What is a concussion and its main symptoms
Any head injury is accompanied by varying degrees of concussion. A distinction is made between a bruise and a concussion itself. In the first case, severe damage to brain tissue occurs, and in the second, only mild injury occurs. Jumps in body temperature are typical precisely with serious bruises, when severe inflammation begins in the brain. This is a very dangerous condition that has serious consequences.
Athletes and people whose professions involve high levels of injury are often susceptible to concussions. Very often young children receive this diagnosis. This happens against the backdrop of unstable first steps, when the baby still cannot fully control his balance and falls under the weight of his body.
Due to the fact that the tissues of the skull are still quite soft, injury can occur. A concussion is accompanied by severe fatigue, headache, dizziness, or loss of consciousness.
Kinds
Depending on the location, hematomas are divided into the following types:
- subcutaneous;
- intramuscular;
- subserous;
- head hematomas.
Subcutaneous hematomas
located under the skin, intramuscular - in the closed space of the muscles. These two types of hematomas manifest themselves with similar symptoms (mild swelling, pain, skin changes, etc.) and do not pose a threat to the life of the victim.
When a subserous hematoma
blood accumulates in the chest or abdominal cavity. This phenomenon is life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
For head hematomas
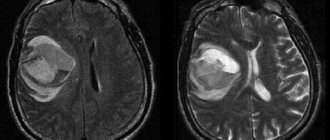
the brain suffers. The main feature of this type of hematoma is the gradual process of bruising, which can drag on for up to several days. There are several types of head hematomas: intracerebral traumatic, epidural, subdural.
Intracerebral traumatic hematoma
usually caused by a blow or fall. It is evidenced by such signs as headaches, dizziness, speech impairment, nausea and vomiting, bradycardia, psychomotor agitation, as well as other brain symptoms depending on the location of the lesion and the extent of the process.
For epidural hematoma
blood clots accumulate in the epidural space (under the skull cap), and
a subdural hematoma
forms in the space between the dura and arachnoid membranes of the brain. If you suspect any type of head hematoma, you should contact a specialist.
hematoma during pregnancy should also be mentioned.
ty (retrochorial hematoma), the development of which is caused by detachment of the fertilized egg from the chorion of the placenta. A hematoma that forms at the site of detachment can cause spontaneous miscarriage, missed abortion, intrauterine growth retardation and other pathologies.
Causes of increased body temperature
This condition may be associated with a number of inflammatory processes not directly related to injury. This symptom may indicate the onset of a fever. According to anatomy, the human brain is protected thanks to several membranes; in the event of an injury, one of them may be damaged, and inflammation will begin.
A temperature above 380 indicates that during a concussion, a person has developed an extensive wound or hematoma, which is the main source of inflammation due to the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
If first aid is not provided, the patient faces severe inflammation of the cerebral cortex (meningitis), and this leads to an increase in temperature above 400 and the development of other complications.
Among the provoking factors that can cause hyperthermia are:
- increased activity of the thyroid gland;
- hypertension;
- —vegetative-vascular dystonia—;
- alcohol intoxication (especially if intoxication caused a person to fall, which resulted in a head injury);
- severe stress after an injury, against the background of which the body temperature increased.
Can a bruised knee cause a fever - how is it transmitted, medications, causes, what is it?
Have you been struggling with JOINT PAIN for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure your joints by taking the product every day for 147 rubles...
Read more "
An overly active lifestyle, which is necessary in the modern world to satisfy all one’s needs, sometimes leads to various injuries, among which a knee bruise is one of the most painful and common.
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
Our readers successfully use Artreid to treat joints. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
The knee joint is one of the most complex structures in the human body; the two bones are connected by numerous ligaments, tendons, cartilage and muscles. It is this complex structure that causes difficulties in its treatment after injury.
When you fall, the entire load usually falls on the kneecaps, since this is the part where you land.
What should you do if you fall and your bruised knee is swollen and painful when bent, or a lump appears in the cup area? What first aid should be given to yourself or someone who has fallen? These aspects have long been studied in life safety lessons, starting from the very first grades.
But, despite all this, by adulthood this is happily forgotten, and helping oneself or others becomes a problem. In such cases, first aid will boil down to the fact that the victim quickly gets up, rubbing the bruised area with his hand.
Meanwhile, a knee injury is fraught with the following possible consequences:
- Bone crack.
- Fracture.
- Meniscus tear.
- Rupture of the posterior horn of the medial meniscus.
- Tendon inflammation.
- Internal hematomas.
- Leg muscle atrophy.
- Twisting knee ligaments.
This is not a complete list of what a knee injury can lead to.
Attention! If a child has a knee bruise, then you should not rely on your own strength, treat with folk remedies, or use any unfamiliar ointment.
