Exercises to treat spasticity after stroke
Relieving spasticity after a stroke turned out to be extremely difficult. The point is a contradiction that arises. We stubbornly restored strength and endurance. They did this with the help of special exercises with high loads and a lot of repetitions. For the treatment of spasticity, this is a hindrance and harm. When relieving spasticity, you need a relaxing massage and light movements in the exercises.
To continue recovery after a stroke, it is necessary to carry out mutually exclusive activities. Quite a puzzle. But we came up with a simple solution. Make two groups of classes. First: to restore strength and endurance. The second is for treating spasticity, restoring balance and coordination. The decision turned out to be very correct.
It became harder to do the exercises. Fatigue has increased. Pain in muscles and joints appeared. This made us realize that we were doing something wrong. The error was corrected by dividing classes on different days. We started with exercises to relieve spasticity of the fingers.
-perform while sitting, with your right hand.
-we relax the left hand and hold it without movement in a comfortable position.
At first she was also tense. This needs to be controlled and relaxed.
- alternately touching the tip of the thumb with the tips of the remaining fingers.
-touch the tip of the thumb in order: index, middle, ring and little fingers.
-without pause we continue touching in the opposite direction.
-touch the tip of the thumb in reverse order: ring, middle and index.
-20 reps x 3 sets.
-We make movements slowly, smoothly and precisely. We do not strain our hand, the touch of our fingers is barely perceptible.
-perform while sitting, with your left hand.
-we relax the right hand and hold it without movement in a comfortable position.
-perform while sitting, with your left and right hands at the same time. Synchronously.
- alternately touching the tips of the thumbs on both hands with the tips of the remaining fingers.
-We make movements slowly, smoothly and accurately. We don’t strain our hands, the touch of our fingers is barely noticeable.
The exercises seem simple. Despite this, they must be done with concentration and attention. The option of combining it with watching TV is no longer necessary. Any distraction prevents you from performing the exercises correctly. Mistakes will be fixed in the brain. We'll have to relearn. Correcting a fixed, erroneous skill is a thankless task. Loss of energy and precious time. Tested on me))).
In addition to relieving spasticity, it is great to practice coordination of finger movements.
The most difficult thing was performing the exercise with both hands at the same time. Slightly less difficult with the left hand.
At first, it is not speed that is important, but accuracy. The brain needs to remember the correct movements. No mistakes. As you master the exercise, gradually increase the speed. The main thing is quality, accuracy and correct order of touches. If during the exercises there was excess tension in the hand, shake the hand two or three times to relax, and after relieving the tension, continue. Movements should be light. This is the essence of the exercises.
Relieving spasticity is an important task. It greatly interferes with everyday life, takes away strength and hinders movement. This makes it difficult to restore lost skills and stamina. To fully carry out recovery after a stroke, it is necessary to cure spasticity. We do this in parallel with other tasks. This is our general approach to treating spasticity.
Hello! I have persistent spasticity. All recovery after a stroke. It is there every minute throughout the day. Very strong, I can’t just turn around or reach anything. It’s not possible to do the exercises against spasticity and, as you write on the website, stop exercising if tension occurs.
Muscle tension is usually not constant. But there are times when it comes, you should start moving.
There are flexor muscles, and there are their antagonists, extensors. Their work must be coordinated. For example, the flexor muscles bend the leg at the knee, the extensor muscles at this moment do not interfere with them and are relaxed. And vice versa. You wrote about the “spring in the knee.” It looks like the extensor muscles are interfering. They start working at the wrong moment and do it in one gulp, convulsively. This means they receive such a signal from the brain.
You need to learn to relax your muscles and not resist movements. For example, start with arm exercises. It's easier to use your hands and you quickly understand the principle. Then move on to leg exercises. They have the same principle. We chose exactly those movements with which we had difficulties.
- performed lying along the edge of the bed, on your back. Right side to the edge of the bed.
- legs straight and extended. Hands along the body.
- completely relax and do nothing.
