Trigeminal neuralgia is a disease of the peripheral nervous system, manifested by severe pain in the area of innervation of several or one branch of the trigeminal nerve.
The nerve received its name due to the fact that it includes 3 branches: the ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular. Patients often call it the facial nerve. The localization of pain will depend on which branch is affected. If the first branch is affected, then pain is felt in the forehead, in the temporal part, above the eyebrow.
When the maxillary branch of the trigeminal nerve is damaged, pain occurs in the area of the nose, facial muscles, and upper jaw. Accordingly, if the third branch is affected, then the symptoms will appear in the area of the neck, chin and lower jaw - the symptoms resemble toothache. It is necessary to distinguish between neuritis and trigeminal neuralgia. Neuritis is a process always associated with inflammation of the nerve. With neuralgia, no inflammation is observed.
What it is?
Trigeminal neuralgia (trigeminal neuralgia) is a lesion of one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve, characterized by paroxysmal pain. In 65% of cases, women over 50 years of age are affected.
The disease occurs in 2 forms: primary (isolated damage to the nerve itself) and secondary (as a consequence of another disease). The trigeminal nerve is part of 12 pairs of cranial nerves. Its purpose is to provide facial sensitivity. This nerve runs on both sides of the face (right and left), and in turn is divided into 3 bundles: the first (ophthalmic) innervates the eye, upper eyelid and forehead; second (maxillary) - lower eyelid, cheeks, nostrils, upper lip and gums; third (mandibular) - lower jaw, lips and gums.
Trigeminal neuralgia is defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain as a syndrome characterized by sudden, short-term, intense, recurring pain in the innervation of one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve, usually on one side of the face.
Where is the trigeminal nerve located?
In the human body there are 12 pairs of nerves located in the cranial cavity. The trigeminal node is the 5th and largest of them. The paired arrangement of fibers means they are located on the face on the left and right sides.
The nerve originates in the temporal part of the face opposite the upper tips of the ears and is divided into 3 branches:
1. The ocular branch provides sensitivity:
- eye;
- upper eyelid;
- frontal skin.
2. The maxillary nerve controls sensation:
- lower eyelid;
- nostrils;
- cheeks;
- upper lip;
- upper gum.
3. The mandibular part is responsible for sensitivity and motor ability:
- lower jaw;
- lower lip;
- lower gum;
- some masticatory muscles.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The exact causes of trigeminal neuralgia are unknown. However, there are several factors that can trigger the disease:
- Viral nerve damage - neuro-AIDS, polio, herpetic infection;
- Odontogenic causes (due to problems with teeth) - dental flux, jaw injury, reaction to anesthesia, unsuccessful tooth filling;
- Diseases of the nervous system - cerebral palsy, meningitis, multiple sclerosis, meningoencephalitis (viral, tuberculosis), hypoxia (lack of oxygen in the brain), encephalopathy due to head injuries, epilepsy, infectious process, circulatory disorders and brain tumors;
- Compression of the trigeminal nerve - brain tumors, injuries and scars, excessive growth of connective tissue due to an infectious process, dilation of brain vessels (aneurysms, atherosclerosis, congenital pathologies of vascular development, ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, increased intracranial pressure due to osteochondrosis).
In neurology, it is also common to identify a number of unfavorable factors that increase the risk of trigeminal neuralgia:
- the patient's age is over 50 years;
- stress;
- chronic fatigue;
- mental disorders;
- autoimmune and allergic diseases;
- avitaminosis;
- metabolic disease;
- infectious diseases (syphilis, botulism, tuberculosis);
- inflammation of the oral cavity (pulpitis, gingivitis).
In neurology, there are two mechanisms for the formation of trigeminal neuralgia. One of the mechanisms involves the destruction of the myelin sheath. This process is also called demyelination. As a result of damage, the nerve fiber becomes unprotected, and the nerve impulse spreads to the nearest nerve fibers. As a result, severe irritation of neurons occurs and pain occurs.
The second mechanism for the development of pathology involves a violation of the regulation of the functioning of the trigeminal nerve of the central nervous system. Due to damage to the nerve fibers, the nerve impulse is inhibited, which leads to irritation of the trigeminal nerve nuclei and, as a result, pain. There is an assumption that both of these mechanisms can sequentially follow each other. Therefore, treatment of the disease should be aimed at both activating the restoration of the myelin sheath of nerve fibers and inhibiting nervous processes.
Preventive measures
It is impossible to avoid all potentially dangerous factors, especially considering that some causes are congenital: narrowness of the canals, pathologies in the structure and location of blood vessels. However, you can reduce the risk of developing the disease by eliminating several provoking factors. As primary prevention you should:
- avoid hypothermia of the face and head;
- promptly treat diseases that can give rise to trigeminal neuralgia;
- avoid head injuries.
