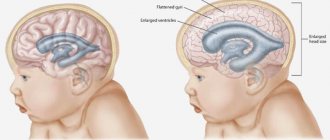
Hydrocele in a newborn is a pathology of the central nervous system. Liquor continuously circulates in the brain and spinal cord. Excessive secretion of fluid or disruption of its outflow into the venous bed leads to pressure on the brain structures. The disease occurs at any age, but is more often diagnosed in early childhood.
Hydrocephalus: what is it?
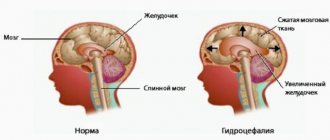
During normal functioning of the spaces and ventricles in the head, cerebrospinal fluid is in a state of equilibrium between its formation and absorption. With the development of hydrocephalus, the balance shifts either towards hyperproduction or malabsorption. In this case, fluid begins to stagnate in the brain, leading to impaired development of the infant. Cerebrospinal fluid is absorbed mostly in the arachnoid spaces of the brain due to the pressure gradient in it and in the venous sinus.
In an infant, the fluid content in the head is subject to strict criteria. It normally accounts for up to 0.1 of the volume of the entire contents of the skull. An increase in the amount of fluid leads to the formation of intracranial increased pressure.
Causes of the disease
The most likely causes of hydrocephalus in a baby can be divided into two groups: those that affect the baby in the womb, and those that provoke pathology during or after birth.
Congenital hydrocephalus in newborns appears due to the influence of such factors:
- Infectious diseases that the expectant mother suffered from during pregnancy (especially enterovirus infection Coxsackie, tonsillitis, herpes, measles).
- Congenital anomalies, defects in the brain and cerebral vascular system. Such defects may be a decrease in the lumen of the cerebral aqueduct, the presence of an arachnoid cyst, or a discrepancy between the size of the posterior fossa of the skull and the size of the structures that should be located in it.
- Rhesus conflict.
It is possible that a newborn develops hydrocele of the brain during or after childbirth.
Then its reasons could be:
- Consequences of infectious processes suffered by the fetus in the early stages of development.
- Birth injuries to the skull, especially if forceps or other physical methods of removing the baby were used during delivery.
- Brain tumors (meningiomas, papillomas) or tumors associated with the bones of the skull.
The risk of hydrocele increases under the following conditions:
- Delivery occurred before 35 weeks.
- Low birth weight of the child (up to 1500 g).
- The expectant mother had a narrow pelvis.
- The course of labor was difficult and led to a lack of oxygen for the baby.
- While carrying the child, the mother smoked or abused alcohol.
There is also a special reason for the development of hydrocephalus in newborns: brain atrophy. In this case, the fluid essentially replaces the place in the skull where the neurons should be. The cause of such changes is defects in embryogenesis and genetic predisposition.
Sign of hydrocephalus
In ⅘ cases, hydrocephalus of newborns is associated with congenital malformations:
- Chiari syndrome;
- Consequences of antenatal infection.
It should be noted that antenatal infection of the fetus is the most common cause of congenital hydrops capitis.
In the remaining ⅕ of cases of hydrocephalus in newborns, this is the result of:
- Antenatal and intranatal trauma;
- Meningoencephalitis in the first 28 days of life.
Interesting: Causes, symptoms and treatment of cerebrastia in children
During the physiological development of a child in the first months of life, the head circumference becomes smaller than the chest circumference. If this proportion is violated, you should suspect signs of incipient hydrocephalus and consult a doctor. Timely diagnosis reduces the risks of complications.
Features of therapy
The method of therapeutic measures largely depends on what stage the disease is at, as well as the main factor that triggered the development. Dropsy is treated in different ways
Conservative method
It is considered effective only in the initial stages of the disease, when there are no aggravating factors. Medical specialists prescribe special medications (hormonal group). Some products help remove sodium from the body, which makes it possible to get rid of excess fluid. There are no drugs to treat the disease; their action is aimed at preventing further development of the disease.
