Definition
Todd's palsy is a transient condition that develops after an epileptic seizure. Patients experience paresis or paralysis of the limbs on one side or both. Such paralysis is the first warning of exhaustion of the nervous system and may be a symptom of cancer or metabolic disorders.
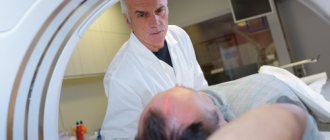
Paralysis can be diagnosed only after magnetic resonance imaging, which will rule out cerebral circulatory disorders and organic damage to nervous tissue. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe electroencephalography (EEG) to identify foci of epilepsy, Dopplerography of cerebral vessels, angiography and other tests.
If the cause of the seizures is not found, then treatment is reduced to stopping the epilepsy.
Todd's paralysis
Todd's paralysis
(postictal paralysis) - transient central paresis or plegia in one or two limbs, appearing after epileptic paroxysm. It is a symptom of central nervous system exhaustion and may indicate the presence of a brain tumor and dysmetabolic disorders.
Postictal paralysis can be diagnosed only if acute cerebrovascular accident is excluded using MRI or CT scan of the brain. Additionally, electroencephalography, examination of cerebral vessels, assessment of the condition of somatic organs, and biochemical blood tests are performed.
In the absence of organic pathology, specific therapy is not required; epilepsy is treated.
The first case of motor disorders occurring after epileptic paroxysm was described by the English neurologist Benkley Todd in 1855. Subsequently, movement disorders in the limbs, which appear after an epileptic attack and are transient in nature, were identified as a separate clinical syndrome.
Currently, several synonymous names are used for it in neurology: “Todd’s palsy”, “postictal paralysis”, “post-epileptic paralysis”. Most often, Todd's palsy occurs in childhood, which is associated with the immaturity of neurotransmitter systems and incomplete processes of myelination of nerve fibers in children.
As a clinical syndrome, Todd's palsy always causes oncological suspicion among doctors, since it often occurs with secondary epilepsy caused by a brain tumor.
In addition, epileptic paroxysm in combination with motor disorders can be a manifestation of acute cerebrovascular accident, and therefore all patients with a first-time episode of postictal paralysis are subject to urgent hospitalization.
Causes of Todd's Paralysis
The etiopathogenesis of postepileptic paralysis is under study. Researchers proceed from the fact that postictal movement disorders are associated with excessively developing inhibition processes that occur in the central nervous system.
Most authors tend to consider this the result of neurotransmitter deficiency and depletion of cerebral functions.
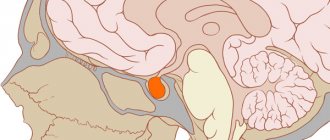
Indeed, Todd's palsy is observed mainly in organic pathology of the brain (encephalitis, central nervous system tumors, cerebral hemodynamic disorders) or in patients with severe concomitant disease (heart failure, liver failure, chronic renal failure, septic conditions, diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis, etc.
), causing toxic, dysmetabolic or ischemic damage to the central nervous system. Clinical observations show that Todd's paralysis is triggered by status epilepticus lasting more than 30 minutes. Some patients are diagnosed with lipid metabolism disorders with increased triglyceride levels and decreased cholesterol concentrations.
Symptoms of Todd's Palsy
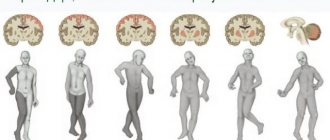
The main symptom is blocking of voluntary movements of the limbs following an epileptic attack. Most often, hemiparesis is observed - muscle weakness of the same arm and leg, less often monoparesis - weakness in only one of the limbs.
Paresis is central in nature, accompanied by increased muscle tone and decreased sensitivity of the affected limb. The severity of muscle weakness varies widely from mild paresis to complete plegia.
The duration of movement disorders usually does not exceed 24 hours, but can be up to 2 days. Then there is a gradual restoration of muscle strength and, accordingly, voluntary movements.
In some cases, after repeated episodes, postictal palsy does not completely regress, and the patient has some residual motor deficit.
Transient paralysis, as a rule, is observed after a paroxysm of focal Jacksonian epilepsy, secondary generalized epileptic seizures, or epileptic status lasting more than half an hour.