The child’s health is so fragile that relying on one’s unqualified knowledge is unwise and dangerous. Therefore, you shouldn’t do anything yourself.
It’s better to immediately entrust the treatment of your child to an experienced specialist, so that later you don’t reproach yourself for the rest of your life for wasted time and mistakes.
First aid for falls
What first aid should be provided after a severe knee injury? So, you feel like your balance is lost and you quickly land on the ground. Your algorithm of actions:
- Gently and slowly stand first on your knees and then on your feet.
- Examine the site of the injury, note whether there are abrasions, bleeding, or hematomas. What is the nature of hematomas?
- Slowly, try to move your knee, walk carefully.
If the pain is tolerable and you can walk, then you can proceed to the next steps to provide assistance. Next, you need to:
- Ensure complete rest for the knee by applying a tight, non-pressure bandage using gauze or, even better, an elastic bandage, before applying an anesthetic ointment (Fastum-gel, Bystrum-gel, Nise-gel).
- If possible, sit down and slowly raise your leg to an elevated position, thereby ensuring the flow of blood from the bruise.
- You can apply cold to the bruised area, but in such a way that direct contact with ice is excluded, for example, a bottle or heating pad with cold water, an ice pack pre-wrapped in a cloth or towel.
All these actions are performed if there is no visible damage. If a knee bruise is accompanied by heavy bleeding or abrasion, then under no circumstances should you apply anesthetic ointment, rub, knead, or perform other actions. If you have wounds you should:
- Rinse the wound with running water.
- Afterwards, treat the knee bruise with antiseptics: hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green, alcohol, iodine (around the wound).
- After this, you need to apply a dry bandage.
What to do if the pain does not go away?
What should you do if you have bruised your knee and the above remedies have not been able to cure it? What symptoms should concern you and prompt you to see a doctor?
If, after providing first aid, it did not get better within a week, or, on the contrary, it became even worse, new symptoms appeared, such as:
- Bump on the knee;
- Extensive hematoma;
- Immobility of the joint;
- Crunching in the knee with simultaneous pain;
- Involuntary flexion/extension of the knee during walking and at rest;
- Swelling and redness of the bruise;
- The knee is hot;
- Shivers, body temperature increased;
- Deformation of the knee joint;
- Bruising.
Here only a qualified specialist can provide assistance and cure a bruised knee.
The doctor will be able to decide how to cure a knee bruise only when he conducts a series of tests to find out the causes of the pain, clarifies the disturbing symptoms, and conducts a survey.
What tests are needed to determine the diagnosis?
No treatment will be prescribed without testing, examination and diagnosis. Therefore, as soon as you walk into the doctor's office, you will be given:
- The question was asked about what happened and when, what treatment was undertaken by you personally, what worries you.
- An examination was carried out, during which the doctor will palpate to determine whether there is internal bleeding, a lump, swelling and redness.
- An ultrasound of the joint was prescribed.
- An x-ray examination was prescribed.
- After receiving all these results, the doctor prescribes treatment.
Treatment of a knee bruise
Depending on what the x-ray shows, the doctor will determine what treatment to prescribe.
- For fractures and cracks, plaster is applied. The length of time you wear it will depend on the rate of bone healing.
- If there is a meniscus tear, then its restoration is prescribed using appropriate equipment.
- When tendons rupture, they are reconstructed.
- For various types of inflammation, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, pain-relieving anti-inflammatory ointment, antibiotics, corticosteroids, and analgesics are prescribed.
Treatment of knee bruises with folk remedies
If there are no signs of a fracture, knee dislocation or crack, and the mobility of the joint is not impaired, then you can try treatment with folk remedies.
- Grate a large onion, apply the mushy mass to the bruise site, wrap it in a plastic bag, wrap it with a light cloth on top and leave for an hour or two. You can do this procedure several times a day, there will be no harm.
- Mix one hundred grams of sea salt without flavorings and additives, half a liter of apple cider vinegar and two teaspoons of iodine, soak a towel in the resulting mixture and wrap it around the bruise.
- Cabbage leaf is an excellent solution for treating bruises with folk remedies; it relieves inflammation and gives a temporary cooling effect. Apply a clean dry sheet to the joint and wrap it with a bandage, keep it overnight.
- Plantain leaf has the same properties as cabbage; apply a couple of clean leaves to the sore spot, secure with a bandage and leave overnight.
- You can lubricate the bruise with arnica tincture (available freely in pharmacies).
- You can treat a bruise with folk remedies using bodyagi; it not only eliminates pain, but also relieves abrasions and bruises. The powder is dissolved in warm water, mixed and the resulting paste is applied to the bruise, wrapped in a bandage and wait until the paste dries.
Treatment with folk remedies is carried out only when there are no wounds or abrasions, and the mobility of the joint is fully preserved.