Surgical method
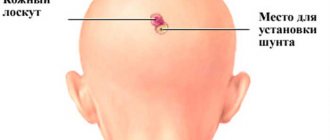
Surgery is the most effective way to combat dropsy. It is carried out by shunting. Among the varieties of this procedure are:
- venticuloperitoneal shunting - insertion of silicone catheters through which fluid is mixed from the head region to the abdominal region;
- lumboperitoneal shunting – connection of the abdominal cavity with the spinal canal;
- ventriculoarthrial shunting – transportation of a substance to the right atrium;
- Torkildsen operation - extraction of fluid into the so-called occipital cistern;
- endoscopic ventriculostomy - the technique does not involve the use of a shunt system; the procedure involves the creation of small incisions using an endoscope.
After surgery, the development of the pathological process stops, which allows the child to actively develop in the future. However, the procedure is prohibited for patients with a chronic form of the disease, as well as when other inflammatory processes, neurological disorders or mental disorders are detected.
Dropsy can be treated using traditional medicine methods. Among the most effective herbal remedies, the best proven ones are freshly squeezed juices of black radish, onions, and pumpkin, which are recommended to be drunk on an empty stomach. Decoctions of parsley, clover, birch leaves, adonis, and lemon balm help well with hydrocephalus.
Before using the above herbal remedies, you must consult a doctor!
Risk factors in children
Parents of children who are diagnosed with health problems are concerned about three main questions:
- Where did the disease come from?
- Who is guilty?
- What to do now, how to treat?
Risk factors for the development of excessive stagnation of cerebrospinal fluid in the head of a newborn can be a variety of factors that acted both in utero and after the birth of the child. The health of the mother plays an important role during pregnancy. Liquor accumulates at any stage of brain ontogenesis.
Antenatal factors (the causes of hydrocephalus affect during pregnancy):
- Genetic abnormalities leading to developmental defects;
- Hemolytic disease;
- High infectious index of the mother in the early stages of gestation;
- The course of pregnancy against the background of severe extragenital pathology;
- Complications of pregnancy (severe preeclampsia, HELLP syndrome);
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Antenatal infection;
- Disembryogenesis of cerebral structures.
The development of dropsy is facilitated by intrapartum factors (affected during childbirth):
- Injuries of the skull and brain with the development of hemorrhages, hematomas of various locations. The occurrence of injuries is facilitated by rapid and rapid labor, fetal macrosomia, narrowing of the mother's pelvis, extension and asynclitic insertion of the child's head, breech and leg presentations.
- Vaginal birth before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
Pathology on the part of the child that occurs after childbirth:
- Neoplasms of the brain and spinal cord;
- Pathology of the hematopoietic system;
- Meningeal infection after birth;
- Low weight of the child, his malnutrition.
How the disease manifests itself, diagnosis
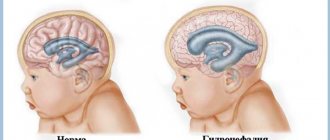
The diagnosis of hydrocephalus (or dropsy) is often made to a child immediately after birth. But this applies to severe forms of pathology, when a non-standard size of the skull is visually noted, and the head circumference of a newborn is several times higher than the normative values. When assessing the neurological status, numerous disorders are revealed.
The development of a compensated form of dropsy does not have a clear clinical picture - the enlargement of the brain and the addition of pathological symptoms occur in stages.
The congenital form of hydrocele of the brain is more severe, this is due to the anatomy of the skull. The bones of the skull are still mobile, as they are not tightly fused. Non-ossified areas of the arch become additional space for fluid accumulation. Therefore, the skull enlarges - the head becomes asymmetrical, and the fontanelles bulge.
The anterior fontanel (connection of the frontal lobe with the parietal lobe) is the largest and is normally completely fused at 12–24 months. In the case of hydrocephalus, the fontanel remains open.
