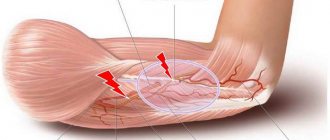
Primary pinched nerve in the hip joint gives an acute clinical picture: a person experiences shooting pain in the outer surface of the thigh, from the greater trochanter to the knee joint. Secondary neurological signs gradually appear. This is a decrease in muscle strength and skin sensitivity, the appearance of paresthesia, etc.
Acute pain from a pinched nerve in the hip joint, even without medical assistance, gradually subsides. This ethos is due to the fact that the trophism of the nerve fiber is disrupted and it atrophies. The brain does not receive signals about trouble and the person does not experience unpleasant sensations. Unfortunately, as the pain goes away, other functions also go away. The leg begins to weaken, lose muscle mass, physiological vascular tone is lost and a lot of complications develop. Most often, the patient experiences paresis of the muscles of the lateral thigh. He cannot fully walk or bend his leg. It will be very difficult to restore these functions in the future. Therefore, it is important to seek medical help promptly.
To understand the mechanism of nerve pinching in the hip joint, you need to know the structural and physiological features of this part of the musculoskeletal system of the human body. The hip joint is formed by the acetabulum of the ilium, which fits into the pelvic ring. It is attached to the spine using the iliosacral joint. The femur has a head and a neck. The femoral head and acetabulum are covered with a layer of synovial cartilage tissue. It ensures uniform distribution of shock-absorbing and mechanical loads during walking and running.
There are two major nerves running near the hip joint. Higher up, the sciatic nerve emerges from the tunnel opening of the piriformis muscle, which then descends along the back of the thigh to the knee joint. In the popliteal fossa there is a bifurcation point at which the sciatic nerve splits into the tibial and peroneal branches. The femoral nerve passes directly in the projection of the hip joint. It is formed by branches of the L2-L3 radicular nerves. Next to it is the inguinal ligament, which ensures the stability of the pelvic bones.
Pinching often affects the femoral nerve, less often the sciatic nerve is affected. But clinical cases are not uncommon when, due to serious pathology of the lumbosacral spine, both nerves are simultaneously pinched. Only an experienced vertebrologist or neurologist can make an accurate diagnosis in such a situation. Therefore, if characteristic pain appears on the outer or back surface of the thigh, it is necessary to consult a specialist as soon as possible. Only an early start of treatment guarantees complete restoration of innervation and all functions of the lower limb.
In Moscow, you can make an initial free appointment with a neurologist or vertebrologist at our manual therapy clinic. Experienced doctors see patients here. They will be able to make a preliminary diagnosis during the first consultation after a manual examination. Each patient is given individual recommendations regarding the diagnosis and treatment of identified pathological changes in the tissues of the hip joint. To make an appointment, fill out the special form at the bottom of the page; you can also call the administrator and agree on a time convenient for the visit to see the doctor.
Definition of disease
Pelvic neuralgia is a pinched nerve in the hip joint .
In this condition, the nerve that is located between the bones, ligaments and tendons is pinched, which causes severe pain. Sometimes the pain lasts only a few minutes, and sometimes it drags on for 2-3 days. Pathology develops in both men and women . The danger is that this disease can disguise other ailments. Therefore, the treatment is carried out incorrectly.
Disease code according to ICD-10: M79.2. Pelvic neuralgia also includes anorectal neuralgia.
This is an inflammation of the nerves in the coccyx and anus, as well as in the perineum. The inflammatory process is accompanied by acute pain. Also a type of pelvic neuralgia is pudendal neuralgia.
Diagnosis of the disease
Quite often, pelvic neuralgia can be confused with other diseases of the musculoskeletal system due to the similarity of symptoms. Therefore, this condition requires complex diagnostics.
First of all, the doctor interviews the patient and thoroughly examines him. However, the data obtained will not be enough to establish the cause of the disease and select the optimal treatment regimen. For this purpose the following is prescribed:
- general and biochemical blood tests, urine analysis;
- radiography of the pelvic bones and spine;
- Ultrasound of the hip joint;
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- electromyography;
- diagnosis of nerve conduction using electrodes.
Read also…. Treatment of back osteochondrosis
Etiology
Pain in the area of the inflamed nerve may decrease and become stronger. All this depends on the degree of load.
