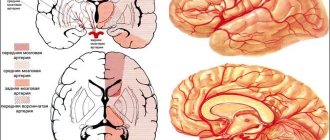
Ischemic stroke occurs due to insufficient supply of oxygen with blood to parts of the brain, and hemorrhagic stroke occurs due to excessive supply of blood to the human brain. Both of these diseases are dangerous to health.
After an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, one of the complications is impaired motor activity. This places restrictions on the patient's daily life.
Air travel after a stroke should only be done if absolutely necessary, after consultation and permission from a doctor.
Stroke: main causes
Is it possible to fly on an airplane after a stroke? We’ll figure it out below. In the meantime, let’s find out what causes the disease.
The main reason for this dangerous pathology is that one of the brain vessels is blocked by blood clots or foreign objects. Blood cannot get through this barrier; as a result, acute oxygen starvation occurs, and some of the cells die. This phenomenon is called “ischemic stroke”. It is better to find out in advance whether it is possible to fly after such a pathology.
A hemorrhagic stroke is when an artery ruptures and blood spills into the outer tissue of the brain, causing swelling that causes the death of cells and nerve fibers.
Course of a microstroke
A microstroke occurs as a result of the negative influence of certain factors or is a consequence of certain chronic diseases. The main factors that can cause a mini-stroke include:
- smoking,
- alcohol abuse,
- drug use,
- stress,
- chronic fatigue.
Each of these reasons or their combination can cause a mini-stroke in a healthy person. Among the diseases that provoke this condition are:
- atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels,
- arterial hypertension,
- pathology of cerebral vessels,
- cardiomyopathy,
- diabetes,
- pathologies of the cervical spine.
If you have any of the above diseases, even at an early stage, you should regularly visit a doctor to prevent a micro-stroke. The Yusupov Hospital employs professional neurologists who specialize in cerebrovascular diseases. Timely contact with a specialist significantly reduces the risk of developing a mini-stroke in the future. You need to know that a microstroke is a harbinger of a full-blown stroke or cerebral infarction, which leads to irreversible damage and can cause disability and death.
With the development of a micro-stroke, a blockage of a brain vessel occurs, as a result of which some parts are left without nutrition. The blockage of the vessel is not complete, so a small amount of blood continues to feed the brain. This explains the reversibility of this state.
A microstroke occurs spontaneously and does not last long. At this time, a person may feel dizziness, pain in the back of the head, the appearance of black dots or light spots before the eyes, nausea, and loss of coordination of movements. If such symptoms appear (especially in the presence of provoking factors), you should immediately consult a doctor. The emergency department of the Yusupov Hospital operates around the clock, so the patient will receive qualified medical care at any time of the day.
The main thing is timely help
This disease is very dangerous for human health; half of the cases are fatal. But if you provide the patient with medical care in time, his life can be saved. After a stroke has occurred, the patient must be placed in the intensive care unit within 3-4 hours, in some cases an operation by a neurosurgeon will be required. The less time it takes to get to the hospital, the higher the chances that the person will remain alive and will not become disabled. However, the area of the affected area of the brain is important: serious complications cannot be avoided if it is large.
Long rehabilitation
Even with a successful operation, the patient will undergo rehabilitation for a long time. Most people after a stroke learn to live again and deal with the negative consequences of the disease. On average, a patient’s normal life can begin only after 2 months. It takes much longer to return to work; Driving a car or business trips to other cities and countries are unavailable to many for a very long time.
Patients who have suffered a stroke in the recent past, whose life was completely or partially associated with travel, ask doctors the question: “Is it possible to fly on an airplane after a stroke?”
Opportunities and limitations of stroke patients
A stroke is an extremely serious pathology that does not go away without leaving a trace. Patients who manage to survive a stroke undergo long-term rehabilitation, as well as an equally long period of social adaptation.
If the recovery period is successfully completed, patients return to their normal lives. And at this moment, as a rule, many questions arise. Is it possible to fly on an airplane after a stroke? Exercise? Get behind the wheel? Take a steam bath? In this article we will answer the questions most often asked by patients who have successfully completed a period of physical and social rehabilitation after a stroke.
