Neuralgia is an acute pain syndrome that has a paroxysmal nature and occurs along the affected nerve.
In most cases, this pain syndrome is a consequence of spinal osteochondrosis, abnormal development of the skull, and herpes zoster.
Pain is often of a high degree, and therefore requires timely treatment. We will talk about the symptoms of nerve inflammation on the right and left side, the treatment of neuralgia in men and women in the article.
Causes and manifestations of the disease
Neuralgia can have different localizations. The most common types of neuralgia and their main manifestations:
- Intercostal - acute shooting pain along the intercostal spaces, intensifying with deep breathing and the slightest movement, pain when pressing along the intercostal spaces.
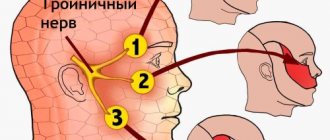
- Trigeminal nerve - pain along one of its branches, a crawling sensation in this area.
Localization of pain: half of the forehead when the first branch is affected; the area from the palpebral fissure to the upper lip is the second branch; the area of the chin and lower lip is the third branch. - External cutaneous nerve of the thigh - shooting and burning along the outer surface of the thigh.
- Pterygopalatine ganglion - pain in the palate, temples and eyes.
- Glossopharyngeal nerve - unpleasant sensations in the ear, pharynx and lower jaw on the affected side.
- Occipital nerve - burning in the back of the head and temples.
Neuralgia pain usually occurs suddenly, sometimes after exposure to provoking factors:
- for neuralgia of the trunk and limbs - heavy lifting, incorrect sleeping position;
- for neuralgia of the facial area - carious teeth, herpes, hypothermia of the nerve zone.
The pain syndrome with neuralgia on the right and left is no different.
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia
To increase the effectiveness of the measures taken, the doctor should have the most complete picture of the current disease.
And the use of various measures that complement each other and increase the effect of each type of treatment makes it possible to quickly relieve pain and ensure the ability to lead a full life.
The general scheme of treatment procedures should look like this:
- The patient should lie on a flat and hard surface (the harder the surface of the bed the patient has, the more effective the pain relief will be. You can even install a hard shield under the mattress), remain completely at rest and avoid any stress. To reduce pain, you should help him perform household activities without giving him excessive physical activity.
- Chest pain relief. Sometimes the pain with intercostal neuralgia is so strong that even breathing is difficult. Therefore, relieving pain will help to quickly return the patient to normal life and begin to eliminate the inflammatory process that became the root cause of the disease. Both tablets and injections that have an analgesic effect can be used as painkillers. Novocaine blockades can relieve pain when it is very severe.
- Inflammation is also relieved by most painkillers.
- Elimination of spasms can be done through the use of muscle relaxants and agents that relieve excess tension.
- Injections and vitamin B preparations (B6 and B12 are most effective for thoracic neuralgia) restore the structure of tissues and nerve fibers.
- Sedatives will help reduce the patient’s anxiety and relieve excessive nervous tension.
- Topical application of dry heat, which can be used in limited quantities, also relieves pain and soothes.
As an additional treatment, the doctor often prescribes the use of various physiotherapeutic procedures, which include massage (relaxing and restoring normal blood circulation), acupuncture and manual therapy, which are also aimed at stopping inflammation and relaxation.
For more effective treatment, after relieving severe pain and underlying inflammation in the nerve roots of the spine, the doctor may recommend a secondary examination.
This is necessary to clarify the effectiveness of treatment and establish the nature of the disease (the different nature of the disease - from an infectious disease, pathological processes in the spine, with severe stress or physical overload requires the elimination, first of all, of the main cause of neuralgia).
Folk remedies
After all, they have been tested for years and by more than one generation of our ancestors.
Their use can be recommended in combination with basic drug treatment.
What alternative treatment methods can be offered for thoracic neuralgia?
- Pain relief can be achieved by taking tinctures of valerian, lemon balm, immortelle, as well as lemon peel mixed with orange, warm tea with honey and lemon;
- The pain will be relieved by regularly rubbing fresh horseradish or black radish juice into the skin of the affected area;
- Baths taken in the evening, with the addition of sea salt and sage decoction, relax and relieve pain;
- The juice of the well-known geranium also copes well with soreness. To do this, a leaf of the plant is crushed and applied to the affected area, covered with a warm cloth (scarf) and left for several hours.
The listed methods will help to quickly relieve pain and reduce inflammation, but do not replace standard treatment prescribed by a doctor.
Many people who complain of pain in the chest area do not consider it necessary to treat this condition, citing a pinched nerve that will go away on its own. However, this disease does not go away on its own. How to treat intercostal neuralgia will be discussed in the next topic.
We will consider groups of drugs for the treatment of intercostal neuralgia in this article. Muscle relaxants, anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins and other medications.
Which doctor should I contact?
A neurologist treats neuralgic pain . When contacting, the specialist conducts:
- visual inspection;
- functional tests;
- prescribes radiography or magnetic resonance imaging of the skull or spine.
