Dear friends, hello!
Today we will talk about a sore that many of you know firsthand. This is the so-called vegetative-vascular dystonia, or VSD syndrome. Sometimes it is called neuro-circulatory dystonia, organoneurosis, or cardiac neurosis.
Raise your hands who have ever been diagnosed with this?
Awww I see a forest of hands!
And I also raised my hands, because my entire childhood passed in an embrace with this sore. And my sister. And my grandmother. From this we could conclude that this rubbish is a hereditary thing.
But don't rush to conclusions.
It’s probably hard to find at least one other disease that seems to be considered not serious, but sometimes you feel as if it’s time for you to order white slippers. And all this, as a rule, happens in the prime of life - at the most beautiful, most productive age.
But you can’t work and enjoy life, because it feels like something in your body has completely broken down, and it refuses to obey your will.
And the torment begins: from doctor to doctor, from clinic to clinic. But they don’t find anything wrong.
What kind of pain is this? Why does it arise? Why is it dangerous? Is it finally curable? And what can you offer to a dystonic sufferer who drops into a pharmacy asking for help?
Let's figure it out.
Description of the syndrome and physiology of its occurrence
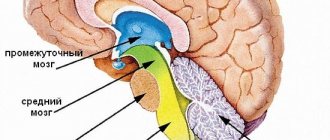
To make the essence of VSD clear, I will first explain how it arises. The nervous system is divided into somatic and autonomic. The somatic part provides motor responses to external stimuli using the senses. For example, when we touch a hot pan, neuromuscular transmission receptors send an impulse to the pain centers, and we pull our hand back.
Anatomically and functionally, the autonomic nervous system (ANS) is divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. The sympathetic part increases our activity, increasing metabolism, as a result of which tissue excitability increases. Parasympathetic, on the contrary, helps the body recover by regulating its functioning during sleep.
The syndrome has many synonyms - neurocirculatory dystonia, cardioneurosis, neurasthenia, autonomic neurosis, autonomic dysregulation, dysvegetosis.
Does such a diagnosis exist?
If you look at the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), there is no disease or syndrome called “vegetative-vascular dystonia” there. However, there are terms with similar or similar content. Some doctors try to subsume VSD under an “official” diagnosis with a name such as: neurocirculatory dystonia (F45.
NCD manifests itself at different ages, with varying symptoms and severity. Most patients experience dystonic attacks, or so-called crises, with extreme difficulty. They worry more psychologically than physically. Attacks of exacerbations can cause pain and inconvenience, disrupt the usual way of life, and give reason to suspect more serious disorders.
One of the branches of the disease is cerebral angiodystonia, a pathology in which cerebral vascular tone is disrupted. Dizziness, pressure changes, headaches and insomnia become frequent companions of NCD, and deterioration of the condition forces one to seek help from specialists.
Is VSD a myth or a real disease?
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is not a disease, but a series of symptoms caused by psychological or physiological pathologies and disorders. Women suffer from pathology more often than men.
In some countries, such a diagnosis does not exist at all. Instead, doctors use the term “neurosis.”
Nevertheless, patients continue to be given a diagnosis of VSD on their cards, the essence of which is not clear, either to the doctors themselves or to the patients. In recent years, the number of people receiving such a “sentence” has been increasing.
Doctors themselves often say that now children are already born with dystonia and shrug it off indifferently. But people suffer, sometimes very much. How can we consider something that causes a bunch of symptoms but has no clear essence to be a disease?
The Directory of the International Classification of Diseases and Problems Associated with Health Disorders does not classify vegetative-vascular dystonia as a separate disease. The syndrome is assigned an ICD-10 code, which includes various functional disorders with extensive symptoms. So what is VSD if it is not a disease at all?
By the way, in foreign countries the term “vegetative-vascular dystonia” is not used. The syndrome is classified as a neurosis and is treated by a psychotherapist, which is essentially correct.
Important!
Under the mask of VSD, other serious diseases may be hidden, especially those related to the endocrine system. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment! All information on the site is for informational purposes only and is not a reason for self-diagnosis or self-medication.
What is VSD - the opinion of doctors and scientists
In fact, doctors and scientists began to study this strange syndrome in more depth and detail not so long ago. And this is due to the fact that the disorder has begun to progress in recent years. But until now, not a single doctor can clearly answer you what VSD essentially is and why you were diagnosed with it. Usually this diagnosis is given to those who do not find any real diseases or pathologies that can cause the symptoms that the patient has.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is, in fact, autonomic dysfunction, a disorder, an imbalance of the nervous system. More precisely, its departments – sympathetic and parasympathetic. Scientists are increasingly coming to the conclusion that such a disorder in the body has a psychogenic etiology. That is, the body suffers due to a person’s psychological problems, which he accumulates and keeps within himself.
