What is the facial nerve
It performs a motor function and regulates the work of facial muscles. The fibers of the intermediate nerve are responsible for the production of saliva, tears, sensitivity of the tongue (also called the lingual nerve), and skin. The nerve trunk consists of long processes of nerve cells called neurons. They are covered with a special membrane, perineuria.
Anatomy
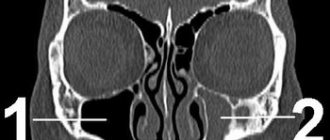
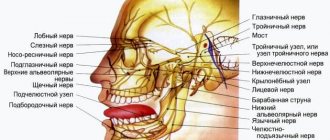
The facial nerve has the following anatomy: nerve trunk - motor fibers; lymph nodes and capillaries that supply nerve cells with nutrients; area of the cerebral cortex, nuclei that are located between the bridge and the oblong bridge. The nucleus of the nerve is responsible for facial expressions, the nucleus of the solitary tract regulates the taste fibers of the tongue, the superior salivary nucleus is responsible for the salivary and lacrimal glands.
From the nuclei, the nerve stretches to the muscles, forming 2 extended knees. The ending approaches the temporal bone along with the fibers of the intermediate nerve through the auditory opening. Then it passes through the petrous part, then the internal auditory canal to the facial nerve canal. Then the ending leaves the temporal bone through the stylomastoid foramen, passes into the parotid gland, and divides into small and large branches intertwined. The latter control the functioning of the muscles of the cheeks, nostrils, forehead, orbicularis oris and eyes. The complex structure and peculiar location of the nerve provoke various pathologies when it is dysfunctional.
Diagnostic methods
Damage to the maxillofacial nerve has specific signs that are clearly expressed. If inflammation is suspected, the doctor conducts neurological tests - the patient performs certain exercises with facial muscles:
- frowns, raises eyebrows;
- blinks, closes his eyes;
- smiles, showing teeth;
- puffs out his cheeks, tries to whistle;
- wrinkles his nose.
Special neurological tests will help determine the presence of the disease
Such movements help the specialist analyze the symmetry of the facial muscles on both sides of the face and identify paralysis or weakening of tissues.
If the development of concomitant diseases (inflammation of the brain, neoplasms, infections and viruses) is suspected, additional diagnostic methods are prescribed:
- electroneuromyography;
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- CT scan;
- electroencephalogram.
Important!
The diagnosis is made based on examination, the results of a neurological test and instrumental studies. Complex diagnostics allows not only to identify the disease, but also to understand what to do in a particular case.
Functions
The nervus facialis innervates the muscles that are responsible for facial expression. It is also responsible for transmitting a signal to the brain when the tongue comes into contact with salty, sour, sweet, etc. The facial nerve ending performs a parasympathetic function, i.e. provides connection between parts of the head and neck with the CNS (central nervous system). Provide a response to external factors of the following glands:
- salivary;
- lacrimal;
- responsible for the production of mucus in the pharynx, palate, and nose.
Causes
Scientists have not yet established the exact cause of trigeminal neuralgia. But factors contributing to deformation and disruption of the functioning of the branches of the facial nerve include:
- Compression of nerve endings by large blood vessels located in the facial area and having lost their normal shape and structure.
- Damage to the outer sheaths of nerve fibers and, as a result, disturbances in their conductivity as a result of multiple sclerosis.
- Past infectious diseases of a viral nature: influenza, herpes, etc.
- Diseases of the middle ear or posterior cranial fossa of a viral nature: otitis media, meningitis, arachnoencephalitis, etc.
- Inflammatory processes in the gums.
- Proliferation of granulomatous tissues.
- A decrease in the thickness of the bone canal, which results in compression of the nerves.
- Complications due to the surgery .
- brain injuries
- Hypothermia of both the whole body and the head area.
- Weakening of the immune system .
- Enduring heavy emotional and physical stress.
- Frequent exposure to stress , nervous disorders, and depression.
