- July 3, 2018
- Neurology
- Voloshchuk Natalya
Diseases of the nervous system are not uncommon. They most often manifest as neuralgia, but there are also hereditary forms of the disease, for example, spinocerebellar ataxia (SA). Neurologists use the term “ataxia” to refer to a condition in which there is a violation of the coherence of movements controlled by consciousness. In other words, this disease is a violation of the joint activity of the cerebellum and spinal cord. What the disease manifests itself in and how it is treated, we will consider below.
Description
Spinocerebellar ataxia is a set of genetic diseases that are neurological in nature, manifested by disruption of the activity of the basal ganglia of the brain and cerebellum and are inherited. As a result, coordination of movements and so on changes. The negative thing about the disease is the fact that today there is no specific treatment. The disease is inherited by the mechanism of autosomal dominance, when enzymes that appear as a result of mutations in the genes of structural proteins are deformed. Typically, inheritance occurs through the paternal line from generation to generation.
Additional symptoms
As spinocerebellar ataxia develops, it acquires new symptoms:
- tremor of the limbs occurs after any action or as a result of a lack of coordination;
- The handwriting changes greatly - the letters become uneven and large;
- Speech gradually changes, but this sign is difficult to notice if you live with the patient constantly;
- disorders of eye movements occur - they become sharp, jerky when a person moves his gaze from object to object;
- in some cases, the functioning of the hearing aid deteriorates;
- Many people have problems with bowel movements and urination;
- in advanced cases, paralysis of the arms and legs appears;
- There is also a noticeable deterioration in habitual reactions and reflexes; over time, they may completely disappear.
In some patients, spinocerebellar ataxia occurs in a mild form, sometimes progressing to a stage with the assignment of temporary disability, but most often does not require it. A similar picture occurs in people whose close relatives suffer from spinocerebellar ataxia of the expanded plan.
With spinocerebellar ataxia, there is always a loss of muscle mass, which ultimately leads to cramps and severe muscle weakness. One of the symptoms is a feeling of twitching, trembling under the skin.
Sometimes, with spinocerebellar damage, involuntary turns and jerking of the head occur, and dementia develops, the symptoms of which are similar to Parkinson’s disease. The disorder is also characterized by vision problems. The severe form is accompanied by a complete loss of eye contact.
Classification
Spinocerebellar ataxia (ICD 10 - G11) in 90% of cases represents six of the twenty genetic variants of the disease. These options were classified by number: 1, 2, 3, 6, 7 and 8 types of ataxia. Pathology is expressed in a change in the number of CAGs in some genes that encode diseased genes. Let's take a closer look at these types:
- Ataxia type 1 is the most common today. It occurs due to the placement of the mutated ATXN1 gene on the sixth chromosome. Normally, this gene has thirty-six repeats, but with a larger number, the disease develops. A gene mutation causes the formation of a DNA protein that takes part in cell metabolism. This contributes to degeneration and disease development.
- SA of the second type is somewhat less common. It is characterized by an increase in repeats on the twelfth chromosome. What function the protein performs in this case is unknown to medicine.
- The third type is called Machado-Joseph disease. In this case, the disorder occurs in a gene located on the fourteenth chromosome. The protein takes part in the exchange of energy between the cerebellum and the nuclei of the brain.
- Spinocerebellar ataxia type six is a rare disease. Here there is a violation in the gene, which is located on the nineteenth chromosome. The gene encodes a protein that is located in the neurons of the cerebellum. This process also causes a hereditary form of migraine.
- Type seven SA is caused by gene abnormalities on the third chromosome. What function the protein performs is unknown to medicine.
- The eighth type is characterized by gene changes on the thirteenth chromosome.
Hereditary forms of genetic abnormalities
In terms of frequency of occurrence, spinocerebellar pathology ranks 2nd among all diseases of the central nervous system. There is no single classification of pathologies, since the symptoms are the same in many species, doctors cannot accurately divide the pathology into different categories. There are 3 common types based on symptoms and causes. But there is a division into forms according to gene damage (there are 8 in total).