- The assistant bends his RIGHT leg. The assistant is located on the side of the bed. With one hand he grabs the ankle, with the other hand under the knee. Synchronously begins to move the ankle towards the buttock, and lift the knee up.
- then straightens the leg and places it in its original position.
- 10 reps x 1 set.
- performed lying along the edge of the bed, on your back. Left side to the edge of the bed.
- legs straight and extended. Hands along the body.
- completely relax and do nothing.
- the assistant bends his LEFT leg. The assistant is located on the side of the bed. With one hand he grabs the ankle, with the other hand under the knee. Synchronously begins to move the ankle towards the buttock, and lift the knee up.
- Unbend the leg and place it in its original position.
- 10 reps x 1 set.
How to treat spasticity using different methods
Treatment of hypertonicity is recommended if spasticity reduces a person’s activity level or is accompanied by persistent pain.
The most important requirement for treatment is that it be as painless as possible, since pain is greatly amplified by spasticity.
An important point is monitoring the activity of the pelvic organs - preventing inflammatory manifestations in them, as well as timely implementation of measures to prevent the occurrence of contractures and bedsores.
A complex of modern treatment to get rid of spasticity:
- medicinal tactics (mydocalm, baclofen);
- physiotherapeutic techniques;
- orthotics;
- massage effects;
- exercise therapy;
- surgical correction.
The treatment package is selected only individually, directly depending on the location of the lesion and the severity of spasticity. It is also necessary to take into account the technical capabilities of the medical institution.
Spasticity after a stroke or brain injury necessarily requires medication. Treatment should be carried out in stages - with a gradual increase in the therapeutic dose of medication, possibly replacing the drug.
Today, two subgroups are in demand:
- Drugs with a central mechanism of action on the negative focus are reflex inhibition.
- Peripheral drugs – significantly reduce the stretch reflex at the level of the spinal cord elements: muscle relaxants.
Like other subgroups of even the most modern drugs, the above have their own contraindications, so only a highly qualified neurologist should prescribe them.
Central paresis
You may be interested in: Glossopharyngeal nerve: symptoms of damage, diagnosis and treatment
In this disease, spasticity develops due to a reduction in inhibitory effects (IT) on spinal neurons (their type: motor- and inter). As a result, the number of impulses reaching alpha motor neurons increases. This is a response to muscle stretching.
A decrease in TV is a consequence of cumulative defects in the pyramidal canals inside the brain (both spinal and cerebral). Most often, muscle spasticity develops due to damage to the cortico-reticular-spinal tract.
If the brain is affected, the TV is also weakened, but this is most reflected in the gamma motor neurons. They set the movement of the anti-gravity muscles. As a result, characteristic post-stroke spastic hemiparesis appears:
- The shoulder and hip are adducted.
- Elbow and wrist joints bend
- The knee extends.
When spinal spasticity develops, TVs to interneurons located in the area decrease. Because of this, excitations spread along nerve fibers to other levels, and pathological symptoms appear.
You may be interested in: Removal of papillomas on the eyelid: methods and medications
Outwardly, this most often manifests itself in convulsions and uncontrolled movements.
To put it differently, when muscle spasticity occurs in cerebral palsy, energy accumulates in them, and communication with the brain is disrupted or absent. They misunderstand his commands and contract chaotically at any time. This is how the accumulated energy is spent.
If central paresis cannot be cured for a long time, for example, more than six months, then the segmental apparatus of the spinal cord changes structurally. This manifests itself in disruption of connections between nerve fibers and the functioning of paretic muscles, tendons and joints. Because of this, there is an increase in movement disorders and resistance that forms in the muscle when it is stretched. Doctors must take this into account when analyzing muscle tone in paretic or paralyzed arms and legs.
