Alzheimer's disease is a severe, as yet incurable neurodegenerative disease associated with organic lesions of various parts of the brain and its vascular system. This is one of the forms of senile dementia, which, according to experts, affects about 50 million people in the world.
According to statistics, women are twice as likely as men to develop dementia. Scientists are actively studying this dependence, but there is no reliable theory yet. Undoubtedly, the leading role is played by fluctuations in the hormonal status of the female body and associated changes in biochemical reactions. This is confirmed by the fact that women who received hormone replacement therapy subsequently retained strong memory and a clear mind for a long time. Some researchers agree that the secret is in women's longer life expectancy; men simply do not live to see their Alzheimer's disease.
Description
The name came to us from the Latin language. The disease affects the brain, causes irreversible destruction of the higher nervous system and manifests itself as cognitive impairment. A person loses knowledge and practical skills and is unable to learn something new. His mental abilities sharply decline, his memory deteriorates, and he begins to suffer from a personality disorder.
Select a service for your relative | |||
| Caring for bedridden people | Disability care | Elderly care | Care after a heart attack |
This common pathology has been studied all over the world for several decades. All studies on this topic have shown that almost 48 million people on the planet are affected by a serious disease. The World Health Organization predicts that cases will almost double by 2030, and by 2050 this figure will increase to 136 million. Statistics provide disappointing facts that show that the percentage of those experiencing the attack is higher in countries with low and middle economic standard of living.
In the Russian Federation, statistical data is not entirely accurate, since relatives consider this phenomenon to be a natural process of aging, and do not go to medical institutions for a diagnosis.
How does dementia manifest in older people?
The disease has become much “younger” in recent years and knows no boundaries. Dementors can become not only those who are over 70-80 years old, as was previously thought, but also fifty. The symptoms frighten those at home who are in the same area as the “monster,” who loses his memory, throws dishes and destroys the apartment, rushes to fight on loved ones, smears excrement on the walls and bed, and often runs away from home. This behavior can last from three months to several years. The result of the disease is absolute immobility. The most difficult time is coming for relatives. Friends and comrades somehow quickly disappear from their lives; it happens that the husband cannot stand it and leaves the family.
Often the population does not have complete information about how to deal with such patients. Doctors prescribe therapeutic treatment, but do not say how the caregiver’s existence will change in the future.
This problem can be solved, because in Russia there are a large number of institutions for the elderly. For example, the network of boarding houses for the elderly “Zabota” presents 10 cozy houses in the Moscow region. They accommodate more than 500 wards. Medically trained staff provide first-class care for the elderly. A complete five-course meal has been developed, where the menu is compiled individually for each person, according to the recommendations of a specialist. The staff takes care of physical and mental health. Every day they try to diversify their leisure time with active games, musical evenings, thematic conversations, and picnics. Gymnastics and classes to restore mental abilities are conducted daily.
Leave a request for selection of a boarding house
for an elderly person with dementia
Causes of dementia in the elderly
Basically, the impetus for negative changes is already existing diseases that arose due to damage to the central nervous system, such as Alzheimer's, Pica and Lewy body syndrome. But the death of brain cells can also be provoked by:
- High blood pressure.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Benign and malignant tumors.
- Stroke.
- Addiction to tobacco and alcohol.
- Head injuries.
- AIDS.
- Meningitis.
- Viral encephalitis.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Endocrine pathologies.
- Lupus erythematosus.
At risk are people whose immediate relatives were already dementors under the age of 65, or suffered from diabetes and obesity.
Leave a request for selection of a boarding house
for an elderly person with dementia
Classification of the disease
Dementia can be classified by type, degree of development (mild, moderate and severe), and localization of the pathological process. Depending on the age of the patient at which the lesion occurred, senile and presenile dementias are distinguished. Presenile symptoms occur before the age of 65 and always occur against the background of other diseases (Alzheimer’s disease, vascular lesions, alcoholism).
Classification by localization
There are four localizations of the disease: cortical, subcortical, vascular, multifocal. Cortical dementia is characterized by damage to the cerebral cortex followed by its atrophy. In this case, memory, speech, and thinking suffer the most, but there is no effect on motor function.
This localization is combined with atrophic changes, most often senile dementia of the Alzheimer's type occurs (in 50-60% of cases of cortical localization), a little less often - alcoholic and caused by Pick's disease.
Cortical dementia more often affects women, this is due to the fact that the weaker sex is more susceptible to Pick's and Alzheimer's diseases, which scientists associate with hormonal problems due to insufficient estrogen production.
Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia have similar symptoms.
But Alzheimer's disease progresses more slowly, its symptoms are less pronounced, the main manifestation is forgetfulness and memory loss, while dementia is a whole complex of symptoms when, in addition to memory loss, a complete change in personality occurs. Comparison of Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia
| Alzheimer's disease | Senile dementia |
| May lead to dementia | May not cause Alzheimer's disease |
| Personality changes are insignificant, sometimes there is a sharpening of personal character traits, tearfulness, vulnerability, sentimentality. | Change from minor to complete destruction of personality |
| Motor activity is not impaired, or suffers only at the last stage | Depending on the location, it may differ in significant disturbances in the motor system (from tremor to complete immobility) |
| The reasons are not fully understood; they are associated with the synthesis of abnormal protein | The cause is damage and subsequent atrophy of the brain. |
With subcortical localization, subcortical structures (for example, the white matter of the brain) are affected, as a result of which many skills are lost, the patient suffers from forgetfulness, and his thinking and speech slow down. This localization can be determined by motor disturbances: tremors, twitching or muscle stiffness appear. Diseases that accompany subcortical dementia - Parkinson's, Huntington's, supranuclear palsy.
The disease senile dementia, when blood vessels are affected and blood circulation is impaired, causing the cortical and subcortical zones to suffer, is called vascular. With this type of dementia, a person gradually (although there are cases of acute onset) loses personality traits, intelligence, ceases to understand speech, and loses motor skills. A patient with the vascular form should be under the supervision of doctors, as sudden death is possible.
Multifocal dementia is the most severe type of disorder, in which many lesions occur and the central nervous system is affected. Progression is rapid, with the severe stage beginning within a few months of the first symptom. The symptoms are atypical, the disease, in addition to personality changes, is manifested by lesions of the cerebellum, that is, drowsiness, impaired coordination of movements, erratic involuntary movements, perseveration (the patient constantly repeats one phrase, one movement).
Other classifications
In addition to the generally accepted classification by localization or degree of development, scientists from different countries define senile dementia by type (vascular, atrophic or mixed), syndrome, and clinical variant.
Scientists who adhere to the classification according to the clinical variant suggest the presence of senile dementia of the following types:
- vascular;
- Alzheimer's type;
- alcoholic;
- frontotemporal (Pick's disease).
Syndromic classification involves division into lacunar and total dementia. Senile senile dementia of the lacunar type affects memory. The personality's character remains almost unchanged, but tearfulness, sentimentality, and capriciousness may appear. Total dementia is more pronounced and, in addition to memory, covers other aspects of the personality. There is a disturbance in thinking and perception, and complete disorientation is possible.
Classification of types of disease in the weaker sex
Senile dementia is divided into three types:
- Atrophic. It is characterized by primary degeneration in the brain.
- Vascular. It is also called secondary, as it develops against the background of existing deviations.
- Mixed. It is based on the two previous points.
- Multifocal. The entire nervous system is affected.
Experts also distinguish cortical and subcortical localizations.
Provoking factors for early signs of dementia in women under 50 years of age
The causes are point mutations in the DNMT3A and TET2 genes, which are responsible for vascular growth throughout the life cycle.
American and Australian scientists have proven that an unhealthy lifestyle also leads to dementia.
For prevention it is necessary:
- Do not abuse tobacco and alcohol products.
- Eat nutritiously and nutritiously. Include fish, vegetables and fruits in your diet.
- Engage in active sports.
- Strengthen neural connections by keeping the brain in good shape by reading and learning foreign languages.
- Work on a computer, master gadgets (brain “training”).
- Don't ignore depressive disorders.
- Treat yourself for hypertension and diabetes.
- Do not ignore hearing loss or deterioration and seek advice from an otolaryngologist.
Leave a request for selection of a boarding house
for an elderly person with dementia
Features of manifestations of age-related dementia in women
Its representatives are by nature more emotional than men, and therefore are subject to frequent mood swings. You should pay attention if you or a loved one exhibits:
- Irritability.
- Sudden aggression.
- Tearfulness or unreasonable laughter.
- Long-term severe depression.
- Excessive suspicion.
- Unreasonable stubbornness.
- Reluctance to communicate.
- Accusations against relatives, neighbors or complete strangers.
