From time to time, every person may notice that the brain is not functioning fully. Such a disorder is expressed in difficulty performing movements (bradykinesia) and in remembering information, inhibition of reactions and thinking disorders (bradypsychia).
It should be said that in most situations these failures are temporary and can be explained by natural factors: fatigue or nervous exhaustion. However, there are cases when the awkwardness of movements, inhibition of thinking and the mental sphere is a pathological process, the causes of which must be promptly identified and appropriate therapy selected.
Features of bradypsychia
Pathological inhibition of thinking is called bradypsychia.
This phenomenon has no parallels with apathy or inertia of thinking, but suggests mental and pathophysiological disorders. Bradypsychia is considered as a kind of neurological symptomatology, which in most cases develops in people in old age. But sometimes people at a young age, as well as children, experience inhibition in their thinking processes.
Poverty and insufficiency of mental processes is a symptom of many psychological or physiological pathological processes, manifested as a decrease in reaction speed, slow speech, slow thinking and motor activity. In difficult situations, the individual is not able to react to what is happening and remains for a long time in an apathetic state or stupor. The following types of inhibition are distinguished:
- complex;
- ideational;
- motor.
Thought processing can be impaired at any age
Retardation also occurs in speech and thought, which has psychological factors. Weak and involuntary movements can cause motor retardation. Memory problems and failures appear. In many cases, such conditions are provoked by a neurological disease, constant fatigue, or psychological pathological processes.
Slowness of movements and emotional inhibition is a pathological process, the causes of which only specialists can detect. They also recommend proper therapy.
Prevention
Unfortunately, there are no specific prevention methods. You should follow a rest and work schedule, protect yourself from nervous experiences and stress, and begin treatment for all diseases in a timely manner.
Some are so inhibited that dying means waking up for them.
Funny aphorisms
Inhibition as a personality quality is a tendency to exhibit a lower, ignorant state of mind, to demonstrate a slow, sluggish speech and motor reaction, a slower pace of thinking and speech, combined with their impoverishment and monotony; to be sour, inhibited, indifferent, devoid of liveliness and activity.
Associated disorders
Bradypsychia is the result of damage to the central nervous system, which is responsible for brain activity. Depending on the element of the lesion, different types of disorders develop. These include:
- bradybasia - slow walking;
Bradykinesia is characteristic of parkinsonism - bradythymia - slow changes in emotions;
- bradykinesia - slow pace and limited range of movements;
- bradypraxia - slow direction of action;
- Bradylexia – slow reading;
- bradyphasia, bradyllalia is a slowdown in speech, at the same time it is almost always correct, observed both in adulthood and in childhood (bradylalia is often observed in patients recovering);
- Impaired articulation may also develop, and during a long conversation the person may become tired.
When bradypsychia is a consequence of Parkinson's disease, it is necessary to focus on the symptoms of the underlying pathological process. These include feelings of fatigue, anxiety, sleep disorders, etc.
What are the symptoms
It’s difficult and time-consuming to select words so that something coherent comes out, but this often still doesn’t work out, but individual words or constructions may acquire new meanings.
Some sounds and words are constantly replaced by others, rearranged and repeated. It starts with a seemingly harmless replacement of “b” with “p”, and ends with still incomprehensible combinations of words and sentences almost backwards. In some cases, such problems occur with written speech.
It's difficult to understand what other people are saying. In addition, the person does not seem to understand his own speech and pours out a stream of consciousness, and in the first two months after an illness or injury it can be a stream of random sounds or words.
The rhythm and melody of speech is disrupted, it sounds unnatural: pauses are too long, the voice is quiet, a half-whisper.
It is difficult to remember information you hear or read. Problems can arise with just four words in a row that are related in meaning. In such a situation, long sentences are difficult to understand, so they become meaningless.
It is difficult to name objects and use figures of speech, catchphrases, and proverbs. It is also difficult to understand them. How to treat and what will happen if you do not treat
Aphasia correction can only be done in a clinic. During correction, a person re-learns to speak correctly, as in childhood. With a speech therapist, he learns to perceive oral and written speech, correctly use the speech apparatus (respiratory organs, tongue, lips), and pronounce sounds.
Treatment may vary depending on the type of disorder, but in any case it is important to start it as early as possible. This is because a person gets used to his way of speaking, and speech defects become fixed. The patient may perceive some sounds instead of others, constantly repeat frequently used words and construct sentences incorrectly. If you delay in correcting aphasia, it will take even longer and more difficult to eliminate established disorders.
Speech therapists distinguish four degrees of dysarthria, but even with the mildest of them, doctors cannot ignore:
- pronunciation disorders can only be identified by a speech therapist; in everyday speech they are hardly noticeable;
- impairments are noticeable to people around, but speech is still understandable;
- speech is understood only by people who are well acquainted with the patient, and by strangers who simply accidentally understand some phrases;
- even close people do not understand what the person is saying, if the sounds he makes can be called speech at all - this is severe dysarthria, or anarthria.
