Arachnoid cyst of the PCF - what is it?
Arachnoid cyst of the posterior cranial fossa is a type of cerebrospinal fluid neoplasm of the brain. The peculiarity of the posterior cranial fossa cyst is that it develops into oncology less often than other types.
The danger of an arachnoid cyst is the increase in unpleasant neurological symptoms and a negative effect on the functions of the brain and sensory organs. There is a possibility of death from cyst rupture or its degeneration into oncology.
Factors influencing the development of arachnoid cysts
The disease can develop as a complication of previously suffered serious illnesses. In particular, the reasons for the development of a liquor cyst in the brain can be:
- Inflammatory diseases of the brain (meningitis, encephalitis);
- infectious diseases (chickenpox, influenza, measles, cytomegavirus, purulent inflammation in the head);
- suffered traumatic brain injuries;
- surgical operations on the skull;
- Marfan syndrome (genetically determined connective tissue pathology);
- congenital pathologies of nerve fibers.
Factors influencing the occurrence of cysts in the brain:
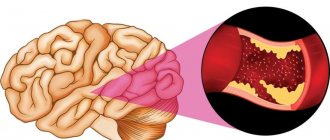
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels that impair blood circulation;
- cerebral hemorrhages;
- diabetes;
- repeated head injuries;
- hereditary predisposition;
- pathologies of intrauterine development of the fetus in the first trimester of pregnancy (with a congenital cyst);
- use of drugs, alcohol, poisoning;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- unfavorable living conditions and work that greatly weaken the body;
- radiation;
- poor living conditions of a pregnant woman (poor nutrition, stress, emotional overload, lack of rest);
- a pregnant woman taking medications, smoking, drinking alcohol;
- difficult childbirth with accompanying complications (craniocerebral injuries of the newborn).
The combination of these factors increases the negative impact. With a frozen cyst, any of them can cause tumor growth.
Differential diagnosis
- expansion of subarachnoid spaces (for example, mega cisterna magna)
- epidermoid cysts often have a more heterogeneous signal on FLAIR
- pronounced restriction of diffusion
- have a more lobed structure
- cover adjacent arteries and cranial nerves
- The MR signal is different from the cerebrospinal fluid signal
- pilocytic astrocytoma
- neuroenteric cyst
- usually multiple when localized in the subarachnoid spaces
Types of arachnoid cysts
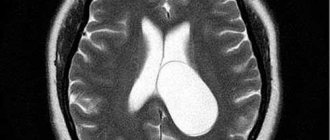
A posterior fossa cyst (PCF) is a cavity with compacted walls with liquid or thick contents. Medicine considers two types of such neoplasms, dividing them based on their origin:
- Congenital – formed before the birth of a person, i.e. in utero;
- Acquired – occurs in a person after birth as a result of exposure to unfavorable factors.
The cyst can be simple (consist exclusively of cells of the arachnoid meninges) or complex (also include elements of other tissues).
In addition, all arachnoid cysts are divided into several types according to location.
Conventional arachnoid and retrocerebellar
A rentrocerebellar cyst is not located on the surface of the brain membrane, like a regular arachnoid cyst, but is located deep in the gray matter behind the cerebellum.
A common cyst is often localized in the gap between the arms of the arachnoid membrane, where liquor fluid can accumulate. A retrocerebellar neoplasm of this kind destroys the cells of the deep layers of the brain, growing in their place.
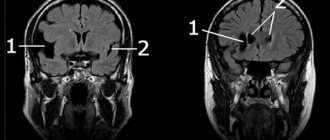
Temporal region cyst
A cyst in the temporal region can form on both the right and left. The symptoms in each of these cases will be slightly different. The reason is the focus of the lesion on different parts of the brain that control various functions in the body.
Posterior fossa cyst
The location in the posterior cranial fossa has its own characteristics. This is where the brain smoothly transitions into the spinal cord. Any neoplasm here can disrupt the connection during the transmission of nerve impulses from the brain to the spinal cord and vice versa.
In addition to the cranial nerves that conduct impulses to the sensory organs, large blood vessels lie here, and there is also the cerebellum, which is responsible for balance and coordination of movements.
This is a very dangerous type of disease, which can cause problems with breathing, heart function, and the ability to move normally. With rapid growth of the PCF cyst, a coma can occur with a fatal outcome.
Symptoms of the disease
Manifestations of the disease depend on the size of the cyst. If they are small, up to 2-3 cm in diameter, then the disease may be asymptomatic.
