How the disease manifests itself, diagnosis
The physiology of the human brain is designed in such a way that this organ seems to “float” in the cerebrospinal fluid, the function of which is to cushion and maintain the constancy of the internal environment inside the cranium. It also participates in the metabolism between nervous tissue and blood and removes the products of their metabolism.
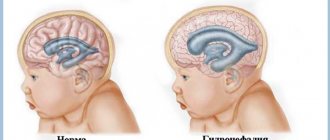
The main characteristic of cerebral hydrocele is the excessive production and accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain structures. This, of course, cannot but affect human health: the fluid, in turn, puts pressure on the brain matter and prevents it from functioning normally, which contributes to the appearance of various neurological and physical abnormalities.
The main physiological signs of cerebral hydrocele:
- rapid growth in head volume (especially in the forehead area);
- bulging brow ridges;
- swelling, pulsation of the fontanelles, delay in their ossification;
- visibility of the venous network in the area of the bridge of the nose, temples.
Neurological signs caused by disruption of the brain:
- nystagmus, exotropia and other visual disturbances;
- pale skin, hypothermia;
- increased muscle tone;
- tachycardia;
- tremor of the limbs, chin;
- frequent and profuse regurgitation;
- increased and excessive excitability;
- disturbance of sleep organization;
- psychological and physical retardation.
The severity of the abnormalities depends on how strongly the pathology affects brain development. If we talk about the manifestations of pathology in childhood, the appearance of the main symptoms depends on the time of onset of the disease and its etiogenesis.
Congenital hydrocele of the brain is usually diagnosed during fetal development using ultrasound screening, and the first sign of pathology is a significant increase in head size and dilation of the ventricles.
The significance of conducting such a study in late pregnancy is that it allows specialists to assess the degree of pathology and prevent the occurrence of complications during delivery: it is not without reason that one of the indications for cesarean section is hydrocele of the fetus. Carrying out this operation allows you to avoid the passage of the child through the birth canal and, accordingly, prevents even greater compression of the nervous tissue.
The development of acquired hydrocele of the brain is usually noticed during a monthly or quarterly examination of the child by specialists. In this case, the first thing the doctor notices is the rapid increase in the volume of the head and protruding fontanelles. If age allows, then in this case, neurosonography is prescribed - ultrasound of brain structures through not yet overgrown fontanelles.
In an older child, dropsy of the brain can be noticed when systematic headaches appear in the morning, nosebleeds, attacks of nausea and vomiting independent of food intake, poor coordination of movements, and enuresis. The appearance of these signs gives rise to a more detailed examination of the head using MRI or CT.
How is it carried out?
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia. Before the operation, it is necessary to carry out certain examinations to select the most suitable bypass methods:
- Cardiogram.
- Fluorography.
- Blood and urine tests.
- Magnetic resonance thermogram.
- CT scan.
- Ultrasound examination of arteries.
As soon as the diagnostic results are known, the patient confirms in writing his consent to surgery. At the same time, possible risks and complications are described to him. If brain shunting is necessary in newborns, parents must give consent.
Before the operation itself, the patient must take a shower and wash his hair. In some cases, it is necessary to shave the hair. All foreign objects (earrings, glasses, piercings, dentures, contact lenses) are removed from the head. Several weeks before the scheduled surgery, the patient is advised to avoid drinking alcohol, smoking, and taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Eight hours before the procedure, the patient does not eat anything (limited amounts of water are allowed).
Bypassing the vessels and arteries of the brain allows you to create a new branch of the blood flow that bypasses the problem vessel. A vein or artificially created blood vessel is used as a shunt. It is sewn behind the site of injury or in front of it. After this operation, blood circulation is resumed in a new area.
Shunting for hydrocephalus proceeds as follows:
- The patient is covered with sheets and the areas where the incisions will be made are left uncovered.
- The sites for liquor shunting are lubricated with an antiseptic.
- A burr hole is made through which a drainage tube (shunt) is inserted to the brain.
Retraction of the tube into the abdominal cavity is performed extremely rarely, as it is associated with a high risk of complications. The ventriculoatrial type of bypass is considered safer, in which a drainage tube is inserted into the left or right atrium. In such cases, the shunt will be short, which means the risk of complications is minimized.
