How does neuritis of the facial nerve appear?
Neuritis of the facial nerve can begin with mild pain in the ear area. Simultaneously with the onset of pain or after a couple of days, the facial muscles partially or completely lose mobility. The patient's face becomes distorted, the affected part freezes in the mask.
With timely treatment, the patient has a great chance of recovery - in 75% of cases the disease goes away completely. If facial paralysis does not resolve within three months, the patient's chances of making a full recovery are greatly reduced.
In order for facial neuritis to pass without consequences, you need to consult a doctor in the first hours after the onset of symptoms.
Treatment of neuritis
The approach to treating neuritis should be comprehensive.
Drug therapy for neuritis is aimed at eliminating the root cause of the disease, restoring nerve function, relieving inflammation and pain, activating blood flow and metabolic processes, improving nerve conduction, strengthening the body's defenses, etc.
Common non-drug treatment methods include therapeutic exercises, acupuncture, manual techniques and massage (in the absence of contraindications).
A special place in the treatment of neuritis is given to physiotherapy: treatment with waves and currents, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, radon and mud baths, etc.
Surgical treatment (suturing or plastic surgery of the nerve) is resorted to in the absence of a positive effect from conservative therapy.
Prevention of neuritis
Simple and effective measures will help to resist the development of the disease:
- avoiding hypothermia;
- proper balanced nutrition;
- timely treatment of viruses and infections;
- strengthening the immune system (vaccination, hardening, vitamin therapy);
- regular examination of the body.
At the MedicCity clinic, the professional experience and knowledge of doctors from 30 medical specialties is at your service. With us you can undergo a complete diagnosis of the body and get advice from the right specialist at a time convenient for you, without wasting time and nerves. Don't give diseases a chance!
Symptoms of facial neuritis
The following symptoms of inflammation of the facial nerve are distinguished:
- partial or complete impairment of facial muscle movements;
- the corner of the mouth lowers, the nasolabial fold on one side is smoothed out;
- the face becomes asymmetrical;
- the eyelid does not close completely;
- the eyeball protrudes and turns upward;
- pain in the ear, taste disorder;
- watery or dry eyes;
- hearing loss or sensitivity to loud sounds;
- the patient cannot whistle or stretch out his lips with a straw.
Paresis and paralysis: what is the difference?
Facial nerve neuropathy is manifested by a sharp weakness of the muscles of one half of the face. This condition is called paresis . The patient is unable to close his eyes voluntarily, smiles only with the healthy half of his lips, and finds it difficult to pronounce words clearly and eat food. With very pronounced weakness, when the muscles practically do not function, they speak of facial nerve paralysis .
Causes
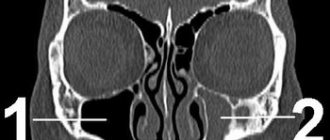
In primary neuropathy, the cause is most often hypothermia or a viral infection. There is a disturbance of blood circulation in the nerve fiber, swelling and subsequent compression of the nerve in the canal of the temporal bone, and the predisposing factor in the development of this pathology is the congenital anatomical narrowing of this bone canal.
Secondary neuropathy can be caused by:
In isolated cases, neuritis is bilateral or recurrent, that is, recurring.
Causes of inflammation of the facial nerve
Primary neuritis of the facial nerve occurs due to:
- hypothermia of the face, cold, wind, drafts;
- insufficient blood supply (ischemia) to the nerve.
Secondary neuritis of the facial nerve is caused by the following reasons:
- inflammatory diseases of the ear: otitis media, eustachitis, mastoiditis;
- infections: mumps virus, measles, herpes;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- vascular disorders - for example, atherosclerosis of the vertebral arteries;
- brain tumors;
- anesthesia of the inferior alveolar nerve by the dentist.
Other factors that provoke inflammation include:
- traveling on a bus or minibus next to an open window;
- long work under air conditioning;
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- endocrine diseases - for example, diabetes;
- hypertension, intoxication of the body;
- nervous stress, emotional instability.
Historical reference
Physiologists back in the 19th century proved that muscle contraction is the result of irritation of the motor nerve belonging to it. V. Yu. Chagovets and P. P. Lazarev studied the principles of action of the neuromuscular apparatus. They found that the accumulation of certain amounts of calcium, sodium, and magnesium ions on the surfaces of myocyte membranes leads to electrical conduction and muscle contraction. At the same time, the irritant that has a similar effect on the neuromuscular system can be diverse: mechanical action, a sharp increase or decrease in temperature, electric current.