Friedreich's disease
Among 120 people in a random sample, 1 turns out to be a carrier of this gene. It is transmitted to both boys and girls. Develops as a result of the following reasons:
- disruption of protein synthesis responsible for the transport of iron ions;
- destruction of cells of the central nervous system, myocardium, and pancreatic islets;
- at a late stage, the cerebellar peduncles and nerve nuclei are affected.
Spinocerebellar ataxia causes the first symptoms in children aged 10-11 years: changes in gait, staggering, difficulty moving in the dark. Coordination of movements gradually changes, handwriting deteriorates. Then the classic symptoms appear - muscle atrophy and loss of mobility.
Neurologists no longer observe tendon reflexes in patients. Gradually, other organs are involved in the dystrophic process. Deformation of the spinal column, fingers and toes occurs . Patients often experience diabetes mellitus, problems with the ovaries, delayed puberty, and obesity.
The atypical form of the disease develops after 30-50 years and is milder than in childhood. Due to its slow progression, it is more amenable to correction.
Ataxia with vitamin E deficiency
The least common form of spinocerebellar ataxia, in which the integration of the vitamin into the protein structure is impaired. As a result, the body's antioxidant defense is severely affected, and symptoms similar to Friedreich's disease occur.
Spinocerebellar ataxia with vitamin E deficiency is characterized by symptoms of the heart, bone and endocrine systems - they practically do not suffer. The reflexes and speech capabilities of a person are most inhibited . By the age of 30, the patient almost completely loses the ability to self-care.
Autosomal dominant forms
This category includes 13 independent diseases that differ little from each other in symptoms. They are caused by mutations of 13 genes.
Each type of spinocerebellar ataxia causes the death of certain cells of the nervous system:
- It is diagnosed mainly between 30 and 40 years of age. The first type is accompanied by gait disturbances, changes in coordination and muscle tone. Dementia, pelvic diseases, tremors, and motor problems gradually develop.
- The second type of spinocerebellar pathology is complemented by ocular disorders, but is generally similar to the first.
- The third type, Machado-Joseph disease, appears when the cerebellum is damaged. The main differences from other types: violent movements, twitching of the facial muscles.
- The fourth type is accompanied by acute pain and sensory disturbances in the area for which the damaged nerve is responsible.
- Spinocerebellar pathologies of types 5 and 6 appear after 50 years, progress slowly and maintain the patient’s standard of living.
- The seventh form is accompanied by movement disorders associated with the eyes, and blindness is often observed.
- The eighth type and subsequent forms of the disease are poorly studied and are extremely rare (less than 1 case per 500,000 people).
Spinocerebellar ataxia is a severe neurological disorder that cannot be completely cured and is accompanied by acute symptoms as it progresses. However, spinocerebellar damage can be slowed down if detected early.
Causes
In any type of disease, a gene mutation occurs, leading to the formation of a pathologically shaped DNA protein that is rich in glutamine. It causes the appearance of deposits in the form of aggregates in the nuclei of neurons of the cerebellum and basal nuclei of the brain, disrupting the properties of proteins. Proteins take part in the metabolism occurring in nervous tissue. The speed of this process depends on the number of turns in the gene, which differs from the norm. This determines the symptoms of the disease. As the germ cells mature, the symptoms intensify.
Symptoms
All types of this disease have the same symptoms; only minor elements can be different. Thus, symptoms of spinocerebellar ataxia do not appear in childhood. The average age of people suffering from the disease is from eighteen to thirty years. Ataxia types three, six and seven develop later, usually after thirty years of age. The first sign of the disease is the appearance of clumsiness when walking and running. Later, there is tremor of the limbs, changes in gait, ophthalmoplegia, and handwriting changes. Over time, the disease leads to the development of parkinsonism. In some types of the disease, optic nerve atrophy is observed. AS types six, seven and eight are characterized by impaired speech and swallowing, which leads to exhaustion. Exhaustion together with pathologies often provoke death. In all types of the disease, coordination of movements is impaired. The average life expectancy of patients ranges from ten to twenty-five years, depending on the form of the disease and the quality of care they receive.