Speech is slurred, incomprehensible, slow. There is a feeling of “blurring” of everything that a person says, as if he has porridge in his mouth, he is trying to say something, but does not yet understand that it is almost useless.
The voice is quiet, weak, deaf, and breathing is rapid and intermittent. Because of this, speech becomes monotonous and it is difficult to speak clearly.
Some sounds fall out, some people pronounce through the nose (nasalization occurs, compare “n” and “b”), speech is basically simplified and it may seem that the patient is trying to pronounce a polysyllabic word in one syllable. Sounds are distorted and replaced by others, as in aphasia.
- Depending on the type of dysarthria, the tongue, lips, facial and neck muscles may work differently. In some cases they are constantly tense, in others they are too relaxed so that their mouth is slightly open. In addition, during a conversation, such overly relaxed muscles can suddenly tense up.
Provoking factors and diseases
The pathophysiology is very complex and not fully understood. It is only known that thinking, behavior, emotional component and other functions of the human brain are associated with the activity of the limbic system. In everyday practice, only conditions are identified - diseases, during which bradypsychia and accompanying deviations are observed:
- Vascular diseases of the brain. Acute, often chronic disorders of blood flow in the brain, which arise due to progressive atherosclerosis, hypertension, embolism and vascular thrombosis, are a factor in the destruction of substances in the brain. The structures that are responsible for quick thinking are also susceptible to disruption.
- Parkinson's disease . A common cause, the characteristic manifestation of which is slow thinking. In addition to such depressing symptoms (patients at a late stage of development of this pathological process do not tend to notice any changes), there are a large number of other unpleasant manifestations. For example, thoughts will become not only slow, but also viscous; the patient will be characterized by importunity and slow, confused speech.
- Epilepsy . At a late stage in the development of the disease, when experts observe the destruction of personality as a result of a progressive disease, inhibition may be noted, as well as other symptoms of altered thinking.
- Schizophrenia . As with epilepsy in schizophrenia, bradypsychia is not considered an initial symptom of pathological processes, but develops gradually over time.
- Depression . A mental illness that is characterized by a large number of symptoms, often disguised as somatic difficulties - including toothache or ischemia. These also include sluggish thinking.
- Hypothyroidism . Improper functioning of the thyroid gland. With this disease, the symptoms are extremely pronounced and are one of the first to occur.
- Toxic lesions . Such a subgroup of diseases does not exist in the international classification. However, the term best describes the causes of painful symptoms - intoxication of the body.
The short-term effect of lethargy appears after lack of sleep, due to exhaustion of the body, or as a result of the use of drugs and alcohol that inhibit thinking and movement. The reasons can be divided into those that block brain activity and those that reduce the possibilities for its implementation.
Naturally, with such an abundance of provoking diseases, treatment can also be different.
Loss of energy or lethargy
- Depression - decreased mood
- Loss of sexual desire
- Loss of energy or lethargy
- Thoughts about committing suicide
- Feeling that you are to blame for much or everything
- Feelings of loneliness, abandonment
- Depression, feeling of "blues"
- Apathy - Lack of interest in something
- Feeling as if you are trapped or caught
- Excessive worry about various things
- Feeling of unexplained debilitating fatigue
- The future is hopeless
- Tearfulness
These are the most common complaints made by patients who contact not only a psychotherapist, but also a general practitioner, gastroenterologist, cardiologist, neurologist, endocrinologist, etc.
With complaints of loss of strength and lethargy, people most often visit a general practitioner, who prescribes a general examination of blood, urine, feces, etc.
Most often, this ends with advice to consult a neurologist or take a rest; vitamin preparations are often prescribed in combination with general restoratives and nootropics.
But a person does not feel a pronounced result in the treatment, although temporary relief may be observed.
Call us and we will not only correctly carry out a complete diagnosis, but will also be able to quickly help you!
An example of complaints from patients who complain of loss of strength and feelings of lethargy.
Patient:
Woman, 35 years old, works, one child, married, has never used drugs, drinks alcohol on holidays - 8-10 times a year, in moderate quantities. I turned to a psychiatrist, psychotherapist (psychotherapist) on the recommendation of friends. She described her complaints this way:
“There has been an incomprehensible state of affairs lately. About a year and a half ago, either my stomach or intestines began to bother me. No pain, but some swelling on the left under the ribs below. I underwent all tests and an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. Everything is fine.
Then some kind of inhibition appeared when moving his gaze. But there was a lot of work, taking care of the house, and I forgot about it for a while, and then here it is again. About five months ago I was very nervous - I had a fight with my husband. Then I read all sorts of nasty things about the end of the world.
