Information about the disease
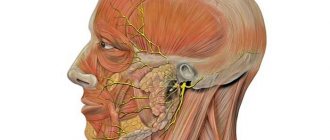
The facial nerve is responsible for ensuring the movements of facial muscles, the lacrimal gland, the tensor tympani muscle, and also innervates the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. It leaves the skull in a narrow canal located deep in the temporal bone. The slightest swelling in this area leads to compression of the fibers and the development of corresponding symptoms.
The pathology most often occurs in middle-aged people, who often neglect preventive measures due to the high pace of life. The peak incidence occurs in the cold season, since low temperatures are one of the provoking factors.
Make an appointment
Brief description of the anatomical structure of facial innervation
Facial expressions are determined by the motor activity of the muscles lying under the skin of a person’s face. Each of them has its own network of nerve endings and blood vessels that provide nutrition and enrichment of tissues with oxygen.
Responsibility for the innervation of the muscles of this area is assigned in the human body to the VII pair of cranial nerves, called facial nerves (nervus facialis). Their location in the head is characterized by symmetry, however, pathological processes can occur on one or both sides.
In its structure, the nervus facialis has an extensive network of nerve endings - structures that cover the innervated area as widely as possible.
Entering the parotid salivary gland from the cranial cavity (through the stylomastoid foramen), the so-called “Crow's Foot” is formed - the division of the main trunk into five smaller branches. They are suitable for:
- Zygomatic bone (temporal branch) - for innervation of the muscles around the eye, fronto-occipital muscle;
- Buccal muscle;
- Mandible (innervates the muscle that lowers the corner of the mouth);
- Neck;
- Stylohyoid and stapedius (participating in the innervation of the eardrum) muscles.
The impact of a stimulus in the area of operation of any of these branches provokes the sending of a signal to the brain and processing of the received information at the reflex level.
In addition, signals entering the corresponding brain structures from the sensory organs (vision, hearing, smell), through neural interactions, activate the delivery of commands to the areas innervated by the nervus facialis.
Causes
Depending on the cause, the following forms of facial nerve neuropathy are distinguished:
- idiopathic: the cause of paralysis remains unidentified (the most common variant of the disease);
- infectious: pathology occurs against the background of infectious damage to nerve fibers due to herpes, tuberculosis, mumps, syphilis and some other diseases;
- otogenic: is a complication of inflammation of the middle ear or mastoid process;
- traumatic: neuropathy develops against the background of traumatic brain injury;
- ischemic: the disease is associated with impaired blood flow and decreased oxygen supply to nerve fibers.
The risk of pathology increases significantly in the following situations:
- for metabolic disorders, including diabetes mellitus;
- with advanced forms of arterial hypertension;
- during pregnancy, especially with severe toxicosis.
The triggering factor for the development of pathology is often hypothermia.
Symptoms
Symptoms of facial neuropathy make it possible to immediately suspect the disease. Signs arise from the affected nerve. Patients note:
- acute pain: it usually begins in the ear area and gradually spreads throughout the face and begins to radiate to the occipital region;
- intense lacrimation, less often dry mucous membranes of the eyes;
- discomfort or ringing in the ear due to sharp sounds;
- disturbance of the sense of taste in the anterior parts of the tongue.
As the disease progresses, signs of damage to the motor fibers of the nerve appear:
- smoothness of skin folds, especially nasolabial folds;
- swelling of the cheek when exhaling or trying to pronounce a consonant sound;
- lack of complete closure of the eyelids, rotation of the eyeball upward and outward (lagophthalmos);
- leakage of fluid from the corner of the mouth;
- food getting stuck between the gum and cheek when eating;
- limitation of facial expressions: the patient cannot frown or smile.
If the cause of neuropathy is an infectious process, the characteristic signs are accompanied by symptoms of general intoxication:
- high body temperature;
- headache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- weakness.
If the innervation is changed
Disturbances in the work of any of these branches are, as they say, “visible.” Symptoms of neuritis of the facial nerve are noted. Among them: smoothing of the nasolabial fold, uncharacteristic position of the corners of the mouth, distortions of the lower or upper eyelids.
It is difficult for a patient with facial neuritis to close his eyes. He cannot smile, frown, or stretch his lips forward to pronounce the letter “u.”
A characteristic sign is the appearance of Bell's sign. At the moment when a person tries to close his eyelids, the white turns towards the forehead, taking on unnatural shapes.
