Modern aspects of treatment
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune pathological process accompanied by paresis and paralysis. Modern drugs for myasthenia gravis allow patients to maintain their ability to work, avoid disability, and improve their quality of life. Electromyography data, a pharmacological test using anticholinesterase drugs, and blood serum testing for the presence of autoantibodies help prescribe effective treatment.
What painkillers are available for myasthenia gravis is determined by the doctor individually depending on the stage of the disease. The following drugs are prescribed for treatment:
- Fortalgin;
- Voltaren;
- Ibuprofen;
- Ketoprofen;
- Spasmalgon;
- Coldrex;
- Tempalgin.
Psychotropic substances - Aminazine, Amitriptyline - can aggravate the course of myasthenia gravis.
Safe drugs are benzodiazepine derivatives and the drug Sonapax. In patients with a generalized form of myasthenia, Chlorophyll is used to treat concomitant diseases of the nasopharynx. Antiseptic therapy ensures the saturation of infected tissues with oxygen. The patient's general condition is improved by Actovegin, which dilates the coronary vessels and improves the functioning of the nervous system. If the patient suffers from heart failure, medications are used to maintain the normal functioning of an important organ:
- Preductal;
- Mildronate.
How is the disease determined?
In addition to the patient’s complaints and medical history, the diagnosis of myasthenia gravis includes various tests, hardware examinations and analyses.
Electromyography helps determine muscle response to stress, and CT or MRI reveals the absence of diseases that could cause similar symptoms. After all, myasthenic syndrome is observed in encephalitis, meningitis, cancer, botulism, and thyrotoxicosis. But the differences in this case from myasthenia gravis are that the facial muscles are rarely affected, and when conducting electromyography, there is not a slowdown, but an increase in muscle potential with repeated stimulation.
It is also necessary to distinguish myasthenia gravis from Duchenne muscular dystrophy in time, although the symptoms are different. Muscular dystrophy occurs mainly in boys and begins in childhood.
Most often, to make a diagnosis, an immunological test is done to determine antibodies to acetylcholine and a proserine test is performed. Its meaning is that after intramuscular injection of 1 ml of the drug “Proserina”, the patient’s condition improves significantly after 30 minutes, and after 2-3 hours the symptoms return.
A very important method for diagnosing myasthenia gravis is various tests that reveal the degree of muscle weakness, as well as which of them are more affected. Since fatigue increases after repetitive movements, the following tests may be effective:
- if you ask the patient to look to the side or up for at least 30 seconds, ptosis and double vision appear;
- to provoke dysarthria and decreased voice strength, you need to ask the patient to read something out loud;
- weakness of the neck muscles can be detected if the patient lies on his back and raises his head, he will not be able to hold it up for more than a minute;
- sometimes with myasthenia gravis the M. Volker phenomenon appears - repeated clenching and unclenching of the hands causes increased ptosis.
Electromyography helps determine muscle response to stress
Immunosuppressive therapy
To treat myasthenia gravis, immunosuppressants are prescribed:
- Azathioprine;
- Cyclosporine;
- Prednisolone.
However, during therapy, the risk of infectious complications and the development of malignant tumors increases.
Azathioprine is the safest drug. It affects the absorption of glucocorticoids and can significantly reduce their dose. Side effects of the drug lead to its withdrawal. The patient complains of headache, chills, and fever. A person develops symptoms of liver dysfunction.
Methotrexate is a strong immunosuppressant, it is used in a small dose, because the drug has significant toxicity. The patient experiences discomfort in the epigastric region, nausea, and vomiting. Many people experience pain in the liver area, enzyme activity changes, and signs of cirrhosis appear.
Leucovorin, prescribed after Methotrexate therapy, reduces its toxicity. For a patient suffering from myasthenia gravis, treatment with antipsychotics and tranquilizers is contraindicated.
It is not recommended to take antidepressants that worsen the patient's condition and contribute to the development of myasthenic syndrome as a complication of drug therapy.
