Characteristic
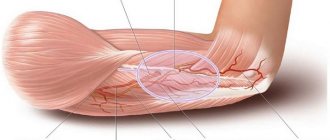
The canal through which the ulnar nerve passes is called the cubital canal. This is a narrow space, so when the nerve is touched and inflamed, swelling begins and touches the walls of the canal.
When this ulnar nerve, which lies in the narrow cubital canal, becomes inflamed, swelling, compression, severe pain, pins and needles and muscle weakness occur.
The process is almost always one-sided. Often, carpal tunnel syndrome occurs as an occupational disease in those who spend a lot of time at the computer.
For differential diagnosis with other types of neuralgia, MRI, ultrasound and other examinations are performed. Treatment is complex, medicinal and physiotherapeutic.
This causes severe pain, as well as paresthesia (that is, tingling, goosebumps, muscle weakness) in the anterior forearm, elbow, at the bend of the hand, in the area of 4 and 5 fingers. Paresthesia often occurs when trying to lean on the ulnar (i.e., from the side of the ulna) edge of the hand or at night.
In Russia, minimally invasive techniques are widely used to treat mild and moderate cubital tunnel syndrome—the injection of glucocorticosteroids into the canal under ultrasound guidance.
If there is no effect from conservative therapy within three months, there is weakness of the hand muscles, severe sensitivity disorders, severe carpal tunnel syndrome, surgical treatment is recommended.The patient should avoid the same type of flexion and extension movements in the elbow joints; it is possible to apply an orthosis to the elbow joint while sleeping; special gymnastics are selected aimed at “gliding the ulnar nerve,” which should be performed 2-3 times a day.
Neurologist
Pershina Natalia Sergeevna
8 years of experience
Almost always the defeat is one-sided. Localization of pain is often noted in the anterior outer area of the elbow. In approximately half of patients, carpal tunnel syndrome has an acute onset, and half experience a gradual increase in symptoms.
Pain is typical during supination-pronation movements (that is, when trying to rotate the forearm around its own axis). Malnutrition of the nerve trunk and microtraumatization of the nerve lead to pain.
The doctor will note their presence during the examination, when he palpates the damaged area. Tapping this area leads to paresthesia in the innervation zone. Skin disorders are observed on the ulnar side of the hand.
Tunnel syndrome is classified as compression-ischemic neuropathic pathology. The essence of this disease is inflammation of a nerve that is regularly subjected to compression or once mechanically damaged.
Neuropathy of the nerve of the elbow joint, features of the disease
Reasons for the development of the disease?
Very often, ulnar nerve neuritis develops as a result of prolonged bent position of the elbow. Pathology also appears when the body is exposed to the following negative factors:
- exposure to low temperatures,
- injuries and various injuries to the elbow,
- infectious lesion,
- inflammation of blood vessels,
- insufficient amount of minerals and vitamin complexes in the body,
- intoxication,
- pathologies of the endocrine system,
- compression of the nerve fiber,
- inflammatory processes in the elbow joint,
- deformation of bone tissue.
What are the symptoms of the disease?
Inflammation of the ulnar nerve is manifested by symptoms such as:
- severe neuralgia in the area of nerve damage in the elbow joint,
- weakness in the muscles of the fingers (adductor and abductor movements),
- discomfort and tingling in the palm,
- thinning and weakening of the muscles of the first interdigital space,
- numbness of the little finger,
- inability to flex and extend fingers due to paralysis,
- loss of sensitivity in the affected area.
Subtleties of diagnosing neuritis of the ulnar nerve
If a patient has developed neuritis of the elbow joint, he needs to go to a medical facility and begin treating the pathology. Upon admission to the hospital, the doctor will find out the progress of the disease and conduct a thorough objective examination. Then the doctor will identify differences with other pathologies in the elbow joint and refer you to special laboratory and instrumental examination methods. These methods include:
- general urine and blood tests,
- plasma biochemistry,
- radiographic examination,
- Ultrasound,
- CT,
- MRI.