Doctors consider only timely treatment of diseases of the trigeminal nerve to be a complete secondary prevention, so at the first symptoms of pathology you should immediately contact the clinic.
First signs
The first symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia:
- sudden paroxysmal one-sided very intense (burning, shooting) pain along the nerve fiber;
- immobility of the patient;
- facial muscle spasm;
- attack duration is up to 3 minutes, in 7% of patients - up to 3 days;
- frequency of attacks 1-10 per day;
- the pain doesn’t go anywhere;
- excessive drooling and lacrimation;
- dilated pupils;
- decreased or increased sensitivity of facial skin;
- in 99% of cases the attack occurs during the day.
Possible complications
Trigeminal neuralgia cannot be triggered; Fothergill's disease causes complications :
- paresis of facial muscles;
- hearing loss;
- irreversible damage to the nervous system, including inflammation in the brain.
It is categorically impossible to relieve pain with analgesics and hope that neuralgia will go away on its own. This is a serious neuralgic disease that should only be treated by a doctor. The sooner the patient seeks help, the more successful and less lengthy the therapy will be.
Symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia
The clinical manifestations that accompany trigeminal neuralgia are quite specific, so diagnosing the disease is usually not difficult for a qualified specialist.
Moreover, only in 23% of patients the initial stage of the disease is accompanied by typical signs; in the remaining 77% of cases, the first symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia appear in the preneuralgic form. At this stage, patients are periodically bothered only by short-term shooting pains of low intensity. Painful sensations usually occur quite suddenly in the absence of clearly defined trigger factors (circumstances that aggravate the disease). Attacks of pain occur several times a day, but do not significantly affect the quality of life.
A course of treatment with acupuncture and physiotherapeutic methods, as well as taking vitamin complexes, can eliminate unpleasant manifestations. On average, the pain disappears after about three weeks. However, after one and a half to two years, a person experiences a full-fledged, fully developed trigeminal attack, which is characterized by:
- Severe intense shooting pain in the face (it is paroxysmal and lasts from 10-15 seconds to 2 minutes);
- The presence of a refractory period between attacks, during which there is no pain (its duration depends on the severity of the exacerbation);
- Localization of pain that has not changed for several years within the innervation trigeminal territories;
- A certain extent and direction of paroxysm (pain occurs clearly in one area of the face and flows to another);
- The presence of areas of increased sensitivity and trigger (painful) zones on the face - most often they are localized in the area of the nasolabial triangle and the alveolar process;
- The presence of trigger factors (for example, trigeminal neuralgia often manifests itself during brushing teeth, chewing or talking);
- Freezing of the patient at the time of the attack in the position in which he found him (patients never scream, cry or attempt to move);
- Trembling of the chewing or facial muscles at the peak of an attack.
In addition, people with Fothergill's disease experience radiating pain upon palpation of the spinous processes of the cervical vertebrae (Kerr's points), and at the peak of exacerbation a characteristic "staircase" symptom appears - a trigeminal lumbago (often weakened), which occurs if the patient stumbles while descending stairs
Another characteristic symptom of trigeminal neuralgia is the so-called “careful touch” syndrome, when the patient, trying to show the localization of pain, does not bring his finger to the skin of the face, so as not to provoke a trigeminal attack. Over time, most patients develop the habit of chewing on the “healthy” side of the face.
Symptoms
The disease is more typical for middle-aged people, most often diagnosed at 40-50 years of age. Females suffer more often than males. Damage to the right trigeminal nerve is most often observed (70% of all cases of the disease). Very rarely, trigeminal neuralgia can be bilateral. The disease is cyclical, that is, periods of exacerbation are followed by periods of remission. Exacerbations are more typical in the autumn-spring period. All manifestations of the disease can be divided into several groups: pain syndrome, motor and reflex disorders, vegetative-trophic symptoms.
Pain syndrome
Patients with trigeminal neuralgia experience attacks of intense pain in the area of innervation of the affected branch of this nerve.
Nature of the pain: the pain is paroxysmal and very intense, excruciating, sharp, burning. During an attack, patients often freeze and do not even move; they compare the pain to the passage of an electric current, or a shooting sensation. The duration of the paroxysm is from several seconds to several minutes, but during the day the attacks can be repeated up to 300 (!) times.