Neuroplasticity beats spasticity
The brain uses muscles to control movements. The muscles will contract and relax so that you can move smoothly. After a stroke, the connection between the brain and the muscles on the affected side is severed. Control of the muscles on the injured side may become weaker (or disappear), and muscles don't like to be left unchecked. Since the muscles are no longer under control, they turn to the spinal cord. It is this relationship between muscles and the spinal cord that underlies muscle spasticity. After a stroke, the brain is no longer able to protect the muscles from being overstretched and torn, so the spinal cord takes over and tells the muscles to remain tight, which protects them from being torn. Muscle spasticity is a protective mechanism. Of course, tense muscles prevent you from moving. No medications, treatments, or therapeutic modalities will eliminate muscle spasticity. All of them give a temporary effect; As soon as such treatment is stopped, muscle spasticity returns. However, hope remains. The obvious answer to this riddle is simple: periodically move the spastic muscles.
Neuroplastic model for reducing muscle spasticity
Muscles get rid of spasticity with the help of our old friend - neuroplasticity. A stroke kills the part of the brain that controls spastic muscles. But what if it was the other way around? What if you could use more of your brain to control spastic muscles? This is the neuroplastic model for reducing muscle spasticity. The idea is to use techniques to transfer control of spastic muscles to other areas of the brain. As the brain regains control over the muscles, spasticity decreases. Muscle tension becomes less intense, which in turn provides greater control of movements, which makes it possible to increase the range of motion. A wider range of motion allows the body to stimulate even more changes in the brain. The better the brain controls the muscles, the more movement is available. The more movement available, the more changes can be stimulated in the brain, etc.
The main way the brain regains control of spastic muscles is through repeated practice. For example, forced movement therapy, which requires a lot of repetitive practice, can often reduce muscle spasticity. But using any standard “therapy” or “treatment regimen” requires no effort on your part to regain brain control over spastic muscles. Getting the brain to take over the muscles requires repeated (repeated) use of those muscles. These repetitive efforts must also be challenging—at the “best” of your current capabilities.
Simply put, repeated and challenging training of spastic muscles reduces spasticity because:
- repeated practice restores brain control over muscles;
- restoring brain control over spastic muscles reduces spasticity.
How it's done?
Downward spiral after stroke
Stroke. —> The part of the brain that controls muscles is affected. —> The brain can neither control the muscles nor protect them. —> The spinal cord protects the muscles by causing them to tense. —> Muscles shorten forever. —> Tight, shortened muscles make movement even more difficult.
Upward spiral after stroke
Repeated practice rewires the brain. —"The brain regains control over the muscles. —> The spinal cord transfers muscle control to the brain. —> Muscle spasticity decreases or disappears. —"Movements become more normal.
The only way to permanently reduce or eliminate muscle spasticity is to rewire your brain to regain muscle control. Muscle spasticity will be reduced by the same recovery options that cause brain remodeling. Improving movement and reducing spasticity are two sides of the same coin.
- When muscle spasticity decreases, the ability to move improves.
- Improving movement reduces muscle spasticity.
Animal studies have shown that if a limb is immobilized (usually by strapping it to the body), the number of brain cells responsible for that limb decreases. This is what happens to stroke survivors who have muscle spasticity: their muscles are immobilized. If spastic muscles begin to move again, the part of the brain that controls those muscles becomes larger. As more neurons are able to control these muscles, muscle spasticity decreases.
Treatments used by physical therapists and neurologists can help you rewire your brain to regain control of spastic muscles. These doctors are specially trained in therapies that reduce muscle spasticity. Certain medications and other therapies provide temporary relief from muscle spasticity. This temporary improvement may make movement easier. It also helps create the opportunity for the hard work of rewiring the brain.
Medicines used to reduce muscle spasticity fall into the following two groups:
- applied locally (in the form of injections directly into spastic muscles) or injected into the fluid surrounding the spinal cord; these drugs only affect certain muscles;
- taken orally; These drugs affect every muscle in the body.
Such drugs can reduce muscle spasticity, which will help:
- improved movements;
- enhancing recovery opportunities;
- preventing potential problems with bones and joints;
- pain reduction;
- increasing strength;
- reducing the risk of contracture ;
- preparing the ground for neuroplastic changes.
Ask your doctor about these options. But remember that these medications do not address the root cause of muscle spasticity (insufficient brain control over muscles). No drug can replace the hard work required to rewire the brain. Drugs and other treatments that temporarily reduce muscle spasticity free you up to do the hard work of rewiring your brain.
