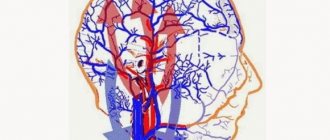
Diabetes mellitus (DM) types 1 and 2 occurs with the development of frequent complications from the kidneys, blood vessels, retina and nervous system. According to WHO, diabetic encephalopathy occupies the largest part (60%) in the structure of complications from the nervous system. The first mention of the connection between cognitive impairment and diabetes mellitus was found in 1922; the term “diabetic encephalopathy” itself was introduced in the 50s of the last century.
Course and diagnosis of the disease
Diabetic encephalopathy can be disguised as other illnesses.
If we talk about older people, these are disturbances in brain activity, and in young people these are the results of acute ketoacidotic attacks. The picture of the disease may include:
- asthenic syndrome (excessive fatigue, decreased performance, excessive anxiety, weakness, insomnia, problems with concentration);
- cephalgic syndrome (headache). It can be squeezing or squeezing. Quite often, pain can be described as a feeling of a heavy head after wearing a tight headdress;
- vegetative dystonia with the development of paroxysms, presyncope and loss of consciousness.
In addition to these signs, there are symptoms indicating various focal disorders. They can be upper trunk (signs of pyramidal insufficiency, anisocoria, convengeria disorder), as well as vestibulo-atactic syndrome (unsteadiness of gait, impaired coordination of movements, dizziness).
Quite telling symptoms in the picture of the course of encephalopathy against the background of diabetes mellitus are also impairments in cognitive functions:
- memory problems;
- slow thinking;
- apathy;
- depression.
Each of these symptoms indicates dysfunction of nonspecific midline structures in the brain. Depression can often occur with any type of diabetes. Approximately 32 percent of patients will suffer from it.
In addition to the negative impact on overall well-being, prolonged depression is dangerous due to the loss of control over the course of the disease, nutrition and the use of insulin.
The main reason for this tendency in patients is certain biochemical changes in the body, as well as constant dependence on the disease and the need to control it.
Some type 1 or type 2 diabetics may develop hypoglycemic encephalopathy as a result of hypoglycemia. It may manifest itself as follows:
- lethargy;
- apathy;
- disorders of consciousness such as delirium;
- adynamia after work or on an empty stomach.
Also characteristic are convulsive syndromes, as well as pyramidal hemiparesis.
To establish a correct diagnosis, in addition to asthenic and vegetative-dystonic complaints, it is also necessary to identify focal neurological symptoms.
Any changes in the electroencephalogram (EEC) in patients with encephalopathy due to diabetes mellitus are considered irregular. They are diffuse in nature, which is manifested by thickening of the EEG, hypersynchronization rhythms, reduction of general and local alpha rhythms, changes in the reactivity of EEG curves, as well as inclusions of pathological waves of delta and theta types.
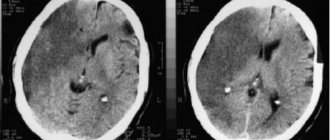
In elderly diabetics, diabetic encephalopathy is highly likely to be accompanied by focal neurological deficits, atrophy, and post-stroke changes in tissues. They can be detected by computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These concomitant pathologies are characteristic of diabetes and the problems associated with this disease: macroangiopathy, atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension.
Stroke, as well as transient ischemic attacks, can be considered from the point of view of the symptoms of central neuropathy.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of encephalopathy in diabetes mellitus is made after a comprehensive examination of the patient.
Laboratory and instrumental studies are carried out to rule out other brain diseases:
- Electroencephalography. Disorganization of the basic rhythms and signs of epileptic activity are recorded.
- MRI, CT. At the initial stage, changes are not detected. At subsequent stages, small focal diffuse changes are noted.
- Laboratory tests of urine and blood. Determine the level of glucose, cholesterol, insulin. With the disease, all indicators are increased.
It is also necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis of infections and brain tumors.
Signs of encephalopathy on CT
Main symptoms
The symptoms of diabetic encephalopathy are quite difficult to determine, since the disease develops slowly and without pronounced manifestations. In fact, any dystrophic changes can form and spread without any noticeable reflections for several years.
Some symptoms can be monitored, but they are usually attributed to another pathology. As an example of such manifestations, consider the following provisions:
- headache; fast fatiguability; dizziness; chronic malaise; short temper for unexplained reasons; panic state (in some situations the opposite is possible - apathy, complete loss of interest in current events); memory impairment; weakening of thinking abilities.