Will flights be allowed?
As a rule, the doctor's answer will be positive. You can use air transport, but there are certain conditions and restrictions. This is important to remember. The problem is that, in fact, flying is a tiring and difficult process even for a healthy person.
Due to severe changes in pressure, stress and panic, and an unfavorable atmosphere in the aircraft cabin, repeated cerebral hemorrhage may occur, which will be fatal for most patients. What is especially scary is that qualified assistance will not be provided, because it is impossible to do this at altitude.
How to transport a sick person by plane?
Many problems during a flight can be avoided if the special state of the body is discussed in advance with the air carrier at the stage of booking a ticket.
It is important to understand that if transportation involves a transfer, then the conditions must be agreed upon along the entire route.
Are there any age restrictions for old people? If an elderly person does not have any special health problems, then a medical certificate and support will not be required. A person needs help only when getting on and off.
At the stage of booking a ticket, you should notify about limited mobility and possible additional assistance (about a special diet, special services - for example, receiving a stroller or gurney at the airport), etc.
Passengers requiring special assistance in the aircraft cabin must be issued a medical certificate by a doctor.
If it is necessary to have an accompanying person, a second seat in the cabin is provided next to the stretcher.
Patients are boarded before the rest of the passengers board, and disembarked after everyone else.
Disabled persons must travel with accompanying persons. If transportation is carried out under the supervision of the carrier, then consent must be obtained in advance from the company itself, and it must be in writing.
People who are blind or hearing impaired must also be accompanied. If this is not possible, a guide dog may be present on board. Typically, such a dog can be kept in a cabin without a crate if:
- man depends on the animal;
- there is a certificate of training for such needs;
- it has a muzzle, the animal is located at the human’s feet.
Before any flight, persons with special medical conditions should consult their attending physician.
In order for a sick, disabled or elderly person to fly on a regular aircraft, and these categories of citizens need care, a certain number of seats are purchased for accompanying persons - medical staff, loved ones.
We looked at the question of whether it is possible to fly on an airplane after a stroke.
What points should be taken into account?
So, what is the opinion of doctors about whether it is possible to fly after a stroke? Typically, attending physicians allow such travel if the following points are taken into account:
- How much time has passed. If more than six months have passed since the operation, but not less than 2 months. It is a big plus if no health-threatening complications arise during this period. That is, after complete recovery from a stroke, you can fly.
- Quality of rehabilitation. The recovery period for the patient was completed successfully, massage and physical exercises were used.
- At what level is your blood pressure? It should be normal, without a sharp rise and fall, the threshold of 140/90 should not be exceeded. Regular intake of prescribed medications is important.
- Is the patient susceptible to aerophobia? Is it possible to fly after a brain stroke if you have a fear of flying? It is extremely important that a person does not suffer from aerophobia, as it provokes severe anxiety and stress.
If all conditions are met and the patient has confidence in his abilities, then he is allowed to fly and is prescribed certain recommendations.
The preparation must be correct
We continue to figure out whether it is possible to fly after a stroke. In advance, the patient must prepare himself and his blood vessels for high load.
The preparation process includes:
- Taking certain medications. Most often, doctors prescribe special blood-thinning medications (aspirin is considered the most popular) that prevent blood clots in blood vessels and relapse of the pathology.
- Passing examinations. Before the flight, an electrocardiogram and ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head are required. This is required to eliminate the possibility of aneurysm formation. During the flight, pressure changes are possible, and an aneurysm may rupture, leading to a fatal brain hemorrhage on an airplane after a stroke.
- Own first aid kit. The patient must plan in advance what medications he will take with him on the plane. The first aid kit should consist of medications that stabilize blood pressure and sedatives; medications against motion sickness are also useful.
If the preparation is carried out correctly by the patient, then it is possible to fly after a stroke.
Also, the trip will be comfortable if you purchase special pillows for the head, in this way the unnecessary load on the cervical spine and blood vessels will be reduced. Excessively fatty foods are contraindicated before a flight; it is better to prefer light foods.