The disorder is completely reversible and with proper therapy has a very favorable prognosis.
In addition to the term “VSD”, doctors also use others, the essence of which is the same:
- Cardioneurosis (neurosis of the heart).
- Cardiopsychoneurosis.
- Vasomotor dystonia.
- Functional cardiopathy.
- Somatoform nervous disorder.
- Angioneurosis.
- Psychovegetative neurosis.
- Autonomic dysfunction.
Symptoms and signs: what patients come with
The symptoms of VSD are so varied that making a diagnosis can be difficult. It is known that the manifestations of dystonia are “masked” as a large number of diseases. Before visiting me, a neurologist, such a patient had already visited many specialists (cardiologist, gastroenterologist, ophthalmologist).
Depending on the participation of certain organs or systems, the following types of vegetative-vascular dystonia are distinguished:
- Cardiac type is characterized by:
- burning, stabbing, pressing pain in the heart area (which may be mistakenly perceived as myocardial infarction), accompanied by shortness of breath, a feeling of lack of air, which does not increase with physical activity, but, on the contrary, becomes less intense;
- instability of blood pressure, feeling of fear. Provoking factors, in addition to stress, can be changes in weather, consumption of alcohol and certain foods. When interpreting the ECG, no pathological changes are found.
- The hypotonic type is characterized by a decrease in blood pressure (up to 100 mm Hg), pallor of the skin, sweating, a feeling of lack of air, increased breathing, nausea, and upset stool.
- The hypertensive type is manifested by increased blood pressure, dizziness, headache, flashing “floaters” before the eyes or a feeling of a veil, increased sweating, vomiting, and impaired coordination of movements. Doctors are often confused about the symptoms: the clinic simulates a hypertensive crisis, but medications are not needed to stop it - you need to relax, let go of the situation, take a sedative “first aid drug” - and the unpleasant sensations will go away. The danger is a protracted crisis with unrelenting symptoms, in which case I recommend immediately seeking help from a psychotherapist. And if visual impairment persists for a long time, visit an ophthalmologist to rule out retinal pathology.
- The cerebral type (in some sources - angiocerebral dystonia) occurs when vascular tone is disturbed, which is manifested by their spasm. Most patients complain of headaches, fainting, dizziness, nausea, tinnitus, numbness in the face and limbs. It is possible that other symptoms may occur - a feeling of chills or heat, shortness of breath, increased heart rate. The most susceptible to this type of dystonia are patients with increased intracranial pressure due to traumatic brain injuries and neoplasms, as well as patients after strokes.
- The vagotonic type is characterized by apathy, suspiciousness, decreased memory and attention, pain in the chest and abdomen without clear localization, loss of consciousness, dizziness, and cold extremities. Symptoms occur when the vagus nerve (n. vagus) is activated, which regulates the functioning of organs, glands and blood vessels.
- The mixed type combines the symptoms of several variants of VSD and is the most common.
Based on the type of flow, paroxysmal and permanent VSD are distinguished. If symptoms are observed every day, but their character does not intensify, we talk about a permanent course. In my practice, I more often encounter the paroxysmal form, which manifests itself with a sharp onset, a long peak, and a periodic decrease in manifestations, which after some time intensify again. The latter option includes vegetative crises and panic attacks.
The symptoms and treatment of VSD in adults are not particularly different, but the fairer sex is more inclined to it. In girls in adolescence, I observe the appearance of the syndrome due to a discrepancy between physical development and the degree of maturity of the nervous system. It is also worth noting that VSD can develop during hormonal changes in the body (pregnancy, postpartum period, menopause). In addition to all of the above, women are more susceptible to the effects of emotions, stress and chronic fatigue.
Manifestations of VSD in women include mainly:
- increased heart rate, increased blood pressure,
- pressing headache
- dizziness without loss of coordination of movements,
- increased sweating of the palms and feet,
- feeling of a lump in the throat, lack of air,
- fear, panic,
- lack of appetite,
- muscle pain,
- feeling of aching joints,
- the appearance of red spots on the skin of the neck and face,
- increase in body temperature,
- general weakness.
Just don't panic!
There are two types of attacks of vegetative-vascular dystonia. In one case, a person may be plagued by loss of strength and apathy. Secondly, on the contrary, very acute attacks occur, accompanied by severe anxiety, which is why they are called “panic attacks.” There are other types of attacks when the pressure, on the contrary, decreases, the heart beats less frequently, it becomes difficult to breathe, and it makes you sleepy.