Risk factors
You should be wary of developing this disease in yourself or your loved ones in the following cases::
- the person’s age is approaching 75 years (and women are more susceptible to developing dementia);
- the patient has been diagnosed with diabetes (this disease is destructive to the blood vessels of the whole body, including the brain);
- one of your close relatives suffered from manifestations of senile dementia (the tendency to the disease is inherent in the genes);
- there have been head injuries;
- suffered a stroke;
- infectious lesions of the brain, such as syphilis, encephalitis, meningitis, tuberculosis, have been diagnosed;
- low level of physical and intellectual activity for a long time;
- excess cholesterol in the blood;
- systematic self-poisoning with alcohol, nicotine, psychotropic drugs;
- Throughout life, a person has been characterized by depressive disorders.
If you notice one of the listed symptoms or a combination of them in yourself or people dear to you, then you should not fall into despair .
You need to consult a doctor promptly if alarming signs appear, follow the recommendations of specialists, and take prescribed medications.
And, of course, it’s time to think about dementia prevention .
What else you need to know about dementia:
- what are the reasons for the development of the disease and is there a connection with other diseases;
- why it develops in children and adolescents and what early dementia is;
- is there a difference in manifestations in men and women, between acquired and congenital dementia;
- how many stages of development the disease goes through;
- what treatment methods exist, what drugs are used;
- how many years do people with dementia live, are they given disability, what kind of care do they need;
- How to behave for relatives of people suffering from dementia.
The first signs and symptoms of dementia in a woman
You will determine the onset of the disease by how the patient formulates her ideas during a conversation, how poorly she has become able to remember information, whether she is able to reason and analyze, how she conducts conversations with others and how attentive she is.
We will also give you 12 signals that you can use to make a preliminary diagnosis.
Our boarding houses
Ramensky
Sheremetyevsky
Difficulty expressing your thoughts
Don't get discouraged if you can't find the right word from time to time. Perhaps the reason is excitement. But if you or your relative call the bed “the thing they sleep on” and are unable to remember the correct name, then this is a signal that there are brain disorders and it’s time to take action. And the sooner the better.
In addition, if you find it difficult to describe your thoughts on paper and feel inhibited, then dementia is already progressing!
Short-term memory lapses
It often happens that out of absent-mindedness we put something somewhere and then look for it. Or we forget the name of a friend, artist and writer. We remember a conversation or event that happened for a long time. Here, a doctor’s consultation is already necessary, since this may become a sign, if not of dementia, then of inflammation or atrophy of the prefrontal cortex of the brain, the main ganglia.
Leave a request for selection of a boarding house
for an elderly person with dementia
But nervous system failures also include the following symptoms:
- request to repeat the same sentence several times;
- the need for constant reminders and notes on paper;
- difficulty remembering what recently happened.
Bad dream
If you notice a disturbance in your relative’s sleep patterns, that is, he wants to stay awake at night and rest during the day, this is often a signal of the onset of an illness.
Personality changes and mood swings
Dementia overtakes people when their character changes dramatically. They become:
- oppressed;
- anxious and suspicious;
- depressed;
- silent;
- aggressive or grouchy.
They usually do this in an uncomfortable environment and when they perform unusual actions.
Errors in judgment
Contact your doctor immediately and get tested if you:
- They stopped filling out bills and documents correctly.
- You can no longer distinguish between the denominations of banknotes, are confused by price tags, and are unable to do basic mathematical calculations in your head.
- You can’t determine by eye the distance from one object to another, you get lost in orientation.
- You forget the order of simple processes (for example, preparing an omelet).
Dementia of the young: myth or reality
Although dementia is most often diagnosed in older people, the disease is often found in younger people. At this age, it is very difficult to determine the moment when dementia begins to develop. Lack of timely assistance complicates the disease. Most often, dementia in young people is a consequence of pathology of the nervous system or brain.
Among the reasons are:
- traumatic brain injuries;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- infectious viral diseases;
- alcoholism.
Chronic alcohol abuse causes vitamin B1 deficiency. This leads to difficulty in perceiving new information and often provokes memory lapses the morning after the feast.
Signs of dementia in young people are associated with the stage of pathology, as well as the intensity of the disease. Each of the three stages has its own specific features:
- Early stage. The disease can remain undetected for a long time. The person continues to go to work, communicate with relatives and friends. Pathology can be suspected by unhealthy forgetfulness, periodic loss of orientation in space and time.
