Akathisia (rabbit syndrome) is a serious disease that causes a lot of inconvenience to a person. This syndrome is often mistaken for ordinary restlessness, since it is characterized by certain psychomotor disturbances.
With the development of this disease, a person has an irresistible need to change the position of the body, which prevents him from sitting still. With this diagnosis, problems with falling asleep and other disorders occur.
In medical practice, akathisia is usually called a disorder of motor activity, which is characterized by constant internal restlessness and the need to be in continuous movement. That is why people with this syndrome constantly sway, raise and lower their lower limbs, march in place or shift from foot to foot.
Such patients cannot sit or stand still. Symptoms usually subside during sleep, but some people experience anxiety even after falling asleep.
Types and categories of violations
The disease is usually divided into categories according to various criteria. Based on the form of the leading symptom, the following types of akathisia disease are distinguished:
- Mental – this type of deviation is characterized by the dominance of neurological manifestations. People with this diagnosis usually suffer from severe internal tension, they may experience restless behavior and increased anxiety.
- Motor – accompanied by causeless movements, the person constantly changes position. Such people are restless.
- Sensory – such people constantly feel itching, which forces them to scratch continuously. Patients often describe their sensations as compression and stretching of muscle tissue, as well as its movement inside the body.
In addition, there are different types of akathisia depending on the time of appearance of the first signs:
- Early or acute – develops within a few days after the start of drug use.
- Chronic or late - may occur several weeks or even months after the start of therapy.
- Withdrawal akathisia – manifestations of the disease occur after stopping the use of medications or reducing the therapeutic dosage.
Prevention
The best prevention of chronic restlessness syndrome is not to take psychotropics, sleeping pills and antidepressants. To do this, you need to lead a lifestyle so as not to bring your body to a state that requires taking them. Try to avoid stress if possible, learn to experience it adequately, perceive life philosophically, and look at it positively.
In cases where drug correction of pathologies is still necessary, it is important to use medications rationally, avoiding overdoses. Experts try to prescribe medications with the least extrapyramidal potential, starting with small doses.
Do not under any circumstances self-medicate for insomnia, depression, chronic fatigue syndrome, vegetative-vascular dystonia and other unpleasant syndromes. Wrong choice of drug without taking into account general medical history and drug interactions can lead to serious consequences.
It sounds like a hackneyed truth, but it’s worth saying again about the benefits of a healthy lifestyle. First of all, you need to completely give up alcohol and drugs. A person who has nothing to give up will never experience akathisic drug withdrawal syndrome.
Relatives and friends of a person at risk need to provide him with all possible support. It is also extremely important to set this person up only for positive changes.
Set of provoking factors
Scientists distinguish two main approaches to studying the causes of akathisia, namely pathophysiological and drug. The first category of factors is much less common and therefore practically not taken into account.
Non-drug causes of the disease began to be studied by scientists only in the last decade, which became possible thanks to the development of accurate diagnostic tools.
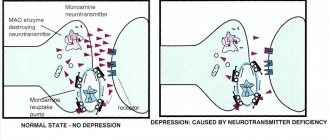
The drug theory of the origin of the disease is one of the classical approaches that have a high degree of reliability. The development of this pathology in most cases is associated with taking medications from the category of antipsychotic drugs. They have a direct or indirect effect on the synthesis of dopamine.
Currently, scientists have not been able to fully investigate this process. However, it is safe to say that the cause of akathisia lies in the long-term use of pharmacological drugs that are responsible for blocking dopaminergic transmission.
It has also been established that akathisia has a definite connection with Parkinson's disease and similar syndromes. However, at present it has not been possible to establish the causative factor - it may be the disease itself or the use of drugs used to treat it.
In addition, antidepressants can lead to the onset of the disease. Researchers note the appearance of symptoms of akathisia when testing these drugs. They manifest themselves in the form of increased arousal, hyperactivity, and emotional lability.
It has now been established that akathisia can develop after using the following categories of drugs:
- neuroleptics – Asenapine;
- SSRIs – Citalopram, Fluoxetine;
- antidepressants – Trazodone, Venlafaxine;
- antihistamines – Cyproheptadine, Diphenhydramine;
- drug withdrawal syndrome – barbiturates, benzodiazepines;
- serotonin syndrome – certain combinations of psychotropic drugs.
