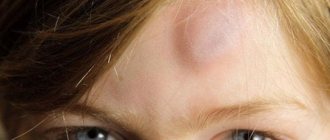
In everyday life, various injuries often occur, some easier, some more severe. If a head injury occurs, everything may turn out to be much more serious than it might initially seem. When a bruise occurs, closed tissue damage occurs, but the skin remains unharmed. Although in some cases, a bruise of the soft tissues of the head can occur with a violation of the integrity of the skin, and can also be combined with more serious injuries, for example, with a concussion or contusion of the brain or a skull fracture.
A severe head injury is also dangerous because such an injury can cause an extensive hematoma to form, pressing on the brain. The consequences of a bruise can be very diverse, therefore, if you hit your head, you should definitely get examined, even if no serious symptoms are observed.
Causes
Head contusions can occur:
- due to falls;
- from a blow to the head with a blunt object;
- in domestic fights;
- during martial arts;
- in the event of a traffic accident;
- during work activity;
- when playing sports;
- due to carelessness during active games.
Contusion of the soft tissues of the head is more common among extreme athletes, construction workers and children. By the way, an infant can hit his head by falling from a changing table, falling out of a stroller or rolling off a sofa, so in no case should small children be left unattended in places that are dangerous for them.
Symptoms
Treatment after a head impact always depends on the symptoms, while the symptoms themselves and their severity depend on the severity of the injury and its location. The following signs may indicate that the soft tissues of the head have been damaged:
- pain arising from vasospasm;
- the formation of a bruise that forms a lump;
- the presence of a small bruise or extensive hematoma;
- nosebleeds;
- short-term increase in body temperature;
- weakness in the arms;
- confusion or complete loss of consciousness;
- the occurrence of nausea and vomiting.
How does a bruise form?
Sometimes just a little pressure is enough to cause a bruise to form on the body. This sensitivity is associated with increased fragility and weakness of blood vessels. In women, the consequences of a bruise are more pronounced than in men. This fact is due to the fact that the female body contains more estrogen hormones, which are produced by the ovaries. Hence - more pronounced hematomas.
After a bruise, darkening will form at the damaged area, then redness, after which the color of the bruise will change depending on the force of the blow: from reddish to dark blue. If the hematoma begins to acquire a yellowish, greenish or brown tint, then the injury is gradually going away. Bruises heal from a week to three, depending on the severity of the bruise and the location of the hematoma. Bruises on the face go away faster than on the body and limbs.
Consequences of a head injury
After hitting your head, especially if you hit it hard, certain complications and consequences may arise. Some of them appear immediately, others gradually, maybe even after several months or years. The main consequences if a bruise to the back of the head occurs and no treatment is given:
- Deterioration in performance due to traumatic asthenia;
- problems with concentration;
- Depressive states;
- Deterioration in memorizing information;
- The occurrence of irritability and insomnia;
- Constant headaches, migraines;
- Reaction to weather changes.
To prevent a head blow from becoming a cause of suffering, at the first sign of it you need to be examined and treated.
Possible consequences of a blow to the temple
With a weak blow to the temple, the victim may experience:
- Stupefaction, tinnitus, spatial disorientation.
- Decreased visual acuity, photophobia.
- Dizziness, nausea, rarely vomiting.
- A hematoma or tumor may form at the site of impact.
- Headache localized on the side of the injured temple.
- Dissection of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, bleeding.
- Pain in the neck area.
Symptoms of injury after being hit in the temple can appear either immediately or after a few days . A blow can lead to displacement or rupture of important functional elements, which will lead to irreversible disorders (headaches that last for years, convulsions and muscle spasms, epileptic attacks).
A strong blow and a blow of medium force pose a great danger to health, and in some cases, to human life. The consequences of such attacks can be:
- Displacement of the skull bones.
- Temporal bone fracture.
- Concussion.
- Internal hemorrhage.
- Loss of vision.
- Speech impairment.
- Paralysis and muscle spasms (cramps).
- After injury to the temple, epilepsy attacks are possible.
- Bruises under the eyes.
- Impaired short-term memory.
- Mental illnesses of a reversible and irreversible nature are possible.
After the blow, the victim’s general condition worsens : appetite disappears, fatigue increases, and the frequency of migraines, which cannot be treated with medication, increases. Headaches can occur over a long period of time, up to several years. In rare cases, a focus of infection occurs at the site of the impact.
A strong, narrowly targeted hit can be fatal . This can be a blow from a fist or a fall on a hard and sharp object. Death occurs for a number of reasons:
- When the vagus nerve is damaged, the heart rhythm is disrupted , even to cardiac arrest. Damage to nerve fibers also leads to paralysis and epilepsy.
- If the temporal artery is damaged internal bleeding and a hematoma is formed. This is life-threatening if the victim is not provided with timely medical assistance. Also, when a vessel ruptures, the nutrition of the brain is disrupted, which is fraught with serious consequences.
- When part of the skull is fractured, a bone or splinter can enter the brain and injure it.
First aid for head injury
Every person who has ever hit their head needs to know what to do if they hit their head. So, if you hit your head on something, you should proceed with the following actions:
- Apply a pressure bandage to the head. With its help you can prevent the occurrence of hematoma.
- Make a cold compress by applying ice wrapped in a cloth or any product from the freezer to the bruise. Such compresses should be left on the damaged area for twenty minutes and repeated throughout the day. This action will narrow the blood vessels, relieve pain and prevent the hematoma from spreading.