Obviously, such symptoms are not specific, nor can they always be mistaken for a manifestation of a specific disease. For this reason, many patients start the disease by ignoring mild signs and refusing to visit a doctor.
After this, the second stage begins, characterized by a deterioration in the general condition and the rapid development of the disease.
The third stage is diabetic encephalopathy with severe mental disorders: prolonged and deep depressive states, inappropriate actions bordering on manic syndrome.
Treatment of encephalopathy in diabetes mellitus involves maintaining constant and stable compensation for the pathology in question. In addition, the use of certain active courses is mandatory. Moreover, this applies not only to vasoactive, but also to other, more specific areas.
However, with any choice, established contraindications must be taken into account, and the treatment process itself must be carried out under the supervision of a competent specialist.
In general, the procedure takes from several months to several years. Depending on the current situation, a course is developed taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient: the state of the body, lifestyle, development of the disease.
In metabolic therapy, the following drugs are used in most cases:
- antioxidants – special agents alpha-lipoic acid; celebroprotectors – piracetam; mixed-use drugs – neuromultivit, miligamma; vitamins – groups B1, B6, B12, as well as A and C.
In addition, vasoactive therapy is widespread, which includes drugs such as piracetam, stugeron, nimdipine. In parallel with this procedure, an additional one is carried out, which is intended to correct lipid metabolism. It is carried out using statins.
If the disease has progressed to the final stages of development, and the patient’s condition has rapidly deteriorated, then there is a need for negative therapy - this is a type of treatment that is considered relevant for the serious consequences of diabetes of any form.
Once a diagnosis of diabetic encephalopathy is made, the entire course of treatment takes a fairly long period of time and covers many aspects of the recovery process of the entire organism.
Symptoms of diabetic encephalopathy
In diabetes mellitus, encephalopathy progresses slowly and gradually. Typically, at a young age with type 1 diabetes, it is preceded by episodes of acute decompensation of the disease (hypo- and hyperglycemic problems, coma). In older people, it may appear after acute circulatory disorders or ischemic attacks. But there may be no history of acute episodes.
Clinical symptoms at the onset of the disease are nonspecific. Patients complain of weakness, frequent headaches, fatigue and decreased ability to work, rapid loss of attention and inability to concentrate. Unfortunately, such symptoms do not make it possible to establish a diagnosis and are not criteria for encephalopathy.
Neurosis-like disorders are more common in young people. These are asthenic, phobic and hysteroid syndromes. With asthenia, patients experience decreased memory, attention, sleep and appetite disturbances. The most significant problem is sleep disorders. Patients have trouble falling asleep at night, are drowsy and distracted during the day. Such problems increase the decompensation of diabetes mellitus, because healthy sleep is important to maintain glycemia.
In obsessive-phobic disorder, obsessive anxious thoughts predominate. The patient expresses them to doctors and people around him or withdraws into himself. Typical phobias for patients with diabetes are fear of gangrene of the limb, hypoglycemic coma.
Hysterical disorders appear in people with a certain personality type. They tend to describe subjective clinical symptoms at length. At the same time, objective data will be quite scarce. Hysterical disorders make patients aggressive, prone to conflicts and defending (sometimes senselessly) their interests.
Depression, dementia, focal syndromes are typical for older people. Typical manifestations of encephalopathy after 75 years are unsteady gait, increased tone, speech problems, and sensory disturbances.
Severe mental disorders in diabetes occur quite rarely. Typically, severe dementia is the result of the influence of atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, and arterial hypertension. In this case, the patient loses the ability to speak, perform simple everyday activities, and care for himself.
Complications
Dementia develops as a result of diabetic encephalopathy. In some cases, Alzheimer's disease develops. Diabetes has been shown to increase the risk of dementia in ApoE4 carriers.
The second serious complication of encephalopathy is hearing loss or the development of sensorineural hearing loss. In a study of groups of healthy people and patients with diabetes, the diagnosis of hearing loss was made 4 times more often in the latter group. The development of hearing loss was influenced by the length of diabetes, taking oral medications or insulin therapy, and the presence of other complications of the disease.
Side effects and results of use
If you have type 2 diabetes, it is important to follow all doctor's orders. By following the instructions, you can use Actovegin effectively and safely
This drug does not cause unexpected dangerous reactions.
Treatment must take into account the level of sensitivity to medications. If there is an individual intolerance to certain substances that are the basis of the medicine, the doctor will not include this drug in the treatment regimen.
Medical practice knows cases when the use of the drug Actovegin caused:
- swelling,
- increase in body temperature,
- allergies,
- febrile state of a person.
