What should be considered dizziness?
Dizziness
is one of the most common complaints among adult patients; most often they only complain of headache or back pain.
However, dizziness can mean completely different symptoms. Patients often call dizziness:
- darkening of the eyes
after a sudden change in position; - a veil before my eyes
; - presyncope (feeling of impending loss of consciousness). In this case, they usually complain of dizziness and weakness;
- imbalance
(instability and
staggering when walking
); - feeling of faintness
, a state reminiscent of intoxication. In this case, the complaint usually sounds like nausea and dizziness.
Such symptoms are certainly significant and may indicate various diseases (anemia, low blood pressure, vegetative-vascular dystonia, diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems), but are not dizziness itself. True vertigo
(or
vertigo
) is a condition in which the patient has a feeling of rotation of actually stationary objects around him or, conversely, a false sensation of his own rotation or movement. Quite often it is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and increased sweating.
Why is it necessary to promptly respond to symptoms of nausea and dizziness, why is it dangerous?
Nausea can be caused by dietary errors and various forms of intoxication of the body, including food poisoning. Some painful conditions, if they are mild or moderate, can be managed without professional medical help. But if you periodically feel nauseous and lose concentration, or feel dizzy even while lying down, you should consult a doctor. These may be harbingers of quite serious disorders that pose a threat to the patient’s health. These include vascular pathologies that can lead to stroke. Therefore, it is important to familiarize your therapist with your complaints and describe all symptoms in detail. This will help determine the direction for diagnostic measures in order to establish the cause of the ailment.
Why suddenly dizzy and nauseous worries many people. You may just need to wait it out if it is due to a side effect of medications or another minor problem. This is a temporary phenomenon and should go away on its own once the course of treatment is completed. But if symptoms such as weakness, drowsiness, nausea and dizziness persist with enviable consistency, the signs of malaise cannot be ignored; it will get worse.
Doctors distinguish several types of dizziness, from systemic, associated with damage to the central or other parts of the vestibular apparatus, to psychogenic, observed in an anxious or depressive state. Dizziness and weakness are defined as sensations of loss of balance and stability of one’s body in the surrounding space.
Dizziness is accompanied by the following accompanying symptoms:
1 ringing in the ears, hearing loss, nausea, sometimes vomiting (in the presence of vestibular problems);
2 an attack of lightheadedness, sudden pallor of the skin, rapid heartbeat (in the case of a pre-fainting state due to cardiac or hypotensive pathology, one often feels nauseous and has dark vision);
3 sensitivity disorder, incoordination of movements, unsteadiness when walking.
It is necessary to master the principles of first aid and know what to do if sudden dizziness and nausea occur in order to reduce negative manifestations before the arrival of doctors and prevent the patient from developing a critical condition.
Causes of dizziness
Control over the position of the body in space is ensured by the joint action of three anatomical systems of the body:
- vestibular. The vestibular apparatus is located deep in the skull and includes sensitive receptors that respond to the movement of the body in space;
- visual. The eyes provide basic information about our position in relation to objects in the world around us and the position of parts of our body in relation to each other.
- peripheral sensory receptors found in muscles, joints and bones, which also provide the brain with information about the position of various parts of the body.
Stimulation of one or more of these systems can lead to dizziness (as, for example, dizziness occurs as a result of riding on a merry-go-round). If dizziness appears without any external reason, then the nature of such dizziness is obviously pathological. Most often, the cause of true (or, as it is also called, systemic) dizziness is a violation of the vestibular apparatus.
Treatment and prevention
For Meniere's disease, treatment is mainly aimed at reducing swelling and inflammation in the canals of the labyrinth. During an attack, the patient should be placed in a room where there are no bright lights or loud sounds. It is recommended to place a heating pad at your feet. Massage the point between the eyebrows.
In severe cases, hospitalization and infusion therapy (using droppers) may be required.
To stop an attack, a meatotympanic (behind the ear) blockade is used - the introduction of Novocaine and Platiphylline. A glucose solution is administered intravenously. Intramuscularly - Pipolfen. It is possible to use Aminazine to relieve psychomotor agitation.
To prevent attacks, drainage drugs are used that improve capillary permeability and microcirculation in the inner ear: Preductal, Betaserc. Antiemetics: Bonin, Kinedryl. Cinnarizine is also prescribed to improve cerebral circulation and as a remedy for motion sickness during seasickness.