This work can be carried out in the form:
- forced movement therapy;
- repetitive, task-oriented, concentrated training;
- some treatments based on electrical stimulation;
- some types of bilateral training;
- mental training.
This list will grow as new research results become available, so keep researching treatments and asking more questions.
What precautions should you take?
Consultations with doctors, therapists and other health care providers will help guide your treatment to achieve muscle spasticity reduction with a minimum of cost and maximum therapeutic effect.
You and your doctor may decide to use spasticity medications for reasons other than neuroplastic changes. There are other good reasons for prescribing oral and other medications for muscle spasticity. The goal of long-term use of systemic drug treatment may be to increase mobility, reduce pain, improve movement, etc.
Spasticity level
Different scales are used to analyze it. The most common is the Ashworth product. The scoring system for muscle tone here is as follows:
- 1 – it is slightly elevated, the condition quickly improves;
- 1a – slight excess, muscles tense in less than 50% of the total number of passive movements;
- 2 – moderate development during 100% range of movements (passive actions are easily implemented);
- 3 – significant growth (movements are problematic);
- 4 – the paretic part of the limb does not straighten or bend completely.
Development mechanism
Upper limb spasticity is a condition in which the arm muscles constantly contract and become stiff. Muscle contraction causes sudden and uncontrollable movements (spasms) of the arms. It may also be accompanied by impaired functioning and coordination of the limbs.
To better understand the mechanism of development of muscle hypertonicity, let's consider the main aspects of movement regulation.
The earlier classes to prevent spasticity begin, the better the result.
Normally, muscle contractions are regulated at three levels:
- spinal cord;
- stem nuclei of the brain;
- cortex.
Any of these sections can stimulate muscle contraction. Thanks to the close cooperation of these departments, a person can perform the necessary movements, and muscle tone remains normal.
Impulses from motor neurons in the spinal cord provide automatic movements, such as sudden flexion when exposed to a painful stimulus. The overlying sections have a regulatory effect on the motor cells of the spinal cord, and it can be both inhibitory and stimulating.
The brainstem nuclei are responsible for maintaining posture and balance. The vestibular nucleus increases the tone of the muscles that extend the limbs. The red core, on the contrary, bends the limbs. In this case, spinal motor neurons of opposite muscle groups are inhibited. This relationship is called reciprocal.
The cerebral cortex regulates voluntary human movements. To date, scientists have compiled detailed maps of the localization of areas that are responsible for the movement of individual parts of the body.
The motor cortex of the brain has an inhibitory effect on spinal motor neurons, which ensures holistic movements rather than individual muscle twitches. In a patient after a stroke, damaged areas of the cerebral cortex lose their inhibitory effect on underlying structures. Externally, this is manifested by the development of muscle hypertonicity.
Increased skeletal muscle tone often becomes a serious obstacle to the recovery of patients after a stroke.
It should be borne in mind that the optimal result can only be obtained with a combination of drug and non-drug treatment methods.
Non-drug treatment of hypertension includes:
- correct positioning of the patient;
- massotherapy;
- gymnastics;
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
An integrated approach will help overcome spasticity and restore motor functions of the limbs
Among the medications, muscle relaxants and botulinum toxin are actively used.
What is this?
Muscle spasticity is a disorder that is rarely discussed in detail among stroke survivors. Clinicians tend to describe spasticity in terms of its effect on the extremities. For example, they might say, “The stroke causes tension in your arm,” or “Your muscles are tight because of brain damage from the stroke.” These are incomplete explanations for muscle spasticity. You need to know the whole truth. Without understanding the causes of muscle spasticity, you have little chance of reducing it. Much of recovery from stroke, including reduction in muscle spasticity, comes from within. Only the person who has suffered a stroke can reduce muscle spasticity. As with many other aspects of stroke rehabilitation, the individual "guides their nervous system" toward recovery. Muscle spasticity is a nervous system problem caused by insufficient control of the brain over the muscles. The muscles are affected, but they are not the cause.
How it's done?