In rare cases, Actovegin may reduce the activity of the cardiovascular system. This may include rapid breathing, high blood pressure, feeling unwell, or dizziness. In addition, there may be a headache or loss of consciousness. When administered orally, if the dosage is violated, nausea, vomiting and stomach pain may occur.
The drug Actovegin is an effective remedy in the fight against diabetes. This is confirmed by the widespread practice of its use. The effect of external use of the drug is expressed quite quickly, on average, after 15 days.
If, during the course of therapy, a person experiences pain in different areas of the body, and also experiences a deterioration in health, then it is necessary to consult with the attending physician as soon as possible. The patient will undergo tests that will show the reasons for the body’s reactions.
The medicine will be replaced with a drug that has similar medicinal characteristics.
Clinical symptoms
Manifestations of pathology may be different, depending on the etiology and type, but there are a number of symptoms that are necessarily present in the presence of a cerebrovascular disorder: intense headaches, frequent dizziness, memory disorders, disturbances of consciousness (apathy, persistent depression, desire to die), absent-mindedness and irritability, insomnia. Indifference to others, lack of interests, and difficulty in communication are also noted. Depending on the etiology, emotional disorders, dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting, stool disorders), jaundice, pain in the extremities, obvious weight loss up to cachexia, signs of metabolic disorders (rashes, changes in the skin, swelling) may also be observed.
Prevention and recommendations
Encephalopathy in diabetics is a progressive disease in a chronic form. The rate of development of complications in the disease is directly dependent on the course of diabetes mellitus.
Constantly visiting doctors, following recommendations for lowering blood sugar, neurological therapy - all this will help slow down the development of the disease, and possibly even stop its progression. The main principle of preventing encephalopathy is considered to be timely diagnosis and comprehensive treatment of diabetes mellitus and related manifestations.
The program “Let Them Talk” talked about diabetes
Why do pharmacies offer outdated and dangerous drugs, while hiding the truth about the new drug from people...
Why is diabetes considered incurable?
Diabetes always leads to fatal complications. High blood sugar is extremely dangerous.
Lyudmila Antonova gave explanations about the treatment of diabetes.
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
Useful video
In this video you will learn what the connection is between encephalopathy and retinopathy .
Diabetic encephalopathy – an incurable disease, characterized according to the international classification of diseases (ICD code 10) as E10.8-E14.8: diabetes mellitus with an unspecified complication.
The pathology is preventable if prescribed diabetes treatment is followed. Encephalopathy progresses slowly, and conservative treatment helps the patient lead a full life.
Side effects of Piracetam
Most often, when using Piracetam, according to reviews, disorders of the central nervous system are observed, such as:
- Motor disinhibition;
- Drowsiness;
- Asthenia;
- Insomnia;
- Balance imbalance;
- Hallucinations;
- Irritability;
- Depression;
- Headache;
- Exacerbation of the course of epilepsy;
- Mental agitation;
- Ataxia;
- Anxiety;
- Confusion.
In addition, in therapeutic doses, Piracetam, according to reviews, can cause:
- Nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain;
- Vertigo;
- Anaphylactic reactions, hypersensitivity, angioedema;
- Decreased blood pressure, fever;
- Increased body weight;
- Itching, dermatitis, urticaria;
- Thrombophlebitis, pain at the injection site.
When using Piracetam in doses that exceed therapeutic doses, the risk of developing bloody diarrhea and abdominal pain increases. Since there is no specific antidote, in case of an overdose of Piracetam the following should be done:
- Symptomatic therapy;
- Induction of vomiting;
- Gastric lavage;
- Hemodialysis (effectiveness 50-60%).
When Piracetam is used simultaneously with iodine-containing thyroid hormones, irritability, confusion and sleep disturbance may occur.
How to get rid of the problem
If we talk about treatment, it is divided into several areas:
- Controlling blood sugar levels - the performance of the body and its general condition depend on this factor. It is necessary to achieve normal blood sugar levels, this is a preventive measure that will help prevent the formation of the disease. In addition, the blood supply to brain cells and nerve tissues improves;
- Therapy of metabolic disorders - for this purpose, various antioxidants, brain protectors, vitamin and mineral complexes are used. All this allows you to maintain the general condition of the body, strengthen the immune system, nourish the cells of the brain and nervous system;
- Therapy for microangiopathy - it includes treatment of vascular disorders, restoration of blood flow and viscosity. For this purpose, pentoxifylline is used, sold in any pharmacy. The drug can improve blood circulation in the body and improve its viscosity.