Treatment
Before starting treatment for akathisia, the doctor must identify the specific type of pathology. Due to the fact that in most cases the syndrome is iatrogenic in nature, a specialist can review the prescribed treatment regimen and exclude the use of certain medications. Either a dose reduction or a complete replacement of drugs was carried out. Almost all patients are advised to take magnesium supplements. Treatment is carried out with the combined use of the following main groups of pharmaceuticals:
- central anticholinergics;
- beta blockers;
- GABAergic agents;
- 5-HT2 blockers;
- antiadrenergic agents;
- dopaminergic drugs.
Clinical picture
Akathisia usually has two main components. Moreover, one of them is leading, and the second is not so strongly expressed.
So, the first component is called sensory or cognitive. It manifests itself in the form of uncomfortable internal sensations that force a person to perform certain actions. The patient is aware of these symptoms and can keep them under control.
The sensory component usually manifests itself in the form of a feeling of anxiety, tension, and increased irritability. Sometimes people experience clear somatic disorders - for example, pain in the legs or lower back.
The second component is motor. It consists in the fact that patients perform repetitive standard movements, which are individual for each person. Some people constantly walk, others sway their bodies or kick their feet, and still others itch or pick their nose.
Quite often, at the very beginning of a motor act, people cry out. They can also make mooing sounds. After motor activity begins to decline, vocalization disappears. It may appear at the beginning of the next motor act.
Symptoms
If akathisia develops in the classic form, then it is characterized by the presence of anxiety combined with hyperactivity. At the very beginning of the development of the pathology, the patient is disturbed by motor disturbances in the legs, which is why the person cannot be at rest while standing, lying or sitting. Such patients are in constant motion, sometimes even marking time in the same place. If the patient occupies a horizontal position, then he constantly changes the position of his body; if he is in a sitting position, then he constantly swings his legs.
Over time, the pathology progresses, causing akathisia to spread from the lower extremities to the upper extremities. In the absence of proper treatment, the patient begins to wriggle his whole body, move in jumps, and in extreme cases, even involuntary movement of the eyeballs is observed.
Sensory akathisia manifests itself in the presence of unpleasant sensations throughout the body. The mental component is expressed in excessive anxiety syndrome, impossibility, tension. Patients claim that while they are in motion, it becomes much easier for them, but as soon as they stop, anxiety and fear begin to increase, which acts as a provoking factor for the start of new movements.
Akathisia often provokes sleep disturbances. A pathology that occurs over a long period of time without proper treatment causes significant changes in a person’s character. Such patients become suspicious, anxious, annoying, and nervous. Unrecognized pathology in time provokes the development of a number of complications.
Diagnostic principles
Akathisia is very difficult to diagnose. This pathology is very difficult to visualize using laboratory or instrumental methods.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor must carefully examine the patient's symptoms and medical history. Some people have difficulty describing the clinical picture. In this case, the doctor can identify only one component of the disorder - for example, motor or sensory. As a result, the patient's condition will be assessed incorrectly.
To accurately determine the severity of a person’s condition, a special Burns scale was invented. In this case, the person is in a standing and sitting position for 2 minutes.
At the same time, the specialist assesses the presence of motor disorders and identifies the degree of emotional activity. Finally, the patient himself evaluates his condition. The final score can range from 1 to 5.
Complications
Antidepressant withdrawal syndrome is characterized by changes in consciousness, exacerbation of the underlying disease, tachycardia, and increased body temperature.
Serotonin syndrome is a complication after taking serotonin uptake inhibitors, antidepressants - mental disorders ranging from euphoria to panic, chills, fever, nausea and other autonomic disorders. Can be considered as normal when starting treatment with antidepressants after the first tablet; in severe cases, seizures may occur.
Serotonin syndrome is sometimes perceived as an exacerbation of a mental illness or as another pathological condition, especially if the history is not taken correctly.