The most common cases of trigeminal neuralgia occur in the off-season, in the first months of spring and autumn. This is due to cold winds, too light clothing and temperature changes.
As a result, hypothermia can lead to inflammation and spasms of blood vessels, and this, in turn, leads to disruption of the passage of impulses along nerve fibers, their nutrition and the development of neuralgia.
Also, one of the reasons for the development of trigeminal neuralgia includes congenital structural features of the skull bones, which can lead to deformation or compression of the branches of the nerve.
Facial nerve diseases
There are twelve pairs of endings on the head. Nervus facialis is one of them. Various kinds of negative influences can cause inflammation of the facial nerve, which is medically called neuropathy (neuritis, Fothergill's neuralgia). There is a lot of research into this pathology, so methods for effective treatment of the disease have been developed. A complex scheme is used, which includes medication, physiotherapeutic treatment or, if necessary, surgical intervention.
Prevention
To maintain the health of not only the central nervous system, but also the entire body as a whole, you need to follow a whole range of health measures, which includes:
- Regular visits to the dentist, otolaryngologist, therapist to identify and treat any signs of the disease.
- Annual medical examinations , including examination of the functioning of internal organs and endocrine glands.
- Avoiding injury and damage, especially to the head and face.
- Avoiding hypothermia , strong winds and low temperatures. This is the most dangerous and main factor in the development of trigeminal neuralgia and facial nerve. You should never go outside with wet hair; you should always wear hats in cold weather and avoid drafts.
- Timely treatment of viral diseases.
- Monitoring the functioning the cardiovascular system, including regular blood pressure measurements, to exclude the development of dystonia or hypertension.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: moderate physical activity, a healthy and balanced diet, proper rest, getting the necessary vitamins, microelements and other nutrients, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption.
- Hardening . Proper and gradual hardening will help strengthen the immune system.
- massage . Regular self-massage of the facial muscles will not only lead to their relaxation, but will also help avoid relapse of trigeminal neuralgia.
You should never self-medicate; you need to trust your health to trusted specialists. Only they will be able to promptly detect the development of pathology and take the necessary treatment measures.
Neuritis
Inflammation of the facial ending is considered a chronic disease. Patients with this pathology suffer from excruciating pain in different places that are applied to the location of the trigeminal ending, for example:
- above, below the jaw;
- area around the eye sockets.
There is unilateral inflammation of the trigeminal nerve and bilateral pathology, when pain simultaneously spreads to the left and right side of the face. According to medical statistics, girls suffer from neuritis more often than men, especially many cases have been registered in people over 50 years of age, so the older generation is at risk.
Forecast
Timely diagnosis, prescription of necessary medications and physiotherapeutic procedures will allow you to quickly eliminate symptoms without deteriorating health.
The prognosis of facial and trigeminal neuralgia depends entirely on the location, degree of damage and the presence of concomitant pathologies, including viral infections, inflammatory processes, etc. In more than 70% of cases, patients with facial neuralgia completely recover.
If within 3-4 months there is no improvement and restoration of normal functioning of the trigeminal nerve, then the patient’s chances of a complete recovery are significantly reduced.
Neuralgia is best treated if the affected area is localized at the very beginning of the trigeminal skull, that is, at its exit from the skull. Patients whose disease is accompanied by frequent relapses also have a better chance of a full recovery. But each subsequent resumption of the disease is much more severe than the previous one.
Symptoms
As a rule, inflammation of only one half of the face is observed, but in 2% of cases both parts are affected. This condition is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- impaired ocular function, the patient cannot look away to the side;
- increased or decreased sensitivity of the affected part of the face;
- face stretching;
- excessive watery or dry eyes;
- curvature of the lips (impaired facial expressions);
- severe shooting pain;
- decreased salivation;
- distortion of individual facial muscles;
- increased or decreased hearing;
- drooping corners of the eyes;
- chills;
- deterioration of taste;
- increase in body temperature;
- severe fatigue;
- small rash on the face;
- migraine;
- severe paralysis of the facial muscles;
- irritability;
- insomnia.
