Find out more about other diseases starting with the letter “Y”: Juvenile parkinsonism; Juvenile absence epilepsy; Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy.
Not all diseases can be completely cured. We are talking, first of all, about those that arise due to genetic conditioning. It is especially sad when it comes to childhood diseases. But medicine does not stand still, and offers treatment options that allow you to maintain an acceptable quality of life for the baby. Such a rare disease as juvenile parkinsonism, although today cannot be completely cured, is successfully corrected by medical treatment.
Classification
Classification criteria help to establish groups of patterns in the dynamics of the course of the disease and facilitate the study of pathology. In practice, when choosing therapy, the main role is played by external manifestations, age, the presence or absence of concomitant diseases, and analysis of the results when using several instrumental diagnostic methods.
| Criterion | View | Description |
| Cause | Primary | Congenital disease |
| Secondary | Acquired (a number of reasons after birth) | |
| Clinical manifestations | Shaking | Tremor of the jaw, limbs, muscle motility is not affected |
| Trembling-rigid | In the initial stages, tremors of the limbs with stiffness of movements; further, impaired muscle motility | |
| Rigid trembling | It begins with a violation of muscle tone, then tremor; due to voluntary muscle tension, the limbs are in a bent state | |
| Akinetic-rigid | No tremor; local increase in muscle tone; no involuntary movements | |
| Mixed | ||
| Intensity of clinical manifestations | Exacerbation | Increased symptoms due to hypothermia and strong emotional stress |
| Remission | Symptoms dull, barely noticeable external signs after fatigue or prolonged lying | |
| Stages of occurrence | 1 | Symptoms on 1 limb. |
| 2 | Symmetrical manifestation of symptoms | |
| 3 | Sudden severe bilateral manifestations - self-care options | |
| 4 | Stiffness – ability to stand and walk independently | |
| 5 | Complete immobility |
In practice, doctors distinguish 3 stages that play a key role when prescribing therapy:
- Partial loss of motor function.
- Partial loss of mental activity.
- Lack of coordination of movements.
Vascular parkinsonism
Vascular parkinsonism most often develops as a result of chronic cerebral circulatory failure, but it can also be a consequence of ischemic stroke. This type of parkinsonism is characterized by involvement of the lower extremities, early disturbances in walking and balance, absence of tremor, as well as a combination with other symptoms of chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency.
Peculiarities
Unlike classic, Hunt's juvenile parkinsonism has a number of differences:
- Extremely low likelihood of mental disorders - less than 0.2% of cases of juvenile parkinsonism.
- In the early stages there are practically no symptoms.
- During puberty, exacerbation or almost complete recovery - residual effects are possible: slight tremor of the hands. Slight disturbance of facial expressions during strong emotional experiences.
- Accelerated mental activity - a feeling of stretched time that does not correspond to the speed of thinking.
- Libido (sexual desire) is more pronounced than normal with appropriate hormonal levels.
- Contrived increase in pain.
Bibliography
- ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases)
- Yusupov Hospital
- Lutsky I. S., Evtushenko S. K., Simonyan V. A. Symposium “Parkinson’s disease (clinic, diagnosis, principles of therapy)” // Postgraduate education. — 2011. — No. 5 (43)
- Glozman Zh.M., Levin O.S., Lycheva N.Yu. Impaired emotional memory and recognition of emotional states in patients with Parkinson's disease. // Human Physiology, 2003. –N6. –P.55-60.
- Golubev V.L. ., Levin Ya.I., Vein A.M. Parkinson's disease and parkinsonism syndrome. M. Medpress, 1999, 415 p.
We work around the clock
Sign up for a consultation by phone or send a request via the feedback form
Causes
The main reason is congenital pathology: genetic predisposition to central nervous system pathologies; exposure to aldehydes, ephedrines, resins, fungi, heavy metal salts, potassium permanganate during pregnancy. (15-20% of cases depending on the environmental friendliness of food, atmospheric air and relative humidity).
Purchased:
- Injuries during pregnancy.
- Birth injuries.
- Excessive physical and or emotional stress.
- As a complication of meningitis, encephalitis.
- Abnormal development of neurons in the black zone of the brain is the progression of a gene of unknown etiology (cause).
- Taking anabolic steroids and other toxic drugs (drugs) before conception.
- Unqualified performance of cosmetic and physical procedures involving radiation or prolonged pain.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the affected area of the brain. Its manifestations intensify according to the stage:
- Tremor.
- Lack of coordination of precise movements.
- Involuntary muscle tension.
- Slow movements (the patient is unaware of their slowness).
- Slowing down speech without losing the coherence of the presentation of thoughts.