Thus, you need to treat knee bruises yourself only if in its place there are no such unpleasant phenomena as:
- Cone.
- Bleeding.
- Deformation.
- Immobility.
- Crunch.
And remember that self-medication can lead to irreversible consequences, so it will be safer for your health not to self-medicate, but to consult a traumatologist.
Source: https://grudnoj.sustav-med.ru/sustavyi/mozhet-li-ot-ushiba-kolena-podnyatsya-temperatura/
How long can a fever last after an injury?
The duration of temperature jumps during a concussion depends on the severity:
- at the first stage it should remain within the normal range, perhaps a slight increase of a few tenths;
- with a second degree concussion, some neural connections are disrupted, this causes the temperature to rise to 380. In this case, it can last about 2 weeks;
- in severe forms of concussion, internal hematomas form in the brain, and the temperature can rise to high values.
In addition, there are other unpleasant symptoms: headache, dizziness, nausea and vomiting. With proper treatment, after a few days the degrees begin to drop. It may take up to 2-3 months for the body to fully recover.
Treatment methods
If the temperature rises above 380, then it must be brought down. It is recommended to ensure complete rest for the patient and call an ambulance. Making independent decisions about the treatment of such a problem is strictly prohibited, as this can lead to the development of serious consequences.
Therapy for this category of patients consists of treating the main problem – the traumatic brain injury itself. For treatment you need:
- keep complete peace;
- protect from bright light and noise;
- regularly ventilate the room;
- It is prohibited to read books, watch TV or sit in front of a computer screen;
- exclude fried, spicy and fatty foods from the diet;
- get rid of stress and nervous tension.
If a traumatic brain injury of the second or third degree of severity is diagnosed, then the patient requires hospitalization. If there is a strong increase in body temperature, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic drugs.
Other medications used in the complex treatment of concussions include:
- nootropics that help strengthen the walls of blood vessels and neutron bonds;
- diuretics remove excess fluid from the body and prevent brain swelling;
- antiemetics and non-steroidal drugs dull the gag reflex, relieve cramps in the head and dizziness.
Treatment of hematoma
Treatment of a hematoma depends primarily on its type, severity and distribution. In case of subcutaneous and intramuscular damage, you can independently implement some measures that will quickly eliminate the symptoms. An excellent remedy for a hematoma is a regular cold compress, but it must be applied immediately after the blow. Ice, some frozen food from the freezer, or cold running water will do. Under the influence of low temperature, the vessels sharply constrict, which prevents the swelling from increasing in size. After a few days, it is recommended to use a remedy for hematoma, such as a warm compress, which promotes the resorption of the spilled blood. Ointments with badyagi, hirudin, medications with a resolving effect for external use, as well as applications with clay have a beneficial effect.
If the clot is not sufficiently resolved, suppuration forms at the site of damage. This phenomenon is typical in cases where the patient did not take appropriate measures in time. At the first signs of suppuration, you should definitely consult a doctor.
If conservative treatments for a hematoma are ineffective, the skin in the area of damage is punctured and the liquid part of the blood is removed. If bleeding continues for a long time, then ligation of the bleeding vessel is required. Suppuration of the hematoma also involves opening the skin area and applying drainage.
For cerebral hematoma, conservative treatment is necessary, but maintaining normal intracranial pressure with the help of barbiturates, hyperventilation and some other measures is also important. If the patient's condition worsens, surgery is required.
Surgical intervention is indicated for epidural hematoma, which is extremely dangerous for the patient.
Hematoma is a tumor that forms from rupture of blood vessels and accumulation of blood in tissues. A subcutaneous hematoma is characterized by painful swelling and a feeling of tissue distension. Superficial tumor manifests itself as bruising and swelling. An increase in temperature may be felt at the site of impact.
Swelling can impair organ mobility. Thus, hematomas on the head can spread to the neck, chest and shoulders, while the mobility of the tongue and lower jaw decreases.
Bruising is accompanied by painful sensations. The extent of which depends on the size and location of occurrence. Particularly severe pain occurs from compression of nerve endings.
Reasons for appearance
The direct cause of bruises, regardless of location, is vascular damage. This is caused by injuries, bruises, compression, blood diseases and infectious diseases, fragility of blood vessels, especially in older people.
For people with weak blood vessels, even a minor blow is enough to cause a bruise.
A special type of hematoma appears in newborn babies - cephalohematomas.
They appear in newborns during premature birth, and if the baby is born premature. But even during the normal course of pregnancy, cephalohematomas are observed in half a percent of newborns. As a child passes through the birth canal, the bones of the head are subjected to compression, causing blood vessels to burst. Blood in newborns does not clot as quickly as in adults, so if a cephalohematoma appears, it accumulates in it gradually over 2-3 days.