In some patients, Todd's palsy occurs with speech (motor aphasia) and visual (hemianopsia) disorders.
In such cases, especially with the primary occurrence of post-epileptic neurological deficit, differentiation from stroke is required.
Diagnosis of Todd's palsy
Postictal paralysis may be supported by an epileptic history and indications of previously observed postictal paresis. When an episode of post-epileptic paralysis occurs for the first time, it is extremely difficult for a neurologist to distinguish it from stroke. This is only possible with an urgent MRI or CT scan of the brain.
In addition to identifying/excluding foci of ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, these studies can determine the presence of a brain tumor, hydrocephalus, and signs of encephalitis. In the absence of data for organic cerebral pathology, dynamic observation of the patient is carried out.
Complete regression of the motor deficit within no more than 48 hours allows the diagnosis of Todd's palsy.
To assess cerebral hemodynamics, angiography or MRI of cerebral vessels is prescribed.
The study of bioelectrical activity of the brain is carried out using electroencephalography, if necessary, supplemented with functional tests. Assessing the condition of somatic organs is of no small importance.
First of all, electrocardiography and ultrasound of the heart, a biochemical blood test, and a study of lipid metabolism are performed; according to indications - consultation with a cardiologist and other specialists.
Treatment for Todd's Palsy
The basis of therapy is antiepileptic drugs (anticonvulsants), which help stop epileptic paroxysm and reduce the frequency of epileptic attacks.
Individual selection of anticonvulsants is carried out by an epileptologist. The drugs of choice are valproic acid, lorazepam, phenytoin, diazepam.
In the presence of pathology of internal organs and dysmetabolic disorders, their therapy and correction are carried out in parallel with the treatment of epilepsy.
If CNS pathology is excluded, additional treatment for paralysis is not required.
If hydrocephalus is detected, a course of therapy with diuretics (acetazolamide, furosemide) together with potassium supplements is prescribed.
If CT and MRI data of the brain indicate the presence of a cerebral tumor, the patient is referred to a consultation with a neurosurgeon to decide on further treatment tactics.
Source: https://MyMedNews.ru/paralich-todda/
Causes
Todd's paralysis remains one of the medical mysteries. And without knowing the cause, doctors cannot develop a mechanism for dissociating the pathological process in order to cure it. Based on indirect evidence, doctors have several assumptions regarding the nature of the disease. According to the most progressive theory, the “phenomenon of inhibition of the nervous system” manifests itself in the form of paralysis. It is associated with impaired neurotransmitter transmission.
In addition, there are several other reasons:
- several epileptic seizures in a row; - brain exhaustion; - malignant neoplasm of the central nervous system; - inflammation of the brain substance, especially of viral etiology; — uncoupling of lipid metabolism; - presence of ischemic strokes in the past; - diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
Symptoms
How does Todd's paralysis manifest itself? The symptoms initially resemble those of an epileptic seizure. For those around you, watching an attack can be quite difficult, since they have no opportunity to help the patient. But even after the cramps end, the person cannot fall asleep and experience blissful oblivion. On the contrary, he freezes and cannot move his arms and legs.
How long will Todd's paralysis last? Symptoms (photos of patients can be traumatic and are considered unethical) sometimes persist around the meshes or more. Doctors most often note the appearance of unilateral paralysis or paresis. Over time, the motor blockade passes without leaving any consequences. Medical periodicals record cases of Todd's paralysis with visual and articulation impairments.
At the first encounter with this pathology, the symptoms can be regarded as manifestations of a stroke, but after all the necessary diagnostic measures have been carried out, the primary diagnosis is removed, and the rapid regression of symptoms confirms the version of paralysis.
Symptoms and Treatment of Todd's Palsy
Todd's palsy is a transient disorder of the central nervous system, which is expressed in paresis or plegia of one or two limbs that appears after an attack of epilepsy. Sometimes this is a symptom of a brain tumor. The disease can only be diagnosed with MRI or CT.
The disease was first diagnosed in 1855 by neurologist Benkley Todd. Due to the fact that status epilepticus can give several clinical manifestations of this condition at once, the disease has received several names at once, one of which will sound like post-epileptic paralysis.