- Involuntary flexion of the limbs, inability to straighten them by volitional effort.
- Basically, there is a slowdown in the motor skills of the muscles of the fingers and feet.
Attention! In 80% of cases, the manifestation of juvenile parkinsonism is observed before the age of 25. 60% of pathology cases occur in wealthy families.
Diagnostic measures ↑
Just as in youth, childhood or adulthood, in order to establish an accurate and error-free diagnosis, a series of examinations is required, symptoms alone are not enough. First of all, the child should be examined by a neurologist; if there is a history of illness, the doctor suspects the possible presence of parkinsonism, he will refer him for instrumental examinations.
The following procedures may be necessary:
- ultrasound and Doppler examination of the vessels of the neck and brain;
- computed or magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, its vessels, as well as the cervical vertebrae;
- rheoencephalography of the head and spine;
- fluoroscopic examination of the cervical spine;
- a test to determine the body’s reaction to the use of levodopa medications.
Diagnostics
Until the age of 20, an experienced neurologist can make a general diagnosis based on external manifestations. If the patient is older than 20-25 years, an initial examination is not enough. A comprehensive examination is necessary to distinguish between the manifestations of juvenile parkinsonism and a number of diseases with similar symptoms: hepatic encephalopathy, encephalitis, supranuclear palsy, normal pressure hydrocephalus, early symptoms of autonomic failure.
| Diagnostic method | What determines | What does it mean for parkinsonism? |
| Neurological examination (physical method - percussion (tapping) of nerve nodes) | Speed of reflex reaction to external stimuli; rate of muscle tension and relaxation | High muscle tone; instability of the limb in a fixed position; slow reflex response to hammer tapping |
| Electroencephalography | The speed of signal transmission in the cerebral cortex; the degree of its functional activity | Decreased neuroactivity of the brain; akinetic-rigid form is diagnosed |
| Electromyography | Muscle fiber frequency and activity | Tremor – volley activity increases to 4-8 bursts per second; akinetic-rigid – asynchronization of activity |
| Magnetic resonance imaging | Disturbances in the structure of the studied area | To differentiate pathology from others - with similar symptoms; in later stages – underdeveloped cells of the “caudate nucleus” |
| positron emission tomography with fluorotope injection | The degree of functionality of brain tissue; if the drug accumulates quickly, the tissues do not need to use third-party substances | Slow accumulation of fluorotopes; diagnosis is possible in the early stages before the first symptoms appear |
| DNA analysis | Detection of a gene – diagnosis of both a disease and a tendency (genetic predisposition to it) | The parkin gene is detected; the type of inheritance is established (dominant, recessive) or a conclusion is issued about its absence |
Reference! A decrease in the level of synuclein or dopamine in the results of a biochemical blood test is not enough to make a diagnosis of juvenile parkinsonism. Deviations from the norm can be caused by a temporary dysfunction of the “caudate nucleus” of the cells of the substantia nigra of the brain. Only 20% of symptoms are characterized by asymmetry of movements.
Symptoms of the disease
Clinically, Parkinson's disease can be suspected in children based on symptoms and signs of impaired motor activity. The first thing that catches the parents’ eyes is tremor (shaking) of the hands at rest. At the same time, as soon as the child begins to make active movements, the trembling goes away. The motor activity itself is significantly slowed down, which is called bradykinesia syndrome.
Trembling in Parkinson's disease is most noticeable in the hands
Symptoms of Parkinson's disease in young people gradually progress, facial expressions become poorer: the face takes on a mask-like appearance, and it is impossible to track mood using it. This is not helped by the patient’s speech, which over time acquires a monotonous character that fades towards the end of the phrase; it is completely unemotional.
The gait takes on the appearance of small steps; if a sick young man is pushed a little, it will be difficult for him to stop; by inertia he will move in the direction of the push. This phenomenon is called propulsion; the patient seems to catch up with his own center of gravity, displaced by the push.
Autonomic disorders may occur. They manifest themselves as symptoms of impaired urination, defecation, possibly increased oily skin, seborrheic dermatitis and other manifestations.
On neurological examination, the most important symptom is muscle rigidity and high tone. The sign is checked with a positive Noika symptom.
Treatment
It is impossible to completely cure juvenile parkinsonism. Until the age of 13, it is possible for the disease to go into long-term remission - absence of symptoms until 55-70 years of age. To increase the effectiveness of therapy, an integrated approach is used: medications. Physiotherapy. Massage, folk remedies. If drug therapy is ineffective, surgical intervention is performed.