- Middle stage. Symptoms of the early stages of dementia become more acute and worse. Previously acquired household and professional knowledge and skills are lost, and there is no opportunity to acquire new ones. A young man sometimes forgets the names of his friends and does not remember the events that happened yesterday. If he often asks the same questions without remembering the answers he received, this is a reason to urgently consult a doctor. The patient begins to walk aimlessly around the house and cannot find himself in any activity. At this stage, he already needs help with self-care. One of the most unpleasant symptoms is fecal and urinary incontinence. In order for a person with dementia to continue to live a normal life, he requires round-the-clock care.
- Late stage. This is the most difficult stage in the development of the disease, during which the first signs of personality disintegration are observed, and previous symptoms worsen. The person becomes completely passive, apathetic, and needs constant care. Memory and thought processes cease to function; the patient often does not remember his name or how old he is. Orientation in space is completely lost, speech and motor activity are practically absent.
Our boarding houses
Golitsyno
Minsky
Clutter in my head
Significant disturbances lead to disorientation. Also, such a person does not remember past events, is not able to choose the type of activity at the moment, does not understand the meaning of the conversation, and does not distinguish the faces of acquaintances.
Elevated amyloid beta levels
The peptide, which accumulates in the brain, destroys neural connections and forms amyloid plaques. Their accumulation leads to anxiety and irritability. Their increase contributes to shifts in the rhythms of sleep and wakefulness.
Loss of sense of humor
Patients lose the ability to adequately respond to sarcasm directed at them, often become offended and begin to behave inappropriately with the joker. And vice versa, they laugh when watching TV shows with tragic news (murder, catastrophes, mass disasters). Illogical and absurd behavior appears in the final stages of dementia.
Leave a request for selection of a boarding house
for an elderly person with dementia
Depressive state
It’s worth thinking about if your loved one has always been active, but recently became depressed, is not interested in the problems of other people, does not engage in his hobbies, has lost all interest in work and avoids the company of friends. If he spends the day from TV to bed, then he should be persuaded to see a neurologist.
Neglect of personal hygiene
Another clear evidence of the onset of dementia, where the following things are present:
- Reluctance to get yourself in order in the morning (comb your hair, brush your teeth, wash your face).
- Ignoring showering procedures.
- Untidy clothing.
- Laziness, due to which the patient does not trim his fingernails and toenails.
To persuasion and calls to take care of yourself, the answer is: “why do it if everyone around you is your own?”
Traffic violation
Difficulties in coordination lead to the fact that the patient often falls when walking. It is difficult for him to go down and up stairs and take a bath on his own. He will not find the right way home, as his spatial vision will change. He is unable to distinguish the parameters of objects, the distance between them.
Stages
Senile dementia (symptoms and signs in women appear with varying degrees of intensity) after the onset of the first manifestations goes through 3 stages of development.
- The initial stage is characterized by periodic deterioration of thought processes. At the same time, the general condition is not disturbed, the person accepts and understands himself, his actions, and is able to independently perform ordinary household manipulations.
- The moderate second stage is more pronounced. Sometimes a woman forgets about the basic rules of using simple objects, such as a telephone or a door lock. However, she usually follows the rules of personal hygiene and takes care of herself without outside help.
- The progressive third stage is considered the most dangerous. The patient becomes a threat to herself and others, forgets about the rules for using cutlery and other things, and relieves herself anywhere.
In the most severe cases, exhaustion of the body is observed; any disease of the internal organs can lead to death.
Our boarding houses
Rublevsky
Dolgoprudny
Putting things in their places
All people, at least once in their lives, have such moments when they have hastily put something away, but in the morning you cannot find it. In a healthy person this happens in isolated cases. He calmly thinks about and reproduces the whole of yesterday evening step by step. Those affected by senile dementia may leave, for example, a comb in the freezer of the refrigerator, and then blame their household members for it.
Forecasts
With a sluggish course of the disease, the patient can live up to 20 years, but full control and care is necessary. With rapid progression of the condition, life expectancy is reduced to 10 years. With the development of Parkinson's disease, Pick's disease, Huntington's disease, vascular dementia or frontotemporal degeneration, the patient lives from 6 to 8 years with proper care.
The prognosis is always unfavorable because the disease cannot be treated. Senile dementia is a common and dangerous disease. Symptoms and signs appear more often in women than in men. Patients need constant supervision by a doctor and relatives.
How not to confuse the symptoms of early dementia and natural aging
Usually, people turn to doctors for help in the late stages of the disease, when the patient one day gets lost on the street, not remembering his address. At this time, it is already difficult to help a patient who has up to seven years to live. That is why doctors warn that if you experience the signs that we discussed above, you must definitely show up at a medical facility. It’s better to come to the clinic just like that than to miss the moment and watch your loved one’s mind fade away.
