Good concentration and memory are integral factors in any effective activity and full communication with others. That is why loss of concentration can cause a lot of difficulties for a person and reduce his quality of life. Unfortunately, in modern society there are more and more people with problems such as the inability to concentrate on a task and difficulty remembering new information.
The main causes of loss of concentration and memory
Conventionally, they can be divided into 2 categories. The first includes those that are voluntarily or unwittingly “provoked” by the person himself and those that are caused by a number of diseases.
Causes associated with poor lifestyle
Mental fatigue due to a large amount of information. Daily, long hours of “surfing” on the Internet is one of the main causes of mental stress.
This is interesting! If you are told that multitasking is very effective and you should strive for it, don’t believe it! It is a myth. It has already been scientifically proven that a person cannot do several things at the same time, because his brain begins to “program malfunctions”, like a regular computer with a processor overloaded with tasks.
Chronic stress and emotional burnout. One of the main reasons for decreased concentration, both in children and adults.
Abuse of coffee. In small quantities, coffee stimulates the brain, but its excess, on the contrary, leads to increased fatigue, inability to concentrate and memory impairment.
Long-term, uncontrolled use of medications that correct the activity of the nervous system: antidepressants, tranquilizers, sedatives, barbiturates, etc.
Alcohol, nicotine, drugs. Such substances have the most negative effect on the functioning of the brain, even to the point of destroying its cells.
Violation of the regime. During sleep, nerve cells not only regenerate, but also form new neural connections. Without enough sleep day after day, you force your brain to work “to wear out”, which has the most negative effect on concentration.
Poor nutrition. Convenience foods, cheap food of synthetic origin, “chemical” drinks and sweets - all of this contains substances harmful to health, many of which tend to accumulate in the body. Gradually, they begin to negatively affect memory and the ability to concentrate on a specific task.
Causes (risk factors)
A decrease in concentration is caused by:
- Emotional stress.
- Lack of rest (sleep). Sleep problems are the underlying cause of constant sleepiness.
- Chronic fatigue syndrome.
- Hormonal disorders.
- Psychological disorders (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder).
- Incorrect (strict) diets, starvation (the consequence is an acute lack of energy and nutrients required by organs and systems).
- Increased anxiety, anxiety.
- The presence of progressive diseases accompanied by painful sensations.
- Malfunctions of the cardiovascular system.
- Depressive disorders.
- Head injuries.
- Side effects that occur after taking certain types of medications and alcoholic beverages.
- Exposure to various distracting factors (in particular, noise, vibration).
- Unfavorable microclimate conditions (low temperature, unsatisfactory air humidity, drafts, poor lighting).
- Behavioral characteristics (lack of the habit of focusing on current activities).
Reasons of a physiological nature
- Lack of vitamins. A lack of vital substances in the body (especially vitamin D) leads to a deterioration in the synthesis of neurotransmitters and disruption of the nervous system. As a result, a person becomes inattentive and absent-minded.
- Some cerebrovascular diseases (for example, multiple sclerosis, hypertension, Alzheimer's disease).
- Hormonal disorders associated with the thyroid gland, adrenal glands or diabetes.
- Metabolic disease.
- Anemia.
- Brain injuries.
- Cervical osteochondrosis (blood circulation in the vessels of the brain worsens).
It is very important to find out the root cause of the problem, because this is the only way to effectively solve it or at least improve the situation.
Decreased attention
Sysuev Oleg Mikhailovich Neurologist
✓ Article verified by a medical expert
Decreased attention is a person’s inability to concentrate on a specific object, task, or stimulus. The problem occurs in children and adults. Absent-mindedness accumulates, leading to neurological and mental disorders. It is necessary to identify the causes in a timely manner in order to undergo treatment and avoid irreversible processes.
Types of violations
Decreased attention is a common problem that affects a person’s quality of life. Children's concentration is quite harmless, but with age the disease worsens.
Types of disorders:
- Absent-mindedness (fluttering concentration) - present in school-age children. Occurs due to lack of interest in activities.
- The inattention of a scientist” - a person stays in his thoughts for a long time, so it is difficult to switch from one process to another.