Possible causes of pelvic neuralgia:
- callus, the development of which leads to joint injury;
- acquired diseases of joints and ligaments (this includes various types of arthrosis and arthritis);
- strong physical activity;
- narrowing of the opening in the tubules of the spinal cord and vertebral hernia;
- bone tuberculosis, which leads to damage to bone tissue in the pelvic area;
- severe illnesses of the circulatory system, including cancer;
- injury to bone and joint tissue.
In women during pregnancy, the uterus increases in size, because of this it puts pressure on the sacral plexus, from which the nerve endings emerge. Such processes lead to pinched nerves and severe pain. In some cases, the symptoms of the disease appear after childbirth - this occurs with malpresentation of the fetus or difficult labor (more about neuralgia during pregnancy in this article).
Also, the causes of pelvic neuralgia include excess weight, diabetes of any type, and in some cases, shingles if it is localized in the lumbar region. In children, injuries most often lead to the development of pelvic neuralgia.
What are the symptoms of a pinched nerve in the hip joint?
The hip joint is innervated by several nerves: sciatic, femoral, external cutaneous, obturator, superior and inferior gluteal. Depending on which one is clamped, the symptoms will vary slightly. Naturally, the main sign of a pinched nerve is severe pain. In some cases, the disease may be accompanied by fever, weakness, sweating, chills and other signs of an acute inflammatory process.
Read also…. Sacrum: anatomical structure, functions, injuries and typical diseases that affect this bone
Symptoms of a pinched femoral nerve are:
- severe pain localized in the hip joint and spreading to the lumbar region and the anterior inner surface of the thigh and lower leg;
- the pain intensifies when pressing on the inguinal ligament;
- there is a violation of knee flexion;
- with prolonged infringement, atrophic changes in the quadriceps femoris muscle, numbness of the skin, and a sensation of “pins and needles” occur.
When the external cutaneous nerve is pinched, the following are typical:
- numb areas of skin on the outer thigh;
- pain is localized on the outer surface of the thigh;
- the pain is accompanied by the appearance of “goosebumps”, burning, a feeling of cold, tingling of the skin of the thigh;
- there is a disruption in the functioning of the skin, manifested by increased dryness, increased sweating, thinning or hair loss;
- pain decreases when you are in a position with bent knees;
- intermittent claudication;
- hypertension and hyperarthria;
- limitation of mobility due to pain.
Obturator nerve entrapment is characterized by:
- pain manifests itself on the medial surface of the thigh;
- pain affects the perineum and rectum;
- increased pain occurs in a sitting position, as well as when trying to move the leg to the side;
- difficulty keeping the body upright due to instability;
- spasms and convulsions that occur while walking;
- limited mobility in the hip joint reduces the amplitude of the step.
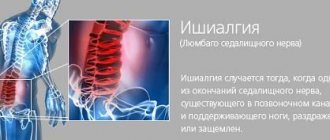
Pinching of the sciatic nerve is accompanied by:
- suddenly arising and disappearing sharp, burning pains;
- soreness along the entire leg on the affected side;
- difficulty bending the knee;
- numbness of the lower leg, buttocks and thighs;
- inability to move your toes.
When the superior and inferior gluteal nerves are pinched, the following are typical:
- pain in the pelvic region, back, leg;
- impaired ability to abduct the leg and extend the knee;
- difficulty moving and holding the body in an upright position.
Clinical picture
Many people confuse this type of neuralgia with a pinched sciatic nerve. The symptoms are indeed similar, the difference lies in the location. Pelvic neuralgia is most often caused by pinching of the hip nerve.
This process is characterized by severe pain while walking and running . The disease also manifests itself as burning and numbness of the lower extremities. If the external thigh nerve is pinched, the pain syndrome will be present at rest, even during sleep.
A peculiarity of pain with pelvic neuralgia is the fact that it does not have a specific localization - unpleasant sensations can appear in different places. Sometimes there is no pain at all, but there is a burning sensation, numbness of the affected area, and limited movement.
Symptoms in men
In addition to all the above signs of the disease, men experience pain during urination and ejaculation , a burning sensation and pain in the urethra, as well as blood in the seminal fluid. These symptoms are characteristic of other ailments, so diagnosis must be carried out especially carefully.
Symptoms in women
Women may confuse the signs of pelvic neuralgia with genital infections, PMS and dysmenorrhea. Characteristic symptoms of the disease can be considered:
- disrupted menstrual cycle;
- pathological discharge;
- papillomatosis;
- infertility.
Signs of anorectal pathology
Additional signs of rectal neuralgia are pain in the anus, pale skin, and increased sweating. Sometimes they are accompanied by heaviness in the lower abdomen and a burning sensation in the tailbone.