The examination should be carried out at the stage of apathy, absent-mindedness, aggressiveness, isolation and deterioration in the ability to remember.
Leave a request for selection of a boarding house
for an elderly person with dementia
Video: all about senile dementia
We offer a visual overview of the entire process about the initial signs and symptoms of dementia in women.
Symptoms of senile insanity. What to consider?
Dementia does not manifest itself with clearly defined signs. Most of them relate to age-related changes. It is necessary to know about the symptoms of the disease in advance, because this helps to avoid serious complications. Relatives of elderly people need to monitor their behavior and its changes. In addition, they should pay attention to the following factors:
- Memory problems. Organic brain damage leads to forgetting of events that happened recently. A person with senile dementia does not remember what happened to him yesterday, but can describe in detail events from the distant past.
- Behavior change. The patient no longer pays attention to his appearance. As a rule, he begins to take care of himself only if he is reminded about it. People with senile dementia are often apathetic. They are not interested in work or hobbies. Sometimes they can persistently prove that they are right or, conversely, become indifferent to the world around them. Shyness in such people also disappears. They can talk about erotic topics and demonstrate promiscuity.
- Disorientation in space. If patients are constantly at home, then, as a rule, they do not have any problems. Finding themselves in a place unknown to them, they may not find their way back.
- Deterioration of thinking. With dementia, people are unable to make final decisions. It is extremely difficult for them to choose the appropriate action in a given situation.
- Talkativeness. Some patients behave adequately in everyday life. Sometimes loved ones don't even notice the changes. But if you ask a person a question about his age, place of residence, date, he will be at a dead end.
Signs of dementia are becoming more pronounced every day. People who have this disease often become stingy. They may collect things in their home that they do not need at all. Symptoms of senile dementia in women at the initial stage are very original. They may experience increased appetite or great sexual desire. Over time, the patient ceases to care for herself independently. She forgets that she has children and grandchildren. In some cases, senile dementia provokes aggression, anger, and tearfulness in people. At an advanced stage, sick people require regular care. They should not be left at home alone, because they can cause a fire, flood, etc. The interesting thing is that they themselves do not notice this.
Comparison of the behavior of a healthy and sick person
Have you noticed strange illogical actions or an unkempt appearance in a relative, and this has alerted you? Then drop all planned activities and watch him for a few days.
Urgently go to a neurologist when you see such abnormalities:
- Decreased mental skills and memory.
- Aggression.
- Absent-mindedness.
- Loss of time and orientation.
- Forgetfulness.
- Substitution of concepts and phrases.
- Stumbling out of the blue.
- Mathematical errors when filling out invoices.
- Night wakefulness.
- Apathy at work.
- Loss of sense of humor.
- Walking aimlessly from room to room.
Select a service for your relative | |||
| Caring for bedridden people | Disability care | Elderly care | Care after a heart attack |
The main signs and manifestations of dementia from the initial stage to total dementia
Everything we listed above is an early stage of the disease. But depending on the lesion, a person may experience:
- Severe mental disorders.
- Hallucative reasoning (when a conversation is conducted with fictional characters).
- Inability to remember past events.
- Complete collapse of personality.
- Impaired speech and ability to recognize things.
- Insanity, in which mental and physical work declines.
In addition, you can easily check for shifts by type of activity. If there is a driver in front of you, then pay attention to the following:
- how he navigates familiar terrain;
- does he drive according to the signs?
- how it reacts to force majeure circumstances;
- which turn signal turns on when changing traffic;
- what is his behavior during traffic jams, will he calmly wait for passage or will he overtake on the side of the road;
- whether control mechanisms are confused.
Dementia symptoms
Dementia belongs to the category of diseases that do not simply go away and progress. Depending on the patient’s current socialization capabilities, three stages of pathology are distinguished. Each of them has its own specific set of symptoms.
- First stage. The patient already has noticeable intellectual impairments. There are complaints that he cannot remember events in his life and forgets his address. A critical attitude towards his condition remains, the person understands that he needs to see a doctor for professional help. Any household activity is carried out in full, self-service remains at a high level. Such patients follow the rules of hygiene, can cook their own food, and clean the house. At this stage, round-the-clock care is not yet required.
- Second stage. The development of the disease is accompanied by severe intellectual impairment. The person does not remember whether he turned off the gas or the iron, closed the doors and other things important in terms of safety. The patient does not realize the criticality of his situation; he does not believe that he is sick. There is a risk that older people with dementia may cause harm to themselves or others through carelessness, without malicious intent. They require regular care; leaving such a person alone is unsafe.