Signs of the disease
The main symptom of the disease is increased muscle fatigue. During physical work, especially with repetitive movements, muscle weakness gradually increases, which over time can lead to paresis or paralysis. But after rest, these symptoms of myasthenia gravis disappear, and in the morning patients feel completely fine for several hours. At various stages and forms of the disease, the following signs appear:
- double vision;
- ptosis - drooping of the upper eyelid;
- salivation;
- voice change;
- impaired chewing function, fatigue when eating solid foods;
- choking when eating;
- difficulty breathing;
- poor facial expressions;
- change in gait;
- weakness of the muscles of the limbs and neck;
- dry skin.
One of the first signs of myasthenia gravis is ptosis - drooping of the upper eyelid.
Medicines to reduce muscle tone
In some cases, non-depolarizing muscle relaxants are used for myasthenia gravis:
- Tracrium;
- Esmeron.
Considering the contraindications, the doctor tries not to prescribe muscle-relaxing drugs to treat patients, since many patients have increased sensitivity to their effects.
Non-depolarizing muscle relaxants are not used, since in many cases the patient develops an unpredictable reaction to their administration. The drug Succinylcholine causes a marked increase in the level of potassium in the blood serum and high temperature in the patient.
Patients suffering from periodic paralysis experience attacks accompanied by muscle weakness. During surgery to remove the thymus gland, the doctor does not use decompensated muscle relaxants. Sodium thiopental provides complete anesthesia.
The use of tablets for myasthenia gravis, which have a muscle relaxant effect, is prohibited for all categories of patients. Mydocalm, Sirdalud, Tolperisone, Meprotan are especially dangerous to the patient’s health. The use of muscle relaxants in patients with the initial form of the disease causes respiratory arrest.
Glucocorticoid therapy
Prednisolone increases the number of cholinergic receptors. After taking it, muscle strength increases. To avoid certain risks in the early stages of the disease, therapy is carried out in a hospital setting. The patient is additionally prescribed anticholinesterase drugs. Treatment with glucocorticoids is long-term. The intermittent method, where the patient takes an increased dose of medication over several hours, is very popular. Side effects may occur during treatment:
- increased blood pressure;
- stomach ulcer.
Azathioprine is used in patients with myasthenia gravis that is difficult to treat with Prednisolone. Dexamethasone is recommended by the doctor, taking into account the patient’s condition, since the drug is 10 times more active than other glucocorticoids. However, it is unsuitable for circadian therapy because it worsens the patient's condition.
Treatment with glucocorticoids involves taking alkalizing drugs: the patient is prescribed Phosphalugel or Ranitidine. To prevent the development of diabetes mellitus, the patient must follow a special diet. Limit consumption of foods containing large amounts of carbohydrates. Blood is drawn regularly to determine glucose levels.
Cholinesterase inhibitors
In mild cases of the disease, the patient is prescribed medications that prevent the decrease in acetylcholine in the area of the neuromuscular nodes. The use of Proserin in the treatment of patients with myasthenia gravis provides active muscle stimulation, but large doses of the drug cause disruption of muscle conduction.
Diclofenac sodium is used for therapeutic blockade in case of nerve damage and intense pain. It is the drug of choice, since procedures using Novocaine and Lidocaine are prohibited in patients suffering from myasthenia gravis.
Axamon (Ipidacrine) is used for diseases of the peripheral nervous system. The medicine is well tolerated by patients. The drug has a double effect, while Proserin, Oksazil and Kalimin act only on the peripheral nervous system.
Patients are prescribed medications containing potassium. For therapy, KCL is used in powder form. Considering its side effect on the gastric mucosa, it is taken after meals with milk. Medicines Potassium-Normin and Kalipoz are intended for oral administration several times a day.
The following medications containing magnesium and potassium should not be prescribed to the patient:
- Panangin;
- Asparkam.
Drugs for myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a neuromuscular disease characterized by extremely rapid fatigue of striated muscles. Just a decade ago, the prognosis for a patient with this pathology was disappointing. Myasthenia gravis is a disease in which the body’s own cells are perceived as foreign, with which it begins to fight. Acetylcholine receptors in postsynaptic membranes are damaged.
Today, effective drugs successfully used at the Yusupov Hospital can significantly improve the quality of life of patients.
Pathogenetic impact
When treating myasthenia gravis, the doctor performs pulse therapy using Methylprednisolone and certain treatment regimens. Corticosteroids are prescribed in a therapeutic dose daily or every other day. The course of treatment lasts a week, and then the doctor reduces the dose of the drug.