Causes
Often the disease manifests itself as a consequence of injuries in the elbow area. Fractures of the shoulder or forearm, damage to the epicondyle of the elbow, which is associated with the muscles - flexors of the hand and fingers - any of these troubles can be the impetus for the onset of the disease.
In addition, often tunnel syndrome develops over time and in the absence of obvious damage.
The risk factors are as follows:
- age over 40 years;
- long periods of work at the computer with the elbow hanging over the edge of the table;
- playing professional sports (especially tennis).
The age characteristics of people who have crossed the 40-year mark are associated with the risk of developing arthritis and arthrosis. Arthritis - inflammatory diseases of the joints, arthrosis - changes in the articular tissue of a non-inflammatory nature, leading to thinning of the joint and the appearance of osteophytes. In both cases, compression of the nerve is possible, resulting in pain and numbness in the 4th and 5th fingers.
Programmers, writers, journalists, accountants and representatives of other professions that require long-term work with a mouse and keyboard are at no less risk: their hand is in a static position for a long time.
The nerve is pinched. Hence the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease. Working without changing position for several hours in a row contributes to the appearance of the first signs of carpal tunnel syndrome.
For athletes, constant monotonous movements are risk factors.
Drivers should also take care of themselves. Often, while waiting in traffic jams, they rest their elbow on the armrest. If this position becomes habitual, then nerve irritation is possible.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Sometimes there are cases of the development of tunnel syndrome in women undergoing menopausal changes. It is caused by the restructuring of connective tissue, which begins under the influence of changes in the functioning of the hormonal system.
There is another risk factor – endocrine diseases (for example, diabetes). In later stages, they can also cause pain in the elbow and discomfort in the hand and fingers.
Pinched ulnar nerve treatment, symptoms
Causes
The most common cause of pinching of this nerve is its constant compression.
This occurs mainly in those people whose professional activities involve regular and prolonged support on their elbows, for example, office workers, those who work at machines, and even disabled people who constantly rest their elbows on the armrest of a chair.
Other causes may be injuries in the lower third of the shoulder (at the elbow joint), fractures of the condyle, that is, the inner protrusion of the shoulder bone, as well as a tumor of the nerve itself.
Symptoms
When the ulnar nerve is pinched, the following symptoms may occur:
- Bending the hand is difficult, as is moving it to the side.
- Feeling pain when moving your fingers.
- Limited or complete absence of movement of the little finger.
- Limited flexion of the fourth and fifth fingers.
- Movement of the thumb is also difficult.
- Lack of extension of the distal phalanges with paralysis of the interosseous muscles.
- Restriction in abduction and adduction of all fingers, subject to complete immobilization of the interosseous muscles.
- Recession of interosseous spaces.
All these factors determine the formation of such an appearance of the hand, which resembles a bird's paw. Thus, the fingers are not located in the same plane; their extension is observed in the proximal (adjacent to the hand) phalanges.
Diagnostics
The main diagnostic method for pinched nerves in the elbow joint is the so-called Foreman test. To perform it, the patient is required to stretch a piece of paper using bent index fingers and straightened thumbs. In this case, both hands are involved in the process.
In addition, an X-ray examination is also carried out, including the use of contrast agents. And if there is a suspicion of the development of a tumor in the ulnar nerve, a puncture biopsy is prescribed, after which a laboratory test of the puncture is performed.
Treatment
Physiotherapy for pinched nerve in the elbow joint
The treatment method for pinched ulnar nerve is determined based on the underlying cause of the disease. But the main treatment is, as a rule, conservative. It is aimed, first of all, at relieving pain, as well as stimulating restoration processes in the nerve endings.
So, to relieve the edematous process, antispasmodic drugs are prescribed. They are aimed at improving blood circulation and nerve nutrition. Painkillers and B vitamins are also used to restore nerve tissue.