Threats encountered during flight
During flight, people face various types of threats. The “sitting” position, in which you have to stay for hours, is not entirely comfortable. A person's ability to move is limited and this leads to physical inactivity. The latter, in turn, is fraught with thrombus formation.
If the flight lasts more than 5 hours, the passenger's feet become numb. You can buy compression underwear, the same tights. This will relieve blood stagnation. The passenger can walk around the cabin if his limbs are numb.
The air in the aircraft cabin is quite dry due to air conditioning. The human body loses moisture from such air. As a result of dehydration, the blood thickens. You can replenish moisture reserves with clean water. But you do not need to use any drinks for these purposes. You should forget about alcohol.
It is unlikely that the time spent on an airplane can be called comfortable. The person is given little space. The distance between the seats is very modest. You can bring a change of shoes on board, for example, comfortable and loose slippers. This will improve blood circulation in the feet.
A person, especially one whose health is at risk and a recurrent stroke is possible, should try to avoid stress and anxiety. Sedatives will help passengers. Suitable tablets include valerian, Novo-passit, and peony extract. The hardest time for people will be during the takeoff and landing of the plane. It is at this time that the atmospheric pressure changes and this negatively affects the cardiovascular system. The amount of oxygen decreases at these moments. The passenger suffers from shortness of breath and dizziness.
If the aircraft gets into an air pocket, unpleasant vibrations occur. The heart rate suffers due to turbulence zones, and blood circulation is impaired. A blood clot may form and block the vessel in the brain.
Lack of oxygen
After a stroke, neurons die in the affected area. Brain cells located around the site of developed pathology suffer from necrobiosis. If there is not enough oxygen during flight, these cells may die.
The air in an airplane becomes rarefied when it is at altitude. This can cause hypoxia. Oxygen deprivation has a very negative effect on a person who has suffered a stroke. Neurons in a necrobiotic state may die very close to the affected area. The performance of the body decreases because of this, since the functions belonging to the dead neurons are lost (memories, body sensitivity, movement control, information about human skills).
Low blood pressure
Traveling by plane is stressful for the heart and blood vessels. The solubility of gases in the blood decreases and because of this, the load increases. The body is trying to adapt to the fact that there is less oxygen. As a result, the heart rate increases. The release of blood into the vessels also increases. This is a saving step from hypoxia. The vessels are not able to withstand such a load, since they have lost their elasticity and become coarser.
If the patient has suffered a hemorrhagic stroke, then this condition is especially dangerous for him. After all, a vessel can easily rupture and a stroke will recur.
Vestibular disorders
If the patient has experienced a cerebral hemorrhage, then he may have increased pressure inside the skull. The development of cerebral edema cannot be ruled out. Such factors cause vomiting and nausea. Air travel enhances the above processes. The patient is not even immune from death.
Physical inactivity
A stationary “sitting” position poses more than just inconvenience. This is fraught with a slowdown in venous blood flow. And this factor, in turn, leads to thrombus formation. Even if a blood clot forms in the lower extremities and not in the head, the clot can still clog the vessel in the brain, which will lead to a second cerebral infarction.
Maneuvers and vibration
The flight threatens the passenger with the formation of blood clots and heart rhythm disturbances. But due to the ascent, turn of the aircraft, or its descent, a small piece of the cholesterol plaque present on the wall of the vessel of the lower limb can come off and enter the arteries of the brain with the bloodstream. If a patient suffers from intracranial hypertension or has had a traumatic brain injury, then headaches cannot be ruled out. Airplane encounters with turbulence further intensify headaches.
Fear
Fear of flying or aerophobia is especially dangerous for a patient after a stroke. The very fact of a human flight is already frightening, even without irritating factors in flight. This fear and stress may well cause another stroke.
Stress hormones cause blood vessels to constrict. If their walls are affected by cholesterol plaques, then a dangerous condition occurs. When the blood is thick, that is, its coagulability is increased, the risk of ischemic stroke increases. The hormone adrenaline, which is released due to negative emotions, causes blood vessels to constrict, the blood thickens and blood pressure rises. If blood pressure is high, it threatens hemorrhagic stroke. With a concussion, blood pressure may increase and this increases intracranial hypertension, which is fatal.
