The functioning of all systems in the body is under the control of the brain. Any failure in the organization of this organ immediately affects a person’s well-being. This is due to the presence of synoptic connections between the neurons of this part of the central nervous system and the tissues of the body, with the help of which the “main analyzer” monitors the work of each organ separately and at the same time ensures the interaction of all systems in the body. Consequently, any disturbance in the organization of the nervous system leads to dysfunction of the entire organism.
Most often, disorders of the central nervous system are caused by pathologies and diseases of the brain, which lead to organic destruction of the brain matter, since as a result the connection between the organ and the nerve centers of the brain responsible for its activity is interrupted.
What are brain diseases
The group of diseases that are characterized by the destruction of the brain matter includes both infectious and oncological processes. This list also includes pathologies in the structure of the organ, abnormalities in development and mechanical injuries, since under their influence a partial disruption of cerebral circulation may develop or the enrichment of the brain with oxygen may completely stop.
All diseases of the central nervous system can be divided into 2 large groups: congenital and acquired. The former are usually diagnosed immediately after the birth of the child or after some time, as they cause obvious abnormalities. These include hydrocephalus and intrauterine growth retardation.
In adults, acquired diseases such as meningitis, Parkinson's disease, etc. are most often found.
List of diseases and their characteristics
The activity of the entire central nervous system is aimed at controlling the body. For example, any movement of the hand or wave of it is under the control of the brain, regardless of whether it was intended or happened spontaneously, at the level of a reflex.
As a result of the work of this organ, a person can talk, think, analyze and remember information. Therefore, any disorder in the organization of the brain is characterized by the development of certain symptoms.
Experts identify several groups of diseases characteristic of the central nervous system:
- Oncological. They can be both malignant and benign. These include, for example, glioblastomas and angiomas.
- Infectious. Develop under the influence of a pathogen: neurosyphilis, meningitis.
- Traumatic brain injuries: bruises, blows, concussions.
- Vascular diseases of the brain: aneurysms, hemorrhagic stroke, vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Autoimmune diseases: multiple sclerosis.
- Parasitic diseases: echinococcosis, toxoplasmosis, rabies.
- Hereditary pathologies: Recklinghausen's disease.
Although the mechanism of development of many brain diseases is poorly understood, modern diagnostic methods make it possible to identify them at an early stage of development. In this case, the main thing for the sick person is not to miss this opportunity: after all, his life often depends on how quickly treatment is started.
The most common brain diseases are:
- Encephalopathy. Characterized by the systematic destruction of brain matter. Develops against the background of a failure of intercellular metabolism. Encephalopathic changes in the structures of the central nervous system can appear against the background of inflammatory processes, exposure to alcohol, toxic substances, and vascular pathologies.
- Senile dementia of the Alzheimer's type (Alzheimer's disease). Refers to neurodegenerative diseases. Most often occurs after 65 years. As a result of the pathological process, a slow death of brain cells occurs, which leads to the development of corresponding symptoms and manifestations of the disease: dementia and impaired motor function.
- Aneurysms of the vascular system of the brain and aorta. Refers to pathologies of the structure of the body's circulatory system structures: under the influence of unfavorable factors, for example, due to surges in blood pressure and weakening of muscle tissue, the wall of the blood vessel becomes stratified, and in its place a protrusion forms in the form of a sac filled with blood - an aneurysm, which can subsequently burst.
- Hemorrhagic stroke or acute cerebrovascular accident. It develops against the background of mechanical damage to the integrity of blood vessels in the brain, resulting in bleeding. The resulting hematoma compresses and displaces the structures of the brain matter, which causes their swelling.
- Parkinson's disease. Refers to chronic neurological diseases. Usually debuts after age 65. Characterized by progressive dysfunction of the substantia nigra.
- Vegetovascular dystonia. Develops against the background of dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. It is characterized by a violation of the regulation of the tone of the walls of the blood vessels of the head.
- Oncological diseases. Sometimes tumors form in brain structures. They can be malignant or benign, be slow-growing and exhibit an aggressive distribution pattern. But in any case, their presence leads to the development of negative consequences: increased ICP, cerebral edema, etc.
- Epilepsy. It can be acquired, that is, develop as a result of TBI, or congenital. During an exacerbation (seizure), the patient cannot control his actions, and his brain refuses to work correctly: foam appears at the mouth, convulsions, shortness of breath, and the tongue sinks.
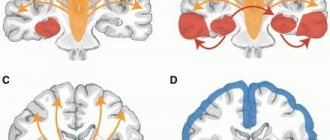
Diencephalic structures in the risk area
Disorders can spread to different parts of the brain, which is reflected in symptoms; for example, when the intermediate part in the area of diencephalic structures is affected, the dysfunction is characterized by problems with metabolic processes, sleep disorders and a clinical picture characteristic of other areas.
Irritation manifests itself as irritation of the brain. Symptoms will vary depending on the area affected. Usually, irritation is not a separate disease, but a consequence of the course of another disease (tumor, neuroinfection, etc.).
Epilepsy attacks are the result of dysfunction of the midline and stem structures of the brain. Speech and autonomic system disorders are also detected. If the lower parts are damaged, problems with consciousness (confusion with time), attention, and memory may occur.
Causes and symptoms
Anything can provoke the development of brain diseases: infection, head injury, genetic disruptions, delay in the development of central nervous system structures, exposure to toxic substances, alcohol, radiation exposure, poor nutrition, playing hazardous sports and neglect of basic hygiene rules, such as in case of injury organism by parasites.