The appearance of a bruise for no reason is a signal that there are problems with the circulatory system, so you should immediately consult a doctor.
Consequences of temperature surges after concussion
If a skull injury is accompanied by such a symptom, the patient also experiences: severe weakness and fatigue, drowsiness, memory loss, mood swings, irritability, nausea and vomiting.
Hyperthermia requires mandatory treatment, otherwise the risk of complications and worsening of the condition increases.
Temperature after a concussion in children
Diagnosing head injuries in children is very difficult. Often this condition is mistaken for a simple bruise and is not given proper treatment. In this case, the risk of complications increases, which are often accompanied by severe inflammation and temperature fluctuations.
Therefore, with any bruise, you must see a specialist and conduct a full examination. Fever during a concussion in a child is an alarming symptom and requires immediate assistance from a specialist .
Source of the article: https://nevrology.net/sindromy-i-zabolevaniya/povrezhdeniya-mozga-i-pozvonochnika/temperatura-pri-sotryasenii.html
If your hand is severely bruised, you may have a fever
Author Marina Reading time: 4 min. .1k. 10.10.2017
A bruise is the most common injury that a person can receive at any time. Stumble over the leg of a chair, hit a jamb or an open door, fall with all your might, slipping or tripping.
Are there many ways to get such an injury? In most cases, this is done by rubbing the bruised area and hissing through teeth, but when the temperature rises during the bruise or the day after the incident, fears creep in, has something more serious happened? And it must be said that these fears are not unfounded.
Temperature during concussion: causes, consequences, treatment
Can the temperature rise with a concussion?
What does her promotion mean? What to do to get rid of the fever? All these issues are discussed in this article. A fall from a height, a blow to the head, a collision with a wall, an accident - all this can provoke a traumatic brain injury and concussion. The main symptoms of this condition are dizziness and nausea. But can there be fever during a concussion, or is this abnormal?
Causes of hematomas
The causes of hematomas most often include traumatic effects on soft tissue - bruises, blows, pinching, squeezing, etc. The main mechanism for the formation of hematomas lies in ruptures of blood vessels. The size of the hematoma, the severity of its condition and the timing of treatment are directly dependent on the number of damaged vessels, their size and location.
In this regard, experts divide hematomas into subcutaneous and those formed on internal organs. In the latter case, the degree of damage, the potential danger to the patient’s condition and the prescription of competent treatment for the hematoma are determined exclusively in a medical hospital. The need to compulsorily go to a medical institution is due to the fact that the accumulation of blood in the organs responsible for the functioning of the body’s life-supporting systems, for example, with a cerebral hematoma, can in a short time lead to complete disability of the patient or even death.
What is a concussion
It is important to distinguish between two conditions - concussion and brain contusion. Both are types of traumatic brain injury (TBI). A concussion is a minor injury, while a bruise is a more serious condition involving tissue damage. Often, as a result of a traumatic brain injury, a person receives both a concussion and a bruise.
With TBI, a concussion is observed in 70% of patients, a mild brain contusion is observed in 15%. It is difficult to draw clear boundaries between a concussion and a mild injury based on symptoms. As a result, ordinary people, and doctors to simplify things, call everything a concussion.
Further in the article, we will also not distinguish between these states, so as not to complicate an already difficult topic. However, let us say right away that elevated body temperature is characteristic of brain contusion. Therefore, when we say “fever (fever, low-grade fever) due to a concussion,” we will mean a bruise or more serious consequences of a head injury.
Types of hematomas
The classification of hematomas involves several types, differing in location, clinical signs, and nature of bleeding.
- Subcutaneous hematoma. It's more like a bruise. Causes of injury and disease, such as tuberculosis, lupus. Subcutaneous hematoma has three degrees of severity.
- Intramuscular hematoma. Blood accumulates in the muscles, causing severe pain.
- Arterial. Occurs when arteries rupture and covers a large area. This type of damage is red in appearance. If a vein is damaged, the color is blue-violet. The most common cases are mixed hematomas.
- Intracranial (divided into four subtypes). Occurs due to head injury.
- Intracavity. Hemorrhages caused by bruises or compression of internal organs.
- If blood from the vessels still enters the formed subcutaneous cavity, the hematoma is called pulsating.
- During a complicated birth, hemorrhages may occur under the periosteum of the baby’s skull. Such tumors on the head are called cephalohematomas.
- From the processes occurring with blood in the cavity, an infected hematoma and a festering hematoma are distinguished.
- A hematoma of the eye is isolated separately. A common cause of its occurrence is head trauma. A hematoma under the eye also appears from rupture of blood vessels. It can be triggered by direct sunlight during prolonged exposure to the sun.
Why does the temperature rise during a concussion?