Symptoms worsen at altitude
At altitude, the typical symptoms of hypertension worsen:
- The occurrence of migraine is a cerebrovascular disease due to prolonged spasm of blood vessels in the head. A dangerous complication is the cerebral form of hypertension (stroke). To prevent arterial hypertension from developing into a malignant form, it is worth defeating migraine at the initial stage.
- The appearance of pressing chest pain. The heart works overtime, so discomfort in the chest may turn out to be angina. If there is a history of myocardial ischemia in hypertensive patients, they should fly with great caution.
- Having severe shortness of breath. Limited space and elevation lead to a feeling of lack of oxygen; reflex shortness of breath may occur in response to stress. To avoid real suffocation, the patient’s breathing must be deep and even; oxygen cocktails can come to the rescue.
- Development of tachycardia. The intense work of blood vessels leads to a rapid heartbeat, because they quickly pump large amounts of blood. This leads to spasm of blood vessels and tension in their walls.
Preparatory stage
Before flying on an airplane after a stroke, it is recommended that the patient be properly prepared. In this case, you need to adhere to certain rules. It must be remembered that recurrent stroke develops during crisis arterial hypertension. That is why preliminary monitoring of blood pressure dynamics in various situations after a stroke is recommended.
If the patient has the opportunity, he is recommended to purchase a special device with which arterial hypertension is measured. This will allow you to determine blood pressure readings and, if the need arises, provide first aid to the patient.
The patient is strictly prohibited from succumbing to stressful situations that can lead to psychosomatic disorders and pathological changes in mood that are manic or depressive. The development of such a pathological process is a risk factor for recurrence or various complications of stroke.
After a stroke, the patient is recommended to undergo special training before flying on an airplane, which will reduce the likelihood of developing undesirable effects.
What are the dangers of flying after a stroke?
However, during the flight, the patient may in any case encounter various kinds of problems that cannot be foreseen in advance.
So, the problems could be the following:
- Dry air. The skin dries quickly due to air conditioning on airplanes, and the unpleasant thing is that the body quickly becomes dehydrated. But this provokes thickening of blood in the vessels, which can turn into a mortal danger for a person after a stroke.
Therefore, you need to drink more fluids, but not tea and coffee, but pure water, and still. Alcoholic drinks are strictly prohibited; their influence is detrimental to the cardiovascular system, and as a result, a heart attack can occur.
Is flying by plane harmful to your health?
Western doctors have come to the conclusion that flying by plane is harmful to health. During a flight, ordinary factors that may not be noticeable in everyday life become hazardous to health. If you are overweight, have hypertension, asthma, or cardiovascular diseases, air travel becomes doubly dangerous. Partial oxygen pressure and low atmospheric pressure aggravate these diseases.
Those at risk include pregnant women, the elderly, smokers, people with diabetes, tall people and people with hormonal imbalances. This, of course, does not mean that you should give up flying altogether, but it is advisable to minimize all risks and visit a doctor on the eve of the flight.
Impaired blood circulation
Nature has programmed our bodies to move, and when flying we are forced to sit for many hours. As a result, the lower limbs become numb and blood circulation in them is disrupted, which does not receive enough oxygen. Therefore, fainting, heart attacks, and strokes are possible.
Thrombosis is a consequence of impaired blood circulation. One of the causes of thrombosis is prolonged sitting. With thrombosis, the vein in the legs is blocked by a blood clot - a thrombus. This causes pain in the limbs, swelling, numbness, and a burning or cold feeling. Thrombosis is also dangerous because the clot can very quickly penetrate the heart or lungs. Excess weight increases the likelihood of thrombosis, since blood circulation in obese people is impaired. Thrombosis has become so common that it is called “economy class syndrome.”
To prevent circulatory disorders and venous thrombosis:
- Try to stretch your legs during the flight. Get up, walk around the salon, stretch, step your feet, massage your limbs.
