Characteristic
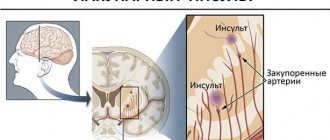
The pituitary gland is a small gland that belongs to the endocrine system and is located in the skull. This is a kind of extension of the brain. The pituitary gland is located in the sella turcica, a notch that is surrounded by bones that provide protection.
Pituitary microadenoma up to 1 cm in size is a benign tumor. Often there are no symptoms.
The first signs attract attention if the neoplasm is involved in the secretion of one of the hormones.
In this case, after specifying the size and localization of the pathology, surgical or radiation treatment is prescribed.
The pituitary gland is one of the most important organs of the endocrine system, regulating the functioning of the peripheral endocrine gland.
Surgery to remove a brain tumor
According to statistics, brain tumors occur in 5–8 percent of all cancers.
The main hormones for which this organ is responsible are:
- Somatotropic.
- Thyroid-stimulating.
- Luteinizing.
- Prolactin.
- Oxytocin.
- Adrencorticotropic.
- Vasopressin.
- Melanocyte stimulating.
- Follicle stimulating.
Microadenoma differs from adenoma only in its size and nothing more. New growths more than 1 cm in diameter are an adenoma; if the tumor is smaller, then it is a microadenoma. For what reason the pathology occurs, medicine cannot fully explain. True, there are some risk factors that experts know.
About the organ
The pituitary gland of the brain is an endocrine gland of complex structural content , which is localized in the subcortical part of the organ. It has rounded outlines and is under reliable protection of the bony frame of the head. It consists of two lobes, with the anterior one being four times larger than the posterior one.
The main function of the organ is the production of the hormones oxytocin and intracranial antidiuretin, which controls the concentration of fluid in the human body.
Causes
The main known risk factors and causes of pituitary microadenoma include:
- open and closed head injuries
- infectious diseases of the nervous system in acute and chronic form;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs;
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- pathologies during pregnancy .
Also, in some cases, the disease occurs for still unknown reasons.
Frequency of occurrence
The incidence of pituitary microadenoma is approximately 15% of all cases of brain tumors. There are no more than 2 cases of the disease per 100,000 people. It usually occurs in women. However, the latent course of the disease leads to the fact that it is not detected in all cases, therefore statistical data are considered to be underestimated.
Prolactinoma is one of the types of pathology that occurs in half of all cases of tumor processes in the pituitary gland.
Types of disease
Microadenoma is divided according to its structure:
- cystic;
- homogeneous.
How to identify a brain tumor
Oncological diseases, being the most difficult to detect and difficult to treat, make up more than 30% of the total number of pathologies that can lead to death.
Histologists also distinguish the tumor according to its staining:
- basophilic shows color when exposed to a dye with a high pH level;
- acidophilus acquires color when stained with dyes with a low pH;
- chromophobic is difficult to stain.
There is also a mixed type - acidobasophilic.
Adenoma is also classified according to hormonal activity:
- non-secretive;
- hormonally active.
Non-secreting pituitary microadenoma does not differ in working activity, that is, it does not produce hormones and does not negatively affect the functionality of various organs.
A hormonally active adenoma tends to secrete normal hormones, and if too much of them is released, the development of various endocrine diseases may begin.
Based on the development of a particular hormone, neoplasms are divided into:
- gonadotropinomas;
- prolactinoma (manifests most often);
- mixed;
- corticotropinomas;
- thyrotropinomas;
- somatotropinomas.
Symptoms of a pituitary microadenoma can only appear if it is of the secreting type, that is, it secretes hormones.
Symptoms
According to statistics, every tenth tumor causes disruption of the endocrine system. This may manifest itself as follows:
- weight gain up to severe obesity;
- high pressure ;
- stretch marks , which are observed in the chest and abdomen;
- changes features , some deformation;
- enlargement of feet , fingers;
- dry mouth;
- disruptions in the menstrual cycle;
- infertility;
- release of colostrum from the mammary glands;
- sexual dysfunction in men;
- decreased libido .
Tumor on the head in the form of a lump
The appearance of a bump on the scalp is not immediately noticed; only when it reaches a fairly decent size does it reveal itself.
It is worth considering that all symptoms can appear simultaneously or partially, it all depends on the characteristics of the patient’s body, the course of the disease or at what stage it is.
External manifestations of pituitary microadenoma GH in the secreting pore:
- enlargement of some facial features;
- thickening of lips;
- increase in body volume and loss of strength;
- muscle degradation;
- arrhythmia;
- hypertension;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- thirst.
In this case, radical treatment is used in the form of surgery or radiation therapy. After this, all signs of pathology become minimal or completely eliminated.
ACTH microadenoma has the following symptoms:
- increased blood sugar
- noticeable external changes in the patient’s figure;
- stretch marks on the skin;
- increased growth of facial hair in females;
- dyspnea;
- increased blood pressure.
