Central pain
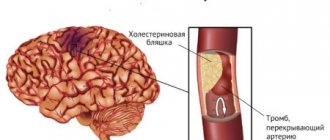
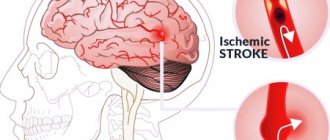
Central pain occurs when such brain structures as the thalamus (thalamic pain), in particular the thalamus optic, are damaged. The thalamus is the highest center of pain sensitivity, and these symptoms occur due to impaired blood flow and lack of oxygen transport to the optic tubercle. With the right treatment, the pain disappears over time.
Characteristics of central pain:
- Excruciating, prolonged pain.
- They are poorly eliminated by NSAIDs and analgesics.
- They occur on the opposite side of the stroke.
- May be accompanied by paresthesia (decreased tactile sensitivity, crawling sensation).
- Often accompanied by an exaggerated reaction to a tactile stimulus (hyperpathy), for example, when pricked with a neurological needle, it is felt as severe unbearable pain.
- Disturbing both at rest and when moving.
- They intensify with movement and psycho-emotional stress.
- Occurs late after a stroke.
Treatment of central pain
- Antidepressants (amitriptyline, sulpiride). These medications not only have an effect on the patient’s mental state, which will help him cope with the current situation, but also have a proven pain-relieving effect.
- Anticonvulsants, particularly carbamazepine, are widely used to treat chronic pain. During treatment, these drugs are used both separately and in combination, it all depends on the patient’s condition and the severity of the pain syndrome.
Diagnostics
In people who have had a stroke, the muscles may become hard and stiff.
Some muscles control the flexion of the arms and legs, while others control their extension. Normally they are in a state of balance. A stroke damages parts of the brain that send nerve impulses to the limbs. The muscles that flex the arms and legs may begin to dominate those that extend the limbs. This problem is called contracture. It causes cramping and severe pain. Muscle spasms need to be treated as soon as possible, otherwise the arms or legs will bend and stiffen so that they cannot be straightened. Treatment includes physical therapy, medication, and strengthening the correct position of the arms and legs using splints. Sometimes botulinum toxin (Botox) injections into the muscles are prescribed.
Contact a specialist to find the optimal combination treatment for you. As mentioned above, you cannot waste time. The doctor will likely prescribe baclofen, tizanidine, or other medications. But the emphasis should be placed not on them, but on physical therapy. Splints may be needed to secure the arm or leg in an extended position. The last radical remedy is tendon surgery.
Watch a video about what rehabilitation methods after a stroke are used in a specialized medical institution. You can do the same thing at home without having to pay a lot of money.
The pain may also be peripheral (paretic). This is a kind of signal from the body, indicating the beginning of the recovery process.
Central pain
This type of symptom occurs in response to damage to the thalamus, one of the parts of the brain. This occurs as a result of impaired blood circulation in the area and the development of oxygen deficiency in the tissues. The severity of symptoms and their duration vary. Most often, sensations originate in the fingers. They disturb the patient during physical activity and at rest. Nervous stress and mental disorders can intensify manifestations.
The following clinical picture is typical for central pain:
- burning sensation in muscles;
- pain is similar to electric current discharges;
- numbness and tingling, changes in sensitivity;
- the appearance of “goosebumps”;
- increased sensitivity to heat and cold.
The sensations are not relieved by taking analgesics and NSAIDs. This sign, combined with the clinical picture, allows you to quickly make a correct diagnosis. With proper therapy, the patient's condition will soon return to normal.
Peripheral pain
A stroke can cause a disruption in the transmission of nerve impulses. This results in a loss of communication between the brain and limbs. As a result, the victim loses the ability to control the affected parts of the body. During the restoration of lost functions, impulses begin to make their way to the final goal.
The condition is characterized by an acute type of pain. The sensations arise in response to an attempt to move a paralyzed limb. The symptom is considered a favorable sign and increases the chances of restoring lost functions. At the same time, it causes significant discomfort to patients and complicates the rehabilitation process itself.