How can you reduce or eliminate muscle spasticity without drugs or surgery? The only way to relieve it is to restore brain control over spastic muscles. Using the neuroplastic process is the only way to regain muscle control. Understanding muscle spasticity will help you use the neuroplastic process to reduce it.
Here's a science-based, and hopefully understandable, explanation for muscle spasticity.
How muscles work
Your muscles send constant messages to your brain about the amount of tension they are under. If the muscles are too tense, they will tear. The brain is in constant communication with the muscles to make sure that the muscle helps you move and is not in danger of tearing.
How the brain controls muscles before a stroke
Your brain tells your muscles when to contract (tighten to help you move) and when to relax.
How the brain works after a stroke
- A stroke kills the part of the brain that controls muscle control.
- The affected part of the brain no longer “hears” these muscles.
- The brain no longer tells the affected muscles when to contract or relax.
If your brain can't fully control your muscles, what causes them to tense up? Do muscles act independently? Or is something telling them to shrink?
How Spinal Cord Causes Muscle Spasticity
- Muscles constantly send signals to the spinal cord, which usually sends them to the brain.
- Because of a stroke, the brain no longer receives messages from the muscles, meaning the brain cannot “hear” the muscles. Muscles don't like being left out of control because it means they can stretch too much and tear (muscles tear easily).
- Since the brain is not able to protect the muscles from rupture, the spinal cord takes on this job.
- Impulses from the spinal cord protect the muscles by keeping them immobile.
The impulse that the spinal cord sends to protect the muscles is similar to the stretch reflex. This reflex occurs, for example, when a doctor checks reflexes with a neurological hammer. When the doctor hits you just below the kneecap, the leg straightens at the knee, whether you want it to or not. The movement of the leg suddenly rising forward is called the stretch reflex. Stretch reflexes prevent muscle tearing by instantly contracting the muscle. Imagine if a doctor kept hitting the knee without stopping. Muscle spasticity can be viewed in a similar way. In other words, muscle spasticity is a repeated action of reflexes.
What does muscle spasticity do?
- The spinal cord tells the muscles to contract (shorten).
- This command is muscle spasticity.
- Within a few days, muscle spasticity permanently shortens some muscles.
- Shortened muscles perceive any lengthening as a threat of rupture.
- The muscle sends more messages “Help! I'm eager! into the brain and spinal cord.
- The spinal cord continues to send signals to the muscle causing it to tense.
Treatment measures
The main goal in the treatment of muscle spasticity is to improve the potential and function of the affected limbs.
Doctors decide how increased tone affects the patient's functional abilities. In people suffering from central paresis, the limbs are less active when compared with patients with 1-2 points on the designated scale.
Some patients with high levels of leg muscle spasticity walk and stand more easily. And when its degree decreases, they move much worse.
Before starting therapy, doctors identify a treatment plan in a particular case (improving movement, reducing negative spasms, etc.) and coordinate it with patients or their relatives.
The specifics of treatment are largely determined by the period from the moment of illness and the level of paresis. The shorter the time since the onset of the disease, the greater the chances of effective therapy.
To achieve a positive result, the following methods are used:
- Physiotherapeutic.
- Pharmacological.
- Surgical.
You may be interested in: Can the lungs hurt from the back? Possible causes of pain, diagnosis and treatment
Its main task is to train movements in problematic limbs and prevent complications.
During the course of this therapy, patients are taught to sit, stand and walk. For this purpose additional means are used.
Patients’ limbs are also bandaged, orthopedic equipment is used, and spastic muscles are exposed to thermal radiation.
To effectively relieve muscle spasticity, specialists perform electrical stimulation of problem areas.
As a rule, these are extensors of the fingers or the anterior tibialis muscle.
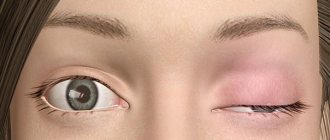
Symptoms of spasticity
The main symptom of spasticity is involuntary muscle contraction. This process is accompanied by a headache and a general feeling of weakness throughout the body. Not always pain can be attributed to symptoms of spasticity. Very often, the cause of this condition is too sudden movements, which cause spasmodic contractions of the muscles of the arms or legs. In addition, pain can occur as a result of a change in the position of the patient's body, in particular at the moment when attempts are made to sit him down.