Physiotherapeutic treatment that is used for pinched ulnar nerve is electrophoresis with novocaine, the use of ultra-high frequency currents, the use of thermal procedures, and electrical stimulation. In addition, reflexology, massage and therapeutic exercises, including in water, are also carried out.
In parallel with conservative methods, folk treatment can be used in the form of the use of dry heat and the use of alcohol rubbing.
The mixture for them is prepared on the basis of bay leaves, as well as potato sprouts.
If conservative treatment does not produce positive results within two months, surgery is prescribed, which involves removing the tumor and then suturing the nerve.
spinheal.ru
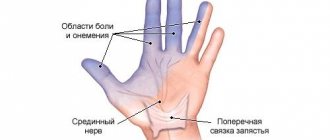
Symptoms
At first, the patient may not experience much pain and for this reason postpones a visit to the doctor. The first thing he notices is a slight feeling of numbness from the elbow to the hand. It is not constant and goes away quite quickly if you rest and change position.
In the future, if no measures have been taken to correct the situation, the disease progresses. Observed:
- recurring numbness of the forearm that occurs immediately after starting work;
- sensation of “crawling goosebumps” , tingling in the hand (this indicates circulatory problems due to compression of the nerve);
- numbness of the little finger and ring finger.
In addition to numbness, pain occurs, mainly at night, when the hand is at rest.
As the disease progresses, the patient notes that it has become difficult for him to bend the 4th and 5th fingers, and in general there are difficulties in performing precise movements on the affected hand. The hand changes somewhat: it becomes deformed as degenerative phenomena in the muscles increase. The man has poor hand control.
You should not wait until such symptoms appear, since in these cases even surgical treatment is not always effective. It is better to consult a doctor when the first unpleasant sensations occur.
Treatment
Therapy is carried out comprehensively, starting with the primary cause that caused pinching in the elbow joint or wrist. Patients are prescribed medications and physiotherapeutic procedures. If conservative treatment is ineffective, surgical intervention is indicated.
In the acute period, it is necessary to reduce the dynamic and static load on the limb affected by the pathology. For patients suffering from cubital syndrome, it is recommended to bandage a soft pad to the flexor surface of the elbow at night. Sometimes splinting is used - fixing the arm in a physiological position.
Medicines
The main symptom of ulnar nerve neuralgia is severe, burning pain. To get rid of unpleasant sensations, patients are recommended to take the following remedies:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – Diclofenac, Nurofen, Celecoxib;
- muscle relaxants – Mydocalm, Spazgan;
- anticonvulsants – Gabapentin, Lyrica.
Antidepressants (Amitriptyline, Paroxetine) help to enhance the effect of analgesics; they are prescribed in combination with painkillers, B vitamins, and Milgamma. If these drugs are ineffective, stronger opiate painkillers are prescribed. They can only be taken with a doctor's prescription.
If a pinched nerve in the elbow is caused by severe swelling, compression of the fiber by tense muscles, the patient is prescribed antispasmodics: Papaverine, Spasmonet.
Postherpetic neuralgia is treated with antiviral agents: Acyclovir, Gerpevir. Additionally, it is necessary to take vitamins (Kombilipen, Neurobion), immunomodulators (Imudon, Polyoxidonium).
For ulnar nerve neuropathy, drugs are used that improve blood flow, nutrition of nerve fibers, stimulate metabolic processes, and have an antioxidant effect. These drugs include Actovegin, Mexidol, Cytoflavin. Restore microcirculation in the upper extremities with Pentoxifylline.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic treatment is prescribed to improve blood circulation in the affected area. The following procedures help enhance the effect of drug therapy:
- electromyostimulation;
- laser irradiation;
- electrophoresis with analgesics and antispasmodics;
- UHF;
- transcranial electroanalgesia;
- darsonvalization;
- massage;
- applications of paraffin, ozokerite;
- mud therapy;
- acupuncture.