- If there is damage to the skin, for example, an abrasion or a small cut, then you need to carry out antiseptic treatment with hydrogen peroxide or chlorhexidine. Covering the wound with brilliant green or iodine is not necessary. If the cut is large, it is necessary to contact a surgeon for suturing.
- Starting from the second day, you can resort to warming up the injured area using warm compresses, lotions, and a heating pad. This helps the swelling to resolve faster. It is unacceptable to heat the bruise on the first day, as this can intensify the inflammatory process.
- To make the bruise go away faster, you can use special ointments, creams or gels for bruises, but it is better to discuss their use with your doctor.
- If a crust forms at the site of skin damage, it is important not to rip it off, otherwise a scar may remain. It is better to use softening creams, then a crust will not form.
- If you have a severe headache, you can take a painkiller. But if there is subcutaneous hemorrhage, then you should not use aspirin, as it interferes with blood clotting and can cause the hematoma to become even larger.
Why is a blow to the temple dangerous?
The temples are a paired area of the head, which is located between the ear, forehead and cheekbone line. It is represented by the temporal cavity, formed at the junction of the sphenoid and temporal bones. The temporal bone itself is one of the thinnest and weakest ( about 2 mm ) and is easily susceptible to fractures.
In the area of the temporal region there is the meningeal (temporal) artery, which supplies the hard part of the brain . The vagus nerve is also localized there , which is responsible for the work of many muscles, including the heart and a large number of nerve fibers. a layer of fiber under the skin , but it is very loose and does not provide much protection upon impact. The skin on the temples is thin and easily susceptible to tearing and injury.
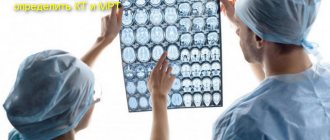
Diagnostics
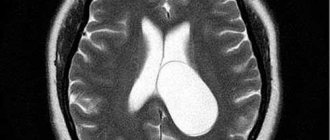
After providing first aid, it is advisable to undergo an examination that can refute or confirm the presence of more serious damage. To make a diagnosis, the patient must be examined by a neurologist, then an x-ray should be taken to see if the integrity of the skull bones is compromised. Magnetic resonance imaging will help the doctor see if there are structural changes in the brain, as well as see how deep the hematoma has gone.
If there is a suspicion of displacement of the cervical vertebrae, which sometimes happens with a head injury, then the doctor may order an x-ray of the cervical spine. Based on the examination results, further treatment is prescribed.
Types of bruise (degrees)
Now you know what a bruise is. In modern medicine, such injury is classified as follows:
- First degree. The skin is slightly damaged. It may show minor abrasions or scratches. Such a bruise goes away painlessly and on its own after 3-4 days.
- Second degree. The injury is accompanied by muscle rupture, which leads to the formation of a hematoma and swelling. In this case, the patient feels sharp pain.
- Third degree. This type includes bone bruise, tendon or muscle damage, as well as accompanying dislocations. Such impacts are especially dangerous when it comes to injuries to the head, knee, joints or tailbone.
- Fourth degree. It is the most pronounced and is accompanied by changes that completely disrupt the normal functioning of human organs and systems. His general condition may be critical.
Treatment
How to treat a head injury should be decided by the doctor, based on the diagnosis. If the bruise does not threaten the health and life of the patient, then treatment is as follows:
- The first days the patient should be completely at rest and adhere to bed rest. Getting out of bed is allowed only if absolutely necessary.
- The patient must impeccably follow all the recommendations of the attending doctor and take the medications prescribed by him;
- For some time after the injury, you need to limit physical activity.
- If the bruise is located on the right side, then it is better to sleep on the left side and vice versa.
- During the recovery period, it is recommended to watch less TV, sit at the computer and breathe more fresh air.
It is very easy to get a head injury. Sometimes it is enough to sneeze, shake your head and hit the table, door or wall. The injury is considered quite mild, but if any alarming symptom appears, it is better to consult a doctor, then recovery will come faster and the consequences of the injury will be avoided.
Bruises: treatment at home and in hospital
Treatment of bruises in a hospital is required only when a significant injury has occurred. For example, bruises of the head, lower back, abdomen and chest require immediate hospitalization of the patient in the surgical department. After carrying out appropriate diagnostic procedures, doctors decide on further treatment of the injury. In the most severe cases, surgery is performed. Access to the damaged area is carried out through endoscopy or open method. In this case, ruptures of parenchymal organs and large vessels are sutured, and the resulting blood is removed. After this, the wound is drained.
At the same time, the patient is prescribed painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
It should also be noted that for minor injuries, they can be treated on their own. Proponents of traditional medicine recommend adhering to the following recommendations:
- On the first day, cold lotions should be applied to the site of the bruise. To prepare them, you should use herbs such as St. John's wort, plantain, wormwood, yarrow and heather.
- Chilled tea leaves are also used to treat bruises.
- Another effective remedy for tumors is bodyaga. Pharmaceutical powder is diluted with water, and then the resulting slurry is applied to the bruise site, and covered with a cloth or compress on top.
- To treat an injury in the joint area, you should do a light massage using a drop of essential oil of fir, geranium or lemon.
- The bruised area can be lightly rubbed with “Star” balm.
- Such a simple folk remedy as cottage cheese helps to get rid of severe bruises of the limbs. The cold dairy product is applied to the sore spot and kept for about ¼ hour.
Using these recipes, you can get rid of a bruise in a short period of time and prevent its consequences.
Source of the article: https://fb.ru/article/231388/chto-takoe-ushib-osnovnyie-vidyi-opisanie-i-lechenie