If neuritis of the facial nerve is noted on one side, the face skews to the other. This can be explained from a physiological point of view. Weak or completely absent innervation of muscle fibers leads to their relaxation and decreased tone. The opposite side, functioning in its normal state, seems to “pull” the muscle tissue towards itself.
If in the initial stage neuritis of the facial nerve leads to a barely noticeable distortion (some muscle tone on the affected side is still present), then as the disease develops the face may take on extremely unnatural involuntary grimaces.
Neuritis of the facial nerve usually does not cause severe pain symptoms, except at the beginning of the disease, when 20-30 hours before the appearance of visual changes, pain behind the ear may be observed.
Diagnostics
Neurological disorders characteristic of facial neuropathy can also occur with other diseases, in particular with stroke. That is why, if any similar symptoms occur, you should urgently consult a neurologist.
Diagnosis of pathology includes:
- collection of complaints;
- taking an anamnesis, during which the doctor clarifies the time and circumstances of the onset of symptoms, records previous and chronic diseases, injuries and other important details;
- neurological examination, during which a specialist checks skin sensitivity, motor function, muscle strength, quality of reflexes, functioning of the central nervous system, etc.;
- tests: general blood and urine analysis, biochemical blood test with mandatory determination of glucose levels, determination of antigens and antibodies to infectious diseases if their presence is suspected;
- X-ray of the chest organs: allows you to diagnose tuberculosis, tumors;
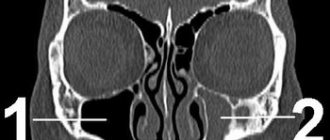
- MRI or CT scan of the brain: helps visualize tumors, areas of acute ischemia, hemorrhages, consequences of injuries and strokes;
- CT scan of the temporal bone;
- electroneuromyography: assessment of the speed of impulse transmission along nerve fibers and muscles, allows you to determine the level of damage and severity of the disease;
- consultations with specialists: therapist, otorhinolaryngologist, endocrinologist, infectious disease specialist, if necessary.
The list of studies can be adjusted depending on the specific clinical situation.
Indications and contraindications for EMG of facial muscles
Neurophysiologists at the Yusupov Hospital perform electromyography of the masticatory and facial muscles of the face if there are the following indications:
- Loss of sensitivity and pain in the facial area;
- Drooping of the upper eyelid and corner of the mouth, smoothness of the nasolabial fold;
- Increased fatigue in the facial muscles;
- Muscle twitching in the facial area;
- Impaired function of the temporomandibular joint;
- Atrophic changes in the facial muscles;
- Local muscle spasms in the facial area.
In some cases, electroneuromyography can detect changes in the condition of nerves and muscles before the onset of symptoms of the disease, which contributes to early treatment and a favorable prognosis of the disease. Electromyography is used to assess the effectiveness of therapy and prognosis for diopathic neuropathy of the facial nerve (Bell's palsy). The most sensitive indicators are:
- In the most acute period (up to the fifth day) - the threshold of nerve excitability;
- In the acute period (from the tenth to the fourteenth day) - the percentage of drop in the amplitude of the m-response on the affected side in relation to the healthy side and the reversibility of impaired excitability;
- Starting from the twenty-first day - denervation changes in the muscles.
The most sensitive parameters of facial nerve electromyography for assessing the effectiveness of therapy are changes in the amplitude and latency of the M-response. The use of electromyography in the acute period of neuritis allows us to answer several basic questions
- Central or peripheral paresis of the facial nerve;
- The trunk or individual branches of the facial nerve are affected;
- What predominates – axonopathy, demyelination or a mixed process;
- What is the prognosis for recovery of nerve function?
The first EMG for facial nerve neuropathy is performed within the first four days after the onset of paralysis. The study consists of two parts: electromyography of the facial nerve and study of the blink reflex on both sides. The second EMG is performed 10–15 days after paralysis. Third – 1.5–2 months from the onset of the disease. If during the treatment process there is a need to evaluate the effectiveness of the therapy, additional studies are carried out on an individual basis.
The procedure is not performed on patients suffering from mental disorders and epilepsy, since manipulations on the face can cause them to have an inadequate reaction or an epileptic attack. EMG of the facial muscles is temporarily postponed if the patient has a high temperature, pustular diseases or a violation of the integrity of the skin at the sites where the electrodes are applied, or with an exacerbation of chronic somatic diseases.