Forecasts
The consequences of the disease and the time it takes to recover depend on age, blood sugar levels and concomitant ailments. The right approach is important, thanks to which a person can spend the years of his life fully and interestingly. The patient must follow a special diet and constantly check the amount of sugar in the blood. With this approach, we can talk about favorable prognosis.
Diabetic encephalopathy with severe mental disorders cannot be completely cured, but symptoms can be mitigated.
If the disease is not treated, the patient will lose the ability to live normally, eat independently, go to the toilet and walk in general. The point here is about possible disability. Due to disturbances in the blood circulation of the brain, even death is possible.
Based on the results of the article, it is clear that diabetic encephalopathy in diabetes is a common occurrence. Treatment and prognosis make it clear that the disease requires special attention. The symptoms are not the most pleasant; in addition, disability and death may occur.
Reasons for development
In the classical definition of DE, the reasons for its development are:
- Diabetic microangiopathy.
- Metabolic disorders.
Predisposing factors are:
- Elderly age.
- Increased body mass index.
- Increased level of lipid peroxidation (can be determined with a special biochemical blood test).
- Lipid metabolism disorders (in the blood increased levels of low-density lipoproteins, decreased levels of high-density lipoproteins).
- Long-term elevated blood sugar levels and high values of glycosylated hemoglobin.
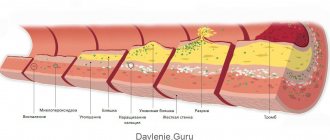
The permeability and structure of the walls of small vessels are disrupted. As a result, the nutrition of nerve fibers and cells is disrupted, and a lack of oxygen and energy resources develops in the cells. As compensation, oxygen-free metabolic processes (anaerobic) are activated. They are less effective and lead to the accumulation of toxic products. As a result, higher brain functions suffer. For these disorders to manifest, a significant period of time is required—a long period of diabetes.
Therefore, DE is a late complication of diabetes mellitus. It often develops in type 1 diabetes, as it begins at a young age. Accordingly, there is a high probability of developing DE in the older age group.
In elderly patients suffering from type 2 diabetes mellitus, encephalopathy is often caused by atherosclerotic damage to the blood vessels of the brain.
Encephalopathy can also develop as a result of a separate significant complication of diabetes - cerebral stroke .
Complications of diabetes mellitus include encephalopathies that develop in acute situations : hypoglycemia, decompensated hyperglycemic states. The brain is one of the most sensitive organs to glycemic levels and metabolic disturbances. These conditions can be early complications of diabetes and manifest themselves, for example, as diabetic precoma and coma. Due to their particular significance and immediate threat to life, they are placed in a separate group. Frequent manifestations of early complications, especially hypoglycemia, subsequently increase the likelihood of developing DE.
Causes of diabetic encephalopathy
The main metabolic factor is hyperglycemia. The first and second types of the disease equally lead to the development of encephalopathy.
In addition to high sugars, pathology is provoked by:
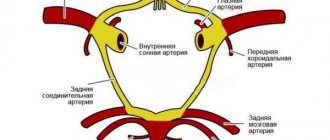
- High cholesterol levels. Impaired lipid metabolism leads to the progression of atherosclerosis. The combination of macro- and microangiopathy is a powerful provocateur of cerebral ischemia;
- Damage to the cerebral arteries and vessels of the neck impairs blood circulation. Chronic ischemia is a depression of cognitive functions and a decrease in recovery capabilities;
- Decompensation of diabetes mellitus is a provoking factor of dementia. However, it is not only hyperglycemia that has a negative effect. Decreased glucose levels and ketoacidosis lead to neuronal suffering. A dynamic study of C-peptide and insulin is also necessary;
- The last provocateur is arterial hypertension. As a rule, this pathology develops in the form of an essential disease. The combination of diabetes and hypertension increases the likelihood of encephalopathic lesions by 80%.
Course of the disease
When the disease first occurs, the symptoms are mild, making it difficult to immediately diagnose the problem.
Diabetic encephalopathy manifests itself very slightly: the patient begins to get worse sleep, forgets minor moments, and becomes a little irritable. Each feature occurs due to a lack of oxygen supply to the nerves.
To compensate for the missing energy, nerve endings use special mechanisms, the long-term operation of which leads to the accumulation of harmful substances.