In any case, the victim must first of all be ensured maximum peace. Bright lights, noise, and loud voices can only worsen the condition. It is also necessary to give the patient some kind of sedative - tincture of peony, valerian, Corvalol. If these measures are not enough and the attack does not go away, it is better to call an ambulance. As a rule, autonomic dystonia, which is based on hereditary dysfunction of specific autonomic centers of the brain, makes itself felt in early childhood. Over the years, the inherited “weakness” only gets worse. But the causes of failure in the body’s autonomic system can also be chronic stress, as well as serious illness, excessive physical activity, severe emotional shock (loss of a loved one, job, divorce).
Diseases can also disrupt the functioning of the vegetative system: neurological, mental, endocrine (diseases of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, etc.). Failure of nervous regulation is sometimes caused by severe infections (for example, influenza), traumatic brain injuries and other diseases that lead to depletion of the body.
Case from practice
Approximately 2-3 times a week similar episodes occur at my appointment, I would like to give one of them as an example.
A 31-year-old woman came for consultation. Complains of attacks of sudden palpitations, shortness of breath, increased blood pressure to 135/80, periodic tinnitus, dizziness, sleep disturbance, anxiety. She noted a pre-fainting state twice. The work involves constant communication by phone (operator of a government agency hotline), and frequent conflicts arise with management. Attacks occur regularly throughout the year due to emotional distress. Comprehensively examined. During an examination by a fellow therapist, he recorded an increase in blood pressure (130/80 mm Hg) and made a preliminary diagnosis of “Hypertension, stage 1.” According to instrumental examinations, there is a slight spasm of the vertebral artery on the right, the venous outflow is impaired. According to the results of ultrasound of the retroperitoneal organs, no pathologies were identified. She was examined by a gynecologist and pregnancy was ruled out.
During a neurological examination: the patient is asthenized, fixed on her own sensations. There is no pathology of the cranial nerves. Reflexes are symmetrical, lively, no pathological. Sensory and motor areas are not impaired. She is stable in the Romberg position and performs coordination tests well. Extremities feel cold to the touch. Increased sweating.
Diagnosis: “Somatoform autonomic dysfunction, hypertensive type.” Taking into account that the symptoms and treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia in women are necessarily emotionally charged, I recommended: normalizing the daily routine, regular exercise, daily warm baths with aromatic lavender oils, and a course of massage. Among the medications, the drug “Afobazol” was prescribed, 1 tablet 2 times a day for a month, followed by a second consultation at the end of the course or in the event of an exacerbation of the condition.
The patient came for follow-up a month and a half later. The condition improved noticeably; after emotional experiences, signs of VSD stopped appearing.
This example shows well how important it is to find the cause of discomfort in time and eliminate it correctly. Symptoms and treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia in women have their own specifics due to the bright emotional coloring. Give the young lady a chance to relax and get some rest - success will not be long in coming. Men should remember this.
Men are less likely to present with complaints characteristic of vegetative-vascular dystonia. I attribute this to the fact that they are more resilient to stress. However, with overwork, prolonged intellectual overstrain, they also experience vegetative breakdowns. More often, the symptom complex debuts in males after 40 years of age, which is associated with incipient changes in hormonal levels, drinking alcohol, smoking, and spending a lot of time in front of the computer.
Signs of VSD in men are no different from those in women; the severity of the manifestations depends only on the degree of lability of the patient’s nervous system and his susceptibility to stressful situations. During a neurological examination, I often note the following symptoms:
- erectile disfunction,
- visual impairment,
- pain in the heart area (cardialgia).
All symptoms of exacerbation
Symptoms of exacerbation of VSD are practically not dangerous, but they significantly worsen the quality of life and cause a lot of trouble. The main and most striking symptoms of exacerbation of vegetative-vascular dystonia are:
- Difficulty breathing;
- Pain in the heart area;
- Drowsiness and weakness;
- Dizziness;
- Chills;
- Disruption of the digestive system;
- Blurred consciousness.
Symptoms of VSD in the acute stage can manifest themselves in different ways. In total, experts counted more than 150 symptoms of exacerbation.
There are three types of exacerbations:
- Vagoinsular;
- Sympathoadrenaline;
- Mixed.
These types differ among themselves in severity and in how long the exacerbation of VSD lasts. There are three degrees of severity of the crisis:
- Mild crises. They last no more than half an hour, and in most cases only a few minutes. The symptoms are pronounced.
- Moderate crisis. The duration of such crises ranges from 30 to 70 minutes. The symptoms are also pronounced and subside only a day after the crisis subsides.
- Severe crises. Such crises last more than one hour and are accompanied by severe symptoms and convulsions. After the crisis subsides, an asthenic syndrome occurs, the duration of which can be several days.
Worth seeing: Symptoms of VSD in men
Each of these types of exacerbations is characterized by a specific set of symptoms and clinical manifestations. However, the causes of exacerbations are the same in almost all cases:
- Infectious diseases;
- Acute or chronic stress;
- External harmful effects (intoxication, radiation, high air temperature, wave exposure to microwaves, poor ventilation, etc.);
- Physical fatigue;
- Bad habits (smoking, alcoholism, excessive coffee consumption);
- Chemical or food poisoning.