In addition, often the cause of neuralgia is herpes zoster . If characteristic blistering rashes along the nerve are detected, the doctor may prescribe a blood test to determine antibodies to the varicella zoster virus.
Consultation with a specialist for this pain syndrome is mandatory, especially if we are talking about intercostal neuralgia. Depending on the location, it may resemble heart disease (read here about how to distinguish heart pain from neuralgia), renal colic, an attack of cholecystitis and pancreatitis.
Sometimes neuralgia is of an atypical nature, as a result of which an electrocardiogram or ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity may be required.
Varieties
Neuralgia can “attack” any nerve, but still more often clinicians diagnose the following types of illness:
- neuralgia of the facial or trigeminal nerve;
- back neuralgia;
- sciatic nerve neuralgia;
- neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve;
- neuralgia of the occipital nerve.
Locations of pain in neuralgia
How to relieve an attack of acute pain: first aid
What to do in case of an acute attack of neuralgia? For quick relief of pain, drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are suitable.
These include:
- Ketonal;
- Diclofenac;
- Indomethacin;
- Ketorol;
- Ibuprofen, etc.
The pain usually subsides within half an hour after taking it . However, pain relief by taking painkillers is not a reason to postpone a visit to the doctor.
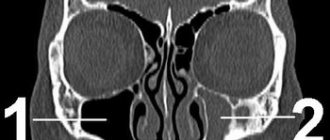
Diagnostics
If the symptoms listed above appear, you must contact a medical facility as soon as possible to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment plan. The doctor can assume the presence of such an illness during an initial examination and assessment of the patient’s complaints. To confirm the preliminary diagnosis, the patient is referred for additional examinations.
Diagnostic methods:
- X-ray;
- CT;
- NMR;
- blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine;
- blood biochemistry.
Features of nervous regulation
Nervous regulation is the second type of communication, built according to a vertical type with bilateral connections. The highest command center is the cerebral cortex. If pain is analyzed in ancient centers that exist even in the spinal cord (primary pain analyzers), then in the cerebral hemispheres pain takes on an emotional connotation. In addition, a change in a person’s emotional background can change the duration of pain, and even turn the bright interval during which pain is expected into suffering.
The impact of stress on health
There are many studies showing that chronic stress worsens the course of all diseases without exception - from mental disorders to a bruised finger. Each of us can remember many similar cases: for example, long-awaited friends have come to visit you, you are happy and happy, and now, you are bringing a treat to the table, everyone is hungry, there is a wonderful boat ride ahead, or a hike to beautiful places - and suddenly you accidentally stubbed your little toe on the door frame.
Most likely, you will forget about the pain in a few minutes, switching to more pleasant and entertaining things.
Now imagine: you lost your job, your wife (husband) left you. Opening the door to your apartment, you discover that you have been robbed. You rush inside and, in the same way, hurt your little finger. The pain will seem a hundred times stronger and longer lasting. Sensitive subjects may even burst into tears, and strong-willed people will try to overcome the sudden onset of despair, and think that the sky itself is against you.
Until the evening you will remember this soul-shaking episode, and your finger will hurt much longer.
In the case of neuralgia, negative pain impulses are consolidated, transmitted to higher analytical centers, where the pain impulse can remain for a longer time, due to the self-induction of neural networks. In addition, the “border zone” expands - the moments of the onset of pain, before its full development, are lengthened, and the period of pain subsidence is also lengthened. It is due to this that the duration of light intervals is shortened.
If special measures are not taken, the pain can reach such intensity that a person, in search of a way out, will resort to the last resort - suicide. This is all the more possible because in our world you can find a large number of people who are ready to do this against the background of complete physical health.
Clinical anatomy
The pudendal (pudendal) nerve is a paired nerve, the branches of which are located on the right and left sides of the human body.
- Nerve roots – S2-S4
- Sensory branches - innervate the external genitalia of men and women, as well as the skin around the anus, anal canal and perineum.
- Motor branches - innervate a number of pelvic floor muscles, the external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter.
- Autonomic - carry sympathetic nerve fibers to the skin of the dermatomal area S2-S4.
Entrapment of the pudendal nerve at different levels (sciatic spine, sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments, Alcock's canal) is the cause of disabling, chronic and intractable pelvic pain. This pain is highly varied and complex because it is often associated with a variety of functional symptoms that are confusing.
Clinical picture
The clinical characteristic of PN is pain in the pelvic area, which increases during the day while sitting and decreases if the patient gets up or lies down. Symptoms also include sexual dysfunction and difficulty urinating and/or defecating. To confirm the diagnosis, it is recommended to use the Nantes criteria. The pain is similar to that experienced by patients with compressive neuropathy.
In most cases, patients describe neuropathic pain as burning, tingling, or numbing, worsening when sitting.
At an early stage, the pain may only appear while sitting, but over time it becomes more or less constant and only gets worse from sitting. Many patients with PN are unable to sit down at all. It is curious that sitting on the toilet is much less painful for them, which is most likely due to the fact that in this case the pressure is not on the pelvic floor muscles, but on the ischial tuberosities. Basically, pain with PN only gets worse as the day goes on.