Helpful information
In 70–80% of cases with Meniere's disease, conservative treatment is sufficient to relieve attacks. Sometimes surgical intervention is indicated, which can be gentle (preserving hearing) and destroy the labyrinth.
Patients with Meniere's syndrome are prescribed a special diet with limited consumption of salty and spicy foods. Alcohol and smoking worsen the course of the disease, so they should be avoided. Prolonged exposure to the scorching sun and diving in water are also not recommended. The consequences of stress also provoke an attack, so you need to monitor your psycho-emotional state. Positive results are obtained from the use of reflexology and physical therapy.
Vestibular gymnastics will help reduce dizziness with BPPV - positional maneuvers: turning the head left and right in a lying position (10-20 times). It is necessary to repeat these exercises until the calcium deposits causing irritation of the labyrinth are displaced.
Hypotonic patients prone to dizziness are recommended to practice a contrast shower (to normalize vascular tone), as well as fairly intense physical activity that promotes the production of adrenaline to increase blood pressure.
In case of poisoning with neurotropic poisons, including alcohol, detoxification and symptomatic therapy are carried out.
If the cause of dizziness is unknown, to alleviate the condition at home you need to sit down, or better yet, lie down, first opening a window for fresh air. You can massage the bridge of the nose, temporal and occipital areas in a circular motion.
It is recommended to measure blood pressure, check pulse, and pay attention to whether there is any speech impairment. If attacks occur repeatedly, you should undergo a medical examination.
It should be remembered that severe dizziness can be a symptom of myocardial infarction or ischemic stroke.
Diseases that may cause dizziness
Most often, dizziness occurs with the following disorders:
- ear diseases
, first of all:- Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV).
BPPV accounts for up to 80% of all cases of true dizziness. The name of this disease means that it does not pose a serious threat (therefore - benign), that attacks of dizziness occur suddenly (therefore - paroxysmal), that the attack begins when the position of the head changes - turning or tilting (therefore - positional). The cause of dizziness is the displacement of hard formations (otoliths) in the inner ear. Although BPPV may cause nausea and weakness, no other pathological changes are found on examination; - labyrinthitis
(inflammation of the inner ear); - Meniere's disease
(characterized by an increase in fluid in the cavity of the inner ear) - causes severe dizziness, accompanied by tinnitus, nausea, vomiting, and a feeling of fullness in the ear; may lead to hearing loss; - tumor (neurinoma) of the auditory nerve
; - barotrauma
– rupture of the eardrum due to a sudden change in pressure; - other ear diseases
- otitis media, eustachitis, cerumen plug;
, including:
migraine
(caused by disorders of the brain structures responsible for pain and other sensations) - dizziness during migraine is a harbinger of a painful attack;
;
;
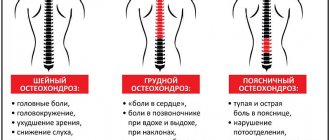
- diseases of the cervical spine
(primarily
osteochondrosis
); - psychogenic dizziness
is not true dizziness (that is, it is not associated with pathology of the vestibular apparatus). Most often described as a feeling of unsteadiness, brain fog, fear of falling and passing out. Occurs as a reaction to stress, usually accompanied by other psychogenic symptoms; - some other diseases.
Increased intracranial pressure
There is a whole group of pathological conditions accompanied by increased intracranial pressure (intracranial hypertension), which occurs in two ways:
- the appearance of a tumor in the brain tissue, which expands and creates excess pressure;
- disruption of the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, resulting in edema (a benign form of intracranial hypertension).
The main symptom is dizziness in the morning after sleep, accompanied by headache, nausea, and vomiting. This occurs because in a horizontal position, fluid in the brain is produced more actively and, when elevated, creates especially strong pressure inside the skull. Frequent surges in blood pressure, increased nervousness, sensitivity to weather, frequent fatigue, depressed consciousness, and fainting are also possible.
Dizziness from changing body position
Dizziness is one of the symptoms that are inherent in many diseases, especially pathologies of the central nervous system.
The main reasons for increased pressure inside the cranial cavity:
- tumors, brain hematomas;
- injuries ;
- infections affecting the central nervous system (meningitis, encephalitis);
- inflammatory processes in brain tissue;
- stroke and aneurysms;
- water-electrolyte imbalance ;
- dropsy (hydrocephalus) of the brain.