Most often, this pathology is diagnosed in children, which is associated with the immaturity of the nervous system and the incomplete process of myelination of nerve fibers.
The disease most often appears with secondary epilepsy, which is mainly caused by a brain tumor, and therefore these manifestations should cause special alertness of the oncologist.
Also, the cause may be impaired blood circulation in the brain, which also requires mandatory hospitalization.
How it manifests itself
Symptoms of Todd's paralysis should be considered the inability to make voluntary movements after an attack of epilepsy. The most common is hemiparesis, that is, the arm and leg are affected on only one side.
Less commonly – monocut, when only one limb is affected. All this is accompanied by increased muscle tone and decreased sensitivity.
Moreover, the severity of symptoms can be very different - from barely noticeable weakness to complete paralysis.
Such violations last no more than a day, but in the most severe cases this time can extend up to two days.
Muscle strength in the limbs is restored gradually, and voluntary movements gradually return.
And only occasionally, with repeated cases of epilepsy, the symptoms do not go away completely, but leave behind certain residual effects, which are expressed in the form of movement deficits.
This type of paralysis occurs only when the duration of the epileptic seizure is more than 30 minutes. With short and less severe seizures, there will be no signs of paralysis. Sometimes speech and visual disturbances are added to it. If this happened for the first time, then differentiation with a stroke is required.
Definition
Todd's palsy is a transient condition that develops after an epileptic seizure. Patients experience paresis or paralysis of the limbs on one side or both. Such paralysis is the first warning of exhaustion of the nervous system and may be a symptom of cancer or metabolic disorders.
Paralysis can be diagnosed only after magnetic resonance imaging, which will rule out cerebral circulatory disorders and organic damage to nervous tissue. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe electroencephalography (EEG) to identify foci of epilepsy, Dopplerography of cerebral vessels, angiography and other tests.
If the cause of the seizures is not found, then treatment is reduced to stopping the epilepsy.
Diagnostics
What should be done to confirm Todd's paralysis? The signs of the disease are quite vague. It is necessary to exclude all other pathologies to be sure of the diagnosis. The first step is to determine the severity of the observed condition and the level of muscle paralysis. To do this, conduct a physical examination and compare the data obtained with a five-point scale:
- Five points means a complete absence of symptoms, the patient’s muscles are in a state of physiological norm.
- Four points – strength indicators are slightly reduced, but the activity of the limbs is still maintained. The patient calmly overcomes the resistance of the doctor's hand.
- Three points - stiffness of the victim’s muscles is noticeable to the naked eye, but the patient is still able to make voluntary movements, although not as quickly as with four points. It becomes more difficult to overcome the resistance of the doctor's hand.
- Two points - the Earth's gravity becomes an insurmountable obstacle for such a patient.
- One point – complete muscle paralysis is observed.
After the examination, the doctor collects a thorough history from the patient’s relatives, studies the medical record, and prescribes a computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging scan. To exclude a stroke, the patient undergoes angiography to identify the focus of epilepsy (if there is a history of one), and electroencephalography is prescribed. To determine concomitant pathologies, ultrasound examination of the heart and electrocardiography are performed.
Only having all the results, the doctor can choose the most probable one among all the possible diagnoses and begin therapy.
Todd's Palsy: Symptoms and Treatment
Todd's palsy is a type of neurological disorder associated with the occurrence of areas of excitation in the brain. It can last from a few minutes to a day. To make this diagnosis, it is necessary to exclude all other similar pathologies, including organic damage to the nervous system.
Todd's palsy is a transient condition that develops after an epileptic seizure. Patients experience paresis or paralysis of the limbs on one side or both. Such paralysis is the first warning of exhaustion of the nervous system and may be a symptom of cancer or metabolic disorders.
Paralysis can be diagnosed only after magnetic resonance imaging, which will rule out cerebral circulatory disorders and organic damage to nervous tissue. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe electroencephalography (EEG) to identify foci of epilepsy, Dopplerography of cerebral vessels, angiography and other tests.
If the cause of the seizures is not found, then treatment is reduced to stopping the epilepsy.