Treatment in Italy
Russian Medical Server / Treatment in Italy / Center for the treatment of rare diseases in Milan / Spinocerebellar ataxia - treatment in Italy
Spinocerebellar ataxia includes various actively developing hereditary forms of pathologies, characterized by impaired coordination of movements. With such lesions of the human body, the main changes occur in the cerebellum, in the spinal cord, and also in the brain stem. Among all known hereditary diseases, spinocerebellar ataxias are in second place in frequency of occurrence after neuromuscular pathologies.
The disease is characterized by a noticeable clinical diversity of symptoms; there is a wide gradation between mixed forms of pathology and cerebellar types. There are many different classifications based on clinical and anatomical principles and on the types of genetic inheritance of disease symptoms.
It is important to know that all known classifications of spinocerebellar degenerative processes are not able to fully satisfy the requirements of medicine. This can mainly be explained by insufficient study of the disease and the lack of basic understanding of the development of biochemical defects that become causative.
Spinocerebral ataxia occurs with a frequency in different populations of approximately 1 - 23 cases per hundred thousand population. The pathology has an uneven ethnic and geographic distribution. In Russia and Italy, the first type of disease mainly predominates; in India, the second type of spinocerebellar ataxia is more common; the third type of disease is most often diagnosed in the population of Germany, the USA and Japan.
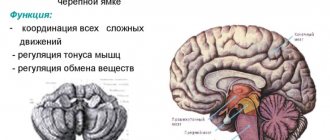
The group of spinocerebellar ataxias refers to cerebellar lesions that are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. At the same time, mutations occurring in genes provoke the formation of pathological protein products that cause the death and death of cells in the cerebellum, spinal cord, and cerebral cortex.
The neurological symptoms of spinocerebellar ataxia develop rather slowly, and the development itself can be delayed for up to twenty years, but the disease can also progress more quickly. Sometimes there are periods of stable conditions.
With the development of concomitant infectious lesions, additional symptoms begin to appear. Patients with very advanced stages of pathology are deprived of the ability to get out of bed, they develop dysphagia, that is, a violation of the act of swallowing, and other similar signs. A person may die due to exhaustion and often from the development of myocarditis, accompanied by severe forms of heart failure. With proper care, the patient lives up to forty to fifty years.
Subsequently, the symptoms are supplemented by tremors of the legs and arms when performing any actions and when coordination of movements is impaired. In addition, handwriting begins to change - it becomes uneven, and the letters are too large, and speech also changes.
The disease is also characterized by eye movement disorders - jerky, sharp movements of the eyeballs when the gaze shifts from one object to another. Often there are disturbances in swallowing, speech pronunciation, disruption of the hearing aid, disturbances in stool and urine output, paralysis of the legs and arms, and pathological reflexes develop. And habitual reflexes simultaneously worsen reactions and then disappear completely.
At times, the disease occurs in an abortive or mild form and provokes minor disability of the patient or is not accompanied by disability at all. Such pathologies can be diagnosed in relatives of the patient who suffer from advanced clinical types of the disease.
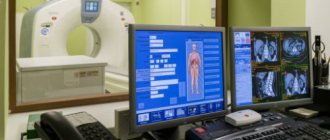
When diagnosing, preference is given to imaging methods such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. They make it possible to identify areas of degeneration of nerve fibers, demyelination of pons neurons, expansion of all components of the cerebrospinal fluid circulation system in the brain, and atrophic changes in the cerebral cortex.
To make a diagnosis, it is also necessary to exclude some other diseases that occur with a similar clinical picture (such as tumors of the posterior cranial fossa, multiple sclerosis, hydrocephalus, vascular pathology of the brain, especially in the spinobasilar region. If, based on the clinical picture, it is possible to confirm the development of ataxia, then it is much more difficult to determine the type of disease (if there are no strictly specific symptoms).