Infants normally have disproportionate head volumes in relation to the chest - the head is several centimeters larger. By 6 months the values should be equal.
| Age | Standard values for head circumference in centimeters |
| Newborn period | 33, 9 — 35 |
| 1 month | 36 – 36,5 |
| 2 months | 38,3 – 38,5 |
| 3 months | 39 – 39,5 |
| 4 months | 40 – 40,6 |
| 5 months | 41 – 41,5 |
| 6 months | 42 – 42,2 |
| 1 year | 44 – 44,9 |
| 2 years | 47 – 47,2 |
| 3 years | 48 – 48,5 |
The table shows average values; when measuring, the gender of the child is taken into account, since higher values (around 1 cm) are considered normal for boys. The hereditary factor is also taken into account in case of overestimated values. If the parents (or one of them) have a large build and a massive skull, then for the child this will be the norm and there is no talk of dropsy, but provided that there are no pathological symptoms.
A gradual increase in the amount of fluid in the cranial space leads to pressure on the brain structures.
Dropsy manifests itself with a number of symptoms:
- The appearance of a clear vascular pattern on the head (forehead, back of the head, temporal region);
- Unreasonable crying (in infants it is a manifestation of headache);
- Refusal to eat;
- Throwing back the head (does not try to hold it);
- By 1 month of life there is no visual fixation;
- Excessive regurgitation (after feeding);
- The frontal lobes are massive, the central fontanel is swollen, there is pulsation;
- Delayed motor development – lack of stages in development;
- The sucking reflex is depressed or completely absent;
- Sleep is disturbed (wakes up frequently, signs of restlessness);
- Development of strabismus;
- Delayed mental development – there is no “revival” complex for loved ones;
- The child is lethargic and sleepy.
The accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid provokes a rise in pressure inside the skull, intracranial hypertension develops, which is manifested by additional symptoms:
- Uncontrollable vomiting;
- Attacks of headache (in the morning), the symptom intensifies with a change in position or a sharp turn;
- Ptosis of the upper eyelid develops (does not droop or does not close the eye completely);
- Convulsive syndrome;
- Paralysis or paresis of the lower extremities (the child loses all acquired motor skills).
In children over two years of age, all parts of the bones are firmly fused and with hydrocele of the brain, no deformation of the skull occurs.
Dropsy can only be suspected based on the characteristic clinical picture:
- The child becomes inhibited or, on the contrary, hyperactive;
- Headaches after stress (emotional or physical);
- Sleep becomes restless, often wakes up, cries;
- Nausea or vomiting;
- Attention is scattered, schoolchildren's academic performance decreases;
- A sharp decrease in vision;
- Motor disturbances (gait changes, often stumbles and falls, moves on tiptoes);
- Muscle spasms (febrile seizures);
- Development of enuresis (the child does not control urination).
The accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain has many causes and symptoms are often similar to other neurological diseases. It is possible to differentiate the pathology and make an accurate diagnosis only after examination.
The main diagnostic method for infants is neurosonography. An open fontanel conducts an ultrasound wave and allows you to evaluate brain structures and blood circulation. The ultrasound method is included in the mandatory preventive brain examination for children in the first month of life.
Early diagnosis of cerebral hydrocele allows conservative treatment to restore cerebrospinal fluid dynamics and avoid serious consequences.
Symptoms
- The timing of closure of the anterior fontanelle lags behind physiological norms;
- Asymmetry of the cerebral part of the skull with a predominance of the frontal part, overhang of the eyebrows;
- Pathology of the visual analyzer (various variants of strabismus);
- Reflex tachycardia;
- Tremor of the lower jaw;
- Venous congestion of the vessels on the head, strengthening of its pattern;
- Regurgitation more often than age standards. The child often spits up to the point of vomiting;
- A sharp cry, agitation, insomnia in a child;
- Convulsions that occur from time to time, loss of consciousness;
- Delayed psychophysical development of the child.
Interesting: Headaches in a 9-year-old child: causes, diagnosis, first aid
Symptomatic manifestations
Signs of pathological changes can be detected during the prenatal period. The main symptom is a significant increase in head size. If intrauterine hydrocephalus is diagnosed, a woman can give birth exclusively by cesarean section. This will avoid compression of the skull, and, therefore, prevent the development of other pathologies of the central nervous system, which are subsequently almost impossible to eliminate.