Physiotherapy can reduce pain when the ulnar nerve is pinched, relieve swelling, improve the nutrition of soft tissues, increase local immunity, launch natural regeneration processes, and prevent the development of contractures. The course of treatment begins in the subacute period after the symptoms of inflammation have resolved or during stable remission in order to prevent relapses. A total of 5–15 sessions will be required.
Surgery
Surgery is performed when conservative methods are ineffective to remove tumors, hematomas, and scar tissue that compress nerve endings. Ulnar nerve entrapment is treated in the following ways:
- nerve transposition;
- simple decompression for carpal tunnel syndrome;
- neurolysis – removal of scar tissue;
- muscle neurotization - restoration of innervation.
For idiopathic neuralgia, corticosteroid injections are given into the affected area. But this method of treatment has a large number of side effects; tissue degeneration often progresses at the injection site, and the risk of additional nerve trauma increases. Persistent hand contractures develop and pain increases.
Diagnostics
Typically, diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome is not particularly difficult. The patient should contact a neurologist who:
- conduct a visual inspection;
- ask in detail about all manifestations of the syndrome;
- will perform a series of tests.
The doctor will take into account the following factors:
- age of the sick person;
- usual professional activities;
- the presence or absence of any injuries in the past (even if a fracture or bruise occurred several years ago).
Common tests are electroneuromyography.
The functioning of the hand muscles is checked. If they do not work correctly, the doctor will immediately suspect carpal tunnel syndrome.
The second study concerns the functioning of the muscles of the forearm and shoulder. The doctor assesses the speed of nerve impulses. If there is a slowdown, this may indicate the presence of carpal tunnel syndrome.
In some cases, additional studies are prescribed. The patient will be sent for an MRI or ultrasound. This is done to clarify the diagnosis and to exclude other pathologies. In addition, the doctor will check whether osteophytes are the cause of the development of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Seeing a doctor and a thorough examination are necessary, since non-specialists often confuse tunnel syndrome with various neuralgia of a different nature, with plexitis, radiculitis, arthritis, and osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
Measures aimed at improving the condition will be different in these cases. Therefore, self-diagnosis and attempts at self-medication are unacceptable if there is a desire to achieve recovery.
How is the treatment carried out?
Patient management tactics are selected depending on the severity of the disease.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
In the first stages, conservative treatment is effective. The main thing that is required from the patient is the elimination of irritating factors, that is, the elimination of repetitive movements that cause tension and pain.
To relieve swelling and pain, the doctor will prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Sometimes the use of hormonal agents is required to relieve pain and quickly restore the damaged area. The patient may be advised to wear a soft bandage - maybe not all the time, but from time to time, to keep the arm at rest.
Hand massage helps a lot. It is made using creams that have a slight warming effect.
The massage should be carried out for a quarter of an hour. The movements begin with the fingers, gently kneading the pads and joints in a circular motion, rising higher. Only after working each finger can you move on to the wrist joint, where you should perform several passive flexion-extension movements.
Next, massage the forearm and shoulder, and again make smooth circular movements in the elbow area. You need to end the session in the area of the shoulder joint.
For acute pain, massage is not recommended - it begins after the process has subsided.
If all these measures do not bring the expected effect, the patient continues to complain, and surgical treatment is prescribed.
The transposition method is most often used. In this case, the nerve is removed from its location and transferred to another area. After the sutures have healed, the patient can freely make any movements - the nerve is no longer stretched or strained, so the painful sensations go away.
The second method is more complicated. It is called a medial epicondylectomy. The doctor performs a resection of the epicondyle, which also frees the nerve and is not damaged by habitual repetitive movements.
After this operation, the recovery period is long, it can take up to 3 months.
During rehabilitation, the patient is first provided with a fixed position of the arm, and then a special exercise therapy complex is prescribed to develop muscles. Physiotherapy, in particular electrophoresis, is also used.