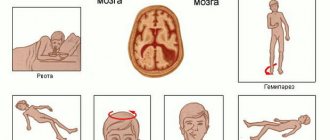
But despite this, all diseases of the central nervous system have common signs of damage, which manifest themselves in specific neurological symptoms:
- headache attacks that do not stop after taking medications;
- a sharp change in behavioral and taste habits;
- problems with remembering and reproducing information;
- forgetfulness;
- deterioration of hearing, vision;
- loss of coordination of movements, tremors of limbs;
- hyper- or hypotonicity of muscles;
- numbness of a body part;
- fainting;
- convulsions;
- throwing back the head.
The neurological signs characteristic of a particular disease depend on the location of the lesion and its size, therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, a comprehensive examination of the head and its structures should be done.
symptoms of disorders of higher brain functions
Category: Neurological Nursing/Clinical manifestations of major neurological syndromesHigher brain functions are provided by the activity of the cerebral cortex
. Therefore, pathological symptoms depend on the location and extent of the lesion. In neuropathology, the most clinically significant are disorders of speech, gnosis and praxis; in psychiatry - thinking, memory, emotions, will, consciousness.
Speech disorders
Aphasia
is a speech disorder. Speech centers are located in the frontal, temporal and parietal lobes of the leading (dominant) hemisphere of the brain.
Motor aphasia
develops when the frontal lobe is damaged, and is expressed in the fact that the patient understands speech addressed to him, but cannot speak himself. With partial aphasia, the patient cannot pronounce individual words or sounds.
Sensory aphasia
characterized by the fact that the patient does not understand the speech addressed to him, but cannot speak himself, sometimes a lot and indistinctly (“verbal okroshka”). It is observed with damage to the temporal lobe.
Amnestic (anomic) aphasia
is expressed in the fact that the patient cannot remember the names of objects, although he knows their purpose.
Occurs when the temporo-parieto-occipital region (angular gyrus) is damaged. Total aphasia
(impairment of all types of speech) is observed with extensive lesions.
Speech impairments may be accompanied by impairments in writing (agraphia), reading (alexia), and counting (acalculia).
Anarthria (dysarthria)
occurs with paresis or paralysis of the articulatory apparatus, primarily the tongue. In these cases, speech becomes illegible and incomprehensible.
Mutism (muteness)
observed in patients who lost hearing in early childhood and in a number of mental illnesses.
Scanned Speech
- described in cerebellar pathology.
Apraxia
Apraxia is a disorder of purposeful complex actions.
.
“ Praxis
” is
action, that is, the ability to perform sequential sets of movements and perform purposeful actions according to an established plan
.
Apraxia is associated with pathology of sensitive analyzers and occurs when the cortex is damaged in the parietotemporal-occipital region. There are: ideational, constructive and motor apraxia
.
With ideator apraxia
the ability to construct an action plan is impaired.
With constructive apraxia
patients cannot make a whole from parts (a square made of matches).
For motor apraxia
patients not only cannot draw up a plan of action, but are also unable to imitate the action.
Agnosia
Agnosia is a violation of recognition of stimuli affecting the body
. The nature of agnosia depends on the location of the lesion in the cerebral cortex. Accordingly, visual, auditory, and taste agnosia are distinguished; agnosia of general sensitivity - astereognosis (failure to recognize an object by touch).
Psycho-emotional disorders
Mental and emotional disorders can occur at any localization of the pathological focus in the cerebral cortex, especially with diffuse lesions.
Most often, mental disorders are observed when the frontal lobes are damaged.
and have characteristic features (“frontal psyche”): a sharp decrease in intelligence, a narrowing of the range of interests, emotional incontinence, indifference to the rules of decency, sloppiness, untidiness, apathy, foolishness, a penchant for flat jokes, hypersexuality.
With bilateral damage to the frontal lobes and anterior parts of the corpus callosum
Abulia
occurs : patients become completely indifferent, indifferent.
Mental disorders with damage to the frontal lobe cortex and cortical-subcortical connections
usually combined with the appearance of reflexes of oral automatism and grasping phenomena.
With damage to the medial surface of the hemispheres and limbic structures
disturbances of emotions, paroxysms of fear, anxiety, general disinhibition, disturbance of orientation, memory, especially for current events, are noted.
See clinical manifestations of major neurological syndromes
Saenko I. A.
Sources:
- Nurse's Handbook for Care/N. I. Belova, B. A. Berenbein, D. A. Velikoretsky and others; Ed. N. R. Paleeva. - M.: Medicine, 1989.
- Bortnikova S. M., Zubakhina T. V. Nervous and mental illnesses. Series 'Medicine for you'. Rostov n/d: Phoenix, 2000.
- Martynov Yu. S. Neurology: Textbook. ed. 4th, rev. and additional - M.: RUDN, 2009.
How to reduce the likelihood of brain disease
There are no uniform preventive measures to prevent the development of diseases of the central nervous system structures. However, there are a number of rules by following which the risk of their occurrence is reduced.
These include the following points:
- periodic medical examinations by a neurologist;
- head protection during the cold season (will help avoid inflammatory processes);
- compliance with safety rules when performing hazardous work and driving;
- correction of lipid metabolism in patients with arterial atherosclerosis and metabolic syndrome.
Unfortunately, at the moment, specialists cannot prevent genetic diseases of the brain.
Brain Features
The trunk is the formation responsible for the vital functions and health of the body. It is located in the human brain. Among the most important body systems for which this structure is responsible are:
- cardiovascular.
- respiratory.
- heat exchange.
- digestive.
But there are often cases when a person gets injured and suffers harm to health. In this case, the brain or spinal cord may also be damaged, as a result of which it ceases to function normally and correctly. This usually happens due to an accident where an injury occurred or a bruise occurred that resulted in a concussion. Today, there are frequent cases of injury during difficult childbirth.
Disturbances in the functioning of the brain will be clearly expressed clinically or they can be diagnosed through special tests.