Localization of pain: pain can affect both the innervation zone of one of the branches and the entire nerve on one side (right or left). One of the features of the disease is the irradiation (spread) of pain from one branch to another, involving the entire half of the face. The longer the disease exists, the more likely it is to spread to other branches. Localization zones:
- optic nerve: forehead, anterior scalp, bridge of the nose, upper eyelid, eyeball, inner corner of the eye, mucous membrane of the upper part of the nasal cavity, frontal and ethmoid sinuses;
- maxillary nerve: upper part of the cheek, lower eyelid, outer corner of the eye, upper jaw and its teeth, wing of the nose, upper lip, maxillary sinus, mucous membrane of the nasal cavity;
- mandibular nerve: lower part of the cheek, chin, lower jaw and its teeth, lower surface of the tongue, lower lip, mucous membranes of the cheeks. The pain can radiate to the temple, back of the head, neck. Sometimes the pain is clearly localized in the area of one tooth, which prompts patients to go to the dentist. However, treating this tooth does not eliminate the pain.
Pain provocation: the development of pain paroxysm can be caused by touching or light pressure on the so-called trigger (trigger) zones. These zones are quite variable in each individual patient. Most often this is the inner corner of the eye, the back of the nose, the eyebrow, the nasolabial fold, the wing of the nose, the chin, the corner of the mouth, the mucous membrane of the cheek or gum. An attack can also be provoked by pressing on the exit points of the branches on the face: the supraorbital, infraorbital, and mental foramen. Pain can also be caused by talking, chewing, laughing, washing your face, shaving, brushing your teeth, applying makeup, even blowing wind.
Behavior during an attack: patients do not cry, do not scream, but freeze, trying not to move, rubbing the pain area.
Motor and reflex disorders:
- spasms of the facial muscles (hence the name of the disease “painful tic”): during a painful attack, involuntary muscle contraction develops in the orbicularis oculi muscle (blepharospasm), in the masticatory muscles (trismus), and in other facial muscles. Often muscle contractions extend to the entire half of the face;
- changes in reflexes - superciliary, corneal, mandibular - which is determined during a neurological examination.
Vegetative-trophic symptoms: observed at the time of the attack, in the initial stages they are slightly expressed, and as the disease progresses, they are necessarily accompanied by a painful paroxysm:
- skin color: local pallor or redness;
- changes in gland secretion: lacrimation, drooling, runny nose;
- late signs: develop with long-term existence of the disease. There may be swelling of the face, greasy or dry skin, and loss of eyelashes.
In the late stage of the disease, a focus of pathological pain activity forms in the visual thalamus (thalamus) in the brain. This leads to a change in the nature and location of pain. Eliminating the cause of the disease in this case no longer leads to recovery. The distinctive features of this stage of the disease are as follows:
- pain spreads to the entire half of the face from the onset of paroxysm;
- touching any part of the face causes pain;
- Even the memory of it can lead to a painful paroxysm;
- pain may occur in response to stimuli such as bright light or loud sound;
- the pain gradually loses its paroxysmal nature and becomes constant;
- vegetative-trophic disorders intensify.
Diagnostics
At the first meeting, the neurologist is interested in the patient’s medical history, finds out what diseases there are in the anamnesis, and what could provoke an attack of neuralgia.
The following data indicate trigeminal neuralgia:
- The onset of the disease is abrupt and unexpected; the patient can always describe how the first attack occurred;
- Alternating attacks with periods of calm;
- Pain begins even with slight irritation of the sensitive areas of the nerve;
- Manifestation of the disease on one side of the face;
- It is not possible to relieve pain using anesthetics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
A visual inspection provides the following information:
- In general, the patient’s condition is satisfactory, but there may be manifestations of a mental disorder and neurotic reactions. The patient is anxious, he does not allow the painful area to be touched, he points to it himself, but does not touch the skin.
- Pathologies from the internal organs are not detected.
- No changes in the skin. With a long course of the disease, changes are still possible; they are manifested by dry skin, peeling, the presence of folds, and signs of atrophy.
Important! If the pathological process has affected the brain, symptoms of focal lesions are present. This may be drooping eyelids, differences in pupils, or respiratory problems. If such symptoms are detected, it is mandatory to conduct a brain examination using instrumental methods.
Laboratory research methods for suspected trigeminal neuralgia are not relevant, since general indicators are usually normal.
Instrumental diagnostics for trigeminal neuralgia involves the use of the following methods:
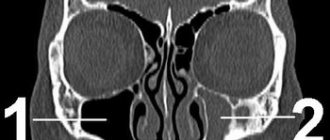
- Magnetic resonance imaging. This is the most informative method of studying the brain, allowing us to identify existing changes in its structures. Thanks to MRI, the specialist receives a three-dimensional image. In the case of trigeminal neuralgia, an MRI is performed to exclude compression of the nerve by tumor formations, vascular pathologies, and sclerosis.
- A CT scan produces a 2-dimensional image. Using this method, existing central nervous system diseases can be detected.
- It is also necessary to evaluate the speed at which the impulse moves along the nerve fibers. This information can be obtained using electroneurography. This method allows not only to confirm the presence of a lesion, but also to find out its level and mechanism of occurrence, as well as assess the scale of the problem.