The symptoms described above do not always indicate inflammation; some other diseases of the face, nose, and neck may give similar symptoms. It is important to be able to differentiate and correctly recognize the manifestations of pathology. For this disease there are two definitions of pain syndrome:
- Typical pain. Diagnosed with acute neuralgia. The character will be shooting, sharp, reminiscent of an electric shock to certain parts of the face.
- Unusual pain. It is localized, as a rule, over most of the facial space, has a constant character, a wave-like course with exacerbation and attenuation. There have been cases where pain lasts for 20 seconds for several hours, preventing a person from falling asleep.
Ointments
As part of drug therapy, not only tablets and injections are used, but also local remedies - creams and ointments:
- warming drugs (capsicam, menovazin) - warm the skin over the affected nerve, increasing blood flow. This principle of action allows you to reduce pain;
- combined ointments (NSAIDs added to the composition) - have an anti-inflammatory, analgesic and warming effect (finalgon);
- painkillers - have an analgesic effect (Anesthetic ointment, lidocaine ointment).
Treatment of facial neuritis requires an integrated approach: a combination of drug therapy and physiotherapy. However, the first stage of recovery is always associated with taking medications.
Doctors are not limited to one group of drugs and prescribe combined treatment: painkillers, hormonal, neurostimulating, diuretics.
Causes of neuritis
This nerve ending is highly sensitive to external factors. Facial nerve neuropathy can develop for the following reasons:
- Consequences of meningitis.
- Staying in a draft, severe hypothermia.
- Herpes, which affects the nerve endings.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Malocclusion.
- Constant pressure on the nerve from blood vessels and tumors.
- Aneurysm.
- Concussion.
- Facial injury.
- Chronic pathologies of the sinuses.
- Dental procedures after anesthesia of the inferior alveolar nerve.
- Viral infections, colds.
- A sharp decrease in immunity.
- Severe psycho-emotional shock.
- Damage to the upper respiratory tract by various bacterial infections.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Immune disorders due to poor nutrition.
There are other reasons that can trigger sudden inflammation:
- blow to the nose;
- shaving;
- smile;
- sharp touch to the face;
- teeth cleaning.
Consequences and complications
Neuralgia of the trigeminal and facial nerves as an independent disease does not pose a dangerous threat to life. But the patient’s general condition can cause the development of depression, loss of appetite, insomnia, impaired communication with other people, and decreased immunity.
As a rule, due to constant pain and the development of facial asymmetry, which so often accompany these diseases, people try to avoid communication, withdraw into themselves, experience nervous disorders and become depressed.
Diagnostics
Making a diagnosis of neuritis is not difficult because the clinical manifestations are very obvious. If there is a need to conduct an in-depth study to find out the root causes that caused inflammation of the nerve ending, an MRI or electromyography may be prescribed. When you visit your doctor, he will ask you to do the following to diagnose:
- smile;
- close your eyes, raise your eyebrows;
- imitate blowing out a candle;
- show a grin of teeth.
If any of these actions cannot be performed or facial asymmetry appears, then this indicates trigeminal neuralgia. The specialist will also check the anterior third of the tongue; for this, light tingling sensations are performed to determine the sensitivity of the organ. Eyes are checked for watery or dry eyes. These steps are sufficient to make a diagnosis and determine the symptoms of neuropathy.
What is trigeminal neuralgia?
The trigeminal nerve innervates both the right and left sides of the face. It got its name from the three branches extending from it. The first branch supplies sensitivity to the skin and muscles of the forehead, dorsum of the nose, eyes and upper eyelids. The second branch innervates the lower eyelids, nostrils and wings of the nose, upper lip and upper gum. The third branch is the lower lip, skin and muscles of the lower jaw, including the muscles of mastication.
Trigeminal neuralgia is an inflammation that is characterized by short and very painful sensations in different parts of the face and head, speech impairment, loss of taste and hearing functions.