A common cause of fever during traumatic brain injury is the presence of an inflammatory process in the body that began even before the injury. If a person had a cold the day before, then after an injury the temperature during a concussion can rise to 38.5 or higher. But this is just a coincidence: the concussion itself does not cause the fever. In this case, the injury became only a catalyst for another inflammatory process.
But the concussion itself also causes fever. Although the human brain appears to be well protected, it is vulnerable to various mechanical damage. Gray matter is located in cerebral fluid, which protects it from impacts on the skull. With a strong impact, the brain approaches the bone tissue and hits it. As a result, brain structures are displaced, which leads to the appearance of microcracks in blood vessels, ruptures in capillaries and disruption of neural connections.
The human neural network is a collection of nerve cells (neurons) of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system. A neural network consists of neurons that are chemically or functionally connected to each other. One neuron is connected to many others using neural connections.
With a traumatic brain injury or concussion, the patient's temperature may rise. Neurologists say that its fluctuations in the range of 37-37.5 degrees are absolutely normal. During injury, the brain's thermoregulation center, the hypothalamus, can shift. And for neural connections to return to normal and the functioning of the thermoregulation center to improve, it takes at least a week. After this period of time, the indicator becomes normal - 36.6 degrees.
As for a significant increase in temperature - above 38 degrees, it can occur when the patient’s condition is serious. Fever is a sign of the development of infection in an open wound or hematoma, which has become an environment for the development of pathogenic bacteria. If you do not provide timely assistance to the victim and do not hospitalize him, then there is a risk of developing meningitis and a rapid rise in temperature to fatal levels of 41-42 degrees.
So, we found out whether there can be a high temperature with a concussion and bruise of the brain. It is worth understanding that its increase in such an injury does not always occur. It all depends on the general health of the victim, the individual characteristics of the body and the nature of the injury.
Hand bruise: symptoms, causes, complications and treatment
articles
A hand bruise is one of the most common problems in traumatology practice. In case of serious injuries, the problem can lead to complications, so experts advise not to postpone a visit to a medical facility. A diagnostic examination will help exclude fractures and identify the level of soft tissue damage.
general information
Closed soft tissue injuries caused by blows and falls lead to bruising of the hand. The pathological condition is characterized by damage to muscle, joint, and bone tissues, with the formation of subcutaneous hemorrhage.
Experts identify several types of injuries, depending on their location:
- In the area of the hand and fingers, they are less common than other subtypes and are accompanied by subluxation and fracture. During a fall, the main pressure falls on the palm area; fingers are damaged by compression or impacts.
- In the area of the wrist and forearm - trauma provokes hemorrhage and hematomas. Violation of the integrity of blood vessels leads to a change in skin tone to purple, swelling of the damaged area.
- In the elbow joint, the pathology is serious, with limited mobility in the problem area. More serious violations lead to dislocations and subluxations.
- In the shoulder area - it is provoked by direct impact, leading to a decrease in free movement and severe pain.
Symptoms
The main symptom of a hand injury is the formation of a hematoma. With excessive hemorrhage, the skin becomes inky in color, and a hematoma occurs after some time. The next symptom is swelling of the damaged area; tissue swelling is combined with painful sensations.
Severe pain is observed when the arm is bruised in the elbow area. At the local level, the temperature level rises, and free movements become limited. The key symptomatic manifestations of the pathology are:
- Problems with sensitivity - paresthesia when a hand is bruised occurs as a response to nerve damage. Loss of sensitivity can be partial or absolute; in case of injury to the ulnar fossa, the disorder affects the entire area below the elbow.
- Lability disorders - appear in some cases when a hand is bruised. Compression and bending of the fingers is impossible if they are damaged; if the area of the radius is damaged, it leads to problems with movements and turns. Difficulties in freely raising and abducting the arms are often caused by shoulder injuries.
- Swelling of the tissues - a bruise on the hand leads to swelling, tension of the skin, and a change in its color to a bluish tint. These symptoms indicate disrupted intercellular connections and ruptured capillaries.
There are no differences between injuries to the right and left limbs; the main problem of injury is that the therapy and recovery period takes longer when the dominant arm is injured.
Causes
Injuries to soft structures are formed in response to falls, hand injuries, sports training, and accidents. Lesions in the form of compression cause compression injuries, with ligament ruptures and fractures.
Diagnostics
In case of a fall or blow, accompanied by a bruise of the arm, it is necessary to visit the local clinic to determine the extent of damage to the structures of the upper limb.
The doctor will conduct an initial medical history: ask about the time of onset of symptoms, conduct a visual examination and palpation examination. To confirm or refute fractures and ruptures, the patient is sent to undergo separate examinations:
- X-rays will help determine the location of the greatest damage and identify bone fractures.
- Ultrasound – ultrasound examination is carried out to assess the condition of soft structures, determine the location and area of hematomas, and damage to the integrity of tendons and muscle tissue.
