General information about thrombosis
Thrombosis
ー the process of intravital blood coagulation in the cavities of blood vessels and the heart. This process is also dangerous because part of the blood clot can break off and be carried by the bloodstream to other organs. For example, with thrombosis of the deep veins of the lower extremities, thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery or cerebral vessels often develops.
Treatment methods
Special means that also restore natural blood circulation are capable of dissolving blood clots in cerebral vessels. In most cases, the administration of tissue activator Plasminogen is prescribed. The drug often causes side symptoms in the form of severe hemorrhage.
To remove the stagnation, a catheter is inserted into a large vessel, through which a special medicine is supplied that dissolves the blood clot. In some cases, the tumor is removed surgically.
Before designating a treatment method, the person’s age and the exact location of the blood clot are determined. To restore the range of motion lost due to an acute disorder of cerebral circulation, sessions of therapeutic massage and physical education are prescribed.
In case of infectious thrombosis, antibiotic therapy is mandatory, which allows eliminating the primary focus.
It is unacceptable to treat cerebral thrombosis with folk remedies. In this case, not only does recovery slow down, but dangerous complications arise.
The consequences of a blood clot in the head can be unpredictable. These are not only severe complications that affect internal organs and systems, but also death. Oxygen starvation of the brain can cause:
- heart attack or stroke;
- paralysis;
- disorders of speech and cognitive functions (dementia, etc.);
- visual impairment.
In severe cases of brain disease, rapid death occurs, which is caused by embolism, when a blood clot bursts in a vessel of the head, thereby completely cutting off the blood supply to the organ. A “wandering” thrombus can break away from its localization in another area, for example, in the neck, reaching a cerebral vessel through the bloodstream, causing a stop in the flow of blood to the brain.
Classification of thrombosis
Depending on the location of the pathological process:
Arterial:
- arteries of the brain;
- hearts;
- intestines (mesenteric thrombosis);
- liver;
- femoral artery and others.
Venous (phlebothrombosis):
- veins of the lower limb;
- hemorrhoidal plexus;
- femoral and iliac veins;
- cavernous sinus (intracranial collector of venous blood);
- retinal veins.
According to the severity of the disease, acute
ー a sharp blockade of blood flow, and
a chronic
ー thrombus grows gradually, the tissues have time to adapt to this and compensate for pathological changes.
The effectiveness of MRI and the complete picture of the disease
In addition to visualizing the formation, MRI allows you to answer a number of questions:
- size and location of the blood clot;
- the presence of an embolus in the bloodstream;
- degree of patency of arteries and veins.
Another important point is that magnetic resonance imaging reveals some of the causes of pathologies. So, it will help to identify malignant formations in the surrounding tissues that put pressure on the blood vessels. If the patient has thrombophlebitis, then it is possible to analyze the characteristics of inflammation of the venous wall, such as thickening, changes in its structure, etc.
Unlike other diagnostic methods, magnetic resonance imaging provides a complete picture of the patient’s condition. The doctor sees small blood clots and simply blood clots that are located in any blood vessels, be it deep veins, the brain, internal organs or lower extremities. The three-dimensional image shows not only the problem areas, the degree of damage, but also, most importantly, the interaction with surrounding tissues.
Control examinations at intermediate stages of treatment
The examination is also important in light of the fact that when a tumor is detected that provokes the formation of a clot and disruption of blood flow, it is possible to assess the consequences of the development of the formation and predict the further course of the disease. The doctor sees foci of ischemia, as well as collaterals in the examined area. MRI is performed not only for making a primary diagnosis. Control examinations are prescribed to evaluate the effect of the chosen course of treatment and make decisions regarding further actions.
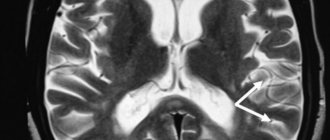
Visualization of blood clots on the tomograph screen
The image displayed on the tomograph screen differs from the image obtained with ultrasound or other research methods. The doctor receives layer-by-layer images of the area of the circulatory system of interest. Thanks to a cut-off pitch of 1 mm, even very small clots are clearly visible on the screen. The presence of an embolism is indicated by the fact that the signal becomes more intense, while in normal areas it returns evenly. Also, a visual image of a blood clot appears on the screen and has a different appearance.
Examination methods and view of blood clots on the screen
Examination of the circulatory system for problems with blood flow is carried out using two methods, which determine the type of clots:
- T1 weighted image;
- T2 weighted image.
Visually, the thrombus has a rounded shape; at the point of attachment to the vessel or with complete occlusion, it becomes denser. Its color depends on the examination method used. At T1 VI it has a neutral color, after which it becomes lighter. For the acute stage of a blood clot (the first 12 hours), T2 VI is used, in this case the clot is dark in color. But these are general characteristics, decoding is carried out by a qualified specialist, and without it it is impossible to begin a course of treatment.