Medicines
The main goal of drug therapy is to increase dopamine levels in the cerebral cortex. The most effective drug is levodopa, a synthetic levorotatory isomer of dopamine. Since dopamine reacts with carbon compounds, there are drugs in the complex that slow down its breakdown - benserazide, carbidopa.
They try to delay the prescription of levodopa before the age of 70 due to addiction, toxic load on the liver, and stiffness of movement.
In the early stages, treatment begins with amantadine derivatives or other drugs that increase the sensitivity of dopamine receptors.
Physiotherapy
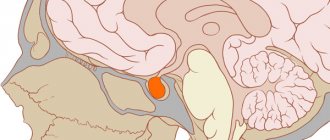
The highest efficiency of electrical stimulation of deep brain structures is the suppression of the activity of cells of the caudate nucleus.
Surgical intervention
The following operations are carried out:
- Talanotomy – destruction of the ventral nucleus of the thalamus (part of the brain): performed only for tremor; efficiency 96%.
- Delivery of Levodopa directly to the area of impaired innervation using a duodenal pump.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are divided into 2 groups:
- Calming - for internal use, for massage.
- To maintain the functioning of internal organs and the endocrine system, juice therapy.
For 200 ml of boiling water, 0.5 tsp. Melissa, mint, chamomile. Boil for 2 minutes in a water bath. Switch off. Do not remove from the water bath. Allow to cool to a comfortable temperature. Strain. Sweeten with honey. Drink instead of tea. Calming collection.
For 0.5 liters of cold water, 150 g of flax seeds. Leave for an hour. Stir. Boil. Add 150 g of honey. Drink in 3 doses. Stimulates the functioning of internal organs. Protects the stomach lining.
For 200 g of boiling fat, 2 tbsp. l. Fresh crushed mint, valerian leaves, chamomile. Quickly add the herbs to the boiling fat. Mix. Switch off. Allow to harden naturally at room temperature. Melt in a water bath until warm. Strain through thick cheesecloth. Keep in a cool place. Use no more than 0.25 tsp for a soothing massage. For the face; 1 tsp. For limbs and back.
Massage
The session should last no more than 10 minutes. 50% - soothing strokes; 25% light pressure with the tips of the index fingers - stimulation of problem areas; 25% - circular movements with the index finger along the problem muscle - normalization of blood circulation.
- Stroking.
- Pressure.
- Circular rotations.
- Stroking.
Carefully! If any movements are unpleasant for the child, replace them with others of similar effectiveness. Massage eliminates pain.
Segawa disease
Segawa's disease, or JP dystonia, or DOPA-dependent dystonia, is dystonia in children combined with parkinsonism syndrome. Etiology - mutations of genes involved in dopamine biosynthesis.
The pathology is characterized by slow progression and onset in children with local dystonia under the age of 10 years. At the beginning, rigid-hypokinetic syndrome predominates, gradually the disease invades new areas of the body. Fluctuation during the day is typical. The clinic can be divided into three groups of disorders: pyramidal disorders (contractures, foot clonus, paraparesis, hyperreflexia); extrapyramidal (tremor, bradykinesia, torticollis, chorea, dystonia) and psychotic disorders (learning problems, emotional disturbances). Dysarthria, scoliosis, sleep disorders, and cauda equina may occur.
Complications
The main complication is the progression of the disease, the transition from stage to stage. If dopamine is not artificially replenished, the disease goes through all stages in 3-5 years without nervous shock in 6-15 months under strong emotional stress.
Other complications:
- Chronic constipation – atony (slow peristalsis) of the intestines.
- Melancholy.
- Stagnation of digestive secretions; hypomotor dyskinesia of the gallbladder.
- Salt deposits at an early age.
Prognosis and prevention
With congenital pathology, there is a 75% chance of the disease going into a long period of remission. After 13 years – 50%. Acquired – after 15 years – 50% chance of avoiding complete loss of mobility until age 50.
There are no preventive measures for congenital pathology. You can slow down the development of the disease by following a few simple recommendations:
- The diet contains a minimum of protein; salt no more than 10 g per day.
- Avoid alcohol and smoking.
- Walking, gymnastics, and moderate mental stress are required.
- Avoid stress, hypothermia; do not be near infected patients (including influenza).
- Soothing massage 3-4 times a week.
- Do not protect the child from peers (inferiority complex - depression).
Patients need to be involved in social activities, feasible physical activity, and taught to adequately perceive the problem. Food is prepared according to the body's needs. In the presence of the patient, eat the same food.
You cannot overload such people with sports. Show their exclusivity for the family. Girls and teenagers should not wear high-heeled shoes - sudden foot tremors and injuries are possible.