In most cases, the type of exacerbation that occurs and the degree of its severity depend on the degree of exposure to these factors.
When are other medications prescribed?
Depending on what caused neurocircular dystonia, treatment will be carried out in several directions.
Treatment of VSD in adults can take into account the inability to change jobs, increased conditions of nervous tension, the inability to completely relax and return to work with the help of physical exercises and psychological practices.
Drugs for the treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia in this situation will be aimed primarily at stabilizing the patient’s mental state, eliminating neurosis, normalizing sleep, concentration and the will to live.
Depending on the individual doctor’s recommendations, a course may be prescribed:
- Antidepressants.
- Neuroleptics.
- Tranquilizers.
- Sedatives.
- Sleeping pills.
- Nootropics.
- Adaptogens.
The use of these drugs must be agreed upon with a specialist! The course of their administration is always limited and, as a rule, does not exceed one and a half to two weeks. Getting rid of panic attacks with the help of antidepressants can quickly become addictive; getting rid of insomnia by taking sleeping pills does not allow the body to truly rest and relax, even if you manage to fall asleep for the required number of hours.
Case from practice
Approximately 2-3 times a week similar episodes occur at my appointment, I would like to give one of them as an example.
A 31-year-old woman came for consultation. Complains of attacks of sudden palpitations, shortness of breath, increased blood pressure to 135/80, periodic tinnitus, dizziness, sleep disturbance, anxiety. She noted a pre-fainting state twice. The work involves constant communication by phone (operator of a government agency hotline), and frequent conflicts arise with management.
Attacks occur regularly throughout the year due to emotional distress. Comprehensively examined. During an examination by a fellow therapist, he recorded an increase in blood pressure (130/80 mm Hg) and made a preliminary diagnosis of “Hypertension, stage 1.” According to instrumental examinations, there is a slight spasm of the vertebral artery on the right, the venous outflow is impaired. According to the results of ultrasound of the retroperitoneal organs, no pathologies were identified. She was examined by a gynecologist and pregnancy was ruled out.
During a neurological examination: the patient is asthenized, fixed on her own sensations. There is no pathology of the cranial nerves. Reflexes are symmetrical, lively, no pathological. Sensory and motor areas are not impaired. She is stable in the Romberg position and performs coordination tests well. Extremities feel cold to the touch. Increased sweating.
Diagnosis: “Somatoform autonomic dysfunction, hypertensive type.” Taking into account that the symptoms and treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia in women are necessarily emotionally charged, I recommended: normalizing the daily routine, regular exercise, daily warm baths with aromatic lavender oils, and a course of massage.
The patient came for follow-up a month and a half later. The condition improved noticeably; after emotional experiences, signs of VSD stopped appearing.
This example shows well how important it is to find the cause of discomfort in time and eliminate it correctly. Symptoms and treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia in women have their own specifics due to the bright emotional coloring. Give the young lady a chance to relax and get some rest - success will not be long in coming. Men should remember this.
Diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia
Treatment of neurocircular dystonia often borders on other similar dysfunctions. The human autonomic nervous system is a complex and multifaceted mechanism. In order to completely get rid of the problem, you need to find out exactly its cause. An ECG, a series of tests and consultation with a neurologist, cardiologist, endocrinologist, psychotherapist (depending on the characteristics of the disease) are extremely necessary.
If the doctor diagnoses astheno-vegetative syndrome, treatment will be aimed at eliminating chronic weakness, dull headaches and prolonged insomnia, apathy, hypotension and fainting.
Treatment of astheno-neurotic syndrome is primarily aimed at stabilizing the patient’s mental state using psychotherapy, sedatives, and in especially severe cases, antidepressants.
Medical consultation is necessary in each specific case: how VSD is treated in a given patient depends on the correct diagnosis - it will determine whether the original cause of the problem is really being treated (be it a protracted illness, psychotrauma or pathology), or whether life-saving remedies only temporarily block the consequences .
Who has recovered from VSD?
Yes, getting rid of a set of symptoms can take time - from several weeks to several months, sometimes up to several years in case of recurrence of crisis situations and a return to an unhealthy lifestyle.
Nevertheless, dystonia is treatable. There are enough of those who have cured VSD and managed to overcome even a hereditary predisposition. On the Internet you can find more than one forum that brings together in communication and exchange of experience those who suffered from vegetative crises, but were not afraid to take the necessary measures.
Due to the fact that, hiding under its masks, VSD can simulate the symptoms of various serious diseases, only a doctor can diagnose dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, excluding the presence of other pathology.