The course of the disease can lead to the appearance of additional syndromes:
- Asthenia appears first. Having an impact on the body as a whole, it makes a person lethargic. The patient begins to complain of weakness, loses his ability to work, becomes emotionally unbalanced - irritable, rarely - aggressive;
- Cephalgia causes several types of headaches. Damage to the organ is expressed in varying degrees of severity: mild, quickly passing; severe, interfering with concentration; prolonged migraine;
- Vegetative dystonia does not appear immediately, but in the vast majority. Symptoms are: constant fever and fainting;
- In the severe stage, brain damage provokes: different sizes of eye pupils, asymmetrical eye movements, dizziness, lack of coordination in space, paralysis ;
- Also, a developed disease causes impairment of cognitive and higher brain functions : the reaction slows down; partial amnesia appears; the opportunity to acquire new skills and information is lost; critical thinking is lost; apathy occurs.
Syndromes can be prevented by improving the quality of food consumed and monitoring the amount of sugar in the plasma.
IMPORTANT!
In the final stage, encephalopathy is expressed by completely disrupted functioning of nerves throughout the body.
The consequences are:
- Loss of motor activity, expressed by complete or partial paralysis;
- Prolonged severe migraines;
- Loss of sensitivity of nerve endings;
- Visual impairment, up to loss for a certain period of time;
- Convulsions, similar in nature to epilepsy;
- Disruption of the excretory organs - liver and kidneys.
In diabetics, in rare cases, when serious violations of doctor's recommendations and loss of sugar occur, hypoglycemic encephalopathy . The complication repeatedly aggravates the course of the disease , causing loss of orientation in space, restlessness and anxiety, muscle spasms, and cramps. With a further decrease in blood glucose levels, the patient turns pale, loses the ability to control muscles and may fall into a coma. The administration of glucose reverses the process, gradually restoring a person's health.
A delay in low sugar levels greatly increases the duration of treatment, in some cases making it unavailable. Excessive administration of a substance, leading to, harms the recovery process more than not administering it at all.
Analogues and cost of the drug
Actovegin is sold in the range of 109 to 2150 rubles.
The price depends on the form of release of the drug. One of the well-known analogues of Actovegin is the drug Solcoseryl. This drug is produced in the form of creams, ointments and injection solutions. The advantage of this product is its almost complete identity with Actovegin. The drug has an active substance - dialysate, purified from protein. The substance is also obtained from the blood of young calves.
Solcoseryl is used for the treatment of diseases caused by a lack of oxygen in cells, as well as for the healing of burns and wounds of varying severity. Admission is undesirable during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The cost of the drug ranges from 250 to 800 rubles.
How does the disease manifest itself?
In the first stages of development, the disorder hardly shows itself at all, and memory deterioration, headaches and poor health are often attributed to age-related changes
In the first stages, diabetic encephalopathy is not very noticeable; it does not manifest itself in any way. Because of this, serious problems arise; the patient is not able to tell when the first symptoms of the disease appeared. At first, you may notice a slight memory impairment, a change in mental and emotional state, and problems with sleep arise. All this suggests that a person suffers from a lack of oxygen and energy. As a result, the body uses additional mechanisms that can compensate for all this. With their prolonged use, toxic metabolic products accumulate. They negatively affect the brain, cells and blood vessels. Depending on the stage of the disease, several syndromes are distinguished:
- Asthenic – with it severe weakness, lethargy occurs, a person quickly gets tired, performance is impaired and irritability increases. All this leads to negative consequences;
- Cephalgic - headaches of varying intensity occur, a feeling of tightness and squeezing, and it is impossible to concentrate on one thing. In some cases, migraine may occur;
- Vegetative – this syndrome occurs in most patients. The main characteristics include a strong feeling of heat, fainting and presyncope. In addition to all this, the patient may experience different pupil diameters, disturbances in the functioning of the eyeballs, paralysis, severe dizziness, and an awkward gait. All this negatively affects the general condition;
- Disorder of cognitive function - the functioning of the brain is disrupted, the patient suffers from memory lapses, is unable to master new languages, correctly understand information, brain function and thinking slow down, and depression develops. The latter is typical for most patients with encephalopathy. To prevent all this, you need to eat only healthy foods, monitor your blood sugar levels, and correct all this with insulin;
- Last stage - at the last stage of the disease, disorders in the nervous system are observed. Key signs include disturbances in motor actions, severe pain in the head, impaired sensitivity of certain areas of the skin, deteriorating vision, the occurrence of convulsions, pain in the kidney, liver and other organs.
With proper diagnosis of the disease, you can get rid of the problem very quickly and without consequences. The main thing is not to delay this matter, but to immediately go to the doctor.
