Most people complain about a problem such as constant noise in their heads, which causes a lot of inconvenience. Whatever the sounds are - sharp, muffled or loud - there is a reason to think about why all this is happening, especially if the symptoms gradually worsen and prevent you from leading a normal lifestyle. Therefore, patients become interested in the question of how to get rid of noise in the head in order to eliminate discomfort.
Classification of pathological condition
If the patient constantly hears or feels extraneous sounds, the causes of noise can be quite serious.
In medicine, there are several types of pathology:
- Subjective.
- Objective.
The last category is noise in the ears and head, which can be recognized by the attending physician using the appropriate technique to diagnose the disease. It is impossible to determine subjective sounds from the outside, since they are felt only by the patient. Doctors gave this phenomenon a name such as “tinnitus,” which means ringing.
If the patient is constantly and quite often bothered by increased noise that radiates into the ears, it is necessary to urgently consult a specialist and undergo a comprehensive examination. This will eliminate the presence of a serious disease or, conversely, identify it in a timely manner to prescribe adequate therapy.
Symptoms of psychogenic noise in the head and ears
Neurotic tinnitus can manifest itself with sounds such as:
- ringing;
- rumbling;
- whistling;
- buzz;
- splashes;
- roar;
- hiss;
- chirping, etc.
The following unpleasant sensations also occur:
- beating, pulsation in the ear;
- hearing loss due to the fact that some sounds fall out, while others, on the contrary, become too loud.
Quite often, neurotic patients complain that the ear is blocked, but does not hurt, but is noisy. It was as if water had gotten into it. And now there is constant congestion and noise, without pain.
Often, extraneous noise in the ears is accompanied by psychogenic dizziness.
All these symptoms can bother a neurotic almost constantly or occur only occasionally. Sometimes their occurrence can be timed to coincide with some stressful event, and sometimes they can appear out of nowhere.
The noise can occur in one ear or in both ears at once.
The intensity of symptoms can vary in the same person, even within one day, from extremely severe to barely perceptible.
Many neurotic patients complain that tinnitus becomes much stronger when resting. Especially before bed. Sometimes at night in bed it is so strong that it does not allow you to sleep.
Origin of the pathological condition
The main causes of noise in the head are damage to the hearing organs due to the negative influence of external sounds (30% of cases).
Other possible provoking factors include:
- chronic or acute stage of hearing loss;
- changes in hearing level with age;
- Meniere's disease;
- inflammation of the auditory nerve;
- brain injury, head injury with or without damage to the temporal lobe, can also cause noise;
- nerve intoxication with diuretics, antibiotics, quinine, salicylates or antitumor medications;
- chronic inflammatory process of the middle ear.
Timely identification of the origin of the pathology is the key to successful therapy. To do this, the patient must undergo examination by an otolaryngologist and other specialists, since severe noise in the head may hide serious illnesses.
Subjective pathology can manifest itself in different ways. Most patients complain of suddenly appearing or constantly present extraneous sounds that they can hear at night or in a quiet room, but which do not cause concern. For other patients, hissing prevents them from leading a normal life, so treatment may be required.
The causes of noise in the head may also lie in the presence of certain diseases:
- hypertension or hypotension;
- osteochondrosis and various pathologies of the spine;
- diabetes, atherosclerosis;
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- meningitis, otitis and sinusitis;
- iron deficiency, hepatitis;
- diseases of the heart and vascular system;
- schizophrenia and brain tumors, sclerosis.
The causes and treatment of the disease are inextricably linked, because only after establishing the origin of extraneous sounds can adequate therapy be prescribed aimed at eliminating the provoking factor.
Treatment
You can only get rid of discomfort with the help of therapy aimed at treating the underlying disease. Courses of medications and physical procedures are prescribed only after a comprehensive examination and accurate diagnosis. But general recommendations in the absence of a serious illness will help relieve or at least reduce pain.
- Those who like to listen to music loudly need to get rid of this habit, otherwise they will soon have to use a hearing aid;
- Patients with seasickness are advised to travel by land or take anti-motion sickness tablets before travelling;
- People working in noisy industries should use earplugs or change their professional activity;
- Self-massage and relaxation in a darkened room with pleasant, quiet music will reduce tension in the nervous system. This method is good for migraines and pain due to stress;
- Warm relaxing bath;
- Taking painkillers relieves occasional attacks.