Pudendal
Symptoms of this form of neuralgia are constant pain in the pelvic area, which is aching in nature.
Additional signs also appear:
- burning, especially when sitting;
- increased sensitivity of the skin in the genital area;
- sensation of a foreign body in the genitals;
- urination disorders (for some they occur involuntarily, while for others, on the contrary, with acute pain).
Patient complaints
Patients complain of pain in the perineum and in the coccyx area . At the same time, discomfort during walking increases, which is why the gait may change - it becomes shuffling, patients move in small steps.
Find out more about the types of neuralgia and their symptoms:
- brachial and occipital nerve;
- glossopharyngeal and pterygopalatine node;
- external cutaneous nerve of the thigh and postherpetic.
Causes of pinching
Pinched nerve of the pelvic femur can be caused by the following main reasons:
- Inflammation of the piriformis muscle, which occurs under increased stress - long running or walking, jumping - in people who are not accustomed to sports, or during a long stay in an uncomfortable position or during hypothermia - the sciatic nerve is pinched by a spasm of the piriformis muscle;
- Osteochondrosis of the lumbar region is a degenerative process that causes destruction of bone and cartilage tissue with protrusion of discs, as well as hernias that compress the nerve roots at their exit from the spinal cord;
- The nerve is also pinched by tumor formations.
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar region
The formation of pinched sciatic nerves is influenced by the following provoking factors:
- Pathologies of bones and joint diseases.
- Sedentary lifestyle and excess weight.
- Severe colds.
- Inflammation and injury to the hip joint or organs in the area.
- Hereditary predisposition, which largely determines the location of the ligamentous apparatus and neurovascular bundles, as well as congenital joint defects, such as hip dysplasia.
It is worth highlighting separately such a cause of pinched sciatic nerve as pregnancy. Pinching of the sciatic nerve can be caused by an increased load on the body of the expectant mother, caused by an enlarging uterus, which puts pressure on nerve bundles and many organs.
Pregnancy also increases the stress on the spine, which is another factor in the occurrence of nerve entrapment. This can also happen when the pelvic bones diverge after childbirth.
Diagnostics
Confusing symptoms with “female” and “male” diseases, patients mistakenly go to see a gynecologist or urologist, who do not see any abnormalities and cannot make any diagnosis.
You cannot wait until the pain goes away on its own, as the discomfort will only intensify.
Experienced gynecologists and urologists, seeing the picture of the disease, immediately refer their patients to a neurologist. Since the most important symptom is pain, the doctor must study all its characteristics: duration, nature, frequency, reasons causing it. After this, the neurologist prescribes additional therapy to determine the inflamed nerve.
The main types of diagnostics are:
- radiography;
- MRI;
- electroneuromyography;
- Ultrasound with dopleography.
Treatment of pelvic neuralgia
Treatment of pelvic neuralgia in women and men should begin by eliminating the potential cause of the development of this disease. For example, if damage to the nerve fiber is observed at the level of the roots during the development of degenerative dystrophic disease of the intervertebral discs, then several manual traction procedures are first recommended. This allows you to eliminate compression from the root nerves and relieve the patient from pain. Then a course of treatment is developed aimed at restoring the structure of damaged cartilage tissue. This is often enough to completely restore all pelvic nerves.
If the disease is caused by biochemical changes and metabolic disorders, including a total deficiency of microelements and vitamins, then it is necessary to work with this cause. The doctor will develop a complete diet for the patient and give recommendations on the selection of vitamin and mineral complexes. In parallel, an individual course of treatment will be carried out aimed at restoring the trophism of the nerve fiber that has undergone degeneration.
A course of treatment is developed in a similar way for other types of lesions. In particular, treatment of pelvic neuralgia caused by inflammatory processes in the pelvic cavity begins with relief of the underlying disease. This may require consultation with a gynecologist or urologist. Once the inflammatory swelling is eliminated, a chiropractor or neurologist will be able to develop an effective course for restoring innervation. This helps prevent future problems with innervation and blood supply.
If you need safe and effective treatment for pelvic neuralgia, we invite you to a free appointment with a neurologist at our manual therapy clinic. You can sign up right now. To do this, fill out the doctor appointment form located further on the page. Our administrator will contact you and agree on a convenient time for the visit.
Treatment
Drug therapy
Medicines are used to relieve pain . Usually a painful attack lasts 2-5 minutes. But because of its intensity, it seems to the patient that its duration is much longer.
