What is rheumatic chorea?
According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), rheumatic chorea is a neurological disorder that affects only children and is a complication that can develop during or after infection with group A beta (β)-hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS).
, which can also cause
rheumatism
. According to NINDS, the disorder is more common in girls than boys and disproportionately affects children between the ages of 5 and 15.
Most children make a full recovery. Symptoms last on average 3-6 weeks, although in some cases they can last for several months.
Causes
The cause of the primary forms of pathology lies in genetic disorders. Certain chromosomal defects cause damage to various neurons of the basal ganglia and, ultimately, the development of one of the variants of primary chorea.
The following factors can lead to the development of secondary forms of the disease:
- infections: whooping cough;
- meningitis;
- borreliosis;
- viral encephalitis;
- neurosyphilis;
- HIV;
- multiple sclerosis;
- hypo- or hyperglycemia due to diabetes;
- neoplasms;
- atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
Video: the nature of hyperkinesis
Rheumatic chorea - symptoms
According to a 2021 review, symptoms of CC appear 4-8 weeks after GABHS infection. Symptoms of CC may appear suddenly or gradually during or shortly after infection, but may occur up to 6 months after symptoms of infection and fever have resolved.
Neurologists divide the symptoms of CC into neurological
, which typically involve movement and balance problems, and neuropsychiatric symptoms that affect behavior and cognition.
Symptoms of CC include:
- erratic, involuntary movements, mainly of the shoulders, hips and face
- inability to remain stable
- twitching movements of the eyeballs
- decreased muscle tone
- motor tics
- clumsiness
- weakness
- difficulty pronouncing words
According to the National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD), sudden movements tend to be worse on one side of the body.
Neuropsychiatric symptoms of CC may include:
- rapid mood changes
- the child is easily distracted and irritated
- anxiety
- age regression, return to a younger state of mental development
Symptoms of the disease
Usually the disease begins to manifest itself a few weeks after a sore throat or tonsillitis. The main symptom of any type of chorea is hyperkinesis, i.e. muscle contractions performed against the will of the patient, causing uncontrolled movements of various parts of the body. This occurs due to damage to the central nervous system.
In general, the picture of the manifestations of the disease looks like this:
- The child constantly makes faces, grimaces or sticks out his tongue.
- When drawing or writing, his hand twitches spontaneously, so the lines come out crooked, the writing goes off the line, etc.
- Extreme restlessness.
- Decreased muscle tone.
- The desire to touch something with your hands, to scratch yourself.
- Cold hands and feet, the skin of which turns blue.
- Often – low blood pressure.
- A state of hyperactivity or, conversely, lethargy.
- Changes in character: anxiety, touchiness, capriciousness.
- Speech disorders: shouting out words, sounds (with spasm of the laryngeal muscles) or loss of speech, difficulty pronouncing words.
Chorea minor is characterized by dysfunction of the neuromuscular connections, which allows the use of three types of movements as tests for the presence of the disease.
- If you ask a patient to stick out his tongue with his eyes closed, he will not be able to do it.
- If you ask him to raise both arms up and put his palms together, he will only be able to lift them with his palms facing out.
- If you lift a child by the shoulders, he automatically pulls his head tightly into his shoulders.
Rheumatic chorea - causes
According to a 2021 article, rheumatic chorea
is an autoimmune response to infection. The bacteria prompt the body to produce antibodies to fight the pathogen. However, once antibodies defeat an infection, they can remain active for too long and mistakenly attack healthy organs. If antibodies begin to attack the basal ganglia cells in the brain, symptoms of CC appear.
According to NORD, researchers don't know exactly why antibodies attack the brain. Scientists believe that the GABHS antigens that activate the body to produce antibodies are very similar to the basal ganglia antigens.
Treatment of types of chorea
Treatment of chorea is carried out under the guidance of a neurologist. The main way to prevent violent movements is to prescribe appropriate medications.
Drug therapy for types of chorea
Pharmacological treatment of varieties of chorea varies somewhat depending on their nature. Chorea in pregnancy imposes significant restrictions on the choice of drugs. In this case, the benefit to the mother and the risk to the fetus are carefully weighed.
