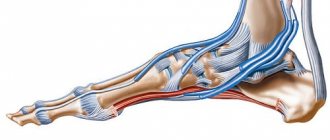
neuropathy (peroneal) is a type of peripheral neuropathy that affects the lower part of the sciatic nerve, the longest nerve in the body, starting at the fourth vertebra and running down the leg to the foot . In the region of the popliteal nerve, it divides into two branches:
- Tibial nerve (exits to the posterior surface of the popliteus muscle, is responsible for plantar flexion of the foot with the muscles of the lower leg).
- Common peroneal nerve (passes along the tubular bone of the leg): Superficial branch (located on the surface of the leg muscle, provides elevation of the outer edge of the foot).
- Deep branch (passes through the peroneus muscle, activates the extensors of the foot and fingers).
Its superficial subcutaneous location on the lateral side of the leg makes the peroneal nerve particularly susceptible to injury or compression, leading to dysfunction and loss of sensation in the foot.
Reference : the disease most often affects girls in adolescence from 10 to 19 years.
Peroneal nerve neuropathy
In 2/3 of cases, neuritis is a secondary disease of traumatic origin, only a third of cases are caused by nerve pathology itself. The most common causes of the disease by group:
- Traumatic . All kinds of injuries to the foot and lower leg: fractures, bruises due to falls or blows, dislocations, tendon injuries, sprains. Injuries to the knee and the outer part of the leg, where the nerve lies in close proximity to the surface of the skin, are especially dangerous.
- Compression . Causes caused by nerve compression. Superior tunnel syndrome (compression at the top of the nerve path) occurs in the area of the fibula under the influence of the biceps muscle. It is usually provoked by prolonged squatting in people of relevant professions: vegetable pickers, parquet floor workers, plumbers, etc. Another reason is frequently repeated actions that put pressure on the accumulation of nerve fibers in this area (the work of a fashion model or seamstress), constant sitting in a position with one leg crossed over the other.
- Inferior tunnel syndrome (compression where the nerve passes to the foot). Develops as a result of wearing uncomfortable tight shoes or after placing a cast.
Other, less common factors of genesis: pinched nerve due to the growth of a malignant tumor, toxicosis of the central nervous system caused by diabetes or drugs, bleeding in the area of the neck of the fibula, infectious lesions.
Symptoms of the disease
Manifestations of neuropathy depend on location
(in which particular route the nerve is affected) and the type of course of the disease (acute and gradual) . Moreover, based on the nature of the symptoms, the location of the disorder can be determined with great accuracy:
- Patellar area within the sciatic nerve: Pain and sensory disturbances on the outer side of the leg.
- Limited finger extension.
- Drop foot.
- "Horse" gait with legs raised high.
- A subtle decrease in sensitivity on the outside of the lower leg.
- Burning all over the leg below the knee.
- Mild sagging and limited mobility of the foot.
Information : a neurologist treats peroneal neuropathy.
With a long course of the disease, symptoms may be accompanied by more or less pronounced atrophy of the leg muscles.
Inflammation, trigeminal neuralgia symptoms
Trigeminal neuralgia is clinically manifested by short-term attacks of excruciating pain, most often in the area of the 2nd and 3rd branches of the trigeminal nerve. It is characterized by the presence of trigger zones on the skin and mucous membranes. Touching them provokes attacks of pain. In most cases an attack of pain is accompanied by severe local and general autonomic disorders, the following symptoms: facial hyperemia (redness of the face) and swelling on the affected side, lacrimation, rhinorrhea (discharge of watery mucous discharge from the nose), hypersalivation (salivation, increased secretion of the salivary glands), Possible increased blood pressure (BP), chills-like trembling, difficulty breathing.
Consequences of the disease
The danger of neuritis of the peroneal nerve is that in addition to sensory disturbances, it leads to immobilization of the foot and acute pain. Paresis and paralysis of the long and short peroneal muscles, tibial muscles and extensors progresses. Untimely therapy can lead to atrophy of the biceps femoris, gastrocnemius, peroneus and other muscles of the leg, extensor dysfunction and disability.