Mechanism of development and causes of thrombosis
There are three pathological parts in the process of intravascular thrombus formation:
- Violation of the integrity of the vascular wall. When the internal lining of blood vessels is damaged, enzyme systems are activated, which trigger the process of blood clotting.
- Slowing blood flow. This occurs when the outflow is disrupted (compression of veins, varicose veins), prolonged absence of limb movement, or heart failure.
- Blood thickening. Caused by dehydration, autoimmune diseases, chemotherapy, and oral contraceptives.
A blood clot often forms against the background of such diseases:
- atherosclerosis;
- heart failure;
- aneurysms of blood vessels and heart;
- diabetes;
- obesity;
- bone fractures;
- hormonal disorders;
- oncological diseases.
Preventive recommendations
It is easier to prevent any disease than to quickly deal with its unpleasant consequences. This also applies to thrombosis of cerebral vessels. Preventive measures are as follows:
- normalization of physical activity: daily morning exercises, visiting the gym 2-3 times a week, warming up when sitting for a long time;
- daily walks in the fresh air;
- giving up bad habits, especially smoking and drinking alcohol;
- changing your diet, following a gentle diet;
- preventive use of medications that thin the blood and strengthen blood vessels.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that blood clots in the head are a dangerous condition that can lead to rapid death. Therefore, if alarming symptoms are detected, you should not self-medicate, but rather consult a doctor.
Thrombosis in children
Possible causes of blood clot formation in children:
- thrombophilia - congenital deficiency of anticoagulant blood factors;
- leukemia, other oncological diseases;
- cutaneous fulminant purpura, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome (develops with severe intoxication, inflammatory diseases: pancreatitis, peritonitis, etc.);
- the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies, lupus anticoagulant, and other autoantibodies (antibodies to one’s own cells).
Episodes of blood clots in a child should prompt a serious examination to determine the cause.
How is the disease diagnosed?
Only a qualified doctor can determine and make the correct diagnosis. He will send you for appropriate examination.
Thus, diagnostic procedures include cerebral Doppler ultrasound. Also in other cases, a specialist may prescribe rheoencephalography and nuclear magnetic resonance. Agniography is also a good examination that can confirm or refute the diagnosis.
The doctor determines which of the listed procedures the patient should undergo. After the examination, appropriate treatment is prescribed. In this case, you should not turn to traditional medicine, since the disease is very dangerous and threatens human health.
Risk factors for thrombosis
The following factors increase the likelihood of developing the disease:
- age over 50 years;
- obesity;
- smoking, alcoholism, drug addiction;
- poor nutrition;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- injuries;
- the need for frequent intravenous injections and procedures associated with violation of the integrity of blood vessels (blood sampling, hemodialysis, installation of a venous catheter) increases the risk of developing phlebitis and inflammation of the venous wall.
Causes of blood clots in the blood vessels of the brain
The formation of a blood clot in the vessels and venous sinuses of the brain is facilitated by three factors: a violation of the integrity of the inner lining of a vein or artery, a slowdown in blood flow, and a disruption in the functioning of the blood coagulation system.
The following conditions increase the risk of illness:
- hypertension;
- pathology of the cardiovascular system;
- central nervous system infections;
- infectious pathology of the middle ear, sinuses (the main cause of sigmoid sinus thrombosis);
- diabetes mellitus and other pathologies of the endocrine system;
- anemia;
- autoimmune diseases;
- frequent stress;
- atherosclerosis (often causes stenosis and thrombosis of cerebral arteries);
- taking oral contraceptives;
- excess weight;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- poor nutrition;
- skull injuries, hematomas.
Symptoms of thrombosis
The clinical manifestations of this pathology vary depending on the location.
Symptoms of venous thrombosis
When a vein is blocked, the outflow of blood is hampered, so the tissues beyond the blockage swell and turn blue. The waste products of cells accumulate, therefore tissue intoxication develops, this is accompanied by pain, impaired sensitivity (the sensation of “crawling goosebumps”). If you do not intervene in time, the tissues begin to die.
Symptoms of venous thrombosis of the lower extremities:
- swelling of the leg, a sharp increase in size, cyanosis;
- cramps of the calf muscles;
- constant pain in the leg, which intensifies when walking;
- increased venous pattern on the thigh.
Cavernous sinus thrombosis:
The dura mater contains channels into which venous blood from the brain drains. Blockage of one of these sinuses, the cavernous sinus, is dangerous because several cranial nerves and the internal carotid artery pass through it. The most common causes of cavernous sinus thrombus formation are inflammatory diseases of the nose, sinuses, facial skin and scalp. Signs:
- headache;
- decreased visual acuity, double vision;
- confusion;
- heat, fever;
- swelling of the eyelids and periocular area;
- pain in the neck when turning or tilting the head;
- impaired facial skin sensitivity.
Among the consequences of such thrombosis: stroke, loss of vision, coma.