Pituitary microadenoma does not cause the secretion of LH, TSH, FSH. Such rare pathologies most often cause disorders in the thyroid gland and genital organs.
Diagnostics
Pituitary microadenoma can be initially diagnosed by any doctor, most often the examination is carried out by a therapist or endocrinologist. Also during pregnancy, a gynecologist may suggest undergoing pathology diagnostics.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
The examination to detect the disease has two stages:
- examination for the presence of tumors in the brain ;
- assessment of the hormonal state of the body.
How long do you live with a brain tumor?
A brain tumor is a neoplasm inside the skull that develops due to pathologically rapid cell division.
The main and main method for diagnosing pituitary microadenoma is magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography. These two types of diagnostics help to identify a tumor and determine its size.
It is also recommended to take tests for all types of hormones. Assess the situation related to visual reflexes, which are checked by an ophthalmologist. The adenoma can put pressure on the optic nerves.
Complications
If the situation is ignored and treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, the disease can lead to serious complications:
- impaired visual function - up to the development of blindness due to a tumor that is too large;
- risk of cerebral hemorrhage followed by apoplexy;
- infertility;
- impotence;
- sexual disorders;
- nervous breakdowns and mental instability.
Adenoma and pregnancy
During the period of gestation, almost all methods of therapy are unacceptable. The only thing that remains is strict control over the condition of the pregnant woman’s body.
Regular examination of general condition, study of hormonal levels, visual indicators - such examinations should be carried out regularly. In addition, an MRI of the brain is performed every three months.
Non-surgical treatment
Currently, pituitary microadenoma has several treatment methods:
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
- operational;
- medicinal;
- ray;
- combined.
Which therapy is chosen depends on the size of the tumor and its hormonal activity. In general, specialists prefer conservative treatment for this pathology. The following disturbances may occur due to the size and rate of increase:
- stressful state;
- insomnia;
- hormonal disorders.
Once these problems are resolved, the adenoma's growth most often stops and the tumor may shrink.
It is especially worth considering cases when the patient is taking antipsychotics or other medications that increase prolactin levels. Such treatment can lead to the growth of tumors, and therefore in some cases they try to replace them or exclude them from therapy.
In addition to treatment, specialists try to choose the right weight loss system and improve metabolism, since all pathologies associated with the pituitary gland contribute to the appearance of obesity.
Treatment for adenoma should begin immediately after diagnosis of the disease. Asymptomatic tumors do not require complex treatment, but it is necessary to periodically monitor the tumor so that it does not increase. To do this, an MRI is performed once a year and regularly meets with an endocrinologist.
Contraindications for MRI of the pituitary gland
Although MRI diagnostics is a progressive and safe technique, there are several absolute contraindications to its implementation.
MRI is not performed if:
- presence of a pacemaker;
- the presence of any metal devices in the body: prostheses, vascular clips. The exception is devices made of titanium, since this metal is inert to the effects of a magnetic field.
MRI of the pituitary gland cannot be performed in the following categories of patients:
- women in the 1st trimester of pregnancy;
- children under 5 years old;
- very plump people whose weight exceeds 130 kg.
Surgery
Surgery is recommended in cases where conservative therapy is ineffective. Basically, the first indicator for surgical treatment is tumor growth. If the tumor is small, craniotomy is not performed; the endoscopic method is used. In this case, the tumor is removed through the nasal passage.
This operation does not provoke major complications and guarantees a short rehabilitation period. Most often, patients do not stay in the hospital for more than three days.
Modern medicine offers radiosurgery. This method very quickly became popular, since the microadenoma is removed without surgery. A radio scalpel is radiation collected in a beam that specifically affects the tumor itself. The accuracy of removal is controlled using MRI and CT.
This operation can be performed on an outpatient basis. After the tumor has undergone irradiation, it begins to shrink and the patient does not experience any discomfort. If the neoplasm produces hormones, then additional medications are prescribed that are responsible for correcting hormonal levels.
Pituitary microadenoma and pregnancy
With an inactive tumor, conception is completely permitted, but throughout the entire period the woman must monitor her hormonal levels and be sure to have an MRI done to know the size of the tumor.
If the doctor recommends removing the adenoma, then it is better to do this to avoid negative consequences. In many cases, pregnancy is the cause of tumor growth.
If the tumor is hormonally active, then drug treatment or surgery is prescribed. If a girl suffers from prolactinoma, then pregnancy will have to be postponed for a year.
This is how long the treatment will take. And even after conception, you will have to constantly monitor the size of the tumor and the patient’s hormonal levels. It is advisable to exclude breastfeeding with pituitary microadenoma.