Other signs develop depending on which branch of the nerve is damaged.
This disease occurs most often due to hypothermia, infection, and compression of the nerve by large vessels.
Treatment is complex, involving medication, physiotherapy and sometimes surgical methods.
Trigeminal neuralgia is a disease that results from dysfunction of this nerve. It is characterized by short-term but very painful sensations in the facial muscles.
Symptoms of neuralgia
Neuralgia is a pathological process that can occur suddenly.
Often, trigeminal neuralgia takes on a chronic form, which is characterized by painless long periods, sometimes followed by exacerbation of the disease.
Experts in the field of neurology believe that neuralgia is not an independent disease, but is only one of the symptoms of a general disorder of the nervous system.
Neuralgia affects not only older people, but also the younger population, especially women. This disease does not pose any dangerous threat to the patient’s life, but may bring some social or everyday difficulties.
Treatment for trigeminal neuralgia involves prescribing antiepileptic drugs to block abnormal impulses in the area of the damaged nerve.
Neurologist
Pershina Natalia Sergeevna
8 years of experience
Treatment
This pathology has been well studied by medicine, so there are working treatment regimens that help relieve a person from excruciating pain. Treatment of neuritis of the facial nerve consists of a set of measures, including a course of medication, physiotherapeutic procedures, and massage. If necessary, you can use traditional medicine; if all the methods described above do not bring a positive result, surgery is prescribed.
Drugs
Therapy is prescribed individually in each case by a doctor. In many ways, the course is drawn up based on the root cause that provoked the inflammation. Traditional treatment of neuralgia includes the use of the following types of medications:
- Hormones (Prednisolone) and glucocorticosteroids (dexamethasone).
- Oral anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, for example, Nimesulide.
- Medicines that reduce swelling, diuretics (Furosemide).
- Analgesics are prescribed for excruciating and severe pain (Analgin).
- Muscle tremors and spasms can be relieved with antispasmodics (Drotaverine).
- To improve blood circulation, vasodilating medications are prescribed.
- In case of significant impairment of the motor functions of the facial muscles, the patient is prescribed metabolic drugs, for example, Nerobol.
- Strengthen the immune system and improve metabolism using B vitamins.
- When nerve inflammation develops due to herpes or other viral diseases, antiviral drugs are prescribed, usually Lavomax, Gerpevir.
- Severe pain syndrome requires strong (narcotic) painkillers (Tramadol, Promedol). Non-narcotic medications for intramuscular injections can also be prescribed, for example, Dexalgin, Ketanov.
- To generally strengthen the body, it is necessary to take vitamin complexes; Neurorubin and Neurobion are good options.
- Braiding hair for medium hair
- How to insert music into a presentation
- Folk remedies for dandruff at home
Acupuncture
This is one of the additional methods of treating inflammation of the facial nerve ending. It is based on the activation of areas of the cerebral cortex using injections that are aimed at specific points on the human body. The effect of acupuncture provides relief from swelling, increases local immunity, and improves the sensitivity of nerve cells. The acupuncture technique has an anti-inflammatory effect. This becomes the main indication for the procedure if the inflammation is caused by a viral herpetic infection.
Physiotherapy helps relieve pain in order to improve the patient’s general well-being, regulate metabolic processes, and restore hormonal balance. Maximum effect in the treatment of inflammation of the facial nerve ending. It is recommended to carry out the procedures at the acute stage of neuropathy, this will help avoid unpleasant complications and a severe course of the disease. When acupuncture, the following rules must be observed:
- Maintain the correct ratio of excitatory and inhibitory methods.
- The latter is needed for the healthy facial part in order to relax the muscles on the diseased half.
- The stimulation method is necessary to increase irritation of the facial muscles.
- To improve a person’s general condition, it is necessary to perform acupuncture on individual points of the legs and arms.
Exposure to needles for inflammation of the face is carried out on six muscle groups. The following areas need to be addressed:
- In the area of the chin and mouth there are muscles that are responsible for the movement of the chin, nose, and upper lip.