- Distraction is a constant switching from one type of activity to another. The inability to bring a single task to its logical conclusion.
- Lack of concentration in old people is the inability to shift attention due to age and neurological conditions.
- Inertia is a pathological fixation of attention. A person does not know at what time to shift attention to another object.
- Aprosexia is complete inattention.
At a certain point, the human brain stops performing tasks, being distracted from the main activity. Inattention is a violation of one of the cognitive functions.
Indeed, problems with concentration are often caused by mental stress and lack of interest. Such symptoms are not a sign of serious illness. They pass as soon as a person rests or switches to a more interesting activity. If we talk about age-related decrease in concentration, this is the cause of serious pathological disorders.
Causes and symptoms
The diagnosis of adult attention disorder is different from childhood inattention. Let's look at the main factors influencing reduced concentration:
- genetic predisposition;
- birth injuries;
- difficult childhood;
- brain dysfunction;
- hormonal disorders;
- emotional stress;
- wrong diet;
- excessive anxiety and pain.
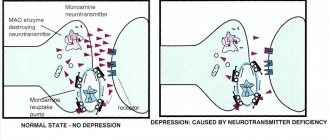
Lack of concentration leads to depression, hyperprosexia, epilepsy, memory impairment, cognitive impairment, dementia (dementia).
Symptoms of inattention:
- Inability to focus on a subject. Characterized by “freezing” and “wandering” of attention. A person cannot concentrate on doing a certain task, misses important details, and is unable to concentrate. For example, he rereads a paragraph in a book several times without understanding what is written there.
- Restlessness is the inability to sit still. I always want to run somewhere. Because of this, there is a lack of attention and inability to concentrate.
- Impulsivity is caused by the tendency to act unconsciously (uncontrollably). Characterized by emotional people. Under the influence of external experiences, a person cannot concentrate on business.
- Fussiness is the rush to do everything quickly. A waste of time on unnecessary things. As a result, important details are missed.
- Fatigue is a symptom of increased fatigue. In such a state, a person becomes inattentive, unfocused, and depressed.
- Increased irritability is a sign of depression. The person is worried and cannot focus his gaze on one object.
- Nervous excitability is a malfunction of the nervous system. The patient instantly reacts to external events, thereby disconnecting from the main activity.
Signs of decreased attention require careful analysis. Make an appointment with a specialist and solve the problem!
Which doctor should I contact?
If you lose concentration, you need to see a neurologist. The specialist will find out the cause, make a diagnosis, and prescribe therapy. Attention disorders are difficult to study. It is necessary to conduct a detailed diagnosis of the brain. Modern equipment and devices make it possible to quickly determine the examination and treatment of inattention. The doctor will develop a health and rehabilitation program based on the individual qualities of the patient.
Diagnosis and treatment
The study of the patient begins with examining the patient and taking samples. Diagnosis of the causes of decreased attention includes modern methods:
- pathopsychological tests - test tasks with stimulus material;
- double stimulation method - diagnosis of modality-specific disorders;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- electroencephalography;
- angiography.
Treatment of decreased attention is based on drug therapy, which depends on the concomitant disease. Memory enhancing drugs and psychostimulants are prescribed. The sooner you address the problem, the faster and more effective your recovery will be.
Rehabilitation methods
In addition to medications, it is recommended to undergo rehabilitation procedures:
- Patients with psychological problems are prescribed psychocorrection - auto-training for emotional relief. They provide explanations on how to behave at home.
- Electrical stimulation of motor nerves is an effective way to improve attention problems.
- The patient is prescribed water treatments, in particular balneotherapy.
- A relaxing massage will improve blood circulation.
- Relaxation methods are modern relaxing activities that the patient can do at home.
- Physiotherapy. Light sports are the basis for vivacity and good mood.
In addition, measures are taken to eliminate negative relationships in the family. Psychological work with the patient is part of the health restoration program.
What you can do yourself
Cognitive function training is the main component of increasing attention. There are special programs that automatically detect the most weakened brain functions and offer a training regimen that is individually suitable for each patient.
A few rules of daily life:
- Plan your vacation. Decreased attention directly depends on fatigue and overwork. On weekends, disconnect from the hustle and bustle and put your thoughts in order.