If the cause of discomfort is osteochondrosis, then in this case an experienced massage therapist, drug treatment and physiotherapy will help.
Neurological diseases are treated using complex therapy. It usually includes vasodilators, anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as those that improve blood circulation and normalize blood pressure. Drugs such as Vinpocetine can be used in case of sudden changes in blood pressure after consulting a doctor.
Treatment of otitis media is aimed at relieving inflammation in the ear. Otitis externa can be treated at home with warm, dry compresses and anti-inflammatory medications. Internal otitis is more difficult to treat; it is worth visiting an otolaryngologist to prescribe therapy. Antibiotics and physiotherapy are usually used.
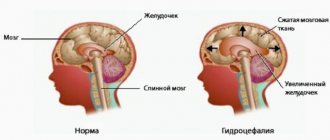
Brain tumors are treated with surgery. Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are used to diagnose the disease. It is important not to skip the initial stage in order to reduce the risk of surgery and its consequences.
If the noise and pain are caused by an insect entering the ear or due to injury, then you should consult a doctor. Self-treatment can only worsen the situation.
Diagnosis of the pathological condition
When a patient complains of noises in the head, the doctor examines the medical history, draws up an anamnesis and sends for a comprehensive examination. To begin with, the specialist rules out damage or damage to the hearing organs and brain. For diagnostic purposes the following are prescribed:
- Testing urine and blood.
- MRI and CT scans make it possible to detect inflammation in the structure of the brain. The results obtained allow us to make an accurate diagnosis (the accuracy of the study is 98%).
- Angiography of the arteries - determines pathological disorders of the veins, as well as atherosclerotic disease of the vascular membranes.
- Audiogram – establishes the acuity of the hearing aid, the speed at which impulses are transmitted from the inner ear to the brain.
In each specific case, an additional study may be prescribed, which will allow the specialist to draw up an accurate picture of the disease and eliminate the noise in the head with adequate treatment.
If the results of diagnostic and laboratory tests cannot determine why extraneous sounds are present, then the patient is recommended to be examined by a psychotherapist, since the cause of the disorder may lie in the patient's depression or state of mind.
If medicine cannot determine the causes of the pathology
There are cases that after a comprehensive diagnosis, the cause of the noise in the head has not been determined, then it is recommended to follow a few simple rules:
- try not to react to hissing;
- give up tobacco products, salt;
- do not drink strong coffee;
- use sedative medications to eliminate nervousness and irritability.
You can try to independently determine the cause of the discomfort. If you constantly have noise and ringing in your head, the patient is advised to cover his ears and listen carefully to himself: if the hissing has disappeared, then he needs to be treated with a hearing aid. Press your fingers on the cervical lateral artery, if the extraneous sounds disappear, then the problem lies in osteochondrosis.
If the noise stops after a long sleep, then it's all about overwork. But only the attending physician can determine exactly why noise and ringing in the head occurs, reasons and treatment, which are of interest to many patients.
Types of noise
In different cases there is noise in the head in different ways. This may be pulsating, knocking, ringing or squeaking, and sometimes people hear several voices at once. Depending on the nature of the sound, one or another disease can be identified. Noise in the head may appear permanently or temporarily. It happens on one side or in both ears at once. Noise can also be objective and subjective. The first group includes a sound that is heard by several people. Sometimes it’s a doctor with a stethoscope, sometimes it’s strangers. And sounds that are heard only by one person - the patient - are considered subjective.
How to get rid of pathology
You can cure noise in the head only by eliminating the cause of its occurrence. For osteochondrosis of the neck, excellent prevention is impact on the collar area, as well as therapeutic and preventive exercises, which involve all the muscles of the cervical spine.
It is recommended to independently develop the problem area daily:
- With all fingers, gently massage the area of the collar zone from the base to the skull, slightly pressing the pads on the muscles;
- perform movements in a circle;
- gradually move towards the head.
At the end of the procedure, the muscles will relax, blood circulation will be restored, and the noise will disappear (quite effective treatment).
If the patient is interested in how to treat the pathology on their own, it is recommended to consult a doctor who will tell you about a simple method of therapy:
- the patient should imagine that he has a thin stick between his teeth;
- using it you need to imaginatively draw various numbers.