- A variant of ENG is electroneuromyography. In addition to the parameters determined by ENG, this method makes it possible to identify the sensitivity threshold and the degree of contraction of muscle fibers.
Causes of development of trigeminal neuritis
Despite the fact that the disease has been well studied, the exact causes of the disorder are not yet fully understood. According to current views, the most common culprit factors are the following:
Infectious processes at the local level
We are talking about a variety of violations. Including such common ones as caries or tonsillitis (throat infection by an infectious agent). Depending on the general level of immunity, the patient can endure the septic process for a long time without any particular reaction to it. But the line is fine. As soon as the body's defenses weaken, the disorder manifests itself and begins with severe symptoms.
Correction of trigeminal neuritis involves eliminating the root cause. It is necessary to sanitize the source of infection. It is also worth noting that infections of a distant nature, prone to dissemination and spread throughout the body, have the same danger. For example, syphilis and tuberculosis have such properties. The likelihood of expansion is high. A common culprit in the onset of the disorder is sinusitis. In particular - sinusitis. Especially with a long course without proper therapy.
Tumor processes
Cranial or facial localization. In this case, compression of nerve tissue occurs. Tumor and large non-tumor formations (such as cysts) cause a mass effect when they are of sufficient size and in a certain direction of growth. In this case, it is not difficult to identify the etiology of the disorder, given that the visual picture is informative. Treatment is very difficult due to the usually complex localization of neoplasia.
Multiple sclerosis
Demyelinating disease. Multiple sclerosis is characterized by damage to a special membrane that covers nerve fibers and is involved in the normal conduction of impulses. The myelin sheath is destroyed, in the early stages the symptoms are represented by pain, but as the disorder progresses, the discomfort disappears and turns into a persistent neurological deficit with paresis and other disorders. Treatment is systematic. Aimed at correcting demyelination itself.
Facial injuries
Damage up to fractures. The normal configuration and anatomical structure of bone structures changes. Even slight displacement or thickening of bones can cause compression of nerve fibers. Is it dangerous.
Recent surgeries
Trigeminal neuritis can develop even after tooth extraction or puncture of the maxillary sinus. Therefore, the advisability of radical assistance is determined separately, in each specific case, after a thorough diagnosis and assessment of the situation. This may also include more extensive interventions. Be it surgical interventions for tumors of the facial area, brain, and others.
Nonseptic autoimmune diseases
They are much less common. They are characterized by an inadequate immune response when the body’s own defenses begin to attack healthy cells. Recovery is possible only with a complex effect on inflammation and pain.
The causes of the development of trigeminal neuritis are determined in the system; all possible factors must be taken into account in order to obtain a complete picture of the pathological process.
Treatment
For many centuries, millions of people suffering from trigeminal neuralgia have been hostage to the disease. After all, there were no effective treatments. And finally, in the middle of the last century, carbamazepine (finlepsin, tegretol, etc.) was synthesized, which began the era of real help for suffering patients. The drug belongs to the group of anticonvulsants (anticonvulsants). Later it turned out that other drugs in this group are effective in preventing and eliminating neuralgic pain. However, carbamazepine is still the most widely used.
Treatment begins with minimal doses, gradually increasing them until a positive effect is achieved. The drug is taken at this dose for at least a month, and then the patient is gradually transferred to lower doses. If the attacks return, the amount of the drug is increased again, but in half of the first-time patients it is possible to completely stop taking carbamazepine. As the duration of the disease increases, the effectiveness of treatment decreases, and patients with “experience” have to undergo treatment for several years, and sometimes even decades.
For approximately one in seven patients, carbamazepine is ineffective. In such cases, other drugs from the group of anticonvulsants are selected. Already in our century, a new drug of this class has appeared, even more effective and with fewer side effects than carbamazepine - pregabalin (gabapentin, Lyrica).
In addition to anticonvulsants, patients receive:
- antidepressants (amitriptyline), which inhibit the conduction of pain impulses;
- myolytics (sirdalud, baclofen) to reduce muscle tone and reduce facial muscle tension;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, ibuprofen).
Medicines play a leading role in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia, but the additional prescription of physiotherapeutic procedures can reduce their doses and shorten the duration of treatment. In such cases, the following are effective:
- sinusomodulated currents (SMC);
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- reflexology.
Treatment methods
Treatment of trigeminal neuritis is carried out depending on the specific root cause of the pathological process. Thus, for infectious diseases, antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and immunomodulators are used as needed. Autoimmune disorders require immunosuppression, that is, suppression of the defenses. Additionally, glucocorticoid drugs are used in short courses so as not to provoke side effects.