Drugs for the treatment of chorea - photo gallery
Voltaren contains diclofenac
Clonazepam is an effective anticonvulsant
Rosuvastatin reduces blood cholesterol levels
Phezam is a combined metabolic drug
Prednisolone is one of the most powerful anti-inflammatory drugs
Bicillin is used to prevent relapses of rheumatism
Drugs for the treatment of chorea - table
| Group of drugs | Mechanism of action | Examples of drugs | Indications for use |
| Antibiotics | elimination of bacteria |
| Sydenham's chorea (rheumatic) |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | elimination of foci of inflammation |
| rheumatic chorea |
| Steroid hormonal drugs | decreased inflammatory activity |
| chorea |
| Anticonvulsants | elimination and prevention of violent movements |
|
|
| Anticholesterol drugs |
|
| senile chorea |
| Metabolic drugs | activation of metabolism in nerve cells |
|
|
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods have a beneficial effect on the activity of nerve cells. The following types of procedures are prescribed:
- electrosleep. A specific type of electricity of a certain frequency and form normalizes the activity of various parts of the brain;
The electrosleep apparatus uses specially shaped electrical impulses
- radon baths strengthen the immune system and normalize metabolism in nerve cells;
- galvanization effectively affects the functioning of nerve cells, including the basal ganglia;
- pine baths are an effective combination of water treatments and aromatherapy.
Traditional treatment for chorea is not provided, as it can aggravate the symptoms of the disease.
Rheumatic chorea - treatment
There are three types of treatment tactics.
Secondary prevention
According to a 2021 article, doctors will first treat the GABHS infection to reduce the risk of rheumatic heart disease with antibiotics. If symptoms of rheumatic chorea appear, doctors may also prescribe additional medications to control neurological and neuropsychiatric symptoms. Drug therapy helps reduce the likelihood of neurological disease and permanent damage to the heart valve.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), some children must continue to take antibiotics for several years, and in some cases until adulthood.
Treatment to suppress chorea symptoms
Although the effectiveness of symptomatic treatment requires more research, doctors may prescribe valproic acid
to control disturbing involuntary movements.
For some behavioral and psychiatric symptoms, doctors may prescribe antipsychotic medications, such as risperidone. Taking risperidone or other antipsychotics may increase your chance of developing tardive dyskinesia
, a disorder that involves sudden, involuntary movements. However, according to NORD, this rarely happens.
Another treatment with fewer side effects is tetrabenazine
, which is a dopamine-destroying agent. However, health professionals are not yet sure how effective it is for this disorder.
Immunotherapy
Doctors may prescribe short-term immunotherapy to help reduce the autoimmune response during the first weeks. Some doctors believe that ongoing acute inflammation is a contributing factor to symptoms. However, to date there is little research to show that this works.
Treatment
In the acute period, bed rest is indicated. Hyperkinesis is eliminated with the help of drugs such as benzodiazepines and sodium valproate. In severe cases, the use of corticosteroids is indicated.
Causal treatment of chorea in children is aimed at eliminating rheumatism.
The information presented in this article is intended for informational purposes only and cannot replace professional advice and qualified medical care. If you have the slightest suspicion that your child has this disease, be sure to consult a doctor!
Rheumatic chorea - diagnosis
There is no specific test that allows doctors to identify people with CC. When diagnosing, doctors evaluate a person's symptoms, including muscle movement and heart function. Doctors may order blood tests to rule out other diseases and conditions that may cause similar symptoms. Doctors may also order MRI, PET scans, and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), which focus on the basal ganglia. Doctors may also order cardiac tests, including ECG and echocardiography.
Doctors can diagnose rheumatoid chorea based on imaging of the basal ganglia. Although other conditions can also affect the basal ganglia, CC presents with certain symptoms.
Clinical manifestations
The general symptoms of the disease are quite clear. The disease can manifest itself differently in each individual case. The main symptoms of minor chorea disease include hyperkinesis (involuntary movements).
There is the appearance of chaotic muscle contractions that occur randomly and which the child is unable to control.
At the beginning of the disease, hyperkinesis is hardly noticeable. Parents do not perceive grimacing, awkwardness of hands, or unsteady gait as a reason to seek the help of a specialist.
Over time, hyperkinesis becomes more noticeable. They usually occur during excitement. If manifestations of the disorder are ignored, movement disorders become more complicated. They become pronounced, up to a choreic storm - a paroxysmal occurrence of uncontrolled movements in the entire body.
What is especially worth paying attention to?
Handwriting of a child diagnosed with chorea minor
There are a number of symptoms that should be alarming. The initial manifestations of the disease are perceived by many parents as banal antics. But timely detection of pathology is the basis for successful therapy. The main warning signs of minor chorea include:
- Awkward movements while drawing or writing . The child is not able to hold a pencil; if he writes, then only clumsy, disproportionate letters are obtained.
- Uncontrolled frequent grimacing.