Additionally, additional laboratory and hardware tests may be required. The approaches are aimed at assessing the structure and condition of the cerebral cortex and identifying areas of problems. Approaches such as MRI and CT are characterized by increased information content.
A neurologist is involved in the selection of medications for any type of pain in the limbs after a stroke. Attempts to drown out unpleasant sensations with the help of analgesics, antispasmodics and NSAIDs threaten the development of side effects in the patient and aggravation of the situation. Profile therapy is not limited to medications alone. It should be multidirectional and complete.
Drug treatment of central pain:
- anticonvulsants – relieve pain, improve the quality of life of patients (“Pregalbin”);
- antidepressants - relieve tension, should be prescribed immediately after the onset of pain (Amitriptyline, Cymbalta);
- opioid analgesics – for extreme pain syndrome.
The listed groups of drugs are used in combination. The duration of therapy depends on the specifics of the situation and the effectiveness of the selected means. A profile course can last from 3-4 weeks to 2 months or even longer.
For paretic pain, treatment should also be comprehensive and systematic. Violation of the drug regimen or refusal of some aspects of therapy threatens the transition of the muscles into a spastic state, which is almost impossible to correct. With this diagnosis, anticonvulsants and antidepressants are supplemented by taking muscle relaxants. This will bring the muscles into a relaxed state and reduce the severity of pain.
Folk remedies
Methods of pain relief from the field of alternative medicine can give a lasting positive effect. They must also be agreed with the attending physician. Reception of products and manipulations must be carried out strictly according to schedule. The average duration of courses is from 2 to 6 months.
Traditional medicine recipes for pain in the limbs after stroke:
- clover tincture - take a glass of meadow clover inflorescences, rinse and dry, put in a liter jar. Pour the mixture with vodka or 40% medical alcohol and seal tightly. Leave the preparation for 2 weeks in a cool, dark place. Strain the mixture, squeeze out the thick part and stir. Take a teaspoon per day after one meal. You need to take 3 courses of 30 days, with a break between them of 10 days;
- alcohol ointment - take 2 parts unrefined vegetable oil, 1 part vodka or 40% medical alcohol. Mix the components and use as an ointment when massaging the affected limb up to 2 times a day. Using the same scheme, you can use bay oil in its pure form;
- medicinal baths - take 3 cups of sage, celandine, pine needles or rose hips (your choice), put in a 3 liter jar. Pour boiling water over the mixture and leave in a warm place, covered, for 1 hour. Strain the mixture and squeeze out the thick part. Pour the liquid into the bathtub for the stroke victim. The manipulation is carried out for 10 baths of the patient, after which take a break of 3-5 baths and repeat the course.
Approaches based on the use of natural ingredients can cause allergic reactions. As they are used, it is recommended to monitor the patient’s general condition and, if necessary, make adjustments to the therapy regimen.
Exercise therapy and massage
The maximum effect in the treatment of pain in the extremities is possible only if physiotherapy is included in the regimen. To receive exercise therapy and massage sessions, the patient does not have to be taken to specialized specialists. A significant part of the activities can be carried out at home through the efforts of the victim’s loved ones. Exercise therapy techniques consist of a number of simple exercises, each of which should be performed daily, performing at least 50 repetitions.
To perform gymnastics, the victim of acute stroke must be in a supine position:
- smooth flexion and extension of the arms at the elbow joints;
- bending your elbows and extending them above your head;
- straightening your arms and spreading them to the sides, lifting them above your head;
- flexion and extension of the hands;
- clenching and unclenching fists;
- rotational movements of the thumbs;
- raising arms extended along the body;
- flexion and extension of the legs at the ankle, knee and hip joints.
Massage of the arms and legs is indicated for increased muscle tone. It is necessary to work not only with the affected part of the body, but also with the healthy one. This will accelerate the development of positive dynamics, relieve discomfort, increase the functionality of the limbs and bring the moment of maximum recovery of the body closer.