Treatment of facial nerve neuropathy
A combination of drug and non-drug methods is used for treatment. As a rule, doctors prescribe medications from these groups:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): ibuprofen, meloxicam, nimesulide, diclofenac and other drugs; necessary to relieve pain and inflammation, eliminate swelling; used for mild to moderate neuropathy;
- glucocorticosteroids: prednisolone, hydrocortisone, dexamethasone; have an anti-inflammatory effect, relieve swelling; used for severe forms of the disease, as well as when NSAIDs are ineffective;
- diuretics: furosemide, lasix; necessary to eliminate tissue swelling;
- vascular drugs: pentoxifylline, nicotinic acid, cavinton; stimulate active blood flow in the affected area, improve tissue nutrition;
- metabolic agents: actovegin; necessary to stimulate metabolism and regenerate damaged structures;
- antiviral and antibacterial agents for the infectious nature of the pathology;
- anticholinesterase drugs: neuromidin, axamon; improve the transmission of excitation from nerve to muscle, help to quickly get rid of paralysis of facial muscles;
- B vitamins: milgamma, combilipen; stimulate nerve regeneration and improve impulse conduction.
If neuropathy has become chronic and muscle paresis has given way to spasm, muscle relaxants are prescribed: mydocalm, carbamazepine, baclofen. They replace anticholinesterase drugs and promote muscle relaxation. If these remedies are ineffective, injections based on botulinum toxin are used.
Drug treatment is complemented by physiotherapy. In the acute period the following are used:
- UHF;
- exposure to alternating magnetic field;
- phonophoresis with hormones.
After one and a half to two weeks from the onset of the disease, these methods are added:
- electrotherapy (diadynamic currents, etc.);
- electrical stimulation of muscles;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- Darsonvalization.
An additional effect is provided by mud applications, therapeutic baths, and acupuncture.
During the acute period it is also recommended:
- sleep only on your side (affected side);
- tie a scarf around your face to prevent stretching of paralyzed muscles;
- carry out muscle taping: tighten the muscles using an adhesive plaster (duration from 30-60 minutes to 2-3 hours);
- tilt your head in the direction of the lesion several times a day and support the muscles with your palm; The duration of the procedure is 10-15 minutes.
After acute inflammation has subsided, it is recommended to perform therapeutic exercises to develop the affected muscles:
- frown and raise your eyebrows;
- open and close your eyes wide;
- widen the nostrils;
- puff out one's cheeks;
- smile with your mouth open and closed;
- stretch out your lips, blow out an imaginary candle, whistle;
- stick out tongue, etc.
The more the patient grimaces, the faster the muscles will recover. During the same period, a light therapeutic massage to stimulate blood circulation is acceptable.
If treatment does not bring effect within 2-3 months, doctors recommend using surgical treatment methods. Two types of operations are used:
- restoration of impulse transmission along the nerve: decompression of the nerve fiber when it is compressed in the canal of the temporal bone;
- reinnervation: replacement of the affected area with a donor nerve (segment of the hypoglossal, phrenic or accessory nerve, as well as healthy branches of the facial nerve);
- partial suturing of the eyelids (tarsophasia);
The choice of a specific treatment method depends on the form of the disease, its cause, severity and level of damage.
Make an appointment
Methods for conducting EMG of facial muscles
Doctors recommend that patients, on the eve of EMG of the facial muscles, in consultation with the treating neurologist, stop taking medications that affect the nervous system and do not drink chocolate, coffee, tea, cola and other tonic drinks. You should refrain from smoking on the day of the procedure. Before applying electrodes to the skin of the face or inserting them into muscles, the patient is asked to remove metal jewelry from the face and ears.
Stimulation electromyography of the masticatory and facial muscles is performed using electrodes that are applied to certain points on the facial skin. Then an electrical discharge of minimal strength is applied. Using a computer program, the speed and volume of excitation passing through the nervous tissue is recorded. Based on these data, the neurophysiologist makes a conclusion about the state of the nervous tissue and the level of its damage.
When performing needle EMG of the facial muscles, the doctor inserts a special conductor needle into the facial muscle. Through it, muscle tissue is stimulated with electric current, followed by registration of the response and processing by a computer program. When performing needle EMG of the facial and trigeminal nerve in the Yusupov Hospital, only special high-quality disposable foreign-made needle-guides are used. The combined use of needle and stimulation electromyography techniques of facial muscles and nerves makes it possible to assess their condition with maximum accuracy, timely establish a final diagnosis and prescribe adequate therapy.