Such exercises will help you do without intensive therapy and relax, restore the muscles of the collar area, and relieve fatigue after a long working day.
Drug treatment of a pathological condition
If there is noise in the head and at the same time there is swelling of a light yellow hue under the eyes, the iridescent contour of the eyes is bordered by a light gray thin arc, then the cause of the discomfort lies in atherosclerosis. A specialist will tell you what to do, but the main recommendation is the same - take drugs such as “Atheroblock”, “Vitrum Cardio Omega 3”.
The following medications will help eliminate noise in the head:
| Name of medicine | Characteristics, application, treatment |
| "Vinpocetine" ("Cavinton") | Used for chronic, acute stages of cerebrovascular accident. With prolonged use of the medicine (tablets), blood circulation and metabolism are restored, and blood pressure decreases slightly. For intensive therapy, injections are used. The duration of treatment is 14 days. |
| "Piracetam" ("Nootropil", medicine "Lucetam") | A fairly effective remedy that allows you to restore blood circulation and improve memory.
Main contraindications:
The medicine can be used both in the form of capsules and tablets, a solution for intramuscular (intravenous) administration. |
| Multivitamin complex | Vitamins and multivitamins contribute to the rapid restoration of immunity and improve the general condition of the patient. For severe headaches and constant noise, vitamins B, E and element A are indicated: such elements reduce nervous tension and strengthen the nervous system. |
| The drug "Vazobral" |
|
If extraneous noises or sounds appear with increased pressure, it is necessary to take medications that lower vascular tone. Discomfort can be caused by excessive accumulation of wax in the ears - it is recommended to consult a specialist to clear the ear canal of wax plugs. Most medications can also cause pathology.
Whistling in the ears and head - treatment
The causes of the ringing in the head are clear, but there is no treatment yet. Treatment for this condition will depend on the specific illness that caused the whistling in the head. In addition to treating the underlying disease, the doctor will prescribe medications to normalize cerebral circulation. A course is often carried out using nootropic medications and antihistamines.
Physiotherapy also plays an important role. It is based on the following procedures:
- laser treatment;
- the use of electrophoresis;
- air massage in the area of the eardrum.
Treatment of noise in the head with cervical osteochondrosis involves physical exercise. In addition, you will probably have to take chondroprotectors.
For atherosclerosis, it is recommended to normalize the level of cholesterol in the blood and strengthen the blood vessels of the brain. For these purposes, the following medications are prescribed:
- Calcium antagonists help strengthen blood vessels, make them more flexible and improve metabolism in the body.
- Herbal preparations, such as Ginkgo biloba, which can improve the nutrition of gray cells, accelerate blood microcirculation, and prevent platelet aggregation.
- Nicotinoids dilate blood vessels and have a general strengthening effect.
Determining the causes and treating whistling in the ears and head is important for a person’s future life, because the phenomenon not only worsens the quality of life, but is also fraught with its consequences.
Ear whistling is not an independent disease, it is only a symptom of some pathology. The following tips will help as auxiliary methods in treatment:
- Reduce salt intake in your diet.
- Lemon juice diluted with water is beneficial.
- Food must contain sufficient amounts of iodine.
What will the ancient sages say?
Traditional medicine offers effective treatment for noise in the head. Among the most popular recipes are the simplest ones - horseradish root, garlic, milk and iodine, as well as strawberry aromatic tea.
| Recipe name | Method of preparation, use |
| Medicinal tincture with horseradish |
|
| Iodine 5% tincture | Dilute with warm milk, starting with a few drops. For the first 10 days, add 1 drop, then gradually reduce. The duration of therapy is 20 days, after two weeks the treatment is repeated. For effectiveness, it is recommended to take three courses. |
| Garlic tincture (effective treatment) | Root vegetable – 200 gr. grind until a paste forms, add alcohol or vodka (250 ml), place in a glass container. Leave for 14 days, filter, add a few tablespoons of natural propolis, honey, mix well. Leave for a few more days. Take during noise three times a day on an empty stomach with milk. The first day - 1 drop, the second - 2 drops, to gradually increase to 25 drops. |
| Medicinal herbal decoction | Tea from aromatic strawberry inflorescences, infuse and take instead of other drinks. An excellent anti-noise product. |
| Hirudotherapy is an excellent remedy for extraneous sounds in the head and ears. |
|
Extraneous noises and sounds prevent a person from leading a normal life. The main task of the doctor is to determine the cause of such disorders and eliminate it; this is the only way to get rid of discomfort and avoid radical treatment.