Diabetic encephalopathy and polyneuropathy: therapeutic possibilities of Actovegin
Diabetic polyneuropathy (DPN), the most common form of diabetic neuropathy, develops as a result of damage to endoneurial vessels, which is confirmed by the relationship between the thickness of the basement membrane of these vessels and the density of nerve fibers in the peripheral nerve in diabetes [7]. More than 50% of patients with diabetes suffer from DPN, the risk factors for the development of which are the time and type of diabetes, the duration of periods of severe hyperglycemia, HBA1C, the presence of microcirculation pathology and smoking. Clinically, DPN is manifested by positive neuropathic symptoms (pain, burning, numbness, paresthesia, cramps) and neurological deficit in the form of decreased Achilles and knee reflexes, sensitivity of all modalities, mainly in the distal parts of the legs, which causes the development of foot ulcers and the threat of amputation of the limb. In diabetes, not only peripheral nerves are affected, but also the structures of the central nervous system (CNS), which is interpreted as diabetic encephalopathy [8]. There is no doubt about the possibility of a connection between acutely or chronically developing changes in the central nervous system with hyper- or hypoglycemia, which can be quite adequately reflected by the term “diabetic encephalopathy”. Another situation arises if arterial hypertension (AH) and atherosclerotic changes in extra- and intracerebral vessels form the basis for ischemic/hypoxic brain damage as part of dyscirculatory encephalopathy. In this case, diabetes and associated metabolic disorders in the central nervous system are rather a risk factor, and the term “diabetic discirculatory encephalopathy” looks dubious. From our point of view, focal lesions of the brain substance that form in patients with diabetes should be considered in a similar way. According to modern concepts, chronic hyperglycemia in diabetes leads to the development of microcirculatory pathology and accelerates the development of atherosclerosis in macrovessels and hypertension. The DCCT and UKPDS studies showed that there is a clear correlation between hyperglycemia and microcirculatory diabetic complications in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. The basic mechanisms underlying the complications of diabetes are the activation of the polyol and hexosamine pathways of glucose metabolism, the formation of end products of excess protein glycation, and an increase in the content of various isoforms of protein kinase C. Most of the known metabolic and vascular mechanisms for the development of extra- and intracellular pathology in late complications of diabetes are united by them dependence on the inclusion in the pathological process of hyperproduction of superoxide in mitochondria [6]. Thus, the main reason for the formation of late complications is oxidative stress - an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the activity of antioxidant enzymes, which is reduced in diabetes [5]. Insufficient activity of antioxidant enzymes in diabetes is determined by genetic factors, which is confirmed by the study of polymorphism of genes for enzymes of the body's antioxidant system - catalase for diabetic retinopathy and superoxide dismutase for DPN [1,9]. Clinical work on the use of drugs that improve the rheological properties of blood and endothelium-dependent reactions of the vascular wall - thioctic acid - has shown an improvement in the function of peripheral nerves in patients with diabetes, according to various scales for assessing positive and negative neuropathic symptoms and the results of electrophysiological testing [10]. Improving blood rheology and the condition of the endothelium in cerebrovascular pathology reduces the severity of cognitive impairment [3]. At the same time, there is practically no work in the literature assessing the effect on cognitive functions and the condition of peripheral nerves in patients with diabetes when using the drug Actovegin, which should potentially be effective in patients with diabetes. The basis for this study was the assumption of Actovegin’s ability to improve the function of peripheral and central nervous system structures due to its main action – improving the utilization of glucose and oxygen [4]. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness and tolerability of the drug Actovegin in patients with type 2 diabetes with distal symmetric sensory-motor polyneuropathy and cognitive impairment. Patients and research methods. As part of an open single-center study, 30 patients with type 2 diabetes (12 men and 18 women) aged from 45 to 75 years (average age 58.9±7.0 years), with a duration of diabetes over 5 years (average 12.0 years) were examined. ±3.1 years) with the presence of diabetic polyneuropathy and cognitive impairment (<28 points on the MMSE). The body mass index in the group was 24.8±5.6 kg/m2, the level of glycohemoglobin (HbA1c) was 8.43±0.19% (less than 10% individually). 