Actually, the pain and symptoms of trigeminal neuritis themselves can be relieved at home with a group of medications:
- antiepileptic, anticonvulsant, anticonvulsants;
- in relatively mild cases, you can use analgesics - Pentalgin and other modern medications to eliminate discomfort, unfortunately, the effectiveness of these in most cases is almost zero, they do not relieve neuralgia;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to correct the condition (use involves short courses);
- If necessary, vitamin and mineral complexes are prescribed.
Drug correction is the main method. The principle of therapy involves minimalism and a gradual transition to more radical measures, first with medication and then with another plan.
How to treat neuritis if the trigeminal nerve hurts and nothing helps?
If the discomfort causes many problems and does not go away, novocaine blockades are necessary. They effectively eliminate discomfort. The effect lasts up to several days, depending on the applied technology of exposure.
In extreme cases, when there is no effect from anything, surgical treatment is necessary. Minimally invasive intervention. On the other hand, surgical treatment is necessary for tumors and anatomical defects.
After eliminating the acute phase using medicinal methods, it is necessary to consolidate the result. The condition is then corrected through massage and physiotherapy.
How to treat trigeminal neuritis is determined by neurology specialists; it is important that the methods of influence are appropriate to the situation and do not create risks for the patient’s health.
Surgery
Unfortunately, in 30% of cases, drug therapy is not effective and then surgical treatment of neuralgia is recommended for patients. There are several methods of surgical treatment, and the doctor chooses the most optimal one for each patient.
Percutaneous surgery can be performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis and is recommended for patients with early stages of the disease. The procedure involves destroying the trigeminal nerve using radio waves or chemicals directed to the affected nerve through a catheter. Reduction or disappearance of pain after this operation may not occur immediately, but may take several days or months.
In stationary conditions, operations are performed aimed at decompressing the nerve, during which the position of the arteries that compress it in the skull is corrected.
Today, the most effective and safe way to treat trigeminal neuralgia is the method of radiofrequency destruction of the trigeminal nerve root. The main advantage of the method is that the size of the nerve destruction zone and the exposure time can be objectively controlled. The manipulation is performed under local anesthesia, which ensures a short and easy recovery period for patients.
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia with folk remedies is acceptable, however, in most cases it turns out to be ineffective, and patients are forced to seek help from a neurologist.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
To quickly relieve pain symptoms and complete healing, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed in tandem with drug therapy. After the start of treatment, surgical or physiotherapeutic, the pain does not recede immediately. The period of complete disappearance of paroxysm is individual and is determined by the extent of the process and the duration of the disease, so the doctor additionally prescribes painkillers.
The following procedures show the greatest effectiveness in the treatment of Trousseau's painful tic:
- laser therapy;
- diadynamic currents;
- electrophoresis using novocaine;
- acupuncture;
- ultraphonophoresis using hydrocortisone.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is an effective measure for relieving pain in trigeminal neuralgia. Depending on the degree of damage, the frequency of relapses, and the cause of neuralgia, one or another method of physical influence on the trigeminal nerve or its nuclei is prescribed.
| Ultraviolet irradiation (UVR) | Ultraviolet irradiation (namely medium wave) promotes the release of neurotransmitters that inhibit the excitation of nerve fibers and natural analgesics. Treatment duration is 10 sessions. |
| Acupuncture (acupuncture) | Acupuncture affects nerve receptors that transmit impulses to nerve fibers. In this case, several points are selected in the trigger zones and several points remotely on the opposite side. Sometimes the needles are installed for a long period - a day or more, periodically scrolling them. The duration of treatment is selected individually; often only a few procedures are enough. |
| Laser therapy | The laser is applied to the localization areas of each branch of the trigeminal nerve, as well as the nodes formed by this nerve. Laser irradiation inhibits the sensitivity of nerve fibers. On average, 10 procedures of 4 minutes are recommended. |
| Diadynamic currents | For this method, Bernard currents are used, which are electric currents with a pulse of 50 thousand hertz. Electrodes are placed on the area of trigger zones of the trigeminal nerve, including the nasal mucosa. Bernard current reduces the threshold of pain sensitivity, blocks the branches of the trigeminal nerve, thereby reducing the intensity of the pain syndrome until it stops completely. The use of diadynamic currents in combination with electrophoresis and other methods of physiotherapy is effective. Several courses of 5 days with a break of 5-7 days are recommended; the procedure lasts for 1 minute. |
| UHF | Exposure to ultra-high frequencies promotes:
15-20 sessions of 15 minutes each are recommended. |
| Electrophoresis | Electrophoresis is the introduction of medicinal substances using an electric current directly into the desired area of the nerves. To relieve pain the following is administered:
These substances block sodium-potassium channels, which facilitate the transmission of nerve impulses along the nerve. Also, using electrophoresis, you can introduce B vitamins, which will improve the nutrition of the nerve and damaged myelin sheath. It is better to alternate these procedures with other methods of physiotherapy every other day, for a total of 10 procedures. |
| Massage | Massaging the muscles of the face, head and neck improves blood circulation and lymph flow, thereby improving their nutrition. The massage is carried out carefully; it should not affect trigger zones and provoke the development of pain attacks. Use movements of stroking, rubbing, and vibration. A course of massage is prescribed only against the background of stable remission of the disease. |
All physiotherapeutic treatment methods should be used in combination with drug therapy and the elimination of factors that led to the development of the disease, since physical procedures are powerless as monotherapy (mono-one).
