and adjacent to it: tissue of the cranial nerves, meninges, pineal gland, lymphoid tissue or pituitary tissue. The development of these neoplasms is associated with mutations that lead to the appearance of abnormalities in the DNA of brain cells.
The occurrence of secondary brain tumors is most often associated with a metastatic process from other organs affected by cancer.
Classification of brain tumors according to Smirnov
This classification involves the division of brain tumors into several types in accordance with cell maturity and morphological characteristics.
According to the degree of maturity, brain tumors can be:
- mature (for example, cerebral ependymoma);
- immature (for example, ganglioblastoma of the brain);
- immature (for example, medulloblastoma of the brain).
In addition to the degree of maturity, this classification is also based on morphological characteristics, combining classification by localization and histological classification.
Classification of brain tumors by histological type
The tissue from which the tumor develops is of great importance for predicting the further “behavior” of a tumor. According to histological classification, tumors are divided into the following types:
- glial tumor of the brain;
- tumor of nervous tissue;
- vascular tumor (eg, brainstem cavernoma);
- tumor of the meninges;
- teratoma.
Glial brain tumors include:
- astrocytoma - a benign tumor of glial tissue localized in the cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum;
- oligodendroglioma - a tumor of glial tissue that is not prone to grow into other tissues and is localized in the cerebral hemispheres;
- ependymoma - brain ependymoma is a benign tumor localized in the lateral or 4th ventricle;
- glioblastoma multiforme - this type of tumor is diagnosed, as a rule, in elderly patients;
- medulloblastoma - a tumor affecting the cerebellum, most often found in children;
- pinealoma is a neoplasm that affects the pineal gland.
Tumors formed from nerve tissue include:
- Brain neuroma (schwannoma): the tumor is formed by Schwann cells or nerve sheath cells. Most often, this type of disease is benign, but sometimes it can be malignant;
- neurofibroma of the brain - is, as a rule, a benign neoplasm consisting of Schwann cells, mast cells or fibroblasts;
- tumors developing in the area of the sella turcica, for example, from the pituitary gland.
A tumor of the meninges is, for example, a meningioma of the brain. This tumor is characterized by slow growth and benign nature.
Teratomas are cancerous tumors that develop from cells with a morphological structure close to stem cells. Most often diagnosed in patients of childhood and young age.