Hemorrhoidal thrombosis
Develops against the background of hemorrhoids. Chronic constipation, physical stress, pregnancy and childbirth, and alcohol abuse contribute to it. Signs:
- pain, burning and itching in the anal sphincter area;
- discharge of blood with feces and regardless of the act of defecation;
- prolapse of hemorrhoids.
Retinal vascular thrombosis
The pathology is a typical complication of diabetes mellitus and hypertension, but can also develop for other reasons. Symptoms:
- deterioration of vision, up to complete loss (usually one-sided);
- the appearance of spots, mesh, veils before the eyes.
Symptoms of arterial thrombosis
Blockage of the artery leads to oxygen and energy starvation of tissues, which quickly leads to their death. Arterial forms of the disease are often acute.
Thrombosis of the cerebral arteries
This process leads to necrosis of the area of the brain that the affected artery supplies blood to - ischemic stroke. Signs:
- hemiparesis ー lack of movement in the right or left half of the body (opposite affected area);
- asymmetry of the smile - one corner of the mouth is lowered, does not take part in conversation and smile;
- unclear speech;
- when the patient sticks out his tongue, it deviates to the side.
Thrombosis of the coronary arteries of the heart
Partial blockage of these vessels leads to attacks of angina pain, complete blockage leads to myocardial infarction. Symptoms:
- pressing, burning pain behind the sternum, radiating to the left shoulder blade, arm, shoulder, half of the face and neck;
- dyspnea;
- with angina pectoris, rest and nitroglycerin help, with a heart attack there is no improvement, urgent medical attention is needed.
Pulmonary artery thrombosis
It is a complication of thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities, endocarditis, myocardial infarction. It develops rapidly and has a high mortality rate. Signs:
- sharp stabbing pain in the chest;
- swelling of the veins of the neck;
- shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air;
- hemoptysis;
- increased heart rate.
Hepatic artery thrombosis
Death (infarction) of liver tissue is a complication of endocarditis, myocardial infarction or liver transplantation and manifests itself as follows:
- severe pain under the right rib;
- nausea, vomiting, bitterness in the mouth;
- yellowness of the skin and whites of the eyes.
Femoral artery thrombosis
This form of pathology is manifested by pain when walking, coldness, and paleness of the limb. The pulse in the popliteal fossa and on the foot is palpable weakly or not detected at all.
Manifestations
A blood clot in the brain can manifest itself in different ways, and its symptoms appear gradually. The main sign that needs to be paid attention to is confusion. A person stops responding to external stimuli, he becomes sleepy, but is conscious.
Signs of the disease:
- headache;
- weakness, paralysis of part of the body;
- impaired coordination and speech;
- fainting.
The disease can occur in all ages, both in the elderly and in infants. However, it is not always possible to notice it with the naked eye; most often it is detected during a diagnostic examination of the patient.
Diagnosis and treatment of thrombosis in Medical
Specialists from the Paracelsus Medical Center will help in diagnosing and eliminating this pathology, provide support during the rehabilitation period, and give recommendations for further prevention.
Our center uses expert-class equipment from leading global manufacturers for diagnosis and treatment. The consultation is conducted by practicing phlebologist surgeons.
On the basis of "Operating Room No. 1" phlebological operations are performed for venous disease. The key advantage of the Paracelsus Medical Center network is highly qualified professional surgeons with extensive practical experience.
Drug treatment
The basis of drug therapy is anticoagulants (thin the blood, prevent the growth of a blood clot), fibrinolytics and thrombolytics (dissolve existing clots), antiatherosclerotic drugs (lower cholesterol levels). If necessary, analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, cardiotonic drugs, vitamins, minerals, etc. may be needed as symptomatic therapy.
Surgery
There are such methods of surgical treatment of the disease:
- thrombectomy ー removal of a blood clot;
- stenting (expansion using a frame) and shunting (creating a bypass path for blood flow) for atherosclerotic artery disease;
- arteriovenous shunting.
If the thrombus cannot be removed, a vena cava filter can be installed - the device is placed in the vein above the level of blockage to prevent it from moving and closing the lumen of the vessels of vital organs.
Complications and prognosis
If thrombosis is diagnosed late, complications may develop. Among them:
- hemorrhagic stroke;
- cerebral infarction caused by thrombosis of cerebral arteries;
- cerebral edema;
- hypopituitarism - a decrease or cessation of production of pituitary hormones, which can affect the functioning of all organs and systems;
- visual impairment;
- drooping eyelids;
- blood poisoning;
- formation of cysts;
- nervous disorders;
- anisocoria;
- inflammatory processes in the kidneys;
- embolism.
If thrombosis causes ischemic injury or hemorrhagic infiltration, it can be fatal. There are factors that worsen the prognosis
- elderly age;
- being male;
- convulsions;
- paralysis of half the body;
- coma;
- high intracranial pressure.
You can reduce the risk of death and the development of irreversible consequences by contacting a doctor when the first symptoms of the disease appear for diagnosis and treatment.