Symptoms of the lesion
The manifestation of any inflammatory process in a variety of localizations is pain. Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve with neuritis is accompanied by paroxysmal pain. It is called prosopalgia. The pain syndrome with neuritis of the fifth pair of cranial nerves has its own clear characteristics.
The trigeminal nerve (symptoms of inflammation include not only pain, but also sensory disturbances) when inflamed gives intense pain sensations, they are shooting in nature.
Some patients compare attacks with electric shocks. The duration varies, but usually it does not exceed 2 minutes. The intervals between attacks without pain may vary in time. It depends on the form and cause of the pathology.
Another important characteristic of prosopalgia is the so-called trigger points. Touching them under certain conditions causes another attack or even a series of attacks of pain. If these zones are absent, the trigger for prosopalgia is movements. This may include chewing or opening the mouth, changing head position, or turning the neck.
Folk remedies
Such means are not suitable as a stand-alone method. After consultation with the doctor, they can be used as additional assistance in complex therapy. Traditional treatment for trigeminal neuralgia is carried out using compresses, infusions or rubbing. You can use the following recipes:
- An infusion can be made from dried burdock and chamomile. Add 200 g of herbs to half a liter of water, boil and keep on fire for another 20 minutes. Strain the prepared broth through cheesecloth and let it brew for one day. Drink 2 hours after meals.
- Compresses are made from marshmallow root, which help restore the nerve during neuralgia and relieve pain. Take a couple of plant roots, chop them and put them in 200 ml of boiling water. The broth should steep throughout the day. Take a clean cloth, soak it in the infusion and apply it to the part of your face that hurts (inflamed), cover with a towel on top. Keep the compress for at least 1 hour.
- If the facial trigeminal nerve hurts, you can rub black radish juice. Mix it with lavender oil in a ratio of 20:1. Rub the product in the direction of the trigeminal nerve. Next, you need to wrap the sore spot so that the effect lasts longer.
Traditional recipes for the treatment of neuralgia
Drug therapy in combination with traditional recipes only reduces the pain symptom in the area of the facial nerve, without helping to remove the root cause of the disease.
The most common recipes for trigeminal neuralgia are:
- in case of severe pain, you should boil a hard-boiled chicken egg, cut it in half, and apply it to the affected area; when the egg cools down, the pain should also decrease or disappear completely;
- garlic oil is used for the treatment and prevention of neuralgia of various types; 1 tbsp. l. oil is diluted in 0.5 liters of vodka; wipe the temples and forehead with the resulting essence 2 times a day, and the attacks should disappear;
- 1 tbsp. l. peppermint is poured with 200 ml of hot water for 10 minutes. it is necessary to cook, then strain; take 100 ml morning and evening; this recipe eliminates pain in stomach diseases, gastritis, nervous shock, and neuralgic diseases;
- for neuralgia, grated horseradish is used, applied to the affected area;
- several leaves of green geranium are placed on a small piece of linen fabric; then this compress should be applied with leaves to the affected area, bandaged and wrapped in a woolen scarf; after 2 hours the pain should subside; repeat the procedure 2-3 times a day;
- 1 tsp. yarrow plants pour 1 cup. boiled water, leave and strain; consume from 1 tbsp. l. up to 1/3 stack. the infusion received on the day before meals;
- you will need 1 potato, pickled cucumber and onion; All this is finely chopped, pour in 1 liter of diluted wine vinegar, leave for 2 hours, sometimes shaking the contents; apply compresses to the painful area for 1 hour in the morning and at night;
- 4 tbsp. l. dry chamomile pour 200 ml of hot boiled water, boil for 10 minutes, strain; use 1/3 cup. three times a day before meals; has an anticonvulsant and sedative effect in trigeminal neuralgia;
- for neuralgia and rheumatism, you can use willow bark; add 1 cup to 10 g of finely ground bark. boiling water, then boil for 20 minutes over low heat, covering with a lid; when the broth has cooled, strain it; take 1 tbsp. l. three times a day.
It is worth noting that abuse of treatment with traditional methods can adversely affect human health and lead to complications. All pain-relieving components of plants are caused by their special composition. Therefore, you should consult your doctor before use to avoid further troubles.