Progressive lethargy appeared, decreased attention, became forgetful, and loss of strength. I can’t do anything, I’ve become like an old woman, and I’m still young, it’s often difficult to do even the simplest things. Periodically - palpitations, resting pulse 100 beats/min., began to choke during physical exertion.
The constant temperature is now 37.2 degrees, visual acuity has decreased in the dark.
Words began to get confused when speaking. The condition is now bad, an ambulance was called. It started with the fact that I came home from work in a state of “fog”, terrible retardation in thoughts and movements, and felt a loss of strength. My husband put me to bed.
And suddenly it became very bad, they measured the pressure, it was 180/110, such a jump in pressure. They did an ECG of the heart, and according to the doctor, everything was normal. They advised me to go to a neurologist. I went to a neurologist.
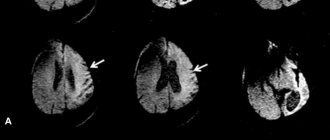
According to the MRI of the brain, “no organic pathology was detected.”
Upon examination by an ophthalmologist, a diagnosis of retinal angiopathy was made (fundus - vessels narrowed 1:2). According to the results of the REG and EEG, the general amplitude background is reduced. They prescribed treatment - nicergoline, neurovital, cardiomagnyl, asparkam, glycine, and I read it on the Internet a week ago and started taking gelarium. Still, there is no improvement from that treatment for three months.
Now I’m worried: I feel inhibited in everything, no matter what I do or think about, loss of strength, bad sleep has begun, it always seems that something is going to happen to me, and in the last week I have been bothered by headaches, the pain is localized in temples, sometimes pulsation, but also a feeling that a hoop is on the head, i.e. There was a feeling of “bloating”, heaviness, a burning sensation in the head, some kind of heaviness in the back of the head.
Everything is fine in the family now. At work, I’ve been on sick leave for a month now, such weakness and general condition, plus fever. And no one can help, they just extend the sick leave and say, continue the treatment. But it doesn't help. They advised me to contact you. Nothing bothered me before, but now I’m worried and afraid that there might be something serious.”
After examination by a psychotherapist, a manifestation of astheno-depressive syndrome, complicated by autonomic dysfunction, was established. Complex therapy was individually selected and recommended to be started in a day hospital.
A week later, the painful sensations of lethargy, loss of strength, headaches decreased significantly, sleep was restored, and the patient wanted to go to work. Treatment continued on an outpatient basis, under the direct supervision of a psychotherapist.
After five weeks, the main treatment was canceled due to the onset of recovery, but to prevent a relapse, the psychotherapist individually selected the daily routine and diet, rehabilitation measures, and supportive therapy.
After completing the main course of treatment, the patient is observed for 2.5 years and follows the recommendations received. He has no complaints about his health.
The most common reasons for a person’s feelings of loss of strength and lethargy is asthenization (burnout, exhaustion) of his higher nervous activity.
This is due to the fact that for some reason, be it external psychogenic reasons, or internal ones associated with a violation of the metabolic processes of the brain, or any injuries to the central nervous system, the brain “overworked” and a breakdown of higher nervous activity occurred, which is expressed in the formation of one or another pathopsychic process, which is expressed in a feeling of loss of strength and a feeling of inhibition in thoughts or actions. It is not uncommon for patients to define this condition as: I am in a fog; lost the rhythm of life; I want to, but “I can’t”; constantly drawn to the sofa. It’s not uncommon for the genital area to suffer as well. With a pronounced loss of strength and lethargy, people often lose interest in their spouses or loved ones.
As a result of the feeling of loss of strength and lethargy, people begin to show concern about their physical condition and begin to visit a wide variety of doctors. At the same time, they completely ignore advice on contacting a psychotherapist, even despite the obvious prerequisites for this.
Absolutely everything that a person can experience, feel, experience, and loss of strength and inhibition is no exception, is formed through biochemical processes occurring in the brain, in its various parts and are transmitted to the cerebral cortex - consciousness, where these reactions are comprehended. This entire large, complex, but often instantaneous process is called mental activity or higher nervous activity.
Loss of strength and lethargy are a fairly specific symptom in a person’s condition, which most often indicates the presence of mental disorders in a person, which can often lead to the development of somatic (physical) diseases.
Such diseases are defined as psycho-somatic, when it is the problems associated with the sensations of bodily illness that come to the fore, “hiding underneath” the true “culprit” of loss of strength and lethargy.
Such mental disorders must first be very carefully studied and correctly assessed by a psychotherapist, who should become a leading specialist in the treatment of loss of strength and feelings of lethargy.
If you feel a loss of strength and lethargy, you should consult a doctor.