First of all, the vegetologist excludes damage to the central nervous system - the brain and spinal cord. In addition to a routine neurological examination, complex diagnostic methods such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging may be required for this purpose. In some cases, the similarity of some symptoms of VSD with signs of heart disease and endocrine ailments explains the need to register an electrocardiogram and take blood tests.
Treatment
If during examination a patient is diagnosed with somatic diseases, they are treated first. Often, successful treatment of the disease that provoked VSD eliminates the autonomic imbalance itself. To quickly eliminate unpleasant symptoms, medications are prescribed that relieve the manifestations of NCD.
But if, during diagnosis, no physiological diseases or serious disorders were found in the patient, the essence of vegetative-vascular dystonia clearly has a psychogenic cause. In this case, the main treatment is psychotherapy.
Treatment methods for VSD
Let's consider what methods are used to eliminate vegetative crises.
Drug therapy
It is important to remember that there is no direct or super-effective cure for VSD, which means that all pills will be aimed at alleviating the general condition and eliminating the consequences, but not the causes. Remember that any drug must be prescribed by a doctor!
To relieve the symptoms of dystonia, the following may be prescribed:
- Sedative (calming) drugs on a plant basis, less often on a synthetic basis.
- Sleeping pills (if you have chronic insomnia).
- Tranquilizers to reduce anxiety, restlessness, and nervous excitability.
- Nootropic medications to improve blood circulation and cognitive functions.
- Neuroleptics to suppress excitatory processes in the brain (in especially severe cases).
- Vitamins that compensate for the lack of substances observed in neuroses (B vitamins, potassium, magnesium, omega acids, iodine).
Physiotherapy
This type of treatment also does not get rid of the essence of vegetative-vascular dystonia, but it perfectly eliminates excess tension in the body, improves organ function and general condition.
Very useful for VSD:
- Massage.
- Manual therapy.
- Acupuncture.
- Sharko's shower.
- Therapeutic baths.
- Cold and hot shower.
This is also interesting:
Treatment of neuroses and VSD with Adaptol
Psychotherapy
Often, it is this type of treatment that allows a person to get rid of the essence of his problem, to eliminate precisely the root of the autonomic failure. First of all, the patient will learn to look at the emerging symptoms without fear and fear for his life, especially if he suffers from panic attacks.
During psychotherapy sessions, a person manages to discover internal conflicts, unconscious problems, unresolved tasks, fears and other negative processes that, being in the subconscious, destroy the nervous system.
A specialist can also teach a neurotic person to react differently to attacks, stressful situations and to look at the world with different eyes.
When treating neuroses in psychotherapy, very effective methods are:
- Cognitive behavioral therapy.
- Hypnotherapy.
- Gestalt therapy.
Sessions with a qualified psychologist will not only enhance the effectiveness of drug treatment (if prescribed), but will also eliminate most of the true causes of VSD, which are the essence of the disorder.
On a note!
Preventing the progression of VSD is not difficult. Patients note an improvement in their well-being and a decrease in the number of attacks not after taking medications, but after they begin to lead a healthy lifestyle. This can be achieved if you choose sufficient physical activity, a balanced diet, and learn to adequately perceive and respond to stressful situations.
Vegetovascular dystonia and prognosis
For everyone who has been diagnosed with VSD by a doctor, it is important to change their usual life to a new, healthy one, patiently and systematically. It is most convenient to approach complex therapy step by step.
1. Set a daily routine. The habit of getting enough sleep should become the same daily ritual as brushing your teeth and washing your face in the morning. The normal duration of sleep for someone who suffers from vegetative vascular dystonia is at least 9 hours. Chronic lack of sleep is a direct road to disruption of the endocrine system and the appearance of deep nervous disorders.
2. Develop a balanced work and rest schedule. Overfatigue from mental stress can be easily relieved by physical exercise and vice versa. But it’s better to give up the habit of working late at the computer without doing eye exercises: this threatens not only with worsening the symptoms of VSD, but also with a serious deterioration in vision.
3. Choose the appropriate type of physical activity. Regardless of the cause of VSD, it is vitally important to make time for exercise. Ideal options for those who suffer from vascular problems are swimming, water aerobics, race walking, skiing, country walks, and hiking. These sports train the heart, equalize blood pressure and naturally strengthen blood vessels.
4. Start to take stress lightly. As we know, there are no unsolvable problems: usually, calmly thinking about a strategy for solving an actual problem has a much more positive effect on a person than emotional “wounding up” and falling into apathy with the cessation of all activities.
5. Contact a psychotherapist and tell him about your health problems. The doctor will tell you how to avoid emotional overload, how to cope with psychological barriers and “blocks,” how to normalize relationships with loved ones and respond competently to stressful situations.