New developments
The most modern and effective methods of treating trigeminal neuralgia can be called radiosurgery using Cyber Knife. This device uses a photon beam for treatment, which penetrates precisely into the area of inflammation and eliminates it. Treatment with Cyber Knife provides high precision radiation doses, comfortable and fast healing. In addition, the procedure is absolutely safe for the patient.
Modern treatment using Cyber Knife can be considered the most effective. This technique is used not only abroad, but also in the vast expanses of the former USSR: in Russia, Ukraine, Belarus. For your information, treatment in Moscow will cost 180,000 rubles.
How did I cure the trigeminal nerve?
First of all, you need to understand: if the trigeminal nerve hurts, it means that the entire central nervous system is not healthy . Problems can also be in the form of smallpox, shingles and even schizophrenia, epilepsy, meningitis, Parkinson's, etc. Therefore, I offer you an algorithm for treating the entire nervous system, which I tested on myself and I believe that this is the only way to heal diseases associated with it.
How and why does the human nervous system get sick and, most importantly, how to heal it?
There is an opinion that nerve cells do not recover. For example, heart cells are completely reborn after 5 years . It is through this time that our heart is renewed. Blood cells (erythrocytes) are renewed after 147 days . This is all very interesting! When you start to understand, you find out that every cell in our body has its own function, and the entire system of the body is designed so wisely that you are amazed - inside us there are entire galaxies interacting with each other.
So, neurons - the cells of the nervous system - do not have the ability to reproduce; they already have a very complex structure.
At the very beginning of our birth, we are given neurons in full. Imagine that 70% of them die before birth. The remaining neurons die gradually during life. When they say that our brain works at a small percentage of capacity, this theory is confirmed precisely by the fact that only 10% of neurons constantly interact, and the rest wait for the death of their colleagues and then replace them. It happens that we remember a lot of things from the past, but we forget what we did yesterday, they say this means that those old cells are strong and continue to live, and those that were turned on recently are weak and quickly die, taking information with them. This is the pace at which modern man lives. Or, for example, Parkinson’s disease, until 90% of the neurons die (and in this disease they die faster than usual), even symptoms do not appear, the person lives and does not know that his hands will soon begin to shake, etc.
So, thinking about how to treat the trigeminal nerve, I came to the conclusion that nerve cells do not multiply and do not divide. True, there are now other theories, for example, that neurons can reproduce from stem cells, but these are theories, although they have been tested on rodents and mammals. But that’s not what we’re talking about now.
The central nervous system monitors everything that happens in the body and transmits information to the brain; this is its task. While studying my illness, I realized that medicine does not treat it, but works with the symptom. And if you rush to fight the symptoms, you will still lose in the end. You will kill other organs with medications and ruin your immune system. Take even viruses or parasites, if you just fight them, sooner or later they will win because they will adapt to their environment. The most important thing that is required of us is not to harm, but to strengthen . Then the body finds reserves within itself and wins.
Treatment of the central nervous system
First you need to deal with your internal problems. It may not surprise everyone, but the central nervous system is most affected by psychological factors. This is logical - if you get nervous, you get a disastrous result. Positive thinking is the key to health in general, and the health of the nervous system especially. This also includes the psychosomatics of the disease. Having lost your true face, as if putting on a mask, you can one day wake up from unimaginable pain in the trigeminal nerve area and be surprised by the face distorted from pain, which breaks out from under the mask. It's good that my cousin is a psychologist. Thanks to her help, it became easier for me to cope with the disease.
Find someone who can help you cope with anxieties, fears, and phobias.
There is an expression “we are what we eat.” So I reconsidered my diet. The diet for the central nervous system is, first of all, high-quality amino acids that can be obtained from greens.
B vitamins are a must, and preferably natural, from foods.
I changed my diet, there were a lot of raw vegetables and fruits in it, and I even noticed that I began to get enough of them, and before I thought that this was just a supplement. At some point I even wanted to switch to a raw food diet and studied this topic, but as a result I simply began to consume more raw foods. Folic acid is especially important for the cells of the nervous system; it is most abundant in sea buckthorn, parsley, lettuce, cabbage, beets, lentils, and peas.
Lecithins, which are found in yolk or soybean oil, are also needed. Of the minerals, zinc is especially valuable and of course strong. And also fatty acids and enzymes.
If you feed your cells well, they will be healthy and work great, and therefore live a long time.
Water and drinks . Poor quality water and sweet fizzy drinks, as well as stimulating, tonic drinks are the main destroyers of the central nervous system. Remember this. It is impossible to stimulate a dead or half-dead cell with any coffee, energy drinks or antidepressants, just as it is impossible to force a dead mare to get up and work. It’s impossible to calm down neurons if they have a huge dose of adrenaline. You just need to dissolve it with water and remove it from the body, clean it and try not to give new portions. Fizzy drinks will acidify the body so much that you will need a lot of time and effort to put everything in order. Good, clean water, fresh juices, green smoothies, herbal teas are the key to a healthy nervous system.