- Restlessness . The baby is unable to sit in one place; he constantly scratches himself and twitches different parts of his body.
- Involuntary shouting of different sounds (due to involuntary contraction of the muscles of the larynx).
- Blurry, confusion of speech . In some cases, tongue hyperkinesis provokes the appearance of choreic mutism (complete absence of speech).
In addition, the disease is characterized by:
- decreased muscle tone;
- psycho-emotional disorders (anxiety, moodiness, touchiness, tearfulness).
There are several neurological manifestations that are characteristic only of this disease, which a neurologist will definitely pay attention to during examination:
- Symptom of “flabby shoulders” - when lifting a small patient by the armpits, the head will sink into the shoulders, as if drowning in them.
- Pronator syndrome . If you ask a child to raise his arms and bend them slightly (so that the palms are facing towards the head), in a sick child they will still turn outward.
- “Chameleon tongue” - a child cannot keep his tongue sticking out of his mouth with his eyes closed.
- Gordon's syndrome - when testing the knee joint reflex, the patient's lower leg will freeze in the extension position for three to five seconds, and then slowly return to its place.
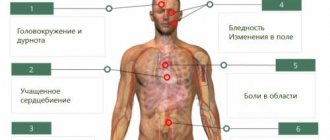
In almost all cases, the pathology is characterized by autonomic disorders: cyanosis of the feet and hands, coldness of the extremities, marbled coloration of the skin, irregular pulse, and a tendency to low blood pressure.
Moreover, a third of children who have had the disease may subsequently develop heart defects.
Rheumatic chorea - differential diagnosis
Rheumatic chorea
has similar symptoms to PANDAS syndrome and Huntington's disease.
PANDAS syndrome
PANDAS syndrome stands for pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorder associated with streptococcal infection.
According to the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), PANDAS syndrome
manifests itself in the following conditions:
- obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
- attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- nervous tic
- personality change
with PANDAS syndrome , according to NIMH
, If:
- OCD, tics, or both appear after a streptococcal infection such as pharyngitis or scarlet fever
- OCD or nervous tics worsen after streptococcal infection
Similar to rheumatic chorea, the body responds to a streptococcal infection with antibodies that end up attacking the brain, mistaking it for bacteria. Just as with CC, children with PANDAS syndrome
may have sudden, involuntary movements.
A history of rheumatic chorea increases the likelihood that the child may later develop PANDAS syndrome
.
Huntington's disease
Huntington's disease presents with a number of symptoms similar to rheumatic chorea. According to NINDS, symptoms include:
- changes in behavior and emotions
- sudden movements
- slurred speech
However, unlike PC and PANDAS syndrome
, Huntington's disease is an inherited disorder, and symptoms usually begin in adulthood.
People with Huntington's disease have a mutation in a protein called huntingtin
. This makes the protein toxic, leading to the death of brain cells, or neurons, resulting in symptoms.
Unlike CC, there is currently no cure for Huntington's disease; it is a progressive disease, and it often progresses rapidly in people with Huntington's disease. Most people with this diagnosis will live 10-30 years after the first symptoms appear.
Diagnostics
To diagnose chorea in a child, a medical history, general and neurological examination, laboratory and instrumental tests are carried out.
In differential diagnosis, it is important to distinguish chorea from hysteria. Hysterical movements differ from choreic ones in their rhythmicity, systematicity, stereotypy and the presence of a psychogenic moment when they occur. In addition, there are other stigmata of hysteria. The diagnosis of hysteria is made easier in the presence of other similar cases or epidemics, for example, in schools, dormitories, which sometimes follow the illness of one of the children with real chorea. With generalized tics, calm pauses between violent movements, systematization, stereotypy of movements, echokinesia, echolalia, coprolalia, and obsessive ideas are observed; the disease usually develops after mental trauma and has a chronic, gradually increasing course.
Epidemic encephalitis localized in the neostriatum may be expressed as choreic hyperkinesis, and sometimes it is very difficult to differentiate this form of encephalitis from chorea. In the diagnosis of epidemic encephalitis, damage to the eye muscles, cranial nerves, drowsiness, inflammatory changes in the fluid, the presence of epidemic encephalitis, high fever, change of various forms of hyperkinesis - choreic, athetotic, change of hyperkinesis with akinesis help.
Rheumatic chorea - complications
Associated complications of CC:
- arthritis
- joint pain
- inflammation of the heart valves leading to irreversible damage
- ongoing fever
Symptoms of CC usually last from 3 weeks to 6 months. And although almost everyone recovers, symptoms can persist for up to 2 years.
RH can recur, according to NORD, young women in the first trimester of pregnancy have a higher chance of experiencing symptoms of recurrent rheumatic chorea.
Signs of chorea
All types of chorea have one common feature - the appearance of violent movements in the skeletal muscles. The remaining symptoms differ somewhat in the minor, senile varieties and Huntington's chorea.
The British say that a child with chorea has to be punished three times before a diagnosis can be made: once for being restless, once for breaking dishes, and a third for making faces at his grandmother.
A. S. Nikiforov, A. N. Konovalov, E. I. Gusev
Clinical Neurology 2002
Signs of chorea - photo gallery
Chorea most often affects the facial muscles
With all types of chorea, gait changes
Huntington's chorea is a progressive disease
Symptoms of various forms of chorea - table
| A type of chorea | Minor chorea (Sydenham's chorea) | Chorea of pregnancy | Huntington's chorea | Senile chorea |
| Symptoms of damage to the basal ganglia | ||||
| Changes in gait and voluntary movements of the arms and legs |
|
|
| |
| Changes in facial expressions and speech |
|
|
| |
| Changes in the nature of muscle tension (tone) in a calm state | muscle tone is reduced | stiffness when moving the trunk and limbs | muscle tone is reduced | |
| Mental and emotional disorders |
|
| not typical | |
Symptoms
To begin with, it is worth noting that rheumatic chorea comes in different types. The symptoms a person will experience directly depend on this. In particular, the disease comes in the following forms: latent, subacute, recurrent, and acute. In the first situation, symptoms may be very mild or completely absent.
At the same time, the subacute and acute forms are most clearly manifested, so the signs of minor chorea will be difficult to miss. As for the recurrent type, it is characterized by outbreaks of pathology. At the same time, the child becomes better, then worse again.
It is definitely worth considering the symptoms of minor chorea so that the disease can be suspected in a timely manner:
- Involuntary movements, as well as muscle contractions that the child cannot control.
- A noticeable decrease in muscle tone, weakness.
- Increased activity of facial expressions. With minor chorea, the child will often grimace.
- Inability to remain in one position for a long period of time.
- It is difficult for the patient to perform even simple manual actions.
- Mental and emotional disorders. With minor chorea, the child may be too aggressive, capricious, and often have difficulty falling asleep.
- Inability to fix your gaze on one point.
- During excitement, the minor will begin to pull himself, scratch himself, or perform other similar manipulations.
- When the muscles of the larynx are tense, caused by chorea minor, the child may make strange sounds and even wheezing.
- Unexpected speech therapy problems. It may happen that the child will not be able to speak.
- Gait disturbance with chorea minor is considered a natural symptom. The child will not be able to move normally, he will jump.
- A sharp increase in body temperature to 38 degrees.
Doctors note that rheumatic chorea can be suspected based on basic symptoms. The child will have problems with gait, facial expressions will change, as well as handwriting. In this case, you should consult a doctor, then the doctor will be able to confirm the presence of Sydenham's chorea.
Affected Populations
According to most studies, rheumatic chorea affects girls more often than boys. The disease usually develops in children aged 5-15 years, most often after a streptococcal infection. One of the hallmarks of chorea minor is that it almost never occurs in children under 5 years of age. Rarely, the disorder has been reported in adults. Rheumatic chorea affects people of all races and nationalities.
The disorder can occur as a complication of rheumatism. About 25 percent of people with rheumatic fever develop chorea. Rheumatism is common in developing countries. Chorea minor is the most common cause of acute chorea in childhood. Rheumatic chorea remains a major public health problem in many developing countries, mainly due to cases of heart valve damage.
How to get rid of chorea?
Currently, thanks to modern capabilities, specialists practicing in the field of neurology are able to find out in advance about the onset of the described disease without the presence of pronounced problems in the patient. To do this, you will need to undergo a study and visit a qualified neurologist or geneticist. Treatment of chorea minor:
- Taking sedative medications and immunosuppressants.
- The use of hormonal pharmacological agents, as well as components with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects.
- Medicines are prescribed to improve sleep, have anticonvulsant effects and antipsychotics.
Huntington's chorea
This type of disease is hereditary. The first symptoms appear, as a rule, between 25 and 50 years. Manifestations of the disease are:
- Choreic hyperkinesis of a relatively slow pace (irregular and sharp twitching of the limbs or torso);
- Progressive decline in intelligence;
- Emotional instability.
In the case of Huntington's disease, the prognosis is unfavorable, that is, the disease cannot be cured.