Call +7405-22-58-158
Brain Clinic specialists will be able to provide quality assistance.
Source: https://brainklinik.ru/upadok-sil/
What does it look like?
The image of a “inhibited” patient falls under the typical characteristics of a melancholic person: weakness, slowness, drawn-out speech, every word is pronounced with effort.
There may be a feeling that the thought process takes a large amount of strength and energy from a person who does not have time to react to information or is completely plunged into a stupor.
In addition to a decrease in the speed of speech and thought processes, muffled words are observed - a very quiet and calm voice, sometimes breaking the silence. Weakness is visible in movement and facial expressions; posture is often too relaxed.
A person has a desire to constantly find support or lie down.
Not all symptoms are always observed. Just one thing is enough to recommend a person to seek medical help from specialists.
Diagnostic criteria and methods
People with speech rate disorders, including bradyllalia, need comprehensive medical, psychological and pedagogical diagnostics carried out by a specialized specialist. During the examination, the patient’s medical history should be studied in detail, which concerns previous illnesses and brain lesions, as well as the presence of disturbances in the rate of speech in relatives.
In certain situations, in order to find out the organic basis of the disease, it is necessary to conduct instrumental studies, including:
- electroencephalography;
- rheoencephalography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- PET scan of the brain;
- Lumbar puncture.
The study of oral speech involves assessing the structure of the organs of articulation and the state of motor skills, expressive speech (pronunciation of sounds, syllables, words, tempo-rhythmic side, voice characteristics, etc.). Diagnostics of written speech involves performing tasks such as copying text, writing from dictation, and reading. In addition to a diagnostic examination of speech function, a study of general condition, manual motor skills, sensory functions, and intelligence is carried out.
When making a diagnosis, it is necessary to differentiate this disease from dysarthria and stuttering.
What does modern medicine offer?
To carry out proper treatment of the disease, you must first consult with a specialist. He will recommend effective treatment, and will also warn about the presence of contraindications to the use of certain therapy methods or any medication.
The following methods of therapeutic and preventive action are used more often than others:
- Activation of thinking processes . For these purposes, you need to read new books, study foreign languages, engage in the creative process, or solve various puzzles. This technique helps train the brain and activate thinking.
- Neuroprotectors and nootropics are prescribed . Drug therapy that is aimed at restoring and strengthening nerve cells and tissues.
- Treatment of vascular pathologies . Products are used that make it possible to cleanse the vascular walls, which is necessary for proper brain function. As a result, mental and physical activity is activated.
- Psychotherapy . It acts as an auxiliary drug therapy. Modern therapeutic techniques help counteract the effects of stress, adjust personality assessment, and form the necessary models of response to specific situations.
- Sports activities and walks in the fresh air . Moderate physical stress and walks give the brain the opportunity to rest and the nerve cells to recover thanks to the influx of oxygen.
If emotional and mental retardation is caused by tranquilizers, then discontinuation of any drugs is required. In most cases, reactions recover over time.
Summing up
The prognosis is relatively favorable with an early start of correction and the presence of psychological causes of disorders of motor activity and speech motor skills. However, after regaining your skills, you should be observed by doctors for a long time and constantly independently monitor your movements and train of thoughts.
As preventive measures, damage to the central nervous system should be prevented, head injuries should be avoided, and asthenic syndrome should be detected in time.
Pathological inhibition of thinking involves various mental and pathophysiological disorders. This phenomenon should be qualified as a symptom that in most situations occurs in older people. But in certain cases, a similar problem can manifest itself in childhood and young people.
If you notice that your thinking processes are slow, you should immediately seek advice from a doctor. It is likely that this condition is the result of dangerous disruptions in the functioning of the central nervous system and requires special correction.
Etiology
Retardation of movements and thinking in a person can be observed in the following pathological processes:
- Alzheimer's disease;
- senile dementia;
- head injuries;
- malignant or benign formations in the brain;
- diseases that affect the central nervous system;
- hypoglycemia;
- mental disorders;
- neuroses.
In addition, a temporary state of slowness of reaction, movement and speech can be observed in the following cases:
- under alcohol or drug intoxication;
- with chronic fatigue and constant lack of sleep;
- with frequent nervous tension, stress, chronic depression;
- under circumstances that cause a person to feel fear, anxiety and panic;
- with severe emotional shock.
Psychomotor retardation in a child may be due to the following etiological factors:
- cerebral palsy;
- vascular diseases of the brain;
- epilepsy;
- encephalitis;
- meningitis;
- stressful situations;
- psychological disorders.
Depending on the underlying factor, this condition in a child can be temporary or chronic. It goes without saying that if such a symptom appears in children, you should immediately consult a doctor, since the cause of the pathology can be dangerous to the baby’s health.