- There is no need to cross your legs, as this impedes circulation.
- Try to drink more water. Avoid caffeinated drinks and alcohol, which can dehydrate your body.
- It is advisable to use compression tights or socks. Clothing should not restrict movement.
- If you are at risk, consult your doctor and take aspirin before your flight to thin your blood.
- After deep-sea diving, take off for a flight no earlier than 24 hours later.
Difficulty breathing
The atmospheric pressure inside the aircraft is lower than on the ground. Along with a lack of oxygen and temperature changes, this can cause an attack of suffocation. This is especially true for those who are overweight or have asthma. People at increased risk need to carry an inhaler or oxygen bag with them.
High blood pressure
Hypertension and excess weight often go hand in hand. The risk during flights for hypertensive patients increases. Due to insufficient oxygen levels, stress caused by turbulence, vibrations, and pre-flight anxiety, the heart begins to work overload, which leads to increased blood pressure, heart attack and even stroke. Therefore, people with high blood pressure should take a pill before flying or increase their usual dose of blood pressure medication.
Long sitting position
Passengers on the plane remain motionless for a long time. Physical inactivity can cause blood clots, resulting in a recurrent stroke. This possibility will be higher the longer the flight lasts. Flights typically last more than five hours, so passengers often experience swollen feet.
Wearing compression garments under regular clothing will help prevent this. Women can buy special compression tights. They will disperse the blood where it stagnates. Sometimes it is acceptable to get up from your seat at least once and walk around the salon, of course, when this is not prohibited. To disperse blood throughout the body, it is good to rotate your hands, feet and neck. In general, simple health-improving exercises will help.
Preparing for the flight and recommendations
If there is a need to fly, the time necessary for the patient’s rehabilitation has passed, and the attending physician has given permission, then before the trip it is necessary to monitor blood pressure for several days, doing this at different times of the day and in different situations. Immediately before boarding a plane, if your blood pressure is high, you need to take a medication to lower it.
You need to collect a first aid kit, where to put:
- antihypertensive drugs taken;
- motion sickness remedies;
- sedative;
- thermal water (carry-on baggage allowance is 100 ml) to make you feel better in the dry air of the cabin;
- apparatus for measuring pressure.
Before departure:
- Wear suitable compression garments to increase vascular tone of the lower extremities in conditions of physical inactivity.
- If you have a history of ischemic stroke, you can take blood thinners as prescribed by your doctor.
In flight:
- Avoid drinking coffee and alcohol.
- Periodically leave your seat and walk around the salon.
- If it is not possible to stand up, perform circular movements with your feet on the spot to prevent physical inactivity.
- If a stressful situation occurs, take a sedative in a timely manner, and if your blood pressure increases, take an antihypertensive drug.
- Drink enough water.
By following your doctor's recommendations and paying close attention to your health, you will be able to minimize the risk of another stroke during or after a flight.
Turbulence
An unpleasant vibration appears when the plane hits air pockets. Under its influence, the heart rhythm may be disrupted, as well as blood circulation and blood supply to the brain. A new blood clot forms, and subsequently another stroke.
The only advice in this case would be the following. You need to calm down and try to sleep. If you follow all the doctors' recommendations, nothing bad should happen, especially if throughout the flight the patient kept his blood pressure under control, consumed enough fluids and stretched his legs. The trip will be comfortable and without serious consequences. How to fly by plane after a stroke?
Is it possible to fly on an airplane after a mini-stroke?
A microstroke is a temporary disruption of blood flow in a certain area of the brain. With a micro-stroke, tissue damage is not as extensive as with a full-fledged stroke and it is reversible. However, a mini-stroke leaves behind unpleasant consequences that can affect a person’s daily life. Many people who are accustomed to leading an active lifestyle are concerned about an important question: is it possible to fly on an airplane after a micro-stroke? Will the negative consequences worsen when using this type of transport?
Read also: How to treat hemorrhagic stroke
Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe treatment based on the individual characteristics and needs of the patient. Drug treatment and a rehabilitation course with experienced specialists are used to help you recover as quickly as possible after a mini-stroke.