A benign manifestation of intracranial hypertension goes away on its own, or after a course of taking diuretics, establishing a drinking regimen, diet, and special exercises. In other cases, intracranial hypertension requires a serious and detailed examination by qualified specialists.
In case of acute attacks of pain and fainting, you need to call an ambulance. Failure to pay attention to the problem in a timely manner leads to complications, including death.
Dizziness and weakness
Dizziness and weakness can occur in many cases. This condition does not always mean that you are sick. Thus, in adolescence, weakness and dizziness are explained by hormonal changes. The autonomic nervous system is being rebuilt and growth rates are accelerating. Against this background, weakness, dizziness and even fainting are possible. Also, dizziness and weakness are typical during pregnancy.
If the cases mentioned do not apply to you, dizziness and accompanying weakness most likely indicate some kind of pathology. Weakness and dizziness are most often observed with:
- anemia (low hemoglobin content in the blood);
- cerebrovascular accident. In this case, tinnitus, decreased attention, and the appearance of black spots before the eyes may also occur;
- a sharp increase in blood pressure (hypertensive crisis). In this case, dizziness and weakness may be accompanied by a headache;
- neurocirculatory dystonia;
- oncological diseases.
Iron-deficiency anemia
Iron deficiency anemia is a condition in which the blood contains little hemoglobin, the component that delivers oxygen to all organs and tissues. Then the person experiences weakness, lethargy, apathy, and decreased performance. He feels dizzy and has bouts of nausea. Symptoms appear even after proper rest and sleep.
The disease is associated with insufficient intake of iron into the body from food (a component of hemoglobin) or with poor absorption of this element. People with a monotonous, inadequate diet, vegetarians, children during periods of rapid growth, and women during their menstrual period are often susceptible to it.
Only the attending physician can confirm the diagnosis and determine the cause. Seeking medical help is necessary, as anemia can accompany more serious illnesses. To prevent iron deficiency, it is recommended to include in the diet red meat, liver, fish, seafood, legumes, fruits and vegetables rich in vitamin C (promotes the absorption of iron).
Medical indications
Constant dizziness, weakness and heaviness in the head is a clinical picture that manifests itself against the background of various diseases.
Other causes of its manifestation are stress, tumor, impaired blood supply to the brain.
The list of possible risk factors that provoke dizziness, weakness and heaviness in the head is quite large.
Establishing the true cause of the clinic in question is the task of a neurologist.
The causes of discomfort in the head may be associated with high irritability, insomnia, neurosis, and depression. Attacks of hypertension are common causes of lethargy and pain in the back of the head.
Additional concerns include dizziness, weakness, and heaviness in the head. In such a clinic, urgent assistance from a therapist is required.
Doctors often identify the following reasons against which the symptoms in question appear:
- nervous disorders;
- loads of different etiologies and degrees of manifestation;
- consequences of head and neck injuries;
- problems with blood circulation;
- intoxication;
- exhaustion;
- migraine.
Additional etiology
Doctors also identify the following possible etiology for the appearance of various discomforts in the head, including pain and heaviness:
- broken bite – symptoms appear over a long period of time, and tend to intensify at night;
- infections;
- cardiac and vascular pathologies - manifested by heaviness in the head, altered blood pressure levels, shortness of breath, constant weakness;
- pathologies in the musculoskeletal system;
- prolonged use of the computer, a sedentary lifestyle, poor nutrition, and bad habits lead to the fact that the vessels do not fulfill their duties, complicating the outflow of blood.
Against the background of this process, blood begins to accumulate in the skull, causing a feeling of heaviness in the head. In such a clinic, urgent treatment is indicated.
Most therapy is aimed at fundamentally changing the patient's habits.
If symptoms appear constantly, an advanced process is occurring in the patient’s body. It is treated only with medications.
Stroke is another etiology that can cause heaviness in the head, nausea, and other symptoms. The clinical course is more difficult if the patient has complete or partial brain damage.
In case of poisoning with medications or narcotic drugs, the vestibular nerve is also affected. When such a diagnosis is made, urgent therapy is required.
Cholestoma is a tumor that leads to the destruction of the eardrums, against which constant dizziness develops.
With hormonal imbalance, there is discomfort in the head. At the same time, other symptoms characteristic of hormonal changes in the body appear.
To eliminate the clinic in question, the help of a gynecologist and endocrinologist is required.
Pain and heaviness in the head can be caused by insufficient oxygen supply, greatly reduced or increased blood pressure, and allergies.