Causes
Todd's paralysis remains one of the medical mysteries. And without knowing the cause, doctors cannot develop a mechanism for dissociating the pathological process in order to cure it.
Based on indirect evidence, doctors have several assumptions regarding the nature of the disease. According to the most progressive theory, the “phenomenon of inhibition of the nervous system” manifests itself in the form of paralysis.
It is associated with impaired neurotransmitter transmission.
In addition, there are several other reasons:
– several epileptic seizures in a row; – brain exhaustion; – malignant neoplasm of the central nervous system; – inflammation of the brain substance, especially of viral etiology; – uncoupling of lipid metabolism; – presence of ischemic strokes in the past;
– diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
Symptoms
How does Todd's paralysis manifest itself? The symptoms initially resemble those of an epileptic seizure. For those around you, watching an attack can be quite difficult, since they have no opportunity to help the patient. But even after the cramps end, the person cannot fall asleep and experience blissful oblivion. On the contrary, he freezes and cannot move his arms and legs.
How long will Todd's paralysis last? Symptoms (photos of patients can be traumatic and are considered unethical) sometimes persist around the meshes or more.
Doctors most often note the appearance of unilateral paralysis or paresis. Over time, the motor blockade passes without leaving any consequences.
Medical periodicals record cases of Todd's paralysis with visual and articulation impairments.
At the first encounter with this pathology, the symptoms can be regarded as manifestations of a stroke, but after all the necessary diagnostic measures have been carried out, the primary diagnosis is removed, and the rapid regression of symptoms confirms the version of paralysis.
Diagnostics
What should be done to confirm Todd's paralysis? The signs of the disease are quite vague. It is necessary to exclude all other pathologies to be sure of the diagnosis. The first step is to determine the severity of the observed condition and the level of muscle paralysis. To do this, conduct a physical examination and compare the data obtained with a five-point scale:
- Five points means a complete absence of symptoms, the patient’s muscles are in a state of physiological norm.
- Four points – strength indicators are slightly reduced, but the activity of the limbs is still maintained. The patient calmly overcomes the resistance of the doctor's hand.
- Three points - stiffness of the victim’s muscles is noticeable to the naked eye, but the patient is still able to make voluntary movements, although not as quickly as with four points. It becomes more difficult to overcome the resistance of the doctor's hand.
- Two points - the Earth's gravity becomes an insurmountable obstacle for such a patient.
- One point – complete muscle paralysis is observed.
After the examination, the doctor collects a thorough history from the patient’s relatives, studies the medical record, and prescribes a computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging scan.
To exclude a stroke, the patient undergoes angiography to identify the focus of epilepsy (if there is a history of one), and electroencephalography is prescribed.
To determine concomitant pathologies, ultrasound examination of the heart and electrocardiography are performed.
Only having all the results, the doctor can choose the most probable one among all the possible diagnoses and begin therapy.
Treatment
How can Todd's paralysis be reversed? The treatment, although purely symptomatic, has low effectiveness, since it is difficult to accurately establish the cause of this condition. Therapy depends on the level and severity of paralysis.
If movement disorders are minor, then specific treatment is not required. The symptoms will go away on their own within a few hours or days.
For more profound disorders, benzodiazepine drugs are used, such as Midazolam, Diazepam, Lorazepam, Fosphenytoin or Phenytoin. Each of them stops convulsive attacks and their consequences.
When prescribing them, it is necessary to remember that abrupt withdrawal of antiepileptic drugs can also provoke an attack.
There are contraindications for prescribing these drugs. First of all, this is, of course, intolerance to the components of the drug, as well as a history of closed-angle glaucoma and drug or alcohol addiction. In addition, renal function plays an important role, since the drug is mainly excreted in the urine.
Prevention
There is no way to prevent Todd's post-seizure paralysis. This condition has not yet been fully studied, so specific prevention, as well as treatment, cannot be developed. Perhaps some time later, when the capabilities of medicine become even greater, we will be able to take some steps to eliminate this pathology.
Today, doctors give very vague advice, such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, giving up bad habits and moderate physical activity. In addition, you should not forget about periodic preventive examinations, because any disease is easier to prevent than to treat.