Currently, there are several opinions regarding the treatment tactics for this pathology. Supporters of the first are of the opinion that ataxia is not susceptible to drug treatment. In this case, it is best to carry out maintenance therapy to slow the progression of the disease. The mandatory complex includes exercise therapy (vestibular training), as well as many methods of social, household and work rehabilitation.
Another theory involves the use of certain drugs, however, the treatment is purely symptomatic or stimulating. Injections of vitamins are prescribed, as well as their oral administration. As an element of such therapy, it is possible to prescribe anticonvulsants (if indicated). Treatment of spinocerebellar ataxia is also supported by certain physiotherapeutic procedures (for example, electrical stimulation).
! Despite the fact that many of the diseases described in this section are considered incurable, the Center for the Treatment of Rare Diseases in Milan is constantly looking for new methods. Thanks to gene therapy, it has been possible to achieve outstanding results and completely cure some rare syndromes.
Contact a consultant on the website or leave a request - this way you can find out what methods Italian doctors offer. Perhaps this disease has already been treated in Milan.
+7 (925) 50 254 50 – urgent treatment in Italy
REQUEST TO THE CLINIC
Diagnostics
First of all, they conduct a neurological examination of the patient, study the medical history, conduct an MRI and various molecular genetic tests and DNA diagnostics. At different stages of the development of the disease, the doctor identifies various disorders associated with neurology. This could be tremor, speech impairment, dysphagia, etc. Some forms of the disease are caused by the rapid development of visual impairment, which leads to complete blindness. The disease tends to progress. When examining the hereditary history, autosomal dominant inheritance from the father may be detected. MRI shows abnormalities in the cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum and basal ganglia. Cerebellar atrophy may also be observed. Molecular research and DNA diagnostics indicate an increased number of repeats in the patient’s genes.
Gene failure
This disease is hereditary and develops as a result of one or another genetic failure.
At the same time, it can manifest itself in two forms - with a violation of the stability and support of the body in space (static-locomotor ataxia with damage to the cerebellar vermis) or with damage to the cerebellar hemispheres and a violation of active movements performed by the limbs (dynamic form of cerebellar ataxia).
The disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. The first signs usually appear over the age of 30 .
Quite rarely, the clinic can develop earlier, and then it most often manifests itself in parallel with other neurological symptoms.
Thanks to the study of the genomic composition, it was proven that genes play a leading role in the development of spinocerebellar ataxias.
It has been proven that there are at least 13 specific genes responsible for the development of ataxia, and more specifically, a certain type of ataxia.
Each of these genes is located on a specific chromosome, and its damage as a result of the action of mutagens leads to the development of the disease.
There are currently 8 known types of the disorder. Spinocerebellar ataxia types 1-13 depend on damage to one specific gene.
The main role belongs to an increase in the number of CAG triplets (cytosine-adenine-guanine). Normally, this sequence of nucleotides encodes the formation of glutamine, an amino acid necessary for the formation of bonds between brain proteins.
Due to an increase in its quantity, protein chains are lengthened, as a result of which insoluble components begin to form, due to which the interaction between parts of the brain is disrupted and a certain number of nerve cells die, which contributes to the development of ataxia.
If we look at the substance of the cerebellum, we can see that its hemispheres have undergone degenerative processes (as well as the main components involved in conducting nerve impulses from the spinal cord to the cerebellum and back (for example, the olives)).
In parallel with this, demyelination of the nerve fibers is observed, which prevents the rapid propagation of the nerve impulse.
Article on the topic: Which sedatives for the nervous system are better and more effective?
Treatment
There is currently no effective treatment for this disease. The effectiveness of maintenance therapy has not yet been proven, but it is carried out to slow the progression of the disease. Thus, spinocerebellar ataxia involves treatment in the form of vitamin therapy and drugs that stimulate metabolism and metabolism in the nervous tissue. Patients are also prescribed nootropic drugs. Physical education also plays an important role. Doctors recommend that patients do a set of exercises to strengthen muscles and reduce balance problems. Massage sessions and electrical myostimulation are performed.