Diagnostics
The primary method of diagnosis is to collect an anamnesis in order to identify the possible cause of the disease (most often, injury to the proximal leg). Based on symptoms such as decreased sensitivity, the ability to straighten or turn the foot, bend the toes, and the nature of the pain, the doctor determines the location of the nerve damage. Using special techniques, the degree of muscle performance and the level of sensitivity are established. Also, during the examination, the doctor pays attention to the preservation of the knee and Achilles reflexes, characteristic of peroneal neuropathy.
It is important to differentiate peroneal nerve neuritis from congenital degenerative neurological disorders, Charcot-Marie neural amyotrophy, diffuse damage to the nervous system, benign and malignant tumors of the spine. The absence of sensory impairment allows one to suspect a stroke or amyotrophic sclerosis. Weakness of supination may indicate radiculitis in the lumbosacral region.
For clarifying diagnostics, the following methods are used:
- Electroneurography . It is performed using two sensor-electrodes. An electrical impulse is applied to the first electrode, installed on the projection of the nerve, which travels along the nerve fiber to the second electrode located on the innervated muscle. This determines the speed of signal transmission and the degree of nerve dysfunction.
- Ultrasound . With its help, it examines the structure of the nerve fiber and adjacent tissues. Depending on the results of the ultrasound, the doctor may prescribe an x-ray of the knee, lower leg, or ankle.
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging (CT and MRI). They are used to visualize tibial pathology or to identify compression of the peroneal nerve at the entrance to the canal.
When diagnosis is difficult, as well as for clinical confirmation of MRI or ultrasound data, selective blockades can be used. By injecting novocaine, the doctor anesthetizes a specific anatomical area. Elimination of pain confirms the location of the lesion.
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia in Saratov, how to treat trigeminal neuralgia in Russia
Sarklinik provides comprehensive treatment of trigeminal neuralgia in children and adults, treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve (nervitis, first, second, third branches) in Saratov, Russia, which includes effective reflexology methods. You can cure trigeminal neuralgia in Saratov!
Sarklinik knows how to treat inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, how to cure neuralgia and trigeminal neuritis ! The following types of neuralgia are treated: neuralgia of the 1st (first) branch of the trigeminal nerve, neuralgia of the 2nd (second) branch of the trigeminal nerve, neuralgia of the 3rd (third) branch of the trigeminal nerve in children and adults. On the website sarclinic.ru you can see a doctor online for free. If you have neuropathy, nerve damage, pain, a cold, the trigeminal nerve hurts on the left, right, you have a cold, a cold, inflammation on the face, paralysis, paresis, you don’t know how to relieve the pain , then contact a doctor at Sarklinik.
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Photo: Aniram | Dreamstime.com\Dreamstock.ru. The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Urinary incontinence, treatment of women, men, children, adults, postpartum, neurogenic bladder, spina bifida
Insomnia, treatment of insomnia in Saratov, what to do for insomnia
Transient ischemic attack: symptoms, treatment of the brain
Poor attention: absent-mindedness, exhaustion, narrowing of scope, stiffness, distractibility
Asthenia, asthenic syndrome, treatment, symptoms, causes, how to treat in children, adults
Comments ()
Treatment
The main goal of treating neuropathy is to eliminate its cause . Sometimes it is enough to remove the plaster that is pinching the nerve or replace the shoes with looser ones. If primary diseases are detected, the neurologist can offer the patient only symptomatic treatment, and provide the main treatment to an oncologist (for cancer) or an endocrinologist (for diabetes).
Help : the prognosis of the disease directly depends on its genesis and time of detection.
Conservative treatment includes:
- Medicines.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Therapeutic physical education (therapeutic physical education).
In some cases, surgical intervention is indicated.
Medicines
The following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs ): Meloxicam, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Nemisulide and analogues. Relieves swelling and inflammation, reduces pain, restoring foot mobility. Prescribed for a short-term period (up to 5 days) due to the risk of side effects.