- Buccal muscle, the maximum effect is achieved when the needle is inserted horizontally.
- It affects the muscle that is responsible for lowering the septum.
- Injections are given in the area of the cheekbones and the orbicularis oculi muscle.
- The action on the frontal belly of the supracranial, pyramidal muscles is carried out in the forehead area.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed if necessary to reduce swelling, inflammation, normalize microcirculation, improve conductivity and metabolic processes. Helps if inflammation or pinching of the facial nerve occurs. When treating neuropathy, the following procedures are prescribed:
- SMV therapy helps to reduce swelling;
- local darsonvalization to improve the nutrition of nerve fibers;
- low-intensity UHF therapy for anti-edematous action;
- infrared laser therapy, which is necessary to dilate blood vessels, accelerate recovery processes, and improve blood circulation;
- You can speed up the recovery of damaged nerve fibers using ultrasound therapy;
- phonophoresis with proserin, hydrocortisone;
- massotherapy;
- Ultratone therapy is prescribed to improve microcirculation;
- paraffin applications;
- myoelectric stimulation to normalize neuromuscular conduction.
Massage
This procedure refers to physiotherapeutic methods. Treatment in this way helps relieve tension from inflamed muscles and increase the tone of joints that have atrophied. Regular massage will improve blood circulation, reduce inflammation, and get rid of severe pain. A procedure is performed to influence reflex zones in the ears, face, and neck. The patient should be in a sitting position, with the head resting on the headrest so that all facial muscles are relaxed.
Movements during the massage should be rhythmic, but light. You should not perform the procedure yourself; it should be done by a specialist who is able to handle it. The massage technique is as follows:
- It is necessary to warm up the muscles using circular, light movements;
- then you need to move to the parotid zone with stroking movements;
- total duration of the procedure – 15 minutes;
- The course of therapy lasts no more than 10 sessions and can be repeated after 14 days.
Surgical methods
Surgical intervention in the treatment of the facial nerve ending is prescribed only if there are no expected results from conservative therapy. Surgery is usually used when there is partial or complete rupture of the nerve fiber. A positive outcome can only be expected if the procedure was performed within the first 12 months after the onset of nerve inflammation.
As a rule, autotransplantation of the facial nerve ending is performed, when the surgeon replaces the damaged tissue with part of a large nerve trunk. This is often the femoral nerve because its topography and anatomy are suitable for this procedure. Surgery is also prescribed in cases where conservative treatment does not help after 10 months of therapy. If the facial nerve is pinched due to the growth of an oncological process, surgeons first remove the tumor.
Folk remedies
You can use home recipes as part of complex therapy to speed up recovery. Before taking it, be sure to discuss with your doctor about the compatibility of the products. A noticeable effect appears only after 10-12 days of treatment. Below are several effective traditional medicine options:
- Warming up with sand or salt. You need to heat a glass of clean sand or salt in a frying pan. Then take a thick cloth and pour it there, tying it in the form of a bag. Apply to the sore spot for 30 minutes before going to bed, repeat for a month. Warming up will improve muscle condition and speed up recovery.
- Rubbing with a 10% mummy solution. The finished product can be purchased at a pharmacy. Apply a little mummy to a cotton pad, then from the center of the ear, with light movements, begin to massage the facial muscles for 5 minutes. Then you need to dissolve 1 tsp in a glass of warm milk. honey, 0.2 g mummy and drink the product. Therapy lasts 2 weeks.
- Black poplar buds. You will need 2 tbsp. l. plants (dried or fresh), chop them and mix with 2 tbsp. l. butter. Apply the resulting ointment to the skin after warming up, rub in gently, repeat once a day. Course duration – 2 weeks. Resins and oils from the kidneys have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
Prevention
If inflammation of the facial nerve ending occurs, the duration of therapy can last from several months to a year, so it is better to prevent this condition. To prevent the disease, you can adhere to the following recommendations:
- Visit your dentist regularly to monitor your dental health.