Is a cure possible?
At the moment, there are several approaches to implementing therapeutic measures for this disease.
Some researchers argue that medications are powerless against ataxia; the best effect will be provided by supportive therapeutic measures that slow down the disease. Complex treatment consists of physical therapy (vestibular training), with other social and household rehabilitation measures.
Others believe that some means should be used for symptomatic or stimulating treatment.
As a rule, vitamin preparations are used, which are administered by injection or taken orally. According to the indications, the attending physician will prescribe anticonvulsants.
It would not be superfluous to carry out physiotherapeutic procedures, for example, electrical stimulation or classical massage.
Forecast
As a rule, the prognosis for this disease is unfavorable, since the disease constantly progresses and leads to disability and then death. Therefore, the answer to the question of whether spinocerebellar ataxia is treatable will be negative. This hereditary disease is incurable. In some cases, the prognosis may not be so negative. This happens when the disease develops in old age and is treated in a timely manner, then a large number of symptoms may not appear. If the disease is discovered at a young age, the life expectancy of such patients will be short. Patients with the fifth and sixth types of the disease live a normal life a little longer, usually their life span does not change. With proper care and timely therapy, doctors manage to increase the life of patients by ten years. On average, people live with a disease such as spinocerebellar ataxia for about twenty years. Death is often caused by heart failure and infections.
Is the disease treatable?
There are several methods for treating spinocerebellar ataxia, and not all of them support the possibility of drug therapy. Some doctors are confident that the best way is supportive therapy using exercise therapy, as well as methods of social rehabilitation. Spinocerebellar disorders, according to this technology, can only be slowed down, but the patient cannot be completely relieved of it .
The second direction of therapy is the use of drugs to eliminate the symptoms of the disease, as well as medications that stimulate the body. This technology prescribes vitamins in various forms, as well as anticonvulsants if symptoms occur. Physiotherapeutic methods such as UHF and electrophoresis can be used, and the effectiveness of these methods is quite high.
Life expectancy upon diagnosis rarely exceeds 20 years. But if you start maintenance therapy in time, you can increase this figure by at least 5-7 years.
The worst prognosis awaits people whose pathology was discovered before the age of 20. The progression of the disease in this case is rapid - within 2-3 years. And people with spinocerebellar ataxia types 5 and 6 live longer, their recovery process is easier, and their symptoms are less severe.
Prevention
Preventive measures include medical and genetic counseling for parents with a history of such conditions. Genetic perinatal diagnostics are also performed. The doctor determines the risk of the disease occurring in direct relatives. The risk of developing pathology for healthy brothers and sisters, as well as children of the patient, is 50%. In turn, the children of these people have a 25% chance of inheriting the disease. All of these individuals are at risk and represent prime targets for counseling. The basis of preventive research is DNA diagnostics of individuals at risk for the presence of mutated genes.
Spinocerebellar ataxia in modern times is a disease that has no cure and leads to death over time. It is possible to prevent the development of the disease using special diagnostic methods, but it is impossible to prevent its development, since this disease is hereditary in nature and is caused by mutations of healthy genes. All this pushes modern medicine to develop research methods at the earliest stages of disease development, as well as to study the causes of mutations that are inherited from father to children.
The forecast is disappointing
As for the prognosis of the disease, patients with ataxia live on average about 15–20 years. With proper care, as well as timely diagnosis of the disease and the use of supportive therapy, it is possible to extend life by 7-10 years.
Patients with ataxia types 5 or 6 can live normally for a little longer (life span usually does not change much).
The worst prognosis is for those who develop the disease at an early age (usually, rapid progression is possible over a couple of years).
Considering that the disease is difficult to treat, it is necessary to improve existing diagnostic methods, as well as try to discover and implement new treatment tactics.