The next stage is to lay a shunt in the soft tissues, synchronizing the path of the drainage tube with the arteries. Next, the shunt is installed in the desired ventricle through a burr hole. Modern doctors use drainage tubes equipped with special valves that prevent the backflow of cerebrospinal fluid, which provides additional reliability and functionality of the operation. Bypass surgery is performed in the same way in children.
How is hydrocephalus formed?
Hydrocephalus of the brain in newborns is usually a congenital pathology of the organ, the degree of which is determined based on the totality of disorders and anomalies of the organ. In turn, depending on the degree of pathology and the defects it caused, the treatment tactics depend.
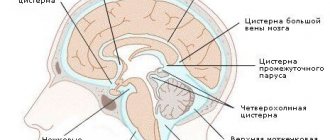
As mentioned earlier, cerebrospinal fluid is a kind of barrier between the brain tissue and the inside of the skull, and in addition to its main function - participation in metabolism - it protects the structures of the central nervous system from the consequences of hitting the head on a hard surface. It also maintains the constancy of the internal environment in the structures of the central nervous system: the amount of intracranial pressure, the efficiency of the autonomic system and the state of water-electrolyte homeostasis depend on its quantity.
The production of cerebrospinal fluid occurs in the ventricles with the help of villous formations - the choroid plexuses. Having passed through all 4 cavities, it enters the cerebrospinal fluid pathways and subarachnoid space of the spinal cord and brain, where it washes them. Further absorption of fluid occurs in the venous sinuses of the dura mater and through granulations of the subarachnoid space. Thus, its circulation occurs in the structures of the central nervous system.
When the balance of production and readsorption of cerebrospinal fluid is disturbed, stagnation and retention of fluid in the cavities occurs, which ultimately leads to constriction of the medulla and an increase in intracranial pressure. All these processes disrupt the process of normal development of the organ, which is manifested in the appearance of various neurological and physical symptoms of the disease.
Causes of the disease
Why does dropsy of the brain develop in children? This question worries not only parents, but also doctors. It is usually believed that this pathology in newborns is a congenital disease, that is, a consequence of a pathological process during intrauterine development, and in adulthood, the activator of the pathology can be the influence of various unfavorable factors.
The main causes of congenital hydrocele of the brain:
- structural changes in the organization of individual chromosomes;
- blood incompatibility between mother and child is the cause of immune edema of the brain;
- infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy, possible intrauterine infection of the fetus (for example, cytomegalovirus);
- gestosis, excess of blood sugar levels in a pregnant woman, anemia, fetal hypoxia;
- intrauterine pathologies of the vascular system, thrombophlebitis, leukemia, Arnold Kizri syndrome; neurotumors.
In older age, dropsy of the brain can be a consequence of complications caused by:
- head injury;
- blocking of the liquor-conducting pathways with tumor-like neoplasms;
- hemorrhages;
- inflammation of the nervous tissue due to the development of infectious diseases (for example, meningitis).
Consequences of a pathological increase in the volume of cerebrospinal fluid
If treatment for this serious pathology - hydrocephalus of the brain in children - is not started in time, the consequences will be visible to the naked eye and will greatly affect the life of the baby and the whole family. Children with this diagnosis:
- rapidly lose vision to the point of complete blindness;
- are lagging behind their peers in physical and mental development;
- suffer from constant cephalalgia caused by increased intracranial pressure;
- speak poorly and have difficulty sleeping;
- suffer from lack of concentration syndrome;
- susceptible to epileptic seizures;
- more aggressive than their peers and suffer from autism spectrum disorder.
Complications of dropsy cause:
- stroke;
- to whom;
- swelling and displacement of the main organ of the central nervous system;
- difficulty breathing;
- epilepsy and cerebral palsy.
The pathology leads to disruption of the blood supply to the main organ of the nervous system and, as a result, to tissue atrophy, which causes the baby’s head and face to become deformed and disfigured.
Risk factors for hydrocephalus in a child
Even with good heredity, the risk of giving birth to a child prone to hydrocele increases with:
- early delivery;
- severe prematurity (weight less than 1500g);
- fetal asphyxia during labor;
- infectious diseases of the expectant mother;
- the use of aggressive methods of delivery using a vacuum installation, forceps, manual opening and expansion of the uterine tract.
Also, the retention and accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid and, accordingly, dropsy of the brain in an infant can be a consequence of a woman’s poor lifestyle, her consumption of alcoholic beverages and smoking during pregnancy.