Pituitary gland microadenoma
If the disease occurs in the pituitary gland, then symptoms develop with intensive tumor growth: a severe headache occurs, the patient suffers from “epileptic seizures,” and excess weight appears, as with any other type of pituitary microadenoma.
Such signs are characteristic of a disease without hormonal activity. If the tumor produces hormones, gigantism or dwarfism may occur.
Danger
If a tumor is detected at the initial stage, then it does not pose a danger; if there are signs of hormonal activity of the tumor, then the doctor will prescribe adequate treatment. If a microadenoma grows, there is a danger of its pressure on tissues and nerves.
The most dangerous neoplasms of this type are considered to be enlarging and untreated adenomas with hormonal activity. In this case, irreversible changes in internal organs may occur, which are caused by hyperfunction of thyroid and adrenal hormones.
Secondary hypertension or emerging diabetes sooner or later leads to life-threatening consequences that can be fatal for the patient.
Also, if you do not receive treatment on time, you may experience vision problems and major complications after surgery to remove large adenomas, which can lead to infection or brain injury.
Myth. It is very difficult to detect a pituitary tumor.
In fact. Diagnosis of pituitary adenomas is well established and includes: hormonal and ophthalmological examinations, as well as neuroimaging of the tumor (X-ray, MRI, CT scan of the brain). With their help, specialists can determine the type and size of the tumor.
The presence and degree of hormonal activity of a pituitary adenoma is detected using modern methods for assessing the level of hormones in blood plasma or urine (saliva). Each tumor has its own set of necessary studies, which is determined by the doctor depending on the clinical picture (symptoms and complaints of the patient).
Consequences
Microadenoma with rapid growth can lead to the following consequences:
- Blindness . Near the pituitary gland there is a place of intersection of the optic nerves, which are each responsible for its own eye. If compression occurs in this area, then the patient’s vision deteriorates and its acuity disappears.
- Smell disorders .
- Headache caused by tumor pressure on the brain. Most often, discomfort occurs in the forehead, temples, and under the eyes. The pain is constant, regardless of the position of the body or the use of painkillers.
During the growth of an adenoma, elements of the pituitary gland come under pressure, which leads to its failure, which is manifested by the following conditions:
- Infertility in women and decreased sexual function in men, both sexes notice a decrease in libido.
- Low production of thyroid-stimulating hormone, which leads to hypothyroidism, and this threatens constant edema, obesity, depression, and loss of strength.
- The occurrence of insufficiency , which leads to hypotension, gray skin color, and can cause death.
- Reduced secretion of growth affects short stature, inhibition of puberty, and decreased muscle tone.
- Severe dizziness .
- Neuralgia in the head area.
- With strong growth, a microadenoma can compress the hypothalamus, which leads to a constant feeling of hunger , changes in body temperature, and insomnia.
Other complications are also observed.
Prolactinoma can lead to:
- disruptions in the menstrual cycle;
- lack of milk during lactation;
- decreased testosterone ;
- facial hair loss
- mood swings ;
- fat deposits in the chest area.
Somatotropinoma has the following symptoms:
- gigantism;
- rough, heavy facial features;
- acromegaly.
Corticotropinoma leads to:
- development of Itsenko-Cushing's disease;
- stretch marks on some parts of the body;
- weight gain;
- moon-shaped face;
- facial hair growth in women.
Thyrotropinoma can cause hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, which is characterized by:
- weight loss;
- tachycardia;
- high appetite;
- mood swings;
- bad dream.
Gonadotropinoma enhances the functionality of the testicles and ovaries, which can lead to oncology in this area.
To sum up all the consequences of pituitary microadenoma, it can lead to obesity, gigantism, weight loss, hyper- or hyposexuality, heart problems, infertility, impotence, and migraines.
Forecast
Most often, a tumor found in the pituitary gland is given a positive prognosis, since small microadenomas are easier to treat than large tumors, which can lead to pressure on nearby structures. If a specialist suggests surgery, the patient should not panic, but rather agree. This is due to the fact that removal is less dangerous than a growing tumor.
If the microadenoma does not manifest itself in any way, then you should not change anything during your normal life and carry out drug treatment. But at the same time, do not forget to periodically visit a doctor and conduct an MRI in the head area once a year.
Pathology prognosis
After timely therapy, with early detection of the disease, pituitary microadenoma is completely eliminated with medications or other surgical methods. In 90% of cases, correctly prescribed treatment relieves patients of the disease once and for all.
However, in any case, a person who has been diagnosed with a tumor must register with the oncology department of the clinic. Regular check-ups with a doctor are recommended - at least once every six months, since any tumors tend to recur within 5 years after removal.
Pituitary microadenoma is a mild tumor pathology that is treatable. With a favorable course, it does not cause discomfort to the patient, but at any moment it can degenerate into a macroadenoma or a malignant neoplasm, which is life-threatening. This is why it is important to diagnose and treat any brain tumor promptly.