- Get out into nature. A walk through the forest or park refreshes the brain and stimulates blood circulation.
- Cope with depression with the help of meditation, which drives away negative thoughts, anxiety, and restlessness.
- Remove objects that distract you. There is time for work - there is time for answering messages and calls.
- Perform complex and basic tasks in the morning, when you have a good energy reserve.
Improve your concentration with games and exercises. Do this during breaks from your main activity. For example, we fill a glass with water and hold it at arm’s length for 3 minutes, without being distracted by anything.
Result and lifestyle
Treatment for decreased attention yields positive results if you are patient. Prevention of loss of concentration is based on maintaining a healthy lifestyle, walking in the fresh air, eating right and giving up bad habits. Get more rest - healthy sleep improves physical activity and increases attention. Visit your doctor regularly!
Symptoms of loss of concentration and memory loss
The most obvious sign is that a person is very bad at remembering information that is not directly related to his personal experiences or problems. He may forget entire episodes from the past, or confuse the past with the present, and “get lost” in the days of the week and even months.
In a conversation, he often forgets some words, and it is difficult for him to clearly formulate a specific thought. When leaving home, such people often worry because they cannot remember whether the water, electricity, gas, household appliances, etc. are turned off.
In addition, loss of concentration and memory is often accompanied by:
- a feeling of absent-mindedness, lack of understanding of what and how to do, even if the task at hand is not very difficult;
- increased suspiciousness;
- feeling of confusion;
- slowness;
- constant feeling of fatigue;
- headaches;
- problems with vision and hearing;
- cardiac arrhythmia.
During work, it is difficult for such a person to concentrate on the task, as a result of which he begins to do many secondary things in parallel. The same thing is observed in everyday life. He is greatly distracted by extraneous conversations, music, and background noise. Everything is done slowly.
Causes and types of attention disorders
Image from lori.ru
Attention impairment is defined by a number of different measures of neuro-behavioral disorders, consisting of:
- abnormal changes in selectivity and direction of activity;
- violation of coordination of individual actions;
- decreased concentration and inconstancy of attention.
Attention disorders manifest themselves to varying degrees in cases of organic damage, mainly to the frontal lobes and other areas of the brain, as well as in cases of ordinary fatigue.
There are three types of attention disorders:
- Type I Distracted attention, also called “fluttering”, which is characterized by uncontrolled switching of attention with poor concentration. This type of inattention can usually be observed in preschool-age children, as well as in adults who are weakened by illness or experience great fatigue.
- II type. Inattention, called “scientist’s inattention,” which is characterized by difficulty switching attention with high concentration and intensity on individual things and thoughts. This type of inattention is characteristic of people with obsessive thoughts.
- III type. Absent-mindedness, which is characterized by significant difficulties concentrating and even greater difficulties in switching it. This type of inattention manifests itself with a temporary or permanent weakening of the intensity and strength of nervous processes. In healthy people, but weakened as a result of overwork, this absent-mindedness can be observed for some time before their strength is restored. As a clinical manifestation, it is observed in patients with oxygen starvation of the brain and in elderly people suffering from cerebral atherosclerosis. The inattention of the latter is also called “old man’s absent-mindedness.”
Impaired attention can be considered a symptom of a disease only in the presence of other neuropsychic or somatic disorders that indicate the disease. Often, attention disorders are classified into one of three main groups:
- hypoprosexia;
- hyperprosexia;
- paraprosexia.
1. Hypoprosexia
This group of attention disorders includes different options for its weakening. This includes:
- Aprosexia, which consists of a lack of ability to concentrate and focus on a background of high distractibility. In most cases, there is a simultaneous decrease in the possible measure of concentration and an increase in the degree of distractibility. Often these two phenomena are accompanied by a decrease in attention span.
- Distraction of attention, which consists of a decrease in the ability to maintain attention on certain things and thoughts for a long time. Concentration is impaired. A patient suffering from absent-mindedness does not control the change in the direction of attention and cannot maintain it on a particular type of activity for a long period of time.
- Attention exhaustion, defined as a change in the intensity of attention from an initial high degree of concentration on the subject of attention to its significant weakening over a period of time. The consequences of attention depletion are a decrease in the efficiency of work activities and the loss of the ability to deeply absorb the process.