12 patients received tablet forms of hypoglycemic drugs (gliclazide, glibenclamide, glivedon) and 18 patients received combination therapy (insulin and oral hypoglycemic drugs). During treatment with Actovegin, the patients' glucose-lowering therapy was not changed. The study did not include patients who had received angioprotectors or antioxidants during the previous 3 months, who abused alcohol, or who had severe liver and kidney dysfunction. Patients received Actovegin at a dose of 400 mg per day (10.0 ml Actovegin in 200.0 ml saline) for 15 days. Patients were examined before and on the 16th day of treatment with Actovegin. The level of glycosylated hemoglobin was determined using the Diastat apparatus. The intensity of lipid peroxidation (LPO) in blood serum and erythrocyte membranes was determined by the level of malondialdehyde (MDA) on a Hitachi 1000 spectrofluorometer. To assess the severity of DPN, patient complaints (TSS scale) and neurological symptoms (NISLL scale) were analyzed. The threshold of vibration sensitivity was determined using a graduated tuning fork C128, the threshold of pain sensitivity using a needle prick, the threshold of temperature sensitivity using the “Tri-term” instrument, and the threshold of tactile sensitivity using the “Tactile circumferencial discriminator” instrument. All thresholds were determined at standard points on the foot. The knee and Achilles tendon reflexes were assessed. An electromyographic study (EMG) was performed before the start of treatment and on the 16th day using a neuroelectromyograph (Russia) at a skin temperature of at least 30°C. We analyzed the velocity of propagation of excitation (RPV), residual latency (RL) and the amplitude of the M response when stimulating the motor fibers of the peroneal nerve, the potential amplitude, and SRV when stimulating the sensory fibers of the sural nerve. The state of microcirculation of the nail bed of the ring finger was studied using a computer capillaroscope “Kapillary” (Russia) in a sitting position with hands located at the level of the heart, at room temperature 21–23°C. Before the examination, the patients were at rest for about 20 minutes and on the day of the examination did not smoke, drink coffee or take medications that affect blood pressure. The determination of capillary blood flow velocity was carried out in at least 6 different capillaries for 10 s. Patients were examined for the severity of cognitive impairment using the MMSE scale (Mini-Mental State Examination, Folstein et al., 1975). Statistical processing of the material was carried out by methods of variation statistics using the Student's reliability criterion, for small samples - by nonparametric methods. Results and discussion. Treatment with Actovegin did not cause a significant change in carbohydrate metabolism in terms of fasting and postprandial glycemia. The level of MDA in plasma before treatment was 1.18±0.03 nmol/ml and 0.82±0.02 on the 15th day of treatment (p<0.01). In erythrocyte membranes, the level of MDA before treatment was 2.14±0.03 nmol/ml and on the 15th day of treatment – 1.42±0.02 (p<0.01). In a control group of 10 healthy volunteers matched by age, the level of MDA in plasma was 0.32±0.05, and in erythrocyte membranes – 1.13±0.12 nmol/ml. In diabetes, one of the main mechanisms of action of oxidative stress on nervous tissues is the formation of lipid peroxidation (LPO) products. In the examined group of patients, an initial increase in lipid peroxidation in serum and erythrocyte membranes was revealed. The administration of Actovegin led to a significant decrease in the MDA content both in serum and erythrocyte membranes. Subjective discomfort of patients caused by DPN (pain, burning, paresthesia, numbness), according to the TSS scale (value before treatment - 7.79 ± 0.85 points) significantly decreased by the 15th day of treatment (3.32 ± 1. 32 points, p<0.01). The dynamics of objective symptoms on the NISLL scale in the form of a decrease in sensitivity disturbances and revival or appearance of tendon reflexes was significant by the 15th day of treatment (at the beginning of treatment - 8.46 ± 2.16 points, on the 15th day - 5.32 ± 1.48 points, p<0.05). The main indicator of the drug's effect in DPN is its clinical effect. During treatment with Actovegin, a decrease in both positive neuropathic symptoms and neurological deficits was noted. EMG indicators did not change significantly, which may be explained by the insufficiently long study time. Computer capillaroscopy of the nail bed showed that initially the patients had severe microcirculation disorders in the form of a depleted capillary pattern, slow blood flow, an increase in the area of pericapillary edema, and the presence of sludge phenomena. Most of the studied characteristics of capillary blood flow significantly improved during treatment with Actovegin. When studying cognitive functions on the MMSE scale before treatment, a significant decrease in the sum of scores was noted compared with a group of 30 healthy subjects of the same age (25.50±1.50 points in patients with diabetes and 29.2±1.10 points in the control group). group). During treatment, an improvement in the state of cognitive functions