Schizophrenia and a number of other psychiatric diseases can be confused with sensory and motor forms of akathisia. With an objective examination, it is difficult to make a diagnosis; a consultation with a psychiatrist, an MRI scan of the brain, and a determination of pathological heredity are necessary.
Correction and therapy of deviations
Therapy for this disease should be selected individually, taking into account the clinical picture and severity of the disease.
The most effective treatment method is complete withdrawal or significant reduction in the dosage of the drug that triggered the appearance of these symptoms. However, in practice this is not always possible, due to the mental state of the patient. Canceling medications can lead to a serious deterioration in his well-being.
The main component of therapy is the prescription of medications that can increase the effectiveness of antidepressants or antipsychotics without causing their side effects. Thanks to this, it is possible to significantly reduce the dosage of drugs that provoke akathisia.
There are a number of treatments for the disease. Antiparkinsonian drugs, such as Biperiden, Benztropine, etc., help to cope with the disorder. Such drugs are often prescribed as an addition to antipsychotics, which eliminates their side effects. The dosage should be selected by the attending physician.
Experts also prescribe the following groups of medications:
- Antihistamines and anticholinergic drugs . They are not included in the category of powerful medications, but they can be part of effective therapy. In this case, the use of Diphenhydramine and Atarax is indicated. An additional advantage of this treatment is the fact that such drugs have a slight sedative effect, which helps calm the person. The drugs reduce agitation and restore sleep.
- Tranquilizers . Such remedies significantly reduce the activity of the disease, eliminating feelings of anxiety, sleep disturbances and spontaneous arousal. Such medications are usually prescribed if the doctor is unable to conduct a detailed diagnosis.
- Beta blockers . A number of experts claim that drugs such as Metoprolol and Propranolol help reduce the effect of neuroleptics and eliminate anxiety.
- Anticonvulsants . Such products are highly effective. Recommended drugs include Pregabalin and Valproate. They help cope with feelings of anxiety.
- Weak opioids . Such drugs as Codeine and Hydrocodone are highly effective for this diagnosis.
In late forms of the disease, discontinuation of the main drug is indicated. It should be replaced with an atypical antipsychotic. Your doctor may prescribe Olanzapine or Clozapine.
With this diagnosis, the prognosis directly depends on the type of disease and the causes of its occurrence. For example, drug-induced akathisia can last from 1 month to six months. In this case, the withdrawal form of the disease lasts about 15-20 days.
Causes of akathisia
The reasons for the development of akatizive syndrome are divided into several types.
- Taking psychotropic drugs.
The most common side effect of chronic anxious restlessness occurs from taking antipsychotics: haloperidol, droperidol, pimozide. A similar effect is less common after atypical antipsychotics (olanzapine, aripiprazole) and antidepressants (mirtazapine). Sometimes sedatives (chlorpromazine) also lead to akathisia. The syndrome can also be caused by excessive use of sleeping pills, especially the barbiturates group.
- Drug use.
Mental changes towards the development of akathisia are characteristic of patients with opium and cocaine addiction. These drugs are strong poisons that depress nerve conduction in the brain. The list of substances that provoke akathisia also includes drugs from the amphetamine group, methylphenidate.
- Chronic alcoholism.
Long-term systematic consumption of alcohol has a detrimental effect on nerve endings and inhibits the functions of the subcortex of the brain. Neuromediation is disrupted, which negatively affects the functioning of the entire central nervous system.
- Parkinsonism, other mental disorders.
Both primary and secondary parkinsonism can cause akathisia. Science has not yet established exactly how great the role of concomitant medication is in treating the disease. The influence of two factors is likely to occur simultaneously. Chronic restlessness also occurs among patients with schizophrenia, anxiety and affective disorders.
Factors that increase the risk of chronic restlessness:
- genetic predisposition; in particular, science associates it with the gene of the first chromosome DRD2;
- various pathologies of the central nervous system;
- suffered traumatic brain injuries;
- dementia.
In addition, cases of akathisia are possible with abrupt withdrawal of psychoactive substances. An example would be someone waking up from anesthesia. Stopping treatment with antipsychotics and antidepressants can also cause a similar effect.