Classification of pathology
When drawing up a conclusion after diagnostic measures, specialists try to indicate as many characteristics of the disease as possible. Usually, this data is then useful when choosing treatment tactics.
Dropsy of the brain can be:
- Congenital.
- Acquired.
The phase of the disease is indicated below:
- Spicy. The amount of cerebrospinal fluid quickly increases, and the patient’s condition sharply worsens.
- Subacute. The child's physiological condition deteriorates within 3-6 months, which leads to serious organic brain damage.
- Chronic. The amount of cerebrospinal fluid increases slowly.
According to morphological characteristics, dropsy is:
- Open. It is characterized by an imbalance in the absorption and production of cerebrospinal fluid, while the ventricular system remains open.
- Closed or occlusal. With it, part of the ventricular system is blocked, which causes uneven enlargement of the cavities.
In children under 2 years of age
In babies under the age of one year, cerebral hodrocephaly is most often diagnosed as a congenital disease. The course of the disease in this case is severe, the little patient’s condition quickly deteriorates and he noticeably lags behind his peers in development. This is due to the fact that during this period the physiological “ripening” of the brain should occur, but this does not happen due to compression of the organ structures by the increased volume of cerebrospinal fluid.
Therefore, the first thing that doctors pay attention to when undergoing a preventive examination is the intensity of growth in the volume of the head. So, at birth in a healthy child, this indicator should not exceed the volume of the chest by more than 1-2 cm.
In the future, the growth rate of this indicator should be as follows:
- From 0 to 3 months – no more than 1.5 cm per month;
- From 3 to 12 months – no more than 9mm for each month.
The following signs will also indicate the development of cerebral hydrocele:
- excessive tearfulness;
- increased intracranial pressure, which is visually manifested in swelling of the large fontanelle and enlargement of the frontal bone;
- poor sleep and weight gain;
- delay in performing physical exercises, for example, children with hydrocele later begin to hold their heads up, later sit down, stand up, crawl;
- inability to fix gaze;
- frequent regurgitation;
- throwing back the head;
- increased muscle tone.
In the future, in the absence of treatment, more serious deviations appear: the appearance of convulsions, vomiting, drowsiness and loss of strength, and acquired skills (sitting, humming) are forgotten.
In children over 2 years old
Due to the fact that by the age of two the sutures between the bones of the skull become less plastic, the development of dropsy of the brain will indicate the appearance of:
- headaches especially in the morning;
- frequent nosebleeds;
- pain in the area of the eyeball when moving them;
- nausea, sometimes vomiting;
- loss of coordination of movements, nystagmus, tremor of the chin and limbs;
- drowsiness;
- enuresis;
- decreased motor activity with increased muscle tone of the body.
At this age, acquired hydrocele of the brain is usually diagnosed, which is a consequence of head injuries, vascular diseases of the brain and damage to the body by neuroinfections.
Treatment
Treatment of hydrocephalus in children can be conservative (medication) and surgical. To provide the child with the best possible prognosis, treatment is prescribed not by a single neurologist, but in a team with a neurosurgeon, focusing on the results of the examination.
Drug treatment
In order to reduce intracranial pressure during hydrocephalus, it is necessary to either reduce the production or accelerate the excretion of cerebrospinal fluid. In an outpatient setting, if the diagnosis is “Open non-progressive hydrocephalus”, this is done in the first way, prescribing the drug “Diacarb” in an age-specific dosage. It blocks the enzyme responsible for the secretion of cerebrospinal fluid, increases the volume of urination and removes potassium from the body. Take it in the morning, on an empty stomach, together with the potassium preparation “Asparkam” or “Panangin”.
If there is a significant increase in intracranial pressure, but in a hospital setting and under the control of neurosonography or computed tomography (as a cheaper method than MRI), treatment with drugs that improve the removal of excess fluid from the cranial cavity is prescribed. These are 2 groups of diuretic drugs:
- osmotic diuretics, causing an increase in plasma osmolarity, due to which water moves from the brain into the vessels and is excreted through the kidneys. These are "Mannitol" ("Mannitol") and oral "Glycerin". They are used after calculating plasma osmolarity, according to strict indications;
- salt diuretics: Lasix, Furosemide. They, like Diacarb, are used together with potassium preparations (Asparkam or Panangin) and remove fluid due to the fact that they block the reabsorption of sodium in the kidneys (sodium attracts water to itself).