Methods for preventing pathological conditions
If a patient is bothered by constant noise or sounds in his head, he can find out how to get rid of them from his attending physician. But you can prevent the symptoms of the disease by following a few simple rules:
- Preventive measures against noise - everyone should undergo examinations by a doctor, which will help to identify the disease in time and prevent its progression. All diseases in the initial stages are treated quickly and do not pose a threat to the patient.
- A proper lifestyle, proper rest, a balanced healthy diet, and long walks effectively support the body, prevent the development of diseases, and help avoid serious treatment.
- If you have a history of chronic pathologies, you need to undergo a long course of treatment, and by all means avoid possible complications or relapses of the disease.
Extraneous sounds and noises in the head are not a disease, but symptoms of some kind of inflammatory process, so it is better to take such discomfort seriously. Treatment of the pathological condition is carried out only after a comprehensive examination and consultation with a specialist. Timely consultation with a doctor is the key to successful noise therapy for the patient.
Causes
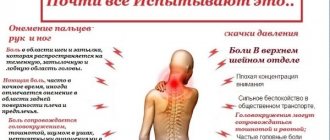
Most often, older people experience headaches and tinnitus at the same time. This is associated with age-related changes in hearing and diseases of the cardiovascular system. However, there is a whole list of diseases in which a person hears extraneous sounds and suffers from pain.
- Migraine is characterized by headaches on only one side. Before the attack itself, a so-called aura appears before your eyes, you hear ringing in your ears and feel dizzy. Women whose mothers also suffered from this disease are more susceptible to migraines.
- With otosclerosis, the mobility of the auditory ossicles is impaired, as a result of which hearing decreases and extraneous sounds occur.
- A brain tumor is characterized by increased intracranial pressure, impaired blood supply and vestibular apparatus. During the disease, the patient experiences a feeling of nausea and vomiting, which does not bring relief. After some time, mental changes become noticeable - aggressiveness, irritability. In severe cases, patients experience visual and auditory hallucinations.
- Meningitis affects the membranes of the brain. Intoxication of the body and increased intracranial pressure lead to headaches and tinnitus. At the same time, the noise is constant, the pain in the head is intense and prolonged. The patient experiences photophobia, vomiting, high fever, and neck muscle tension.
- Acute or chronic otitis media is inflammation of the middle ear. With this disease, the pain is intense, shooting. Localized in the temple and ear area.
- Sunstroke or heatstroke is often diagnosed in the warm season. It is characterized by dizziness, nausea, increasing headache, tinnitus, and often loss of consciousness.
- Hypoglycemia is a drop in blood sugar below the acceptable level. It develops against the background of concomitant diseases or during fasting.
- Traumatic brain injury is one of the common causes of headaches and tinnitus. For mild injuries, symptoms will go away on their own.
- During the initial stage of development of Meniere's disease, the pressure in the ear increases as the volume of endolymph in the labyrinth becomes larger.
- One type of stroke is subarachnoid hemorrhage. With this pathology, a vascular aneurysm or congenital vascular pathology (malformation) ruptures. At this moment, blood penetrates the meninges. The cause of rupture is most often a sharp jump in blood pressure. The pain occurs suddenly and is pronounced and intense. In addition to pain, tinnitus, nausea, vomiting, dizziness and loss of consciousness occur.
- Vascular insufficiency occurs against the background of atherosclerosis, hypertension, stroke, inflammatory processes and injuries. Discomfort often brings pain and noise on both sides. In addition, the patient may have weather dependence, deterioration of memory and sleep quality, and dizziness.
- Seasickness occurs when traveling by water or in the air. An attack is characterized by dizziness, nausea, and painful sensations in the head. Most often, people with vegetative-vascular dystonia suffer from seasickness.
- Acoustic trauma. When listening to music at high volume for a long time, being in a noisy workshop or similar exposure, tinnitus and headaches appear. Symptoms usually go away on their own within a short time.
- Pathology of the cervical spine. Most patients who come to a neurologist with complaints are diagnosed with cervical osteochondrosis.
Most diseases respond well to treatment if you consult a specialist in a timely manner. In some cases, you will have to resort to surgery.