Later, physiologist Emile Dubois-Reymond proved that a gradually increasing continuous current will not lead to excitation of the neuromuscular apparatus, no matter what value it reaches. But if such a current becomes intermittent - it will be turned on and off, then at certain parameters the muscle contracts. Scientists have given the name rheobase to the current strength at which muscle contraction occurs.
Complications of the disease
Neuritis of the facial nerve can lead to contracture of the facial muscles. It appears 4-6 weeks after the onset of the disease due to incomplete restoration of the motor functions of the facial muscles. Contracture is a contraction of the muscles of the affected half of the face. At the same time, it seems that it is not the diseased part of the face that is paralyzed, but the healthy one.
To avoid complications of inflammation of the facial nerve, you need to consult a doctor in time. For prevention, we recommend doing facial exercises. You will find examples of exercises at the end of the article.
Neuritis
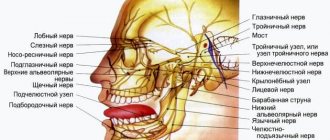
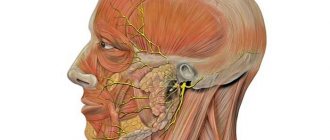
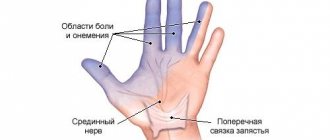
Neuritis is an inflammatory disease of a peripheral nerve (intercostal, occipital, facial or limb nerves), manifested by pain along the nerve, impaired sensitivity and muscle weakness in the area innervated by it. Damage to several nerves is called polyneuritis. Diagnosis of neuritis is carried out by a neurologist during examination and carrying out specific functional tests. Additionally, electromyography, electroneurography and EP study are performed. Treatment of neuritis includes etiotropic therapy (antibiotics, antiviral, vascular drugs), the use of anti-inflammatory and decongestants, proserinotherapy, physiotherapy, massage and exercise therapy. Neuritis is an old name meaning inflammation of a nerve. However, the name neuropathy is now accepted, since most lesions of peripheral nerves are non-inflammatory in nature. The most common neuropathy of the facial, radial nerve, and small tibial nerve. Neuropathy of the facial nerve is 70% of vascular nature. Occurs after hypothermia, the peak incidence occurs in September and March, i.e. when the winds start in the off-season, and people walk around without hats and scarves, in light jackets, returning from their dachas, sleeping in trains near open windows. The facial nerve leaves the cranial cavity in the area behind the ear; hypothermia leads to spasm of the vessels supplying the nerve. Poor nutrition leads to swelling and jamming of the nerve in the walls of the bone canal. Jamming further deteriorates the supply of the nerve - the circle closes.
Symptoms
The patient, getting up in the morning, while trying to brush his teeth, suddenly notices that water is flowing out of the corner of his mouth, while eating breakfast, he is surprised that food constantly gets between the cheek and teeth, preventing him from chewing food, and behind the ear there is an aching, constant, mild pain. Approaching the mirror, he sees that his face is immobilized on one side, and his mouth is pulled to the opposite (healthy) side. The eye on the affected side does not close, the forehead does not wrinkle, and when teeth are bared, the corner of the mouth is motionless. Sensitivity on the face (when tingling with a needle) remains.
Neuropathy of the radial nerve - the patient cannot straighten the fingers and raise the hand upward, while making a good fist. He cannot fold his hands with his palms, clap, put his hand on the table, and cannot tap his fingers on it. Most often, such disorders occur after drinking alcohol the night before and having an uncomfortable night's sleep. For example, if the patient sleeps without a pillow, placing his arm under him, or the spouse sleeps on his shoulder at night. This is why this radial nerve palsy is called “garden bench palsy” or “honeymoon palsy.”
Neuropathy of the peroneal nerve - the patient has a “drop foot”; such a patient cannot stand on his heels and cannot put on slippers on his own. When walking, he stumbles out of the blue; his gait is also unusual: the person tries to lift or throw his leg forward and upward so that the foot does not cling to the floor.
This disorder occurs after severe radiculitis, hypothermia of the legs, an allergic reaction (bee sting), chemical poisoning (alcohol, insect repellents), atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities, diabetes mellitus, prolonged forced sitting, especially cross-legged.