Along with diuretics, medications are prescribed that improve the functioning of neurons in conditions of increased intracranial pressure. These are “Encephabol”, “Calcium hopantenate” and others.
If there is no decrease in intracranial pressure within 2-3 months of taking diuretics, as well as with a closed form of hydrocephalus, surgical interventions are resorted to.
Surgery
In many cases, surgery for hydrocephalus is an opportunity to stop the progression of intracranial pressure growth and save the brain. The method of operation is determined by the form and stage of hydrocephalus.
Closed hydrocephalus
In this case, there may be 2 situations:
- If it is possible to remove an obstacle that prevents the cerebrospinal fluid from circulating normally, such an operation is performed. This way you can remove a tumor, hematoma, cyst or dilation (aneurysm) of a vessel supplying an area of the brain. Then the cerebrospinal fluid will flow normally to the place where it is supposed to be absorbed.
- If the tumors have grown into the brain (no one “cuts” the substance), or they do not have a clear boundary, then the operation is aimed at creating a path for the cerebrospinal fluid that will bypass the “congestion”. For this purpose, shunting (the word “shunt” means “transition to another path”) operations are performed.
Most often, cerebrospinal fluid is diverted through a system of silicone catheters into the abdominal cavity, where the end of the bypass is placed between the layers of the peritoneum (the film lining the walls of the abdominal cavity), which has remarkable suction ability. This is a ventriculo-peritoneal shunt. It is carried out 200,000 times a year around the world, saving countless children.
The cerebrospinal fluid can be diverted into the right atrium - ventriculo-atrial shunting. It is also removed into a large “collection” of cerebrospinal fluid, where it is absorbed – the cistern magna. The connection can also be made from the spinal canal to the peritoneum (lumbo-peritoneal shunt).
Sometimes you can avoid installing silicone tubes, and make a way for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricle using a tube with fiber optics - an endoscope. This operation, endoscopic ventriculostomy, is effective only for certain forms of occlusive hydrocephalus.
As a matter of urgency, if the pressure in the cranial cavity increases rapidly and shunt surgery carries a high risk, external ventricular drainage is performed. Here a catheter (tube) is inserted into the ventricle, through which excess cerebrospinal fluid will be drained into a sterile container. The flow rate of cerebrospinal fluid will be regulated by the level of location of the container in relation to the head.
Open hydrocephalus
If the cerebrospinal fluid is not absorbed where it should happen, then it needs to be “brought” to where this is possible. To do this, shunt operations are performed (they are described earlier):
- ventriculo-peritoneal shunt;
- ventriculoatrial shunt;
- Lumboperitoneal shunting.
Interventions can be carried out that should “turn on” the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid. This is, for example, dissection of arachnoid adhesions.
If there is an established increase in the synthesis of cerebrospinal fluid, operations are needed that will suppress this process. This is the placement of clamps on the choroid plexuses of the ventricles (their clipping) or cauterization (coagulation) of these structures lining the walls of the ventricles.
Diagnosis and treatment
As mentioned earlier, you can see signs of hydrocele in a newborn during pregnancy using an ultrasound of the fetus. This diagnosis is subsequently confirmed in the newborn using neurosonography - an ultrasound examination of brain structures through open fontanelles of the skull.
If the development of the disease in adulthood (children over 1 year of age) was facilitated by head trauma or inflammation, then in this case it is advisable to perform an MRI or CT scan of the brain. In order to obtain reliable data, the child will have to be immobilized for some time using medical sedation (light anesthesia). To identify neurological abnormalities, an examination is carried out by a neurologist and an ophthalmologist.
When diagnosing an acute condition, measuring the level of intracranial pressure is also prescribed to compile a complete picture of the disease. To do this, a puncture of the cerebrospinal fluid is taken.
Treatment tactics depend on the course and extent of the disease: if the pathology does not threaten the child’s life and minimally affects the intensity of its development, then in this case drug therapy is prescribed aimed at suppressing the secretion of cerebrospinal fluid and accelerating its removal from the body.
If the disease is in an acute stage and the child’s condition quickly deteriorates, then surgical intervention is indicated: brain shunting. During this operation, a catheter is inserted into the cavity of the skull, through which excess fluid is removed from the body. Typically, brain shunting is used in cases of congenital hydrocele when other treatment methods are not effective.