Forecast
Todd's palsy can have a good or bad prognosis. It all depends on the severity of neurological symptoms and the duration of paresis or paralysis.
If a neurologist gives a rating of “three” or “four” on a five-point scale, then in this case the disease does not cause significant concern, and the prognosis for life and health is favorable.
The body quickly recovers after attacks; the condition does not require drug intervention.
If the paralysis lasts a long time, the functions of the limbs are restored for a long time, and the number of attacks becomes more frequent over time, then the prognosis for life is, of course, unfavorable.
Latest research
Right- and left-sided Todd's palsy can progress, and over time muscle weakness remains, even after long-term treatment. For such patients, as well as other paralyzed people, science has a couple of revolutionary ideas to offer.
The first of these is the creation of prosthetics. Today, there are prototypes of bionic limbs controlled by the power of thought, that is, the device connects to the nervous system and perceives nerve impulses, deciphering the signals.
The second method is rather biological. It is based on the restoration of nerve endings using stem cells.
Since they have a tendency to almost endless division, and can also differentiate into any cell of the human body.
Experiments are currently being carried out on laboratory animals, but if they are successful, one can hope for a significant breakthrough in the treatment of neurological diseases.
Source: https://2qm.ru/zdorove/bolezni-i-lechenie/paralich-todda-simptomy-i-lechenie.html
Treatment
How can Todd's paralysis be reversed? The treatment, although purely symptomatic, has low effectiveness, since it is difficult to accurately establish the cause of this condition. Therapy depends on the level and severity of paralysis.
If movement disorders are minor, then specific treatment is not required. The symptoms will go away on their own within a few hours or days. For more profound disorders, benzodiazepine drugs are used, such as Midazolam, Diazepam, Lorazepam, Fosphenytoin or Phenytoin. Each of them stops convulsive attacks and their consequences. When prescribing them, it is necessary to remember that abrupt withdrawal of antiepileptic drugs can also provoke an attack.
There are contraindications for prescribing these drugs. First of all, this is, of course, intolerance to the components of the drug, as well as a history of closed-angle glaucoma and drug or alcohol addiction. In addition, renal function plays an important role, since the drug is mainly excreted in the urine.
Todd's palsy and paresis symptoms
Epilepsy is accompanied by seizures, after which the patient begins to have convulsive seizures, known as Todd's palsy. This syndrome is characterized by blocking motor activity and impaired muscle tone.
Causes of pathology
Todd's palsy is a direct consequence of epilepsy. Such paresis develops as a result of depletion of the central nervous system and an imbalance between the processes of excitation and inhibition.
The exact cause that provokes the development of such paresis has not yet been determined, but the most likely hypothesis is the exhaustion of the nervous system.
This can also explain the fact that the first symptoms of Todd's paralysis are detected in childhood, when the child's nervous system is highly susceptible to any negative influences due to the fact that it is not fully formed.
Possible causes of Todd's paralysis include:
- epilepsy;
- CNS depletion;
- tumor diseases of the brain;
- encephalitis that develops as a result of infection by the herpes virus;
- vascular ischemia.
All these reasons have one thing in common - a shift in the balance of nervous system processes towards inhibition.
Symptoms of pathology
After an epileptic seizure, patients experience convulsive conditions.
The main symptom of Todd's paralysis is the absence of voluntary motor activity after a seizure for the next two days, but the duration of paralysis can vary.
Todd's paralysis is also accompanied by a decrease in muscle activity and reflex activity. Paresis is usually asymmetrical and affects only one side of the body.
Restoration of muscle function occurs without specific therapy, independently. The duration of this condition can vary from several hours to two days, after which muscle activity gradually increases until it returns to normal.
Rare symptoms of Todd's paralysis include blurred vision and speech problems. These conditions are often confused with a stroke.
Symptoms in children
Todd's palsy in children has some differences from the manifestation of the same pathology in adults. This is due to the peculiarity of the fragile children's nervous system.
As a rule, epileptic seizures in childhood are more intense than in adults, which is due to the instability of the processes of inhibition and excitation of the nervous system due to incompletely formed metabolism. Therefore, Todd's paresis in childhood is expressed more clearly than in adults. However, in this case, the neurological symptoms disappear on their own after 24-48 hours.