Rules for massage for pain in the arms and legs:
- procedures begin no later than the 4th day after an ischemic stroke and the 7th after a hemorrhagic stroke;
- The minimum course duration is 15 sessions. After completion of treatment, at least 1-2 more preventive approaches are indicated;
- If possible, sessions are carried out daily. The exception is days when the pain syndrome is severe and does not allow the patient to relax.
At the initial stage, the degree of impact on the affected limb should be minimal. The load is increased gradually, increasing the intensity of classes, their duration, and adjusting the set of exercises. The absence of positive dynamics in the first days after the start of therapy is not a signal to revise the treatment regimen. Sometimes you have to spend more than one week to achieve positive changes.
Pain in the limbs after a stroke is a serious and unpleasant complication. It can cause a lot of unpleasant moments for the victim and become a provocateur of psycho-emotional disorders. The fight against such manifestations should begin as early as possible and be carried out under the supervision of a professional. Improper treatment of paralyzed limbs threatens a permanent decrease in the functionality of body parts or their complete inactivity.
Treatment of pain after stroke
First, it is important to determine in which part of the body the pain after a stroke is concentrated, to understand where and when it occurs. Check the moment of its appearance: whether any of your actions or movements cause it, after which it appears. The best way out in a situation of pain after a stroke is to contact your doctor to select the appropriate methods for its elimination, medications, physical therapy, etc.
After all, everything is always individual and depends on the specific organism, and only a doctor can most accurately determine the reasons. There are patients who are embarrassed to tell their doctor about their pain after a stroke, because they believe that it is weakness. This is fundamentally wrong, because such a position can provoke a slowdown in the body’s recovery after a stroke, and sometimes even worsen the condition. Therefore, experts strongly recommend monitoring your sensations, even writing down in a diary where and how often pain occurs after a stroke.
Peripheral pain
Peripheral pain, or so-called paretic pain, occurs during the recovery of a paralyzed limb. From the moment a stroke and brain damage occurs, connections between the brain and the paralyzed arm are disrupted, i.e. no nerve impulses are received to perform movements.
During recovery, these impulses begin to flow, an increase in muscle tone occurs, when you try to move a limb, the muscle tone does not correspond to a certain movement, and pain appears.
Characteristics of paretic pain:
- Occurs when the limb moves
- Period of occurrence: from two weeks to a month
- Sharp, muscle pain
- Prevents limb movement
Treatment of paretic pain
Since pain occurs when moving the arm, often during rehabilitation activities, this may cause unauthorized termination of exercise therapy, but the patient must be explained that this cannot be done. With long-term and persistent rehabilitation, pain decreases over time and then disappears.
It is worth noting that similar pain can occur with joint contracture, which is directly related to paresis or paralysis of the limb due to prolonged lack of movement. In this case, due to the lack of rehabilitation measures, scar changes occur in the joint, which limits its movement and causes pain.
To alleviate the patient’s condition and thereby continue treatment measures, the following are used:
- Muscle relaxants (mydocalm, baclofen). These drugs affect the central nervous system, which is involved in the regulation of muscle tone, thereby reducing it.
- NSAIDs (diclofenac, nimesulide). This group has some anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, in this case I note the low effectiveness of use.
- Antidepressants (amitriptyline, sulpiride)
- Anticonvulsants (carbamazepine)
Why do my legs become paralyzed after a stroke?
Often patients are faced with the fact that the leg has paralyzed after a stroke or sensitivity has been lost, paresis, bedsores and ulcers have begun. This is due to the location of the lesions in the right hemisphere of the brain . It is responsible for motor activity, emotions and mental state. Leg paralysis can also develop due to a spinal stroke, hemorrhage in the right hemisphere or cerebellum. In this case, the symptoms and consequences will most clearly manifest themselves on the reverse side of the location of the foci of inflammation. If the stroke is located closer to the left hemisphere, then the paralysis will be less pronounced. Sometimes problems with legs and arms develop against the background of repeated thrombosis in bedridden patients.