Treatment:
It is carried out only in a hospital, where further examination is required, because a similar picture can be caused by inflammation of the inner ear, acoustic neuroma, multiple sclerosis, brain tumor, stroke in the brain stem, diabetes mellitus. The sooner the patient consults a doctor, the greater the chance of success. 3-4 days without treatment and the face will remain motionless forever.
Dry heat, aspirin, nicotinic acid, chimes, hormones, adhesive traction, electrical stimulation, and acupuncture are used. If neuropathy of the facial nerve is a manifestation of another disease, the cause is treated first, but at the same time all measures to restore the nerve are carried out so as not to waste time.
Therapy for neuritis is primarily aimed at the cause that caused it. For infectious neuritis, antibacterial therapy (sulfonamides, antibiotics), antiviral drugs (interferon derivatives, gamma globulin) are prescribed. For neuritis resulting from ischemia, vasodilators are used (papaverine, aminophylline, complamin); for traumatic neuritis, the limb is immobilized. Anti-inflammatory drugs (indomethacin, ibuprofen, diclofenac), analgesics, B vitamins are used and decongestant therapy is carried out (furosemide, diacarb). At the end of the second week, anticholinesterase drugs (prozerin) and biogenic stimulants (aloe, lidase) are added to treatment.
Physiotherapeutic procedures begin at the end of the first week of neuritis. Ultraphonophoresis with hydrocortisone, UHF, pulsed currents, electrophoresis of novocaine, proserin, lidase are used. Massage and special physical therapy aimed at restoring the affected muscle groups are indicated. If necessary, electrical stimulation of the affected muscles is performed.
In the treatment of tunnel syndrome, drugs (hydrocortisone, novocaine) are administered locally directly into the affected canal.
Surgical treatment of neuritis refers to peripheral neurosurgery and is performed by a neurosurgeon. In the acute period of neuritis with severe compression of the nerve, surgery is necessary to decompress it. In the absence of signs of nerve recovery or the appearance of signs of its degeneration, surgical treatment is also indicated, which consists of suturing the nerve; in some cases, nerve plastic surgery may be required.
Neuritis in young people with a high ability of tissue to regenerate responds well to therapy. In elderly patients with concomitant diseases (for example, diabetes), in the absence of adequate treatment for neuritis, paralysis of the affected muscles and the formation of contractures may develop.
Stages of electrical stimulation
Before performing electrical stimulation itself, electrodiagnostics are carried out and specific optimal current parameters for the procedures are determined.
Physiotherapy procedures are carried out in courses, and between several courses of electrical stimulation, the doctor must carry out control diagnostics in order to understand whether it is necessary to continue treatment and, if so, at what current parameters.
In order to select parameters, you need to make sure that time has passed. Thus, electrodiagnostics should be carried out only when at least 2 weeks have already passed since the damage to the neuromuscular system, otherwise incorrect data will be obtained.
Electrical stimulation has its own varieties, which can also be stages of the procedure algorithm.
- Passive electrical stimulation. Doctors use it when voluntary contractions are impossible in the affected muscle, and the muscle is often completely denervated. To perform the procedure using this method, a current with the parameters that were determined earlier during electrodiagnostics is used. After 5-10 procedures, a control study is carried out, during which the body’s response and new optimal current parameters are determined.
- Active electrical stimulation is the second stage. During this procedure, the patient tries in every possible way to contract the affected muscle voluntarily. It turns out that the muscle is stimulated not only by the current supplied to its surface through the electrodes, but also by the impulses that the damaged nerve is capable of producing.
Electrical stimulation
Determination of current parameters for electrical stimulation
Electrical stimulation is a therapeutic method of using pulsed currents of various shapes and frequencies to restore the function of the damaged neuromuscular system. Various injuries, wounds, bone fractures, infectious diseases, intoxication, degenerative-dystrophic diseases often lead to damage to the nerve fiber with the development of a degeneration reaction in the neuromuscular system with clinical manifestations of flaccid paralysis. Under the influence of electrical stimulation, the contractile function of the denervated muscle is preserved, blood circulation and energy potential in it increase, the activity of enzyme systems increases, oxidative processes and the transformation of glycogen in the muscles are stimulated. Favorable conditions are created for nerve regeneration. With preserved muscle innervation, the use of electrical stimulation prevents the development of muscle atrophy due to physical inactivity, increases performance and quickly increases muscle strength. In case of central paralysis, most often caused by impaired cerebral circulation, electrical stimulation creates centripetal afferentation, which promotes the disinhibition of blocked brain centers around the intensified area of the brain, improves nutrition and trophism of paralyzed muscles. Prevents the development of contractures.