6. Engage in targeted treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia. Sanatoriums and resorts, medications and physiotherapy, herbal medicine and acupuncture - all these methods help remove the physical manifestations of VSD and prevent their relapses after the sick person has changed his life and really wants to finally cope with the disease.
The prognosis for treatment of VSD is extremely favorable, provided that the person strictly follows the doctor’s recommendations and wisely changes his lifestyle to regain health.
It would seem that if VSD is not a disease, then there is no need to treat it. However, in some cases, in the absence of control, the course of VSD can become more severe, vegetative crises occur more often, characterized by the sudden appearance of vegetative disorders against the background of complete health. In addition, the decrease in the number of patients with VSD is due to the progression of autonomic dysfunction and the development of cardiovascular diseases: hypertension, vascular pathology of the brain, etc.
Non-drug methods play a major role in the treatment of VSD. Medicines are usually used for severe autonomic dysfunction.
First of all, it is recommended to limit and, if possible, eliminate the impact of provoking factors (psycho-emotional stress, harmful working conditions, excessive physical and mental stress), to sanitize foci of chronic infection, usually the oral cavity, tonsils; compensate for chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine system, etc. It is important to give up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol).
Seemingly banal recommendations for maintaining a daily routine become of great importance. Insufficient restless, shallow sleep causes great damage to the stability of nervous processes and contributes to the exacerbation of symptoms of VSD. Mental stress should alternate with physical stress. Sleep duration should be at least 8 hours.
The room for sleeping should be ventilated, the air temperature should not exceed 18-20 degrees, since cool air makes breathing rarer and deeper, which contributes to sufficient oxygen supply to the body and proper rest during sleep. It is recommended to limit the time spent watching TV shows and working on the computer to 2 hours a day; if this is not possible, it is necessary to take breaks from work every 45-60 minutes.
It is advisable to conduct gymnastics sessions during the day, allowing you to warm up, relieve tension, and give rest to your muscles, eyes, and central nervous system. Relaxation exercises are useful for VSD.
Sometimes the help of a psychotherapist and psychotherapeutic correction with the prescription of sedatives, hypnotics, and antidepressants is required.
Moderate, gradually increasing physical activity helps restore balance in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, normalize vascular tone, and enrich tissues with oxygen. Aerobic loads have this effect: walking, dosed by distance, time and angle of elevation - health path;
In case of moderate VSD, sanatorium-resort treatment is recommended at the rehabilitation stage. The main therapeutic factors of sanatorium treatment are climatotherapy, mineral waters, balneotherapy (the nature of the baths: pine, pearl, radon, carbon dioxide, etc. - is determined by the most pronounced symptoms of VSD), circular and fan showers, sea bathing, massage, reflexology, physiotherapy ( electrophoresis, electrosleep, aeroionotherapy), exercise therapy and breathing exercises.
A diet that is complete and balanced in protein, fat, carbohydrates, and calories, enriched with vitamins, calcium, and magnesium is included in the complex treatment of VSD.
Medicines for VSD are prescribed by a doctor. However, in a number of situations, the use of herbal medicines and agents that are classified as so-called adaptogens is permitted - substances that increase the adaptive abilities of the body. For stabbing pains and discomfort in the heart area, soothing herbs and herbs help (during breastfeeding, you can take any medications, including herbal ones, only with the permission of the attending physician, since the medications pass into the milk and affect the baby). In agreement with the doctor, you can use CORVALOL, VALOCORDIN drops containing valerian, motherwort, and dissolve VALIDOL containing menthol.
Numerous symptoms of VSD, as a rule, do not pose a danger, although subjectively they can be very difficult to tolerate. However, given the harmlessness of VSD in relation to the development of serious diseases and complications of heredity, the “many-faced” imbalance in the work of the autonomic nervous system should not be allowed to get out of control, leaving without attention the factors that provoke the development and progression of symptoms of autonomic dysfunction.
Therefore, if you are concerned about symptoms that can be attributed to manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia, do not dismiss them as frivolous, consult a doctor, because often normalizing your daily routine and other restorative procedures can help now and serve as the prevention of serious diseases in the future.
Herbal medicine will help you
hypotension
(low blood pressure, accompanied by weakness, lethargy, increased fatigue, etc.) courses of stimulating adaptogens help: ginseng, eleutherococcus, Schisandra chinensis 20-25 drops 2-3 times a day, zamanikha, Manchurian aralia 30 drops 2 once a day. Course duration is 3-4 weeks. Treatment is carried out 4-5 times a year, always in the spring and autumn, as well as after epidemics of ARVI and influenza.
Yulia Lukina, General Practitioner, Moscow
When a child or teenager is diagnosed with vegetative-vascular dystonia, treatment, medications and the course of their administration must be strictly agreed with the doctor. Usually a balanced diet, a healthy daily routine and physical activity are recommended, and in addition to them, herbal infusions and phytoelements that help normalize sleep, stabilize heart rate and vascular tone.