Diagnosis of pathology
Manifestations of Todd syndrome are symptomatically similar to stroke. They are accompanied by partial or complete paralysis of muscles, problems with speech and focusing of gaze. This causes difficulties in diagnosing the pathology.
Diagnosis is facilitated by a history of epilepsy. The diagnosis is made only after assessing the level of muscle stiffness and weakening. This is done by examining the patient; also, to assess muscle strength, the doctor observes the resistance of the affected limb to external pressure. This requires a physical examination, which evaluates the condition of the muscles on a five-point scale:
- 5 – muscles are normal, no paresis;
- 4 – reflexes are normal, muscles are not weakened enough;
- 3 – motor impairments are visible visually;
- 2 – muscles are weak, it’s impossible to even raise your arm;
- 1 – motor activity is almost completely absent;
- 0 – complete paralysis of muscles.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is mandatory to exclude vascular ischemia. To rule out a stroke, it is necessary to do a CT scan of the brain, which allows one to detect foci of hemorrhage if they are present.
It is necessary to examine the activity of the brain and exclude heart pathologies.
Therapy
Treatment largely depends on the severity of the symptoms of paralysis. For mild symptoms that go away on their own after a short period of time, drug therapy is not used.
For severe symptoms, treatment is with a benzodiazepine. This is a substance from the group of psychoactive drugs that acts on gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors. The medicine has the following effects:
- muscle relaxation;
- anticonvulsant effect;
- sedative effect;
- relieves increased anxiety.
Treatment of Todd's palsy with this drug is due to an unknown cause of the pathology. Drugs containing benzodiazepines have a pronounced therapeutic effect and help to quickly relieve symptoms when used regularly, but this method will not completely get rid of the problem. However, patients respond well to this treatment, noting a decrease in the intensity of paresis.
Drugs for the treatment of pathology have a number of contraindications:
- glaucoma;
- alcohol addiction;
- addiction;
- liver or kidney dysfunction;
- individual intolerance.
When choosing treatment, it should be remembered that psychoactive drugs are potent drugs and often have a withdrawal syndrome.
Treatment of infantile paralysis
If the pathology manifests itself in children, treatment with psychoactive drugs is not carried out due to the weakness of the children's nervous system. In this case, the disease is caused by a disorder of lipid metabolism, so treatment is carried out with the help of drugs that improve metabolic processes in the body.
If a child’s disease is due to a genetic predisposition, and one of the parents is also susceptible to Todd’s paresis, drug therapy is often not prescribed.
Prevention
There is no way to prevent Todd's post-seizure paralysis. This condition has not yet been fully studied, so specific prevention, as well as treatment, cannot be developed. Perhaps some time later, when the capabilities of medicine become even greater, we will be able to take some steps to eliminate this pathology.
Today, doctors give very vague advice, such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, giving up bad habits and moderate physical activity. In addition, you should not forget about periodic preventive examinations, because any disease is easier to prevent than to treat.
Forecast
Todd's palsy can have a good or bad prognosis. It all depends on the severity of neurological symptoms and the duration of paresis or paralysis. If a neurologist gives a rating of “three” or “four” on a five-point scale, then in this case the disease does not cause significant concern, and the prognosis for life and health is favorable. The body quickly recovers after attacks; the condition does not require drug intervention.
If the paralysis lasts a long time, the functions of the limbs are restored for a long time, and the number of attacks becomes more frequent over time, then the prognosis for life is, of course, unfavorable.
Latest research
Right- and left-sided Todd's palsy can progress, and over time muscle weakness remains, even after long-term treatment. For such patients, as well as other paralyzed people, science has a couple of revolutionary ideas to offer. The first of these is the creation of prosthetics. Today, there are prototypes of bionic limbs controlled by the power of thought, that is, the device connects to the nervous system and perceives nerve impulses, deciphering the signals.
The second method is rather biological. It is based on the restoration of nerve endings using stem cells. Since they have a tendency to almost endless division, and can also differentiate into any cell of the human body. Experiments are currently being carried out on laboratory animals, but if they are successful, one can hope for a significant breakthrough in the treatment of neurological diseases.