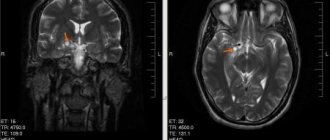
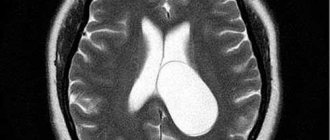
Diagnostics
MRI is one of the methods for diagnosing hydrocephalus
At the first symptoms, you need to go for examination to a specialist, in this case we are talking about a neurologist.
- Examination of the patient, measurement of the circumference of his head, as well as chest, is observed in dynamics. The doctor will evaluate muscle tone and the presence of reflexes.
- Visit an ophthalmologist for a fundus examination. If there is hydrocephalus in the child’s eye, the so-called “stagnant disc” of the optic nerve may be detected.
- Neurosonography. It is a screening method and is carried out until the baby’s large fontanel is overgrown. Thanks to this method, it becomes possible to study the structures of the brain, as well as measure the size of the ventricles.
- X-ray of the skull.
- Angiography of cerebral vessels.
- Study of cerebrospinal fluid.
- MRI. Using this study, it is possible to obtain images of each part of the brain. Computed tomography may also be prescribed, but this method is less informative.
It is very important to undergo a complete examination in order to rule out a brain tumor or rickets.
Prevention
The basics of preventing cerebral hydrocele in a newborn are for the woman to maintain a healthy lifestyle throughout the entire period of pregnancy and undergo all types of examinations in accordance with the schedule.
Later, after birth, care should be taken when caring for the child: protect him from head injuries, wear protective equipment when rollerblading or cycling, use only a car seat or other child restraint device when transporting him in a car, and avoid traumatic games.
If, however, the pathology begins to develop, then in this case you need to follow all the doctor’s recommendations and not progress the disease.
Is it possible to cure hydrocephalus?
Six months or six months sounds significant! This is not just 2 or 3 months, when all the time it seems that he was just born, that he has not yet adapted to everything - food, environment, proper sleep... No, now Kolobok is big! He shows his character, he has favorite activities and habits. Such a small, but absolutely full-fledged member of the family 
As for character, Pashka is basically a lazy person)) Yes, he already knows how to roll over (finally!), reaches for toys, likes to lie on his stomach and slowly moves around his axis. He grabs everything he can reach and puts it in his mouth)) Once I was washing his butt, and there was a rag lying next to him; I didn’t even notice how he grabbed it and let’s suck it)
Most of the time, Kolobok prefers to lie on the couch, watch me cook, and “walk.” The basic requirements remained the same - sleep and food. Then Pashka turns into an ideal child - minimum worry, maximum smiles
He also began to sleep almost perfectly: we put him to bed at nine o’clock, and he wakes up once a night (in the morning), eats and then sleeps until seven or eight in the morning. During the day, Pashka also falls asleep without problems. When I see that he is rubbing his eyes and starting to be capricious, I do the following: I wrap him in a blanket, give him a pacifier, turn on the mobile, close the curtains and close the door to the room. Usually, after 5-10 minutes he is already asleep, while at this time I am minding my own business in the kitchen. But during the day, sleep duration can be short - 40 minutes, that stupid deep sleep phase! I tried in every possible way to fight this, since the child naturally does not get enough sleep during this time. Within five minutes of waking up, I turned on my mobile, gave her a pacifier, and rocked the crib. Then I got tired of it... Now such quick awakenings happen less often - I don’t know what helped.
We have also made progress with recovery: dysplasia has been cured (most likely, massage + electrophoresis helped), we plan to have a general massage in a month and start going to the pool. But with dilatation of the ventricles of the brain, no obvious improvement has yet been observed. Although the neurologist says that the baby is developing well. But she still prescribed treatment (according to ultrasound, the third ventricle decreased by only 0.4 mm) - diacarb + asparkam. I read Komorowski, diacarb is used for hydrocephalus, but we don’t have such a diagnosis. Probably, even without this medicine, Kolobok would have gone through everything, but she decided to start treatment anyway, although the list of side effects is long (not counting the fact that diacarb is a diuretic drug, and you need to often give the child something to drink and monitor the humidity in the children's room).
Well, for the rest, the baby, of course, makes everyone happy)) Smiles (especially for mom), laughs like a plush toy)) becomes stronger, more active, bathes with pleasure)