- Third stage. It is the most severe, characterized by complete collapse of personality. The symptoms of dementia are especially pronounced here. Usually such changes in the brain are irreversible. At this stage it is very difficult to stop the further development of dementia. Patients do not recognize their friends, family and loved ones. They cannot feed themselves and must be spoon-fed. Even if in rare cases hunger prompts them to search for food, older people cannot distinguish good foods from bad ones. They cannot maintain good hygiene, so they need constant care around the clock. The ability for logical thinking gradually fades away, they cannot connect two facts together. Verbal communication with others is reduced to zero; they are constantly in silence. The third stage is characterized by apathy and a depressed mood. There is no feeling of thirst or hunger; if the patient is not fed for a long time, he will not ask. Movement disorders lead to the fact that a person cannot perform the simplest movements - chew, swallow, walk. Unfortunately, this stage sooner or later leads to the death of the patient.
Disease detection test
There are several ways to determine the onset of senile dementia. We present one of them, which will help distinguish the natural decline of the body from dementia. It should be remembered that only a qualified physician can obtain the most reliable result. Check:
- How does a person navigate space, can he find his way home if something happens, can he distinguish between units of time.
- Short-term and long-term memory.
- Performing tasks to decompose a simple process into algorithms, for example, making coffee or washing clothes.
- Visual perception - asked to draw one or more simple shapes on paper.
- Patient's speech. It also turns out how the subject hears others.
- The client's knowledge of the world around him. The doctor asks to announce the purpose of the items.
- Intelligence. For this purpose, different research methods are used.
| Considered normal | Signs of Alzheimer's |
| Forgot to put lunch in the refrigerator | Didn't prepare food |
| Can't find a word when speaking | Speaks in an incomprehensible language where sentences are off-topic |
| I forgot the exact address of my friends | Forgot my place of residence |
| I don't remember how much 6x7 is | Forgot all the easy math operations (addition and subtraction) |
| Lost my apartment keys | Doesn't remember that he has his own place to live |
| Short-term mood swings and apathy | Constant suspicion and dissatisfaction |
Leave a request for selection of a boarding house
for an elderly person with dementia
Distinctive features of the weaker sex
According to statistics, the number of women suffering from dementia is almost twice as high as men. The reasons for this distribution have not yet been identified, but there are hypotheses:
- Representatives of the stronger half of humanity have a 10-15 year shorter lifespan, so they simply “pass away” earlier and do not live to the point of senile insanity.
- Scientists have found in them a new biological material that protects the cerebral cortex from the development of Alzheimer's.
After fifty years, hormonal changes in the body occur. During menopause, we recommend contacting a gynecologist who will prescribe comprehensive treatment. If after therapy your nervousness and tearfulness do not go away, then you need to see a neurologist.
Onset of dementia
Dementia is a multifactorial disease that develops when several risk factors combine. It is believed that the pathology is partly related to genetic predisposition, since cases of occurrence are often identified in relatives.
Autoimmune processes leading to damage to the nerve membranes and brain cells are a common mechanism for the development of dementia in the elderly and senile. In such cases, there is a progressive decline in neurons, which leads to a decrease in memory, attention and other functions of the nervous system.
Among the provoking factors are:
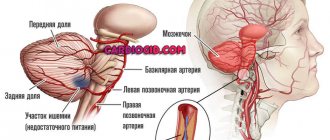
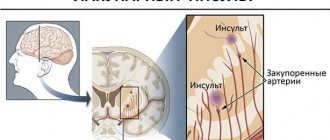
- vascular pathologies (atherosclerosis and arteritis of cerebral vessels, arterial aneurysms), leading to a decrease in the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to the nervous tissue (such ischemia underlies vascular dementia);
- neuroinfections (meningitis, encephalitis) and chronic infectious diseases in the body lead either to direct damage to the structures of the central nervous system or cause the development of autoimmune damage;
- malignant neoplasms;
- chronic intoxication with alcohol (alcoholic dementia), salts of heavy metals, etc.;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- mental illnesses.
Based on the identified cause of dementia, doctors classify dementia into three main types:
- vascular, associated with damage to cerebral vessels and ischemia;
- neurodegenerative, observed in Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and Pick's diseases;
- mixed, when combining two of these components.
Such a classification is necessary, since the specific form of the disease will determine how to treat the pathology.