However, as the tumor grows, symptoms will appear in one way or another, the main ones being constant headaches and nausea with the urge to vomit.
Other manifestations of the disease:
- Loss of coordination of movements, unsteadiness of gait, difficulty maintaining balance;
- periodic paralysis of the limbs;
- changes in a person’s mental state;
- as the cyst grows, hallucinations occur;
- the appearance of seizures.
If a cerebrospinal fluid cyst has formed in a child during intrauterine development, then its first signs are restlessness, multiple regurgitations, difficulty moving arms and legs, lack of response to an adult’s voice, and bright objects.
The more fluid accumulates in the cavity, the worse the patient feels. If the volume of cerebrospinal fluid is up to 30 ml, the cyst is considered small; it manifests itself as a change in the local functions of the brain area. With a volume of 30 to 70 ml it is considered medium; symptoms increase and appear in a more distant period. If more than 70 ml of cerebrospinal fluid accumulates, it is a large cyst that puts pressure on the brain tissue and poses a danger to the patient’s life.
Features of tumor symptoms in men and women
The male part of the population is more often susceptible to arachnoiditis. According to world statistics, this disease occurs 4 times more often in men than in women. So far medicine has not been able to answer the question of why this happens.
In addition, affected men experience faster growth of the cyst, as well as a more frequent spread of growth to adjacent tissues. In women, the cyst causes fewer complications and remains in a dormant stage longer.
If a cyst is detected in a man of military age, he is given a deferment from military service and sent for additional examination and treatment. Further actions depend on their results.
People are not immediately drafted into the armed forces if intracranial hypertension is detected and symptoms of the disease appear. This also applies to single disorders associated with coordination, vision, hearing, etc.
General
Arachnoid cyst of the brain in the fetus is often associated with other pathologies. These are mainly Marfan syndrome and dysgenesis or agenesis of the corpus callosum.
According to the structure, arachnoid cysts of the brain in adults and children are:
- Simple.
- Complex.
A simple formation inside is lined with cells of the arachnoid mater. Such a volumetric process is prone to the production of cerebrospinal fluid. A complex disease consists of a variety of tissues, most often the structure includes glial cells of the brain. This classification is not used in practical neurology. However, data on the histological structure are taken into account when making a diagnosis according to the international classification of diseases.
According to the dynamics of development there are:
- Progressive.
- Frozen.
Symptoms of an arachnoid cyst increase rapidly with the first option. The negative dynamics are explained by an increase in the diameter of the tumor, due to which the formation compresses neighboring tissues and causes the clinical picture of neurological disorders. Frozen cysts have positive dynamics: they do not increase in size and proceed secretly. This classification is used in practical neurology: the choice of treatment depends on the type of dynamics.
Life expectancy depends on dynamics. So, with a frozen cyst, a person can live his whole life and die a natural death, because the formation has not reached a critical size. Due to the lack of a clinical picture, such people usually do not know that they have a massive process in their head.
Progressive cysts reduce a person’s quality of life. The cyst is dangerous due to complications, for example, acute occlusive hydrocephalus, due to which the stem sections of the brain are displaced and the person dies from a violation of the vital functions of the medulla oblongata (breathing and the functioning of the cardiovascular system).
Conscription into the army depends on the severity of the clinical picture. Thus, a young man is completely exempt from service in the case when the clinical picture includes hypertensive syndrome and severe neurological disorders. A deferment of 6 months or a year is given to a young man if his clinical picture reveals moderate neurological disorders and there is no syndrome of increased intracranial pressure.
Diagnostics for identifying an arachnoid cyst
Detection of the disease should begin with a visit to a neurologist who will conduct proper examinations. It is important to differentiate a PCF cyst from diseases with similar neurological manifestations: various types of tumors, hemorrhage, hematoma, abscess and others.
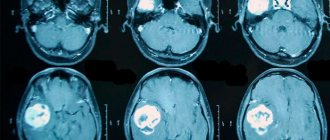
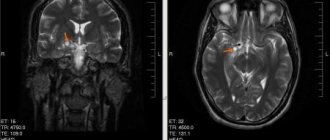
MRI with contrast enhancement of blood vessels is rightfully considered the most accurate method for diagnosing tumors in the brain. It allows you to establish not only the presence of a neoplasm, but also its type and exact location. There is also a variation of this method – multislice computed tomography.