was noted (up to 27.47±1.00 points, p<0.01). Taking Actovegina did not cause side effects in any patient. Actovegin is a deproteinized hemoderivative from the blood of young calves, which contains electrolytes, trace elements, amino acids, nucleosides, lipids, oligosaccharides, intermediate products of carbohydrate and fat metabolism. The drug, without having a direct vasodilating effect, improves the consumption (utilization) of glucose and oxygen by cellular structures, including the peripheral and central nervous systems. A significant increase in the energy supply of various tissue cultures as a result of the use of Actovegin has been shown. In this regard, the point of application of Actovegin in conditions of diabetes becomes clear, in which the main disorders of micro- and macrovessels are associated with hypoxia and energy depletion of cellular structures. The study showed that Actovegin, by reducing the severity of lipid peroxidation, improves microcirculation, the function of peripheral nerves and central nervous system structures, leading to a significant clinical improvement in the condition of patients with diabetes. Considering the virtual absence of side effects, Actovegin can be used to treat elderly patients with type 2 diabetes with DPN and cognitive impairment. Literature 1. Dedov I.I. Diabetes mellitus in the Russian Federation: problems and solutions. // Diabetes mellitus – 1998 – No. 1 – P.7–18. 2. Efimov A.S. Diabetic angiopathy. M., 1989. 3. Zakharov V.V., Yakhno N.N. Use of tanakan for disorders of cerebral and peripheral circulation // Russian. honey. magazine – 2001 – T.9, No. 5 – P.3–9. 4. Rumyantseva S.A., Benevolenskaya N.G., Evseev V.N. Antihypoxants in resuscitation and neurology // Russian medical journal. – 2004 – T.12, No. 22 – pp.1263–1267. 5. Baynes JW, Thorpe SR Oxidative stress in diabetes // Antioxidants in diabetes management // Ed.: L.Packer, NYMDekker Inc, 2000 – P. 77–92. 6. Du XL et al. Hyperglycemia–induced mitochondrial superoxide overproduction activates the hexosamine pathway and induces plasminogen activator inhibitor–1 expression by increasing Sp1 glycosylation // Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97 – 2000 – P.12222–12226. 7. Giannini C., Dyck PJ Pathologic alterations in human diabetic polyneuropathy // In: Diabetic neuropathy. Eds: Dyck PJ, Thomas PK, 2nd ed.: Phyladelphia: Saunders WB, 1999 – P. 279–295. 8. Reske–Nielsen E., Lundbaek K., Rafaelsen OJ Pathological changes in the central and peripheral nervous system of young long-term diabetics // Diabetologia – 1965 – No. 1 – P.233–241. 9. Strokov IA, Bursa TR, Drepa OI et al. Predisposing genetic factors for diabetic polyneuropathy in patients with type 1 diabetes: a population–based case control study // Acta diabetologica – 2003 – Vol.40 – P.375–379. 10. Ziegler D., Reljanovic M., Mehnert H. et al. ?–Lipoic acid in the treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy in Germany: Current evidence from clinical trials // Exp.Clin. Endocrinol Diabetes – 1999 – Vol. 107 – P. 421
Treatment of encephalopathy
The main therapy for diabetic encephalopathy is diabetes therapy. It should be carefully followed to avoid the onset and progression of encephalopathy. In addition, it is imperative to follow the diet prescribed by the doctor. If such a pathological condition is diagnosed, 2 types of treatment are prescribed:
- Metabolic - affects metabolic processes. This type of treatment includes medications “Actovegin”, antioxidants: alpha-lipoic acid preparations); nootropics: Piracetam, Cytoflavin, Bilobil, Noofen; vitamins A, C, preparations of B vitamins: “Magne-B6”, “Neovitam”, “Neurorubin”.
- Vasoactive - aimed at improving the condition of the blood and blood vessels. This also includes nootropic drugs, it is possible to use drugs that strengthen the walls of blood vessels (Ascorutin), venotonics.
When seizures occur, anticonvulsant therapy is administered - Carbamazepine, Finlepsin, Lamotrigine. In addition, in the presence of concomitant pathology: hypertension and atherosclerosis, treatment for these conditions is prescribed, including antihypertensive drugs and statins. In addition, overweight patients are recommended to normalize their body weight. Light physical activity, walks in the fresh air, swimming, yoga are recommended.
Prevention
The symptoms of diabetic encephalopathy are unpleasant, so it is easier to prevent the disease than to try to cure it later.
It is important to control blood glucose levels and include an active lifestyle: jogging, dancing and walking in the fresh air. If the patient suffers from hypertension, a consultation with a therapist and cardiologist will first be required.
Preventive measures include a change in diet. We include foods with a low glycemic index in the diet, which have a good effect on the circulatory system.
These include: oranges, lemons, sweet peppers, plums, tomatoes. We add foods that lower blood pressure and are rich in fiber - apples, walnuts, hazelnuts, kiwi, legumes.
Diabetics who drink alcohol or smoke should give up these bad habits.
Olive oil rich in vitamin E is very beneficial.