The use of more serious measures is not recommended due to the incomplete formation of the young body, hormonal changes and the risk of further disrupting the fragile balance of the patient’s autonomic functions.
As soon as a person begins to be bothered by changes in pressure, a drop in performance, or headaches due to VSD, it is important to start treatment at the stage of the first signs in order to prevent the condition from worsening. The larger the complex of symptoms manifests itself, the more acutely each of them is felt and the more severe the crisis.
Prevention of the disease in the early stages can relatively quickly return a person to a healthy and harmonious life. Sleep disturbances, inability to exercise (the appearance of shortness of breath and weakness after activities that previously did not cause such consequences), a general feeling of anxiety and restlessness, growing day by day, are important bells that you should listen to and take action.
Hereditary predisposition. If either parent suffers from VSD, there is a high chance that the child will inherit the disorder.
Temporary hormonal imbalances or diseases of the endocrine system. Hormones take part in regulating the functions of the nervous system, and any changes in hormonal balance can lead to VSD. This explains why vegetative-vascular dystonia often debuts during puberty, during pregnancy or after childbirth, during menopause - natural hormonal changes provoke this disorder.
Prevention
If a person once developed vegetative-vascular dystonia, regardless of the essence, it means that his nervous system has weaknesses. To prevent a relapse, experts recommend following preventive measures:
- Avoid stress if possible.
- Incorporate any kind of sports into your life on a regular basis. Particularly effective for neuroses are: yoga, swimming, qigong gymnastics, Pilates, and light running.
- Switch to a proper, balanced diet.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Be outdoors more often.
- Do your favorite things and hobbies.
- Limit the flow of destructive information (news, yellow press, gossip).
- Master relaxation methods (meditation, auto-training).
- Balance your work and rest schedule.
- Work independently on your psycho-emotional state.
Nootropics - vitamins for the brain, necessary for VSD
What are the alternatives to traditional treatment?
Anyone who has gone through a crisis of chronic pain and panic attacks and managed to cope with them will tell a unique story. For some, monastery teas, herbal infusions from great-grandmother’s recipes and therapeutic relaxing massages become salvation. Others admit that auto-training, affirmative techniques and psychoanalysis solved the physical problem through positive thinking.
As an alternative, the network often offers treatment for VSD with hypnosis, psychoprogramming and courses of physical practices in the conditions of sanatorium-resort prevention.
Brief conclusion
- It should be remembered that the manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia are so diverse that they can be mistaken for diseases of organs and systems and undergo treatment for a long time without effect.
- The diagnosis is made based on examination and examination by a doctor.
- Prevention of VSD is effective if carried out regularly.
- Deterioration of the condition is provoked by stressful situations, pregnancy, menopause.
- Treatment should only be carried out under medical supervision.
Since it is impossible to accurately establish the boundaries of VSD and say which symptoms and processes are characteristic of it and which are not, there is no consensus on whether such a disease exists or not. Considering that VSD is not associated with pathological processes in organs, the main therapy is aimed at normalizing the functioning of the nervous system and psyche and correcting lifestyle.
Asthenic syndrome
When an attack of VSD occurs, asthenic syndrome almost always occurs. Asthenia is characterized by a whole complex of psychological abnormalities:
- Emotional instability;
- Irritability;
- Photosensitivity;
- Increased fatigue;
- Apathy.
The duration of asthenia can reach several days, but most often ends within a day after corrective measures are taken. In the absence of timely treatment, asthenia can lead to more dangerous consequences, including serious mental disorders.
Irritability is one of the symptoms of asthenic syndrome
This feature of VSD is noted - each time there are new symptoms and the degree of their severity. That is why it is necessary to always be prepared and have on hand means of effective treatment of VSD.
Worth seeing: Insomnia with VSD
Psychotherapy
In order to know how to cure VSD in a patient, the doctor is obliged to refer him, among other things, for help to a psychologist (psychotherapist, psychiatrist - depending on the severity of the case).
The vegetative state of the human nervous system is influenced both by changes in the functioning of the central nervous system (responsible for the conscious control of all physical and psychological processes) and directly by the internal organs. This means that it is under a “double blow” and it is impossible to “fix the breakdown” on one side while neglecting the other.
Exacerbation of VSD in winter
In winter, VSD, as a psycho-emotional disease, ideally correlates with the general atmosphere and environment. When it gets dark early and blooms late, and the whole day flies by in almost a couple of hours, patients with dystonia experience additional exhaustion of the nervous system. During this period, they develop a feeling of melancholy, hopelessness and uselessness of existence. Apathy and constant thoughts of suicide lead to the patient losing his sense of reality. He ceases to understand others, time, simple sentences. Everything around him becomes one big gray blur.