- A narrowing of the scope of attention, manifested in the pathology of concentration of attention caused by the weakness of its distribution. A patient suffering from a narrowing of the scope of attention is able to retain in consciousness only the most significant impressions for him. All attention can be directed exclusively to individual or situationally significant objects.
Hypoprosexia is observed in various cases of asthenic syndrome associated with a change in the degree of wakefulness. Trauma to the skull and other organic diseases of the brain can cause progressive fatigue of attention. Confusion and manic syndromes can cause an increase in the degree of distractibility, which is accompanied by an uncontrolled redirection of attention to neutral and random stimuli.
A number of certain disorders of consciousness provoke the appearance of a symptom of hypermetamorphosis, which is similar to a high degree of distractibility. Patients with this symptom constantly monitor the transformation of shape and the displacement in space of surrounding objects, constantly confirming their observations by touching objects in the field of vision with their hands and their movement.
2. Hyperprosexia
This group of attention disorders is characterized by excessive concentration, in most cases associated with its one-sided focus. For example, patients diagnosed with hypochondriacal syndromes demonstrate an excessive concentration of attention on their painful sensations, thoughts and things related to their health.
Epileptics and patients with depression are characterized by stiffness and stuckness of attention - the opposite disorder to the symptom of distractibility. This is also accompanied by reduced activity of the main nervous processes in the cerebral cortex, which impairs the ability to switch attention from one thought or thing to another.
In some cases, an increase in concentration of attention manifests itself in the form of obsession with certain ideas or thoughts. This phenomenon can be expressed by perseveration, that is, the frequent use in speech of the same words related to ideas and thoughts “stuck” to consciousness. In pathological cases, the appearance of prevailing ideas is often explained by the exclusive focus of attention on individual thoughts. At the same time, such patients fully understand that the ideas that dominate in their minds are given an unfair amount of space.
3. Paraprosexia
This group of attention disorders is mainly characterized by a concentration of attention on phenomena of a pathological type, that is, on hallucinations and delusions. Paraprosexia is expressed in the contradiction between the initial setting of attention and the result obtained. A patient suffering from this disorder of attention strains the nervous system so much by concentrating on some subject that it cannot stand it and causes inadequate, contradictory reactions from attention.
Healthy people can also be susceptible to paraprosexia. So, for example, an athlete on the starting line concentrates so much on waiting for the starting pistol to fire that he does not hear it as a result.
Attention deficits can be accompanied by diseases such as:
- Hypoprosexia
- Hyperprosexia
- Paraprosexia
- Depression
- Epilepsy
- Brain injury.
The following can make a diagnosis and provide assistance to a patient in cases of attention disorder:
- Neurologist
- Psychologist
- Psychiatrist
Ways to solve the problem
The best option is to visit a good neurologist. Such a specialist will help you find out the real reasons for loss of concentration and suggest ways to eliminate them. It is also possible to correct the situation on your own, but only on the condition that we are not talking about any disease - here you cannot do without a specialist.
To strengthen your memory and increase concentration you need to:
- Adhere to the correct daily routine.
- Eat well.
- Drink enough water.
- Spend as little time as possible at the computer, with gadgets or in front of the TV.
- Take medications that improve concentration and memory. For example, Esprico vitamins are considered one of the best, containing 2 types of Omega-3, Omega-6, magnesium and zinc (by the way, they are available in our online pharmacy).
- If possible, avoid alcohol, smoking or using drugs.
- Be sure to play sports!
- Be in the fresh air for at least 1.5-2 hours a day.
- Every day, learn poetry or a foreign language by heart, play logic games.
At the same time, certain “exercises” should be performed. So, you should try to do ordinary things in an unusual way. For example, walking backwards for a while (you can do it at home, when no one sees you), brushing your teeth and combing your hair with your left hand if you are right-handed (and vice versa), going to work on a different route, etc. All this will give a powerful an impetus for the formation of new neural connections.
And remember that it is much easier to prevent the problem with the same lifestyle adjustments and regular intake of vitamins than to get rid of its consequences.