The main symptomatic manifestations also include:
- prolonged closure of the “fontanelle”;
- bulge/disproportionate increase in the forehead area;
- bulging and increasing size of the fontanelle;
- uncontrolled eye movement (nystagmus), divergent strabismus;
- overhanging brow ridges;
- disturbance of visual activity;
- change in the appearance of the skin, mainly its pallor;
- increased heart rate;
- chin trembling;
- involuntary twitching of limbs;
- transillumination of the venous network on the forehead, temples, and back of the head;
- frequent regurgitation;
- excessive tearfulness, capriciousness;
- general restless state of the child, sleep disorder and subsequent developmental delay.
In older children, a venous network appears in the facial area, an increase in the size of the fontanel, which prevents the possibility of its overgrowing, an increase in muscle tone in the limbs, and insufficient mental and physical development of the baby.
As for patients older than 2 years, the disease, as a rule, is severe. The general condition often worsens due to damage to the structural elements of the brain. Symptoms that appear during this period: a significant increase in head size, morning headaches, nosebleeds, attacks of nausea, vomiting, poor coordination of movements, enuresis.
Classification of the disease
Doctors and parents should understand that the accumulation of fluid in the ventricles of the brain of newborns can be present from birth (congenital hydrops) or occur postnatally (acquired hydrops).
Depending on the mechanism of fluid stagnation in the head, it is customary to distinguish the following pathogenetic forms:
- Communicating dropsy;
- Closed dropsy.
Communicating dropsy
The accumulation of fluid in the ventricles of the head occurs as a result of its overproduction without disrupting the absorption process. From the first days of the disease, there are signs of increased intracranial pressure. This is typical for metastasis of cancer, meningitis, sarcoidosis.
Closed hydrocephalus
The closed form is formed in infants as a result of organic disorders, such as scars. These pathological formations lead to an increase in intracranial pressure.
Two forms of the disease:
- Compensation – the child has no clinically significant manifestations, his development corresponds to his age;
- Decompensation - an increase in intracranial pressure and an increase in cerebrospinal fluid leads to the development of specific symptoms; the child may experience a developmental lag behind his peers.
How is hydrocephalus formed?
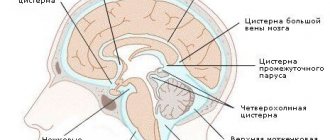
Cerebrospinal fluid continuously circulates in the spinal cord and brain - in the ventricles, between the membranes and in the cerebrospinal fluid conductors. The fluid is produced by special cells that are located in the ventricles of the brain, namely in the vascular tangles.
The ventricles of the brain communicate with each other, which allows the cerebrospinal fluid to flow into the subarachnoid space, in which the vessels are located. These vessels absorb fluid and drain it into the cerebral sinuses. Next, the cerebrospinal fluid is drained through the jugular venous system.
Functions of cerebrospinal fluid:
- Acts as a shock absorber under mechanical stress;
- Maintains stable intracranial pressure;
- Removes decay products;
- Maintains water and electrolyte balance.
Hydrocephalus of the brain in newborns is diagnosed when the normative values are exceeded. The amount of circulating fluid has age-related characteristics. In a newborn, the volume is 10–20 milliliters (in an adult it is almost 1.5 liters), but this difference does not affect functionality.
Regardless of age, the cerebrospinal fluid is renewed several times a day (up to 6). Thus, the presence of pathology can be judged by the volume of fluid in the brain.
Failures in cerebrospinal fluid dynamics:
- Excessive secretion;
- Absorption is impaired;
- CSF drainage is impaired.
The absorption of cerebrospinal fluid is directly dependent on intracranial pressure. Its decrease completely stops the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid.
Diagnostics
To diagnose congenital hydrocephalus, antenatal ultrasound screenings are used. When dropsy is detected, its degree is assessed, and the question of the method of delivery is decided. To verify anomalies, cordocentesis and chorionic villus biopsy are performed.
If you suspect excess fluid in the head, parents should first contact their pediatrician. When identifying the symptoms of this disease, the doctor will determine the scope of the normal diagnosis.
The diagnosis of increased intracranial pressure is made based on compliance with the examination algorithm:
- Clinical picture. Identifying symptoms first.