- B vitamins : Thiamine (B1), Nicotinic acid (B3), Choline (B4), Inositol (B8) improve conductivity and restore the structure of the nerve fiber. Contained in high concentrations in the following drugs: Milgama, Neurorubin, etc.
- inhibitors : Neuromidin, Proserin, Ipidacrine. Stimulate the conduction of nerve impulses and activate smooth muscles.
- Vasadolytic agents : Trental, Cavinton, Pentoxifylline. They improve the rhiological properties of blood, dilate blood vessels, and improve blood circulation.
- Metabolics : Berlition, Thiogamma, etc. They have an antioxidant effect similar to B vitamins, improve cholesterol metabolism and muscle conduction.
Drug therapy goes well with physical therapy.
Physiotherapy
The following physiotherapy procedures are used:
- Electrophoresis . Allows you to deliver medications through the skin directly to the lesion.
- Magnetotherapy . Exposure to a controlled magnetic field in a local area alleviates pain symptoms, improves blood supply and nerve fiber performance.
- Ultrasound therapy (UT) . Ultrasound waves penetrate 6 cm under the skin and can affect deep-lying nerve fibers. UST improves intracellular metabolism and accelerates the regeneration of damaged tissues.
- Amplipulse therapy . Short-term pulsed exposure to low-frequency electric current has a beneficial effect on the affected area of the leg: eliminates swelling, relieves pain and stimulates smooth muscles.
Exercise therapy
In order to eliminate inflammation and restore muscle function, active (dynamic, improving coordination and functionality of the vestibular apparatus) and passive (carried out with the help of an instructor) exercises are used. Exercises are carried out with the participation of both the diseased and healthy leg, with the exception of the joint closest to the affected nerve (knee or ankle - depending on the location of the neuritis).
The optimal starting position for exercise is considered to be sitting with the leg bent at the knee and a hard cushion placed under the heel. To restore the function of the knee joint, stretch the tourniquet when bending the leg. To restore the ankle – adduction and abduction of the foot.
As the functionality of the limb is restored, the instructor complicates the set of exercises, with the goal of complete rehabilitation of the patient. In severe cases (including during postoperative recovery), special orthoses are used to fix the foot and help in learning to walk.
Surgery
Indications for surgical intervention are: failure of conservative treatment, significant compression of the nerve with complete disruption of nerve conduction, recurrent neuropathy.
Important : the likelihood of restoration of nerve fibers directly depends on the timeliness of surgical treatment.
The operation involves releasing the pinched nerve and plastic restoration of the canal walls. If there is no electrical excitability of the muscles, a tendon transplant is performed.
Peroneal neuropathy is a dangerous disease, which in severe cases can lead to disability and loss of ability to work. Treating this disease is much more difficult than following a few simple preventive rules:
- Wear comfortable shoes.
- Watch your posture.
- Walk up to 6 km a day.
- Do not engage in traumatic sports.
What is tibial nerve neuropathy?
First, let's understand the terms - what tibial nerve neuropathy is and how it develops. So, this disease belongs to the group of single neuropathies (affects only one nerve). It is very rarely bilateral, only in the case of an equivalent traumatic impact on the bifurcation point of the sciatic nerve in the popliteal fossa.
Often this disease develops at a young age in people who lead an active lifestyle and engage in sports, including gaming and weightlifting. Regular physical overload and the influence of stress factors lead to the disruption of the trophism of this nerve and the corresponding symptoms of its damage.
Anatomically, the tibial nerve is a kind of continuation of the sciatic nerve, which in the popliteal fossa is divided into two branches that innervate the tissues of the lower leg, ankle joint, foot and toes.
After division, the branches pass along with large arteries between the muscles of the leg and are directed to the foot, then, passing through the ankle joint, they break up into even smaller branches and innervate different parts of the foot. Therefore, if several structural parts of the foot are simultaneously affected, the doctor will always suspect damage to the tibial nerve at a higher level (in the area of the popliteal fossa or lower leg).
Neuropathy of the tibial nerve is a partial or complete loss of its functional abilities, which leads to dysfunction of the muscles, skin, vascular wall, etc.