Many people have known everything about other harmful products for a long time, I won’t list them here, everything is standard.
There may be other reasons besides stress and nutrition. Therefore, I advise you to start treatment of the trigeminal nerve by taking tests . It is likely that your body is fighting a virus, bacteria or parasite, it succeeds, but there are failures - and at such moments the trigeminal nerve begins to become inflamed.
Viruses, bacteria and parasites are one of the causes of nervous system failure
After getting tested, I found out that I am a carrier of herpes, and it, and not only it, affects the nervous system. We had to fight it as a family, because it is transmitted both at birth and through sexual contact. They say that nowadays almost everyone carries this insidious virus within themselves.
Viruses are a significant cause of nervous system failure that can cause trigeminal nerve disease.
In addition to herpes, there is a cytomelogavirus, due to which not only the trigeminal nerve can become inflamed, but also schizophrenia, autism and other ailments develop.
This also includes papillomavirus and encephalitis virus, which is most often transmitted by insects.
I learned that a person becomes aggressive because of viruses . He himself may not understand why he is so nervous and why he has such mood swings. The whole point is that a virus simply settled in his nervous system.
Bacteria can also cause problems with the nervous system .
Treatment for trigeminal nerve disorder can sometimes come down to identifying harmful bacteria and eliminating them.
The most famous bacterium of the central nervous system is meningitis. This is the same bacterium that causes meningitis in people.
And also parasites.
Parasites affect the functioning of our nerves and can cause trigeminal nerve disease.
For example, pork tapeworm is a terrible parasite that subsequently even causes epilepsy, or toxoplasmosis, which our cats carry.
Dear friends! If, after all, treatment of the trigeminal nerve is an urgent problem for you, then be sure to examine yourself - get tested. It is likely that your body is fighting a virus, bacteria or parasite. Perhaps he succeeds, but there are failures - at such moments the trigeminal nerve begins to become inflamed .
In this case, in order to prevent the treatment of the trigeminal nerve, maintaining personal hygiene is no less important .
Prevention
Facial neuralgia can have very serious and dangerous consequences, since the trigeminal nerve becomes inflamed and the pathological process even affects the brain in some cases. That is why it is important to carry out timely treatment of the disease, and special prevention is also indicated.
Naturally, it is impossible to influence all the causes of this disease, however, some factors in the formation of the pathological process can be easily prevented, in particular such as:
- hypothermia of the face should be avoided;
- treat chronic diseases in a timely manner;
- avoid head injuries.
In addition, it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle and avoid stressful situations that can adversely affect your health.
Symptoms of an advanced case of neuralgia
In advanced cases, a number of other symptoms are added. Eliminating the cause of the disease no longer leads to recovery in one hundred percent of cases; complex treatment methods are required.
Signs of advanced trigeminal neuralgia are:
- Swelling of the face, loss of eyelashes, changes in the secretion of the skin glands.
- Spread of pain to other parts of the face.
- The appearance of pain from the slightest pressure on any part of the face on the affected side.
- The occurrence of pain in response to any irritant, even a loud sound or bright light, can even be a contributing factor, even a reminder of a previous attack.
- Permanent nature of the pain.
- Changes in the location and duration of pain attacks.
- Increased vegetative-trophic symptoms.
Forecast
The optimistic prognosis for trigeminal neuralgia is determined by the cause that caused the development of neuralgia and the age of the patient. Trigeminal neuralgia in a young patient caused by facial trauma is usually easy to treat and does not recur in the future. However, in old age, trigeminal neuralgia, accompanied by metabolic disorders in the body, cannot always be cured.
Optic nerve atrophy Herpes zoster Optic neuritis Glaucoma Hepatitis C: first signs and treatment regimen Psoriasis
Risk group and characteristics of the disease
Trigeminal neuralgia is a very common reason for visiting a neurologist. This is due to a large number of factors that provoke the development of the disease, painful attacks of extremely high intensity and long-term therapy for advanced cases. The number of people at risk for trigeminal neuralgia is quite large.
Middle-aged people are more often susceptible to neuritis; the disease mainly manifests itself between the ages of 40 and 50 years. The percentage of patients suffering from trigeminal neuralgia among women is much higher than among men. An important determining factor is the presence of chronic diseases in the patient’s history that contribute to the development of neuralgia.
In seventy percent of cases, the right side is affected; both sides are extremely rarely affected. The course of the pathology is cyclical: the acute period is followed by remission. Peaks of exacerbations occur in autumn and spring.