Prevention
Compliance with the rules for the prevention of facial nerve neuropathy can reduce the likelihood of pathology occurring. This is especially true if there is an increased risk of developing the disease. Doctors recommend:
- avoid hypothermia and facial injuries;
- observe safety precautions at work to prevent eye damage;
- consult a doctor in time for infections and otitis media;
- control blood sugar levels;
- promptly diagnose and treat chronic diseases.
Reviews
05/16/2017 This is not the first time I have contacted a neurologist, I am very pleased with the service.
Thank you very much for your work. I will come to you again. Meshkova
01/15/2018 I am very grateful to all the employees for their attentive attitude towards people and the qualifications of a neurologist.
Povozhilova
04/21/2020 I visited the orthopedist Alexey Vadimovich Abzianidze.
Doctor is great! An excellent professional and sincere person! T XXX E.V.
Read all reviews
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
Facial nerve neuropathy requires the fastest and most accurate diagnosis and comprehensive, comprehensive treatment. Only in this case can a rapid restoration of impaired functions be achieved. Neurologists at the Energy of Health clinic use the most effective techniques:
- modern drug regimens that affect the cause of the disease and relieve symptoms;
- physiotherapy courses for tissue restoration;
- massotherapy;
- training in facial gymnastics techniques;
- taping the affected areas;
- observation throughout therapy, adjustment of dosages and medications if necessary;
- a full range of measures for quick and complete rehabilitation;
- organization of sanatorium-resort treatment for the most complete recovery.
Advantages of the clinic
The Health Energy Clinic provides each visitor with medical care of the highest level, regardless of his age and reason for visiting. We offer:
- screening diagnostic programs to assess health status;
- accurate and quick diagnosis of obvious and hidden pathologies;
- modern methods of drug therapy, physiotherapy, exercise therapy, massage;
- minor surgical operations within the walls of the clinic;
- course treatment of chronic diseases in comfortable day care wards;
- organization of hospitalization in a specialized hospital if necessary;
- preparation of documents for sanatorium-resort treatment, selection of sanatorium;
- remote consultations with foreign doctors to obtain an alternative opinion;
- modern rehabilitation programs.
Facial nerve neuropathy is a fairly common pathology. To prevent it from leading to irreversible facial asymmetry, contact a specialist as soon as possible. Neurologists at the Energy of Health clinic will always come to the rescue.
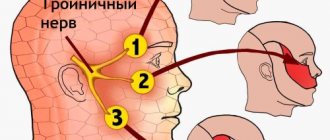
Electromyography of the facial and trigeminal nerve
Electromyography of the facial nerve helps determine the cause of weakness or increased excitability of the masticatory and facial muscles. Electromyography of the trigeminal nerve is necessary to establish the cause of pain, disturbances in facial sensitivity and function of the masticatory muscles. Neuroscientists record the electrical activity of facial muscles and the nerves that control these muscles using various types of electrodes.
When conducting electromyography of the facial and trigeminal nerve, neurophysiologists at the Yusupov Hospital conduct a study of the blink reflex. The trigeminal nerve primarily consists of sensory fibers. Through them, excitation is transmitted from sensitive receptors of the face to brain cells. The facial nerve consists of motor fibers. It sends commands from the brain to the facial muscles. In the brain, both nerves form a reflex arc: in response to an impulse from the trigeminal nerve system, the facial nerve sends an exciting signal to the facial muscles. This reflex arc is examined using electromyography.
The neurophysiologist places electrodes on certain points of the face to stimulate excitation in the trigeminal nerve system and record the response in the facial nerve system. It then administers a series of stimuli and records the responses to them. The information is subject to computer processing. A neurologist-neurophysiologist receives measurement results, draws up a conclusion and gives recommendations for treating the disease.
In order to undergo EMG of the facial and trigeminal nerve, masticatory muscles of the face, call the Yusupov Hospital. The contact center operates 24 hours a day, seven days a week, including lunch breaks. You will be scheduled for a consultation with a neurologist-neurophysiologist at a time convenient for you. The price of EMG of the facial and trigeminal nerves and facial muscles at the Yusupov Hospital is lower than in other Moscow clinics, despite the high quality of the research.