- Treat all bacteriological and infectious pathologies in a timely manner so that they do not cause inflammation.
- Support the body's immune defense, harden yourself.
- Avoid hypothermia to prevent primary neuritis.
- If any symptoms of illness appear, consult a doctor immediately.
- Avoid any neuroses (shocks, stress, etc.)
- Stop smoking, which lowers your immune system, and start actively playing sports.
- Eat more vegetables and fruits to get sick less often.
- Stop drinking alcohol completely or reduce it.
- Avoid drafts, facial and traumatic brain injuries.
Tablets and injections
How to treat inflammation of the facial nerve, what is drug treatment based on? The choice of specific medications is made by the attending physician based on the primary cause of nerve damage.
These may be drugs:
- anti-inflammatory;
- antiviral;
- antibacterial;
- painkillers and antispasmodics;
- neurotropic;
- vasodilators;
- decongestants;
- B vitamins.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
This group includes two types of drugs:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs);
- corticosteroids.
The purpose of the treatment is to reduce nerve inflammation and reduce pain . NSAIDs have a wide range of actions: anti-inflammatory, analgesic. Their use forms the basis of drug treatment for facial neuritis. You can take medications either in the form of tablets or injections.
Injections act faster and have high bioavailability (better absorbed). In addition, intramuscular administration of NSAIDs helps to avoid their side effects on the gastrointestinal tract.
The main NSAIDs with the fewest side effects (second generation):
- Meloxicam;
- Nimesulide;
- Celecoxib.
Available in the form of solutions for intramuscular administration and in tablets.
NSAIDs with a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect include:
- Indomethacin.
- Diclofenac.
- Piroxicam.
Painkillers
In case of severe pain, the doctor may prescribe analgesics . Most of these drugs also belong to the group of NSAIDs.
The fact is that non-steroidal drugs have both an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. Moreover, one of these actions in a particular medicine may prevail.
NSAIDs with a pronounced analgesic effect:
- Ketorolac.
- Ketoprofen.
- Diclofenac.
- Indomethacin.
Drugs in the form of injections are prescribed for severe pain, which is “shooting” and unbearable.
Immunomodulators
Immunomodulator drugs stimulate the immune system , helping the body fight viruses and infections and recover faster in the process of fighting the disease.
The choice of immunomodulator to combat neuritis depends on the causes of nerve inflammation. The use of drugs of this series for herpetic lesions will be effective.
Basic remedies for the treatment of herpes:
- interferons - Viferon, Anaferon, Leukinferon, Poludan;
- synthetic – Polyoxidonium;
- immunostimulants of microbial origin - Likopid, Imudon, Bronchomunal.
Taking them activates the production of antibodies to fight the disease.
The drugs are available in the form of tablets, injection solutions, and rectal suppositories. As a rule, oral use of immunomodulators is sufficient.
Antibiotics
The use of antibiotics is necessary to combat neuritis caused by bacterial infections . In this case, the drugs will help fight the root cause of the disease.
The specific drug group depends on the type of infection and is selected by the attending physician.
As a rule, antibiotics are prescribed in the form of injections as part of inpatient treatment. This type of therapy allows you to defeat the infection as quickly as possible.
Hormones
In the treatment of neuritis, glucocorticosteroids are often prescribed . They belong to a subclass of corticosteroids and are produced naturally in the human body from the adrenal cortex.
Hormonal drugs are used as an anti-inflammatory agent . At the same time, they have an additional immunoregulatory and antiallergic effect, which contributes to a general improvement in well-being, relieving swelling and reducing pain.
Basic corticosteroids:
- Prednisolone;
- Metipred;
- Dexamethasone.
The drugs are taken in tablets, injections are prescribed for severe pain and swelling.
Antiplatelet agents
These are drugs that prevent the formation of blood clots . As a rule, they are limited to the use of antiplatelet drugs in tablet form.