How to use psychology for recovery?
In practice, this means that VSD is treated in half with physiological (including medication) help and psychotherapy. Very often, the patient himself can name the period from which the deterioration of his condition began, prompting him to see a doctor. As a rule, this is the appearance in life of a series of strong stress factors, conflicts in the family or at work, the presence of unsolved problems, the fear of not being able to cope with which unconsciously undermined the body from the inside, fixating on the same problem.
Fear and a feeling of helplessness in front of an unsolved task, which holds the body and all life support systems in the background, lead to the development of clinical neurosis.
Why does neurosis affect autonomic dysfunction?
The state of stress does not only keep the brain tense. Any psychological state, be it anxiety, restlessness, emotional high or low, despondency or fear, is associated with a change in the functioning of internal organs, contraction and relaxation of the smooth muscles of the heart, stomach, vascular walls, etc.
That is why significant changes in the psychological state cause the heart to contract more often, blood vessels to narrow and dilate, strain the muscles of the musculoskeletal system, and metabolism to speed up or slow down.
If the situation develops negatively, the result is acquired astheno-neurotic syndrome, the treatment of which is also included in the list of tasks of a doctor helping a patient with dystonia. Thus, treatment of dizziness with VSD can be carried out on a psychologist’s couch - with the help of a verbal analysis of the situation that forced the body to “drive” itself to a similar state.
The functions of all our internal organs are under the control of a special department of the central nervous system - the autonomic (or autonomic) nervous system. This is the main conductor, regulating the functioning of all organs and systems and ensuring the normal functioning of the human body in various situations.
We don’t have to think that during physical activity, in order to provide the working muscles with oxygen and nutrients, we need to breathe more often, and the heart needs to contract faster and stronger; we don’t worry about the composition of digestive juices depending on what we ate, and we don’t worry about how many and what enzymes and biologically active substances the liver should produce: the autonomic nervous system (ANS) does all this for us.
the sympathetic nervous system causes increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, spasm of blood vessels and muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, etc. Evolutionarily, such reactions of the body were necessary in stressful situations, for example during an attack, when it was necessary to fight or, conversely, run away from the enemy. Vasospasm prevented severe blood loss.
heartbeat, “jumps” in blood pressure, etc. The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for reducing the heart rate and increasing gastrointestinal motility. Parasympathetic nerves approach the respiratory tract and lungs, innervate the excretory and genital organs. The “main theme” of the parasympathetic division of the ANS “sounds” at night when a person is sleeping.
The work of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the ANS is in relative balance with the predominance of one of them. The imbalance of the tone of these departments - dystonia - is what determines the appearance of the term - VSD. With VSD, no structural changes occur in the parts of the ANS, but the delicate balance that ensures the coordinated functioning of all body systems is disrupted.
Symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia
There are a great many of them in VSD. See:
- heartache,
- pressure surges,
- heart rhythm disturbances,
- heartbeat,
- dyspnea,
- lack of air,
- labored breathing,
- dizziness,
- nausea,
- vomit,
- diarrhea,
- stomach ache,
- bloating,
- frequent urination,
- sweating,
- hand trembling,
- redness of the skin, etc.
Moreover, some of these symptoms are constantly present, while others experience them periodically.
If a person is vagotonic, i.e. if PNS tone predominates, gastrointestinal and respiratory symptoms come to the fore.
If the tone of the SNS predominates, he will be more often disturbed by matters of the heart.
And some people have so-called panic attacks - a subjectively very serious condition when a person experiences a panicky fear of death, accompanied by palpitations and suffocation.
Maybe some of you have had a low-grade fever for a long time. At the same time, blood tests, urine tests, etc. were normal, ENT and other specialists also found nothing of their own. Most likely, vegetation was also involved here.
Drug treatment
In addition to regulating the daily routine, analyzing the human psychosphere and basic physiological exercises to stabilize the patient’s harmonious state, drug intervention is also possible. However, this is one of the few cases where homeopathic remedies are more acceptable than pharmacological ones.
There are several reasons. Firstly, the patient’s firm intention to take control of the situation and get out of depressive, self-depressing states is much more important than direct physical impact. Secondly, self-medication is strictly not recommended. Because the symptoms of VSD are multifaceted and complex, chemical exposure to one organ system can negatively affect the functioning of another.
Is surgery possible?
The case of each patient must be considered strictly individually. For example, one of the rare hereditary manifestations of disorders in the nervous system is torsion dystonia. Treatment is carried out not only with the use of vitamin complexes and tranquilizers, but also with the help of orthopedic operations.
But, as a rule, with a methodical approach, psychotherapy, a cycle of physical procedures and light pharmacological adjustments are enough to get rid of dystonia of any type.
- Fear of death is a problem