Treatment
Inflammation of the ulnar nerve can be treated on an outpatient basis, since this disease does not require inpatient observation, with the exception of surgical intervention.
- conservative;
- surgical;
- folk
Conservative treatment involves the use of medications, which, in turn, include:
- anti-inflammatory drugs (glucocorticosteroids, diclofenac, ketorolac);
- painkillers (metamizole sodium, anesthetics);
- anticholinesterase drugs (ipidacrine, neostigmine);
- vasoactive drugs (nicotinic acid, pentoxifylline);
- metabolites (B vitamins, alpha lipolic acid).
The greatest effect is caused by injections of the above drugs, as the absorption of the active substance increases.
In addition, the doctor may prescribe a compress with dimexide and cold on the painful area.
At the acute stage, when the pain syndrome has just appeared, it is important to perform a motor blockade of the arm and elbow joint, especially at night. . The patient is recommended to have a fixing bandage, in most cases using a splint made from improvised materials (a needle or a strong stick)
The patient is recommended to have a fixing bandage, in most cases using a splint made from improvised materials (a needle or a strong stick).
In addition to drug treatment with tablets, physiotherapy is prescribed, which includes:
- UHF;
- phonophoresis;
- magnetotherapy.
An excellent way to eliminate the unpleasant consequences of inflammation (muscle atrophy) is massage and electrical myostimulation.
Surgical intervention (operation) is indicated in case of lack of effect from medications, the presence of a hematoma, tumor, and also in the case of the development of tunnel-type neuropathy.
Types of surgical intervention:
- nerve decompression;
- neurolysis;
- removal of adhesions;
- nerve transposition;
- tumor removal;
- scar removal;
- removal of hematoma.
Any operation, especially one performed on nerves, is performed under anesthesia. Pain relief can be performed using either general or local anesthesia.
Surgical option
Naturally, home remedies are used to treat ulnar nerve neuropathy, which in most cases are aimed at eliminating the pain symptom.
Before you start using traditional medicine, we strongly recommend that you consult your doctor for advice and obtain his permission to use a particular recipe.
Horse sorrel tincture:
Soak the roots of horse sorrel in vodka in a ratio of 1 to 1. Namely, half a jar of roots and half a liter of vodka are used for a liter jar. Infuse the root for at least 10 days and apply as a compress to the sore spot. The effect is enhanced if the compress is done at night.
Bay leaf ointment:
Mix 200 grams of vegetable oil and 4 tbsp. l. finely chopped bay leaf. Leave the ointment for a week. Rub the resulting product into the area that hurts until the pain stops.
Horseradish compress:
Horseradish is ground with raw potatoes in a ratio of 1 to 1 and 1 tbsp is added to the resulting mixture. l. honey The resulting mixture is wrapped in thick cloth and applied to the left or right hand, depending on the location of the pain syndrome, for an hour. Horseradish acts as an anesthetic, and potatoes compensate for its burning effect.
Hand rehabilitation exercises
Additionally, during the recovery stage, the patient is shown physical therapy exercises (PT), as well as classes on specialized equipment.
Consequences
If measures were not taken in time to eliminate carpal tunnel syndrome, this leads to consequences, including loss of ability to work.
A person suffers from constant pain, and then he begins to experience dystrophy of a number of muscle groups, leading to a decrease in the volume of the limb. He cannot move his arm freely, which significantly limits his ability to carry out professional activities.
In addition, due to constant pain, a person becomes irritable, suffers from insomnia, and suffers from appetite. All this can lead to diseases of the nervous system. Carpal tunnel syndrome sometimes becomes a trigger for the development of depressive conditions.
In itself, it does not pose a threat to life, that is, with such a disease a person can live until his physiological old age. But the quality of life is noticeably reduced, so tunnel syndrome must be diagnosed and treated in a timely manner. It is important to prevent the process from becoming chronic, so that you do not then have to deal with its manifestations for years.