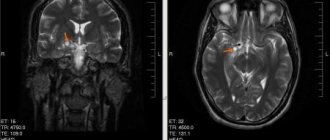
- Conservative method. Diagnosis of increased intracranial pressure is performed by neurosonography. This ultrasound examination is performed on all children one month after birth. The advantage of neurosonography is its speed, non-invasiveness, and accessibility. If the diagnosis is questionable, the child is indicated for additional examination. It is performed using X-rays using magnetic resonance imaging. This study is very informative and perfect.
- Surgical method. A small patient sometimes needs to be examined using a drainage test. The test method involves draining the lumbar cistern. The procedure is prescribed by a neurologist.
Interesting: Headaches in a 10-year-old child: causes, treatment, prevention
Diagnostic measures
Intrauterine hydrocephalus is diagnosed during a routine ultrasound examination of pregnant women. If cerebral hydrocele is detected, the frequency of procedures may be increased. Additionally, intrauterine fluid/blood may be collected from the umbilical cord for laboratory testing.
The disease in young children is detected as a result of medical patronage. To confirm the diagnosis, neurosonography is prescribed - an ultrasound of the brain performed through the fontanel. This procedure is now mandatory for every child who has reached the age of one month.
However, based on the results of an ultrasound examination, it is not always possible to accurately determine the causes of the disease, which is extremely important for prescribing subsequent treatment.
In such cases, a magnetic resonance or computed tomography procedure will help to study the causes in more detail and establish the type of hydrocephalus. To undergo it, the small patient is put into a state of medicated sleep. Layer-by-layer study helps to identify even minor deviations and changes in the structure of the brain.
Additional measures include consultation with a neurologist and ophthalmologist with mandatory fundus examination.
Often, specialists resort to electroencephalography, which records the electrical activity of the brain. If necessary, intracranial pressure can be measured.
Treatment
Treatment of dropsy of the brain is carried out only after confirmation of the diagnosis. Parents are recommended to regularly attend examinations by a neurologist and pediatrician.
There are several ways to rid a newborn of fluid in the head. Dropsy is eliminated by medication or surgery.
Drug therapy
The main goal of using medications for fluid in the head is to alleviate the patient’s condition before performing surgical correction methods, and rehabilitation after it. An exception may be the treatment of children born prematurely. The drugs used include furosemide, isosorbitol, and acetazolamide.
Surgery
The operation can not only correct the pathological accumulation of fluid in the head, but also improve the well-being of patients. The treatment method depends on the form of hydrocephalus. Neurosurgeons perform various types of shunting (lumboperitoneal, ventriculoarthrial, ventriculostomy).
Traditional methods
Traditional methods in the treatment of hydrocephalus in newborns are practically not used. Products such as freshly squeezed vegetable juices are contraindicated in the first month of life. Herbal decoctions should be given with great caution to avoid side effects.
Forecast
Mild congenital forms of hydrops usually do not have any consequences, since early detection and therapy help to correct the liquor dynamics.
In other cases, the prognosis depends on the form of dropsy and timely treatment.
Severe forms of cerebral hydrocele or advanced cases inevitably lead to cognitive depression and the development of paralysis. Timely treatment will not completely restore the central nervous system, but can significantly improve the quality of life, since organic lesions do not go away without a trace.
Possible consequences and prevention
Increased cerebrospinal fluid due to this pathology without treatment can lead to the following complications:
- Delayed psychophysical development of the child;
- Epilepsy;
- cerebral palsy;
- Death due to decompensation.
A child’s life expectancy and its quality are determined by timely treatment and compliance with preventive measures:
- Avoid psycho-emotional shock or stress;
- Protect from head injuries;
- Mandatory examinations by a neurologist.
The prognosis is determined by the degree of parental responsibility in following the recommendations.
Prevention
Preventive measures boil down to a thorough examination of pregnant women; for this purpose, 3 screenings are provided throughout pregnancy.
Mandatory preventive examinations by specialists are provided for infants. On the part of parents, the main method of preventing dropsy is vigilant monitoring and the use of protective equipment (chair, helmet) - this will prevent severe traumatic brain injuries.
Surgical treatment is not always effective, but it significantly reduces the risk of death.