If the patient's condition worsens, a stepwise therapy regimen is used, based on increasing the single dose until the maximum allowable amount of medication is reached at one time. Metypred is a drug with high mineralocorticoid activity, therefore it is often used for treatment and stabilizes the patient’s condition.
Contraception for myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rather dangerous disease, which, if left untreated, can lead to serious conditions and have a bleak prognosis. At the same time, medicine does not stand still and every day more and more effective drugs appear on the market to combat pathology. Leading Russian doctors work at the Yusupov Hospital, who develop an individual treatment regimen for each patient. At an appointment with a specialist, you can consult about any nuances associated with myasthenia gravis.
Many girls are interested in whether it is possible to take contraceptives with this diagnosis. There is no clear answer to this question; doctors determine contraindications for each patient individually.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital explain to their patients in great detail which actions and medications are contraindicated when diagnosed with myasthenia gravis, and which can be used without health hazards. To avoid exacerbations, the patient must understand how he himself can aggravate the course of the disease and unwittingly harm himself.
Under no circumstances should you become depressed when diagnosing myasthenia gravis. Medicine is developing every day, modern drugs allow patients to lead their usual full-fledged lifestyle. The main thing is that the course of therapy is determined by an experienced doctor who has knowledge of modern advances in medicine and applies them in practice.
Use of immunoglobulins
For the treatment of myasthenia gravis (MG), infusions of immunoglobulins (IVIG) obtained from donor blood are prescribed. The purpose of the method is to increase the patient’s body’s defenses. Functional changes in patients with MG reach significant values. Immunoglobulin administered to the patient does not cause serious side effects. The following drugs are used in the treatment of patients:
- Gamimun-N;
- Pentaglobin;
- Octagam 10%;
- Intraglobin.
During a crisis, immunoglobulins are prescribed only after emergency resuscitation measures. Human specific protein prevents the development of severe complications. It is administered every other day at the dose prescribed by the doctor.
Often, patients with myasthenia gravis complain of nausea and headache after infusion. The doctor evaluates the functioning of the patient’s immune system and notes the number of T cells. During the study, defects in immune particles are detected, and in the serum - increased activity of thymic humoral factors.
The concentration of immunoglobulins reflects the state of internal organs that affect the body's defenses. Normal human protein containing a special fraction, administered in a standard dose for the first time, causes the appearance of flu-like symptoms:
- heartbeat;
- drowsiness;
- convulsions;
- high temperature.
There is another serious problem - it is necessary to constantly monitor the patient’s condition, in case of collapse and increased blood pressure, discontinue treatment, administer intravenous plasma solution and antihistamines.
In the treatment of myasthenia gravis, cytostatics are used:
- Cyclophosphamide;
- Cyclosporine;
- Cyclophosphamide;
- Methotrexate.
Often, after achieving the effect, the dose of the medicine is reduced. Taking Cyclophosphamide causes side effects:
- leukopenia;
- hepatitis A;
- inflammation of the pancreas;
- septicemia;
- intestinal disorders;
- dizziness,
- visual impairment.
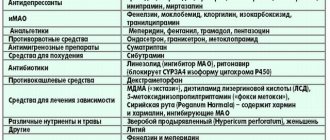
Harmful drugs
The following drugs are contraindicated for patients with myasthenia gravis:
- anticonvulsants;
- antibiotics (aminoglycosides);
- B-blockers;
- Lithium carbonate;
- Procainamide hydrochloride;
- Trihexyphenidyl hydrochloride;
- antimalarial and antirheumatic drugs;
- eye drops;
- hypoglycemic drugs.
Illicit drugs contribute to the development of myasthenic symptoms and increase skeletal muscle weakness. Antibacterial medications worsen the symptoms of the disease. The following drugs are not recommended for use:
- Ampicillin;
- Imipenem;
- Erythromycin.
Sleeping pills are contraindicated for myasthenia gravis. Treatment with benzodiazepine derivatives and barbiturates is unacceptable. Medicines containing magnesium significantly worsen the patient's condition. You should not take diuretics that affect the conduction of neuromuscular impulses.
The patient must take the medications prescribed by the doctor in courses, monitor his well-being and lead a healthy lifestyle.