As a result of spastic contractions, the arms or legs cease to obey, become too weak, or acquire additional rigidity. In this case, a sick person with spastic muscle contractions may feel both weakness and some resistance from the cramped muscles. These factors are a consequence of the conduction of muscles and nerves. When taking medications, there is some relief from tense muscles, but the feeling of weakness remains.
Other symptoms of spasticity include involuntary contractions of individual muscle groups, as well as a feeling of general fatigue and loss of dexterity in the muscles. Numerous testimonies from patients characterize spasticity as excessive tension in the muscles, weakness in the legs, and resistance when moving the legs and arms.
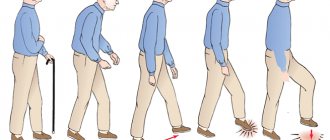
Spasticity after stroke
Stroke is an extremely important medical and social problem, since it is one of the causes of many cases of disability, usually related to disorders of human motor activity. In the vast majority of all cases, the acute period of stroke is characterized by the detection of hemiparesis; in approximately two-thirds of all cases, the presence of residual effects after a stroke is noted. In the majority of cases, stroke occurs in people of retirement age, and women are 20% less susceptible to it than men.
Immediately after the onset of a stroke, there is a decrease in muscle tone in the limbs, but after three days it recovers, eventually returning to average values. Depending on the severity of the stroke, the duration of the painful condition and the degree of muscle spasticity may vary. The basis of spasticity after a stroke is a disruption of the activity of the parts of the human cerebral cortex responsible for the motor activity of the limbs.
Spasticity with cerebral palsy
The spastic form of cerebral palsy is a very common phenomenon. At the same time, individual muscles of the child’s body are in increased tone, which occurs due to failures in the full functioning of the muscles of the arms and legs. A state of extreme tension is very typical for muscles with cerebral palsy and this is the cause of a strong slowdown in their growth. In this case, there is a significantly faster growth of bones than muscles, which causes a significant difference in the length of muscles compared to bones and tendons. In this case, there is a decrease in the size of the affected limb and the joints of this limb become less mobile.
To prevent all this from happening, immediately after the child is diagnosed with cerebral palsy, classes should be conducted with him. You can start with regular exercises using physical therapy exercises, the results of which will determine the methods of combating spasticity. Such an approach will help achieve the necessary results.
Spasticity in multiple sclerosis
Spasticity is a symptom that is directly related to multiple sclerosis. However, when describing the symptoms of their condition, patients do not always interpret it correctly. Often, by spasm they mean a sharp wave of surging pain, while a spasm is an involuntary contraction of muscle groups. To avoid confusion, the meaning of these terms should be understood.
Spasticity in people suffering from multiple sclerosis often manifests itself in the form of unexpected contractions of certain muscles. These contractions may occur spontaneously or may be a reaction of the body to external stimuli. The degree of manifestation of such symptoms is very diverse, from a mild form to severe spasms that last a long time. In this case, the patient will need to move in a wheelchair. In multiple sclerosis, spasticity may change over time. In this case, the muscles of the arms and legs are mainly involved, and much less frequently the muscles of the back or other parts of the body.
There are some cases in which spasmodic muscle contractions may even be beneficial. This refers to conditions in which the sick person is too weak in the legs and spasm helps him to take a stable position. In this case, when spasticity is removed, the person’s legs give way and he will not be able to stand on his own.
Patient position
One of the main points in the treatment of muscle hypertonicity in patients after a stroke is giving the paretic limb a physiological position.
An effective way to combat spasticity
The affected hand should be placed on a chair next to the patient's bed. Due to increased muscle tone, it will be drawn towards the body. To prevent this phenomenon, a soft tissue roller is placed in the armpit.
The arm is extended at the elbow joint and turned palm up. Sandbags or other devices are used to hold the limb in this position. It is advisable to bandage the fingers and hand to a splint.