Ultrasound of the brain, EEG, and reencephalography are also used. For congenital arachnoid cysts, examination by a neurologist and psychiatrist is recommended, even if the child has no visible mental abnormalities. This is necessary to study the nature of neural connections affecting higher nervous activity.
Laboratory blood tests are performed for coagulation, cholesterol levels, autoimmune diseases, and neuroinfections.
3.Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of cysts includes their detection and identification of the factors that caused their occurrence. Often a cyst is discovered by chance, especially if its presence does not cause any clinical symptoms. Only with a characteristic symptom complex can a doctor suspect the presence of an arachnoid cyst and prescribe an appropriate clarifying examination. To diagnose cysts, the following are used:
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- Ultrasound examination.
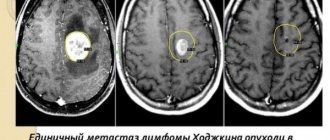
Contrast agents are used to differentiate cysts from cancerous formations
, which do not accumulate in the fluid of the cyst, but are visible only in the tumor areas of the brain.
Research aimed at identifying the causes of cysts can be very diverse. A conversation with the patient allows us to narrow down the range of possible factors that served as the basis for the formation of an arachnoid cyst. Sometimes, seemingly unrelated symptoms indicate possible causes of cysts. For example, heart rhythm disturbances, blood clots, and cholesterol plaques can reduce the blood supply to brain tissue, which leads to their partial death with the formation of capsules filled with liquid.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Treatment of cerebrospinal fluid cyst
If the tumor is small and there are no symptoms, the patient is monitored by a neurologist. At least once a year, a computed tomography scan of the brain is performed to monitor the further progression of the disease. The doctor may prescribe drugs that improve vascular function, diuretics, and analgesics.
However, more radical treatment in the form of surgery is often prescribed. Usually the indications for it are:
- Rapid increase in cyst size;
- severe increase in intracranial pressure;
- epileptic seizures;
- progression of the disease due to compression of brain tissue;
- ineffectiveness of previously prescribed medications.
Surgical intervention for PCF cyst can be performed in three ways:
- Shunting (pumping out the contents of the cyst into the abdominal cavity through a special shunt);
- endoscopy (pumping out cerebrospinal fluid from the cyst through a hole in the cranial bone, after which the empty cavity is connected to the cerebral ventricle or membrane);
- excision of the cyst (if there is a threat of cyst rupture or hemorrhage).
The third type of operation requires the longest recovery for the patient.
Classification
The arachnoid cyst, located in the temporal lobe on the left side, can be of two types. Pathology is classified depending on the reason for which it appeared. The primary nature is determined when the cyst is formed during intrauterine development .
For example, it can occur if the mother smoked, drank alcohol and took illegal medications during pregnancy. Also, the primary pathology may be due to a difficult birth, or trauma received during birth.
The secondary type appears due to various pathologies present in the body. For example, it can be caused by various viruses and infections that affect the brain. In a situation where it was the pathology that led to the appearance of the cyst, the neoplasm will be formed from scar tissue. If there is another reason for the occurrence, then the tumor consists of arachnoid material.
Doctors divide cysts into complex and simple . In the first case, the neoplasm is formed from several types of tissue. In a simple type of pathology, the tumor consists of cerebrospinal fluid. It is important to determine the specific type in order to make it easier to prescribe further treatment.
Possible consequences and complications
After a radical intervention with excision of the cyst, some neurological consequences may remain. This depends on the condition of the patient’s body, concomitant diseases, and compliance with medical recommendations.
The most severe consequences (disability, blindness, deafness, intractable headaches, rupture with effusion of cerebrospinal fluid, death) are possible in case of late detection of a large cyst.
An arachnoid cyst is a type of benign tumor. Practice shows that it can degenerate into cancer, but in fact there are not many such cases.
Prognosis and prevention for patients
The best prevention is a healthy lifestyle, strengthening the immune system, minimizing stress, and regular medical examinations for timely detection and treatment of diseases. This is especially true for expectant mothers.
But if a cyst is still detected, there is no need to panic. It is necessary to see a doctor and follow his recommendations, and get more rest. In some patients, a recurrence of the cyst occurs after treatment. In case of relapse of the disease, regular monitoring of cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and treatment of existing diseases is necessary.
With timely treatment, however, the prognosis is good. Many patients recover completely and say goodbye to the cyst forever.