Determination of current parameters for electrical stimulation is based on electrodiagnostic data and is carried out strictly individually, since under pathological conditions the excitability of the neuromuscular system varies widely.
Pulse shape. Modern devices for electrical stimulation can generate impulses of rectangular, triangular, trapezoidal shape. The selected impulse shape must correspond to the functionality of the muscle. During the degeneration reaction, the trapezoidal shape of the impulse will be more physiological.
Pulse duration. In the presence of quantitative changes in the neuromuscular system, an impulse with a duration of 1-5 ms will be optimal, with a partial degeneration reaction - 10-50 ms, with a complete degeneration reaction - 100-300 ms.
Pulse repetition frequency. With preserved muscle innervation, an alternating current of a carrier frequency of 2-10 kHz, modulated by a low-frequency voltage (50-100 Hz) or a neofaradic current (unipolar) of a frequency of 50 Hz, is used. A series of impulses alternate with pauses for muscle rest. With electrical stimulation, tetanic muscle contraction occurs.
With a partial degeneration reaction, a correctly selected combination of pulse duration and frequency can provide tetanic muscle contraction. The most rational combination is proposed: pulse duration 3-5-10-20-30-60-100 ms, pulse repetition frequency 80-60-40-25-10-8-5 Hz.
With a denervated muscle, electrical stimulation is carried out only with single impulses with pauses of 3-20 s. The more pronounced the degeneration reaction is, the longer the pause should be.
Polarity. The active electrode is selected in accordance with the polar Pfluger-Brenner formula. It can be a cathode or anode. With preserved innervation, the cathode is, as a rule, active, and with a severe degree of degeneration, the anode is active.
When stimulating skeletal muscles with impaired innervation, both electrodes (cathode and anode) with hydrophilic pads, the optimal area of which is 4 cm2, are applied to the stimulated muscle. When innervation is preserved, the anode is placed on the motor point of the stimulated nerve, and the cathode is placed on the motor point of the muscle it innervates. When stimulating smooth muscles, electrodes with hydrophilic pads with an area of 200-300 cm2 are placed over the area of the stimulated organ (stomach, intestines, uterus, ureter) using the transverse technique.
For peripheral paralysis with impaired muscle innervation, only single impulses are used with a repetition frequency of 1-0.25 Hz or less and a duration of 100-200 ms. The pulse repetition rate, as well as the duration and shape (triangular, trapezoidal, rectangular) are selected individually.
For electrical stimulation of skeletal muscles with preserved innervation, an alternating current of 2-5 kHz is used, modulated by a voltage with a frequency of 50-100 Hz, which follows in an intermittent mode (current sendings alternate with pauses) or a neo-faradic (half-wave) current with a frequency of 50 Hz.
To stimulate the smooth muscles of internal organs, alternating current with a frequency of 2-5 kHz with low-frequency amplitude modulation of 5-30 Hz is used.
Indications:
- flaccid paresis and paralysis associated with nerve injury, toxic damage, nerve inflammation, degenerative diseases of the nervous system and spine;
- central paresis and paralysis associated with impaired cerebral circulation;
- muscle wasting due to physical inactivity and immobilization bandages;
- hysterical paresis and paralysis;
- postoperative intestinal paresis, hypomotor dyskinesia of the stomach, intestines, biliary tract;
- atony of the sphincters of the bladder and rectum;
- ureteral stones, chronic prostatitis, dysfunctional diseases of the female genital organs;
- metabolic disorders: obesity, cellulite.
Contraindications: contracture of facial muscles, bone fractures before immobilization, joint dislocations before reduction, bleeding (except for uterine dysfunction), acute inflammation, purulent diseases (abscess, phlegmon, carbuncle, furuncle), thrombophlebitis, cholelithiasis, the first 3-4 weeks. from the moment of development of acute cerebrovascular accident, epilepsy, implanted pacemaker, loose metal bodies in vital organs, which, with oscillatory movements, can cause damage to the blood vessel.
Some methods of conducting electrical stimulation procedures with pulsed currents
Electrical stimulation of the peroneal nerve and the muscles innervated by it in peripheral paresis (paralysis)
Plate electrodes with an area of 4 cm2 are used. The anode is located in the upper third of the leg on the outer posterior side at the motor point of the peroneal nerve. During the procedure, the cathode is periodically moved to the motor muscles: tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum communis, peroneus longus, peroneus brevis, extensor pollicis intrinsic. Current parameters: pulse current shape - rectangular or trapezoidal, pulse duration 100-200 ms, pulse repetition frequency 0.5-0.25 Hz or less, current strength 10-15 mA in amplitude value. Duration of exposure is 15-20 minutes daily or every other day. The course of treatment is 15-20 procedures. Courses of treatment can be repeated many times.
Electrical stimulation of limb muscles for central paresis (paralysis)
For afferent stimulation of the cerebral cortex of patients who have suffered an ischemic stroke, electrical stimulation is prescribed after 2-3 weeks. from the onset of the disease (the appearance of limb paresis). One pair of plate electrodes with an area of 4 cm2 is located: the cathode - in the middle third of the shoulder on the outer side at the motor point of the radial nerve, the anode - in the middle third of the outer surface of the forearm. The second pair of the same electrodes is placed: the cathode - on the inner surface of the middle third of the shoulder on the ulnar and median nerves, the anode - on the inner surface of the forearm.
Current parameters: rectangular pulses with a duration of 1 ms with a repetition rate of 0.5 Hz (two pulses per second) are sent to the group of muscles innervated by the radial nerve (extensors), and after 1 s - to the ulnar, median nerves and the muscles of the flexor group innervated by them; amplitude current value 3-5 mA, duration of exposure 5-8 minutes.
Next »
Physiological basis of electrical stimulation
Muscle contraction in the body is initiated by action on the corresponding motor nerve. Special protein structures – myosin and actin – are responsible for this process in the body.
Actin filaments are connected to myosin filaments through cross bridges - myosin heads. During muscle contraction, these heads temporarily attach to actin filaments and pull them up with a rowing motion. Next, actin and myosin detach from each other and fasten again for the next movement. In the body, all this happens at tremendous speed; it is precisely such movements that ensure muscle contraction. When the muscles relax, the actin and myosin filaments are not connected and take their original position relative to each other.
If we talk about physiotherapeutic procedures carried out in a hospital and affecting the neuromuscular system, then the closest thing to physiological is the use of Lapik current - exponential current. However, any stimulating effect must be balanced by pauses, since prolonged muscle contraction is not physiological - it leads to the accumulation of large amounts of lactic acid in the muscles, and can also provoke trophic disorders.
How does the procedure work?
RTI sessions must be carried out in a sanitary clinic by a reflexologist certified as an RTI specialist. It is very good if, in addition to this, the doctor has received training in clinics in China or Tibet. Conducting acupuncture sessions in dubious establishments that do not have a license to provide medical services is very dangerous. Damage to the facial nerve in such conditions cannot be cured, but getting a permanent contracture is quite possible.
A preliminary examination of the patient is required, both using eastern and modern instrumental techniques. During a course of acupuncture for neuritis, you should not drink alcohol. It is also necessary to limit or completely stop smoking - nicotine promotes spasm of blood vessels, which prevents this therapeutic effect.
During an acupuncture session, the patient takes a comfortable position lying on his back, and the doctor inserts disposable sterile needles into the pre-selected AT. The needles are very thin, and the needle screwing technique makes the procedure painless. The patient should not be concerned if the doctor begins the course from distant points, for example, on the leg: the meridian can run from the lower limb through the whole body to the face. The effect on distant points is more gentle; it is used in the acute course of the disease.
The duration of the session is determined by the doctor; it can last from 15 to 30 minutes. After the procedure, it is recommended to rest for some time (10–20 minutes) and only then leave the clinic. You should not get behind the wheel right away, as during the session the spasm of vascular smooth muscles and a decrease in blood pressure are relieved - slight dizziness is possible.
Acupuncture is an effective treatment for facial neuritis, but only in the hands of a well-trained, experienced professional. In ancient China, doctors studied this method for decades, as it is not just a technique, but a real art based on philosophy. It is very important to choose the best clinic for treatment. In Moscow, Paramita is rightfully considered such a clinic, since all its reflexologists were trained in Chinese traditional medicine clinics.
Themes
Parez Date of publication: 04/18/2019 Date of update: 04/18/2019
Reader rating
Rating: 5 / 5 (3)
Efficiency
If the slightest symptom of neuritis occurs, you must immediately contact a neurologist. The disease cannot be delayed; the sooner treatment is started, the higher the likelihood of fully restoring muscle functionality.
The mechanism of action of physiotherapy is aimed at:
- improve blood circulation;
- accelerate regeneration;
- reduce swelling and nerve compression;
- increase conductivity;
- relieve inflammation and pain symptoms;
- accelerate metabolic and reparative processes;
- increase the effectiveness of drug treatment.
With timely diagnosis and treatment, in 95% of cases the result is a favorable outcome. But there is a high risk of relapse of the disease. To avoid this, you must not forget about preventive measures.
Types and scheme of physical treatment
There are a large number of types of physiotherapy. And each has its own characteristics and mechanism of action. The treatment plan is described below.
- Before each stage of treatment, electromyography is required. This allows you to assess the degree of excitability and conductivity of the nerve fiber and correctly configure the equipment parameters.
- On 2-3 days after diagnosis, heat treatment can be performed in the affected area. Sollux lamp and Minin reflector use infrared rays to improve blood circulation, reduce pain, and reduce swelling. Due to the small size of the reflector, you can buy it at a pharmacy and use it at home.
- Manual massage of the occipital and behind-the-ear areas, collar area. Finger pressure dilates blood vessels and accelerates the regeneration process. An easy but effective home method to improve blood flow.
- Myogymnastics is recommended from the very beginning until the end of treatment. The goal is to avoid contractures and teach facial muscles to work correctly.
- Electrophoresis for neuritis of the facial nerve can be performed from the 4th-5th day of the disease. It is carried out using a Bergonier half mask. Thanks to electric currents and the formation of a depot, the effect of medicinal substances occurs quickly and lasts for a very long time. Potassium iodide, vitamin B1, calcium chloride, novocaine, magnesium sulfate, proserin, aminophylline and others are used as medications.
- UHF and UV therapy has an anti-inflammatory, regenerative effect and stimulates tissue trophism. Ural irradiation has antiviral and bactericidal effects.
- From 10-14 days of illness, laser, SMV or ultrasound therapy, magnetic therapy, myoelectric stimulation, and darsonvalization can be performed. Under the influence of current, magnetic field or laser, blood circulation and nerve fiber regeneration improves. Everyone has the opportunity to buy a Darsonval device at a pharmacy and use it at home.
- After 1-2 months, paraffin treatment and ozokerite applications are used. Helps restore damaged tissues and improve blood flow. Can be performed both on an outpatient basis and at home. But do not forget to take precautions.
- After completing the full course of treatment for rehabilitation, it is better to go to a sanatorium or resort with a favorable climate. It is important not to overload the nervous system, strengthen the immune system, and treat all systemic diseases. All this will speed up recovery and reduce the risk of relapse.
After diagnosis, a competent specialist will select the optimal treatment plan for you. There is no need to self-medicate or try to undergo all types of physical procedures that exist on your own. The process of restoring nerve fibers and muscles is quite long and difficult.
Physiotherapy for facial neuritis is one of the most common procedures performed in a hospital. The ratio of the number of cases to the population is 25 to 100 thousand.
Contraindications
Electrical stimulation is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- Individual intolerance – the occurrence of pain when the current parameters are normal or when rashes appear on the skin in the area where the electrodes are applied.
- Blood clotting disorders.
- The presence of an acute purulent process in the body.
- Increased body temperature.
- Status epilepticus.
- Muscle contractures.
- Gallstones or urolithiasis.
- Malignant neoplasms.
- Pregnancy.
Childhood is not a contraindication; it is possible to prescribe this procedure to a child. During pregnancy, the decision to prescribe this type of physiotherapy is made by the doctor on an individual basis.
Mechanism of therapeutic effect
Currents used for therapeutic purposes, in addition to provoking muscle excitation and contraction, also produce the following effects:
- Reflexively increase local blood circulation and metabolism.
- Improve lymphatic drainage and prevent venous stagnation.
- Stimulates recovery processes.
- They enhance the activity of the peripheral and central nervous systems, causing a response in them.
- They inhibit atrophic changes and sclerotic processes in the muscle even with a complete interruption of the conduction of impulses along the motor nerve.
- Improves the condition of the motor nerve.
This is the basis of the mechanism of the therapeutic effect of electrical stimulation in medical practice.