The leg should be slightly bent at the knee, and the foot should be at right angles to the shin.
The duration of positioning treatment is about 2 hours. It can be repeated several times during the day. As soon as the attending physician allows, the patient is helped to sit down and taught to walk.
Massage relieves increased muscle tone well. It must be carried out from the first days of the disease. From massage techniques, you need to choose stroking and light rubbing. They help reduce muscle tone, improve blood circulation and lymph flow in the paretic limb. The duration of the first sessions should not exceed 10 minutes.
Over time, it is increased to 20 minutes. The duration of the course depends on the individual characteristics of the patient and is determined by the attending physician. As a rule, after 20–30 sessions a break of 10–15 days is required. After this, the course is repeated. The decision to discontinue massage treatment depends on the results achieved.
Types and types of violation
According to qualifications, three main types of spasticity can be distinguished:
- The flexor type is the increased tone of the flexor muscles when bending the limbs at the joints and lifting them.
- The extenotic type is an increase in the tone of the extensor muscles in the process of straightening the limbs in the joints.
- The adductor type includes an increase in tone when crossing in the area of the legs and closing the knees.
Pathogenesis of post-stroke spasticity
Spasticity often occurs in patients who have had a stroke. In such cases, physiotherapy is ineffective, and the presence of spasms complicates the patient’s recovery.
The muscles are constantly toned, pathological changes begin to occur in them, and joints and tendons also suffer. In addition, contractures (deformations) occur, significantly aggravating the problem.
The development of spasticity does not occur immediately; as a rule, it occurs 2-3 months after a stroke, but the first signs can be noticeable to a specialist much earlier.
The shoulders, elbows, wrists and fingers are usually affected, while the lower body is affected by the hips, knees, ankles and toes. In this case, spasticity affects the flexor muscles in the upper extremities, and the extensors in the lower extremities.
In the absence of the necessary treatment, contractures appear in the joints and bones over several years.
Pathogenesis of spasticity in multiple sclerosis
Spasticity is a concomitant phenomenon of multiple sclerosis in most cases. It manifests itself as an unexpected contraction of a muscle group, occurring spontaneously or as a reaction to an irritant.
The severity of muscle spasms in patients with multiple sclerosis can vary, ranging from mild to severe, manifesting as severe and prolonged spasms. The shape of gravity can change over time.
In multiple sclerosis, spasticity occurs in the muscles of the limbs, and in rare cases affects the back muscles.
Physiotherapy
Massage for cerebral palsy is one of the main methods of rehabilitation. Cerebral palsy is a term that refers to a range of symptoms that characterize neurological disorders. The main goal of rehabilitation is to restore the functions of the nervous system and muscles.
Only a qualified specialist can help the patient restore normal functioning as much as possible. Techniques and techniques of therapeutic massage are selected for each patient individually, taking into account the main symptoms. Therapeutic massage for cerebral palsy includes various types, differing in technique and techniques:
- classical medicinal;
- point-reflex;
- hardware types;
- alternative types.
The complex of therapeutic exercises consists of active and passive movements. Passive movements consist of flexion and extension of muscles, which is carried out by caring staff. If possible, the patient makes passive movements using a healthy limb. Due to increased tone, movements may initially be intermittent and abrupt. Over time, the tone decreases and they become smoother.
Exercise is very important for developing muscles and joints
As soon as a patient after a stroke is able to perform active movements, he should engage in therapeutic exercises independently. In addition to flexion and extension exercises, exercises aimed at stretching muscles are added. When performed correctly, they relieve hypertension well and help the patient recover faster.
If the patient has increased muscle tone after a stroke, exercises with expanders, elastic bands, and the like are strictly not recommended - they only intensify spastic phenomena and worsen the situation.
Skeletal muscle spasticity in neurological diseases
Skeletal muscle spasticity occurs as a result of many neurological diseases, in particular multiple sclerosis, spinal and traumatic brain injuries, cerebral palsy, and stroke.
Skeletal muscle spasticity can be caused by:
- brain damage due to lack of oxygen (hypoxia)
- meningitis - inflammation of the tissues that cover the brain
- encephalitis – inflammation of brain tissue
- phenylketonuria, etc.