- CT – computed tomography is prescribed when fluoroscopy results are questionable and questions remain about bone structures. The manipulation is carried out over the entire forearm area.
- MRI - magnetic resonance imaging for a bruised hand is rarely prescribed. The procedure allows you to identify minor violations of the integrity of the tendons and hidden hemorrhages.
After receiving all the examination data, a final diagnosis is made and a treatment regimen is selected.
Treatment
Therapeutic manipulations begin with first aid to the victim with a bruised hand. The following algorithm of actions must be followed:
- a heating pad with ice is applied to the affected area for no more than 10 minutes, in order to avoid cold burns, the procedure will reduce pain and swelling;
- skin wounds are cleaned with antiseptic solutions: hydrogen peroxide, Miramistin;
- The upper limb is fixed in a stationary state with an elastic bandage;
- pain is suppressed by taking painkillers: Analgin, Pentalgin, Baralgin, Spasmalgon, Tempalgin.
To speed up the treatment of a hand injury, suppress tissue swelling, and pain, it is recommended to apply an ointment or gel with an anti-inflammatory, analgesic spectrum to the affected area. Therapy is carried out with Diclofenac, Gevkamen.
It is prohibited to apply drugs with a warming effect several hours after a hand injury - Apizatron, Virapin, Finalgon, Rescuer Forte, or the use of warming compresses.
Their use is allowed after 1-2 days, for the resorption of formed hematomas, after swelling and pain have reduced. After two days, warm compresses are allowed to warm up the local medications.
To speed up the disappearance of bruises, problem areas are covered with Indovazin, Troxevasin, Badyaga, Bruise-off.
If a child’s arm is bruised, it must be shown to the attending physician within the first hours of injury. Diagnostic tests will help eliminate the possibility of rupture, sprains, and fractures. Ignoring the recommendation can lead to improper fusion of bone structures and the formation of pronounced scars in the tendon area.
Possible complications
When a hand is bruised, in addition to damage to soft structures, the following pathologies may occur:
- fracture, hemorrhage;
- tendon ruptures;
- violation of the integrity of the walls of large blood vessels;
- formation of blood clots, purulent processes in places where blood accumulates.
Damage to the blood vessels with disruption of the integrity of their walls provokes the formation of blood clots; the consequence of the problem can be tissue necrosis. Scratches, abrasions, and small cuts can lead to the penetration of pathogenic microflora.
Common mistakes
Patients confuse a bruised arm with a fracture, although each pathology has its own symptomatic features. When a fracture occurs, severe pain is observed at the time of injury; it also occurs when attempting to move the broken upper limb. Patients cannot lean on their arm or bend their fingers.
There is marked swelling and an extensive hematoma, which increase rather than decrease several hours after the incident. When a fracture occurs, the limb may not move at all, is in an unnatural position, and an unusual bulge is detected at the site of injury. These features relate to fractures; when a hand is bruised, there are no increasing symptoms.
Traumatologists remind that the deterioration of the condition can be provoked by the following actions:
- warming up the injured area immediately after a hand injury - an increase in temperature will lead to blood flow into the tissues and an increase in the amount of swelling;
- massage or rubbing of the upper limb - actions will lead to an increase in bruising, and in case of fractures, fragments of bone tissue will disrupt the integrity of nerves and blood vessels;
- Constant attempts to move the injured arm will lead to increased pain;
- pressure on bruises, opening of a hematoma.
Prevention
Preventing a hand injury involves increased caution during icy conditions, sports training, and avoiding household injuries. Prevention is based on preventing consequences and complications.
Proper nutrition with a sufficient amount of nutrients will strengthen bones and normalize the functioning of defense mechanisms. The main diet includes dairy, fermented milk products, fresh fruits, vegetables, and herbs. Periodic training to the best of your body's strength and capabilities will strengthen your muscle tissue - to protect your body in case of falls or bruises.
Normal elasticity of the skin, stable blood circulation process allows hematomas to resolve faster. The normal functionality of internal systems leads to a reduction in the severity of accidental injuries.
A hand bruise is a common pathology that requires careful attention. If on the third day the condition does not change, but worsening is observed, then it is better not to postpone a visit to the doctor. There is a possibility of a fracture or crack in the bones, which requires professional help from traumatologists.
Source: https://artosustav.ru/ushib/ruki/
Other symptoms of a concussion
Concussions manifest differently in children, adolescents and adults. The characteristic symptoms, in addition to temperature, in an adult are:
- sudden darkening of the eyes;
- loss of consciousness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- twitching of the eyeballs;
- noise in ears;
- dizziness;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- increased drowsiness;
- feeling of numbness in the face;
- decreased sensitivity of fingers;
- increased anxiety, excitability, irritability;
- inability to focus the gaze at one point;
- absentmindedness;
- restless and sensitive sleep, insomnia.
A mild concussion has less severe symptoms than a severe one. But in both situations, a doctor’s consultation and possibly hospitalization are required.
You can read about the characteristics of concussions in children in a separate article on the website temperaturka.com.
Types of hematomas
Depending on the location of the hematoma, there are the following types:
- Subcutaneous;
- Subserous;
- Intramuscular;
- Hematomas of the brain (head).
Subcutaneous hematomas are localized directly under the skin, intramuscular hematomas are located in the muscle mass. In both cases, there is no need to worry, since visiting a doctor is not necessary. Symptoms include pain, mild swelling and changes in skin color. Such hematomas do not pose a threat to human life.
Subserous hematomas are characterized by the accumulation of blood in the abdominal or chest cavity, and seeking medical help is mandatory. Such violations of the integrity of blood vessels pose a potential danger.
With brain hematomas, bruising gradually develops, which can last for several days. There are the following types of damage to the blood vessels of the head: epidural, intracerebral and subdural hematomas.
In the first case, blood clots collect in the space under the skull cap, that is, in the epidural place. With the intracerebral type of brain hematoma, the patient complains of dizziness, headaches, nausea and vomiting, speech impairment, psychomotor agitation, and bradycardia. The problem occurs due to a fall or hit to the head. A subdural hematoma appears in the space between the arachnoid and dura mater of the brain. However, regardless of the typology, if even the slightest signs of impairment appear or after falls and blows, you should urgently consult a doctor.
How long does the temperature last after a concussion?
The increase in temperature and its duration as a result of traumatic brain injury depend on the severity. It can be light, medium, heavy.
- With a mild degree of concussion, the temperature remains normal, sometimes rising by a few tenths of a degree (maximum temperature - 37). The norm of 36.6 is restored within a few days.
- With moderate severity, the thermometer can rise to 37.5-38 degrees. This suggests that neural connections are broken and need to be restored. In this case, the temperature after a concussion can last up to one to two weeks.
- In severe conditions, a process of hemorrhage occurs and there is a risk of the temperature rising to a higher level, up to 40-42 degrees. A person suffers from severe headaches, nausea, vomiting, and memory disorders. This continues for several days, and then the degree gradually declines, subject to adequate treatment. But full recovery will take several weeks or even months.
Is it necessary to reduce the temperature during a concussion?
If the temperature does not exceed 37.5 degrees, then there is no need to bring it down. Provide the patient with bed rest and complete rest. If, during a concussion, the temperature rises above 37.5 degrees, and there are concomitant inflammatory diseases (ARVI, colds, etc.) in the background, then they need to be treated. But in the case of fever during a concussion in adults and children, it is strictly forbidden to take any measures on your own. You need to call a doctor at home or arrive at the hospital with an ambulance, after which it is the doctor who, after all the tests, will decide on hospitalization or home treatment, and also prescribe a course of therapy.
Treatment of concussion with fever
There is a general set of therapeutic measures that are used regardless of the presence of fever. If the condition is mild, the patient is sent home. You need to put it in a dark, regularly ventilated room, and also:
- protect from watching TV, computer and reading books;
- allow you to get out of bed only when necessary;
- do not give junk food - spicy, fried, pickled, sweet;
- avoid irritants such as loud music;
- relieve stress.
A complex of medications is used to treat concussion:
- diuretics to avoid tissue swelling and for better circulation of fluids;
- medicines containing potassium to maintain normal functioning of the heart muscle;
- sedatives to relieve anxiety and tension;
- nootropic drugs strengthen blood vessels and restore neural connections;
- non-steroidal medications relieve headaches and prevent general malaise;
- antiemetic tablets eliminate nausea, improve the functioning of the stomach and intestines;
- anti-inflammatory medications are used in case of a significant increase in temperature;
- vitamins and minerals accelerate the processes of regeneration and rehabilitation.
In the event of a sudden increase in temperature due to a concussion, you should inform your doctor about this change, who will adjust the treatment regimen.
Treatment
The choice of treatment tactics for hematoma is made depending on its type. If you are firmly convinced that you have received a subcutaneous or intramuscular hematoma, then you can do with independent measures. To do this, apply a cold compress to the damaged area. If the bruise is small, instead of a bandage and compress, it is enough to hold the damaged area under cold water for 10 minutes to feel relief. Under the influence of cold, the blood vessels will sharply narrow, and the hematoma will stop increasing in size. In case of a hematoma of a limb, a tight pressure bandage is applied to the damaged area.
1-2 days after the injury, warm compresses should be applied to the site of the bruise or physiotherapy should be performed to help speed up the process of resorption of the spilled blood. For the same purpose, you can use ointments with hirudin, badyaga, heparin ointment and other external agents that have a good absorbable effect.
If the process of resorption of the blood clot is not active enough, suppuration may occur in the area of the hematoma, so during the first days after the injury you should monitor your condition and, if necessary, seek emergency medical help.
Treatment of hematomas in a hospital setting usually involves puncturing the skin in the area of injury and removing the liquid part of the blood. If bleeding continues, the hematoma is opened and the bleeding vessel is ligated. When suppuration occurs, the hematoma is also opened, and then drainage is applied.
Treatment of head hematomas (intracerebral traumatic and subdural) involves the use of conservative methods, with a lot of effort going into maintaining normal intracranial pressure with the help of barbiturates, hyperventilation and other measures. Surgery is indicated if the patient's condition worsens.
In most cases, epidural hematoma requires emergency surgery.
Sincerely,
A hematoma is a blood-filled cavity in the muscles or organ tissues that occurs as a result of internal bleeding. Most often, the causes of this phenomenon are associated with various bruises, impacts, squeezing, pinching and other types of traumatic effects on soft tissues. Hematomas occur when blood vessels rupture. Popularly, such a violation of tissue integrity is called a “bruise.”
Hematomas are characterized by the following symptoms:
- Swelling in the injured area;
- Pain in the area of injury;
- Change in skin color from pinkish to green or purple-bluish;
- Local increase in temperature (in the area of the affected skin).
If hematomas form internally (retrochorial hematoma, cerebral hematoma, for example), then symptoms of dysfunction of the corresponding organs appear.
Consequences of temperature disturbances in head trauma
After an injury, if it is complicated by an increase in temperature, the following symptoms persist indefinitely:
- increased fatigue;
- irritability;
- weakening of attention and memory;
- sudden change of mood;
- apathy;
- slight dizziness;
- nausea, vomiting.
So, a concussion is sometimes accompanied by fever and fever. There are two reasons for this - natural (disruption of neural connections due to injury) and pathological (infection during severe traumatic brain injury, inflammation due to another disease). In both cases, the patient must be under the close supervision of a doctor and follow his recommendations. If you consult a doctor and strictly adhere to the prescribed treatment regimen, the risk of complications will be minimized. If you ignore the advice, then there is a possibility of complications even if the concussion was mild and occurred without fever.
Source of the article: https://temperaturka.com/bolezni/sotryasenie
Causes of head injuries in children
A healthy child is active, purposeful and curious. Children constantly try new things and persistently study the world around them. This is why they often find themselves in dangerous situations. Unattended children are at risk. Some of the most common causes of head injuries in children include:
- falling from a bicycle, skateboard, scooter;
- falling from a swing;
- children's fight;
- sport;
- falling from a height (tree, roof of a house);
- falling under the wheels of a car;
- in older children, a fall may be caused by drinking alcohol;
- hitting your head during a car accident.
Also, schoolchildren are injured as a result of experiments with loss of consciousness. Waves of children fainting, caused by deliberate rapid breathing and subsequent falling without memory, periodically pass through schools. Usually at this moment the experimenters are held by their peers, but it happens that they are not held. Try to find out if your son or daughter practices this. Explain why this is harmful.
A baby who has just begun to walk is also not immune from a concussion. Even an unsuccessful fall on your butt can cause damage to a fragile head. Infants also suffer traumatic brain injuries from falls from beds, changing tables, and strollers. In some cases, mothers are to blame, because... during swaddling, especially when using a washing machine as a table, they don’t think that they can’t be distracted for even a second: children twitch and fall at the same time.
Dr. Komarovsky : “A fundamental feature of children in the first year of life is the fact that the amount of fluid in the cranial cavity is much higher than that in older children and adults. The baby's brain is not rigidly closed in the cranium, since there are fontanelles, as well as pliable and movable sutures between the bones of the skull. This creates cushioning and reduces the risk from impacts to the head and head to some extent.”
On the one hand, the brain of a small child is well protected. It is placed in cerebral fluid, which absorbs shock. But the shock-absorbing capabilities are not enough if the blow is too strong or the fall was from a great height. In addition, in children, the back of the head protrudes more than in adults, the head is proportionally larger in relation to the body, the neck muscles are weak, and the skull bones are thinner. Therefore, children are more susceptible to head injuries and serious consequences as a result. So, for example, the force of an impact, at which an adult will only have an intracranial hematoma, can cause cerebral edema in a child.
The most common consequences of head injuries in children are:
- rupture of cerebral vessels;
- formation of hematomas;
- disruption of neural connections;
- development of infection;
- cerebral edema.
A traumatic brain injury is not a reason to panic, but an examination by an experienced traumatologist, neurosurgeon and pediatrician is mandatory, even if there are no visible consequences.