If the pain is caused by the pressure of muscle tissue on the nerve endings, then it is advisable to take antispasmodics. NSAIDs - this group of drugs is used to relieve swelling, inflammation and pain. The course of treatment is short - 3-5 days.
Medicines with a diuretic effect are prescribed to relieve swelling. Reparants - prescribed to improve and accelerate the recovery of nerve fibers . Even after pain relief, you need to consult a doctor and find out its cause.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are necessary to warm up the joints and tendons. The most commonly used procedures are:
- electro- and phonophoresis;
- Magnetotherapy;
- UHF;
- hot baths;
- wraps;
- splinting;
- applications.
Massage is a separate item of physiotherapy.
It is most often prescribed to treat neuralgia. The procedure is aimed at relieving pinching and reducing the inflammatory process. However, please note that all procedures should be carried out only under the supervision of the attending doctor.
Gymnastics for inflammation of the pudendal (genital) nerve
Gymnastics is aimed at improving blood flow in the inflamed area. Start with a regular walk. Often in the first days of walking you may feel pain, but you need to overcome it and walk for at least 10-15 minutes at a slow pace.
As soon as the patient's condition improves, you need to move on to gymnastics. Basic exercises:
- Lie on the floor (or other hard surface), exhale, bend your knees and clasp them with your hands, while inhaling, rise slightly and touch your forehead to your knees.
Stay in this position for a few minutes, then relax, straighten up completely and rest for a minute. - Slowly sit on your heels, straighten your arms forward and stretch towards the floor, keeping your back straight.
- Lie on the floor, put your legs on the wall and bend them at a right angle, slightly lift your buttocks off the floor (literally a few centimeters) and stay in this position for 10 minutes.
- Stand straight, but at the same time bend your legs slightly at the knees, straighten your back and tilt forward a few degrees, rest your palms on your thighs and begin to press - this way the lumbar vertebrae are stretched.
- Sit on the floor, straighten your legs completely, put your hands behind your head and fasten them with a lock, slowly lie on your back and begin to raise your legs as high as possible and at the same time spread them to the sides, stay in this position for 2 minutes.
Radical methods
Doctors try to treat the disease using conservative methods. However, in some cases it is necessary to resort to surgery, which most often involves destroying the affected nerve or neutralizing the pressure on the nerve.
Radical methods are used in the following cases:
- lack of positive results after conservative treatment;
- rapid progression of the disease;
- the presence of serious motor and sensory contractures;
- the appearance of tumors.
Folk recipes
Effective recipes:
- Take a medium-sized onion, peel, finely chop and boil in a glass of milk for 5 minutes. Strain the finished broth and drink a glass of milk three times. The course of treatment is seven days.
- Take 50 g of thyme and boil it in a glass of water. Cool the broth and soak a gauze bandage in it. Apply to the affected area and insulate. Leave the compress overnight.
- Grate 100 g of horseradish on a fine grater, squeeze out the juice, soak gauze in the juice and apply again to the inflamed area. Insulate and leave for at least 5-6 hours, preferably overnight.
This method of treatment cannot be independent; it goes in combination with traditional therapy. Before using any folk remedy for neuralgia, you should consult a doctor.
Diagnosis and treatment
Pain is often the only manifestation of pelvic neuralgia, which is why patients try to cope with it themselves with the help of analgesics and warming.
These include x-rays, MRI, ultrasound with examination of blood vessels, electroneuromyography. Additionally, a biopsy of the affected root may be prescribed.
To eliminate pain and restore motor activity in the hip and knee joints, an integrated approach is used. The patient is prescribed NSAIDs, analgesics, antispasmodics, sedatives, and anticonvulsants. Physiotherapy methods must be used, including phono- and electrophoresis, therapeutic baths, and the use of ultraviolet light. In extreme cases, radical techniques are used, during which the affected nerve is destroyed or the pressure created on it by surrounding tissues is neutralized.
Treatment includes electrophoresis.
Prognosis and prevention
To avoid the recurrence of nerve inflammation, you need to move more, but not overload the body , and also eat as many healthy foods as possible.
You also need to promptly treat infectious diseases, avoid hypothermia, and get proper rest.
With proper and timely treatment, the prognosis for recovery is favorable. However, if the situation is neglected, the following complications are possible:
- limitation of limb mobility;
- degradation of the myelin sheath of the nerve;
- painful attacks that cannot be controlled with the use of painkillers.
At the moment, there is no way to restore the damaged nerve, but it is possible to reduce the manifestation of inflammation and stop the further development of the disease. To do this, you need to contact a doctor for qualified help at the first sign.