All of the above diseases can lead to serious complications and consequences. Therefore, at the slightest ailment, it is imperative to seek medical help. The earlier the disease is diagnosed, the easier it is to treat.
Treatment of all neurological diseases is a complex and lengthy process. Only an experienced and highly qualified doctor can determine the true cause of the disease and prescribe correct and effective treatment.
Pharmacology
Here central muscle relaxants have the greatest effect. Patients take them orally. These drugs have the following advantages:
- reduce muscle tone;
- improve motor potential;
- relieve painful spasms;
- enhance the effect of therapeutic exercises;
- facilitate the care of paralyzed patients;
- prevent the appearance of contractures.
If muscle spasticity is mild, muscle relaxants have a rapid positive effect. For complicated diseases, they are used in large doses. This is fraught with negative side effects.
Treatment with these drugs begins with a minimum dosage. It gradually evolves to achieve the required task.
Combinations of drugs against this disease are not allowed.
In Russia, the following tablets for muscle spasticity are also most often used:
- “Sirdalud”. Suppresses polysynaptic reflexes in the spinal cord and has a moderate central analgesic effect. Particularly effective in the treatment of cerebral and spinal muscle spasticity. The minimum daily dose is 3 times 6 mg, the average is 12-24 mg, the maximum is 36 mg. Side effects: drowsiness, slight drop in blood pressure.
- “Baclofen.” Mainly used to treat spinal spasticity. It effectively suppresses the generation of tonic amino acids and has a central analgesic effect. Minimum daily dosage: 15 mg x 3. Gradually it increases daily by 5 mg. Maximum – 60-75 mg. Side effects: nausea, constipation, diarrhea, hypertension. Therefore, the drug should be used with caution in older people.
- "Tolperisone". Powerfully suppresses spinal reflex activity, has a mild vasodilator and central analgesic effect. Reduces spasms. It is used in the fight against two types of spasticity: spinal and cerebral. The initial dose per day is 150 mg. It develops systematically up to 300-450 mg. Side effects: drowsiness, muscle weakness, arterial hypotension.
Spasticity treatment
Treatment methods for spasticity can be different, some of them can be distinguished:
- Physiotherapy is used to stretch muscle groups and maintain joint mobility, while reducing the risk of injury. When muscle mobility is low, physiotherapy can be used as a means of gradually and smoothly stretching them. In some cases, it may be advisable to undergo minor surgery to increase the length of the ligament by making an incision in the leg;
- Drug therapy is used in cases where it is necessary to take medications to relieve increased tension in the leg muscles. The mechanism of action may be different; some drugs affect the spinal cord, others affect brain receptors;
- Botulinum toxin is a remedy that provides the appropriate effect when used when it is necessary to relax a spastic muscle for a short time. Ethanol or phenol can be considered an alternative, despite the fact that these drugs are suitable for short-term innervation of large and strong muscles, which may cause pain in certain nerves.
Exercise for spasticity
Spasticity manifests itself as a violation of motor activity, manifested in partial or complete immobility, increased muscle tone, as well as involuntary movements. There are certain exercises that can reduce spasticity, restore motor activity and eliminate synkinesis in paralyzed limbs.
Performing exercises requires a certain synchronicity, and both affected limbs participate in them, moving in the same direction at different or the same speed. You can do the exercises yourself, or you can use someone else’s help. Execution involves an average and slow pace, the number of repetitions is limited to four. You can rest by placing your arm or leg in a position that relaxes the muscles most effectively.
Massage for spasticity
For spasticity, the following massage methods can be used. The arms are joined on the chest, the legs are pulled towards the abdominal area, the body bends slightly and in this position you can carry out free light rocking, which ensures a decrease in muscle tone after a certain time. The time during which a decrease in muscle tone occurs should be used to provide high-quality stimulation for the restoration of certain motor functions that were impaired as a result of muscle spasm. When muscle tone increases, it is recommended to repeat the described massage method. This technique is most effