What is the trigeminal nerve
The human face has many muscles and nerve endings. Not only the mucous membranes of the nose, pharynx, and conjunctiva, but also the nerve endings can become inflamed. This is most often associated with neurological disorders that change the sensitivity of the fibers that conduct impulses.
With neuropathy of the facial area, acute shooting pain occurs on the right or left. Mirror inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is extremely rare. It is located in the temporal region, near the base of the auricle. And from it there are branches along the entire half of the face:
- jaw nerve (upper and lower);
- optic nerve;
- infraorbital nerve.
The trigeminal nerve passes through the bone tissue in several places, which plays an important role in the occurrence of inflammation associated with pinching. Thus, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve can result in acute pain both in the upper and lower jaw, and in the forehead area, covering the eye sockets.
Symptoms
As statistics show, neuritis most often manifests itself in patients of the older age group, or more precisely, over 50 years. If such a patient has caught a cold of the trigeminal nerve, treatment cannot be delayed, since the disease in this case will progress quite rapidly. For what reason the nerve was cold, what to do in this case and how to treat it, only a neurologist can determine. Self-medication in the treatment of neuritis is contraindicated.
If a patient of a different age category is admitted with suspicion of neuritis, most likely we are talking about a serious pathology in the body. Symptoms that the facial nerve is cold are manifested in the following factors:
- severe pain in the facial muscles;
- while chewing food, discomfort and painful shootings are felt - trigeminal neuralgia has appeared;
- pain appears only on one side of the face;
- the skin on the face becomes too sensitive, or vice versa – loses sensitivity. In this case, the affected part of the face may become distorted, and the corner of the mouth may go down.
This symptomatology manifests itself in cases where the brain center is affected by a cold nerve. Often, individual branches of the trigeminal nerve are affected. In this case, the following symptoms are observed:
- dull, monotonous pain in the lower part of the face;
- changes in taste and hearing sensations;
- numbness of some parts of the face. These are the wings of the nose, lips, nasolabial triangle, chin and other areas;
- hyper- or hyposecretion of conjunctival fluid;
- often the patient experiences a sharp increase, and then an equally sudden decrease in body temperature;
- numbness of the entire tongue or part of it;
- too active salivation.
If the patient has caught a cold of the trigeminal nerve during pregnancy, under no circumstances should you start self-treatment. In most cases, it requires taking antibiotics, most of which are contraindicated for pregnant women.
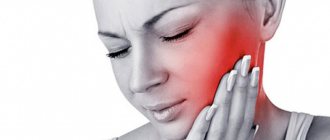
If the nerve gets cold, the symptoms often resemble toothache, which only complicates treatment. The sensations are quite strong and unpleasant. The pain can “shoot through”, radiating to the chin and lower part of the nose.
Pain in the temple and cheek is often observed. This happens when the pain innervates the outer part of the ear and the parotid gland. This may affect the ear canal and the skin of the temporal part.
Causes of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
There are several reasons leading to inflammation of the nerve ducts:
- Poor blood supply associated with physical compression of the nerve. First of all, this is swelling caused by diseases of the ENT organs. The resulting tumor can also pinch the nerves.
- Inflammation associated with dentistry. This includes gingivitis, periodontitis, caries, pulpitis, and eruption of wisdom teeth. Each of these diseases can lead to suppuration, abscesses, swelling and bacterial infections of tissues.
- Medical error by an anesthesiologist - if the injection was given unsuccessfully and the needle got into a nerve, pain cannot be avoided.
- Hypothermia causes muscles to lose their elasticity, which leads to pinching of the nerves passing between the fibers.
- Bacterial infections, in particular tetanus and polio.
- The cause of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, which is difficult to diagnose, is the psychological state of a person - frequent experiences, stress, and nervous disorders.
To determine the cause of inflammation, you need to consult a specialist.
Ointment for restoring the functions of the trigeminal nerve
According to reviews from people who have experienced pain in the facial area, an ointment based on lilac buds helps a lot. The dried raw materials should be poured into a jar and filled with lard in a ratio of 1 to 5. Place the glass container in a water bath and let the mixture boil for an hour. The healing ointment must be rubbed into the affected part of the face twice a day.
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia at home gives positive results when using fir oil, which must be rubbed into the affected area using a cloth or a piece of cotton wool.
It is recommended to repeat the procedure 6 times a day. At first, the skin becomes red and swollen, but then its color and structure are restored. The trigeminal nerve stops causing concern 3 days after the start of therapy.
In herbal treatment, an infusion of marshmallow roots, flowers, and leaves is effective. 4 teaspoons of the dried product must be filled with cooled water and left for about 8 hours. Make a compress from the infusion, which must be applied to the facial area for about 50-60 minutes before going to bed. Then you should put on a warm scarf and go to bed. This treatment lasts about 7 days.
Treatment methods
Depending on what caused the inflammation, a course of treatment is prescribed. For bacterial lesions, the emphasis is on antibacterial therapy through systemic administration of drugs.
However, regardless of the reasons, the doctor prescribes painkillers to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. It could be:
- ibuprofen;
- paracetamol;
- analgin;
- ketorol;
- diclofenac.
All of the listed drugs can be prescribed either in the form of tablets for oral administration, or prescribed in the form of solutions for intramuscular administration.
When conservative methods are not possible, the help of a surgeon may be needed. This primarily concerns abscesses due to the eruption of wisdom teeth, pulpitis or other dental diseases. In this case, the abscess will be opened, pus will be removed, the wound will be treated with antiseptic, and the tooth will be removed, if necessary. If a pinched nerve occurs as a result of pathologies in the structure of the skull, the surgeon will perform an operation to correct the situation and free the nerve bundles.
As a complex therapy, massage, heating or exposure to a magnetic field and electric current can be prescribed. You cannot massage or warm the inflamed area yourself, because this can lead to complications associated with rupture of the purulent capsule, blood poisoning and paralysis of the facial nerve.
Separately, you may need to consult a neurologist who will determine the cause of the inflammation if other specialists have not found obvious foci of infection and abscesses.
Traditional methods of treatment are permissible only as an addition to the main therapy. For example, rinsing with chamomile decoction will relieve inflammation and reduce swelling. But you can resort to such procedures only with the permission of the attending physician.
Therapeutic massage of the facial area
Treatment of the trigeminal nerve of the face at home is a set of measures, including drug therapy, massage and heating, aimed at relieving inflammation and normalizing the sensitivity of the facial apparatus. Self-therapy should be carried out only under the supervision of a doctor after an accurate diagnosis of the disease and initial treatment in a medical institution.
Treatment of the facial trigeminal nerve at home is effective through the use of massage, which must be done very carefully, since touching sensitive points can cause a wave of unbearable pain. It is recommended to massage the neck in a circular motion on the painful side, starting from the shoulders and moving towards the chin. With mild and moderate forms of trigeminal neuritis (that is, with not very acute symptoms), the face can be massaged from the center to the outer part - along classic massage lines. To obtain a more effective result, it is recommended to use massage oil. You can prepare it yourself using bay leaves. 100 grams of fresh or dried product must be filled with 0.5 liters of any vegetable oil, left for a week, strained and used as directed. If it is not possible to massage, it is recommended to lubricate the skin in the area where the trigeminal nerve is located with this product. Treatment at home, reviews of which are positive, is possible only after consultation with a doctor, which is necessary to avoid possible complications.
Possible complications
Doctors call facial paralysis the first complication that appears in the absence of adequate treatment. This means that a person who does not receive medical care in a timely manner is deprived of the opportunity to express his emotions through facial expressions on one side of his face. This condition can no longer be corrected, which will certainly affect the quality of life. Distortion of facial expressions will lead to the development of depression and constant dissatisfaction with one’s appearance. Not every patient can come to terms with irreversible changes in their appearance without deep distress.
One of the most unpleasant manifestations of paralysis is the inability to close the eyelids on the injured side of the face. In this case, the eye will have to be regularly instilled with artificial tears to prevent the cornea from drying out, since natural hydration through blinking becomes unavailable for this eye.
Why does the facial nerve become pinched?
Facial neuralgia is possible due to many factors. The most common causes of pathology:
- injuries to the facial part of the skull as a result of blows;
- inflammation of the hearing aid (otitis);
- damage to some parts of the brain (meningoencephalitis);
- hypothermia (most often of one half, for example, with an open window while driving in a car);
- head tumors (anywhere);
- genetic disposition;
- inflammation after surgery (including plastic surgery).
Additionally, neuralgia of the facial nerve can be provoked by:
- TBI (cranial injuries, concussions);
- purulent-inflammatory processes of the head;
- violation of the integrity of the skull on the front side (crack).
In each individual case, the disease is of a purely individual nature.
Symptoms of the disease
The symptoms of neuralgia of the facial nerve are quite obvious, but they appear alternately:
- frontal folds are smoothed out;
- the shape of the eyes changes, the size increases;
- the oral line “breaks”, the lower lip droops;
- those around you get the feeling that your interlocutor is grinning;
- a smile twists the mouth and lips into a grimace;
- raising the eyebrows on the affected half of the face does not form frontal folds;
- an attempt to close the eyes leads to incomplete closure of the eyelids (hare's eye);
- when opening the mouth, the lips become deformed;
- a patient with facial neuralgia cannot kiss or whistle (movements involving the lips);
- taste sensations, reflexes of the eyebrows and cornea decrease;
- rashes appear on the ear around the ear canal.
Additionally, some patients may experience watery eyes while eating, difficulty brushing teeth, chewing food, and pronouncing sounds.
Individual manifestations of facial neuralgia combine two common manifestations for all patients: pain and impaired facial expressions.
Treatment requires preliminary diagnosis, since the signs of facial neuralgia are similar to some other pathologies. But the characteristic feature - damage to only one half of the face - makes the diagnosis easier.
Prevention of inflammation
To prevent the risk of developing inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, it is recommended to follow a number of measures:
- monitor oral hygiene and consult a dentist in a timely manner;
- do not stay in the cold for a long time or protect your face from freezing with a scarf;
- do not self-medicate otitis media.
At the first manifestations of pain on the face, you should immediately consult a doctor. This will stop the development of inflammation. In addition, early diagnosis allows for conservative treatment methods.
Treatment using traditional medicine methods
At home, therapy is carried out with regular consultations with a neurologist. Inflammation of the nerves is treated with herbs together with medications, physiotherapy, and other methods. Heat compresses are allowed to be used only if there is no purulent focus in the facial area.
When treating inflammation of the nerves, the following drugs can be used:
- bay oil (to lubricate);
- beet juice (gauze pads in the ear);
- marshmallow root, fresh wormwood (compresses);
- hibiscus, chamomile (tea);
- aloe juice (inside).
Externally, folk remedies are applied to areas of nerve damage, to the submandibular lymph nodes, maxillary sinuses, and into the ear canal. Before starting treatment, be sure to familiarize yourself with the contraindications of the herbal medicine.
Frequently asked questions about the trigeminal nerve
1. How to distinguish trigeminal nerve pain from facial neuritis?
The trigeminal nerve mainly contains sensory fibers, and the facial nerve contains motor fibers. Therefore, the main symptoms of the first lesion are acute or aching pain and numbness, and the second - unilateral paresis or paralysis of the face. With diseases of the facial and trigeminal nerves, similar symptoms are possible. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
2. Is it possible to cure the trigeminal nerve with folk remedies?
It is impossible to cure the trigeminal nerve with folk remedies. You can alleviate the symptoms somewhat, but you can also do harm. To choose the right treatment, you need to know the cause of the symptoms. And it’s better if a doctor does it.
Review of effective drugs
There are a lot of medications used to treat colds of the trigeminal nerve. The most popular of them are the following:
- Anticonvulsant medications. They increase muscle tone and also improve nerve patency. The pain subsides after 1-2 days of taking the drugs, and the period of time between attacks increases. Carmabazepine, Phenytoin, Clonazepam, Lamotrigine;
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process in the body. Taking them also helps to get rid of pain. Ibuprofen, Nimesil;
- Painkillers and antispasmodics. Relieves pain. This is a very important group of medications, since in some cases the pain is so severe that the patient cannot lead a normal lifestyle. Baralgin, Ketonal, Baclofen, Ketorol;
- Sedatives and antidepressants. They are taken when necessary, since constantly felt pain can provoke increased anxiety and insomnia. Sodium hydroxybutyrate, Amitriptyline;
- Glucocorticosteroids. They relieve existing swelling and accelerate the process of regeneration of nerve tissue. Alclomethasone;
- B vitamins. Stimulate metabolism, reduce pain, and have a beneficial effect on the immune system. Neurobion, Neuromultivit.
Ibuprofen is prescribed to relieve inflammation in the body.
Additionally, the following may be prescribed:
- Antiviral agents. They are aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process in the body. Rimantadine, Arbidol;
- Antibiotics. Perform similar functions with antiviral agents.
The difference is that this group of medications is used in the presence of a bacterial infection. Levofloxacin, Amoxicillin.
As you can see, in order to prevent trigeminal neuralgia, it is necessary not only to monitor your health, but also not to come into contact with the flow of cold air. This can cause not only a common cold, but also more serious health problems.
THERAPEUTIC EFFECT OF THE MAGOFON-01 DEVICE
The therapeutic effect on the trigeminal nerve region is the combined effect of an alternating magnetic field and acoustic vibrations. This enhances the therapeutic effect and accelerates recovery in acute and chronic diseases.
The magnetic field of the device has a certain frequency and induction - optimal for normalizing the cells’ own electrical charge and their electromagnetic conductivity. At the same time, the change in the field does not allow the body to get used to the effects of radiation, which increases the effectiveness of the course of treatment.
The magnetoacoustic effect of the MAGAFON-01 device on the trigeminal nerve area allows you to reduce the sensitivity of peripheral nerve receptors, improve blood supply and reduce pain after the first use.
It has been noted that exposure to an alternating magnetic field can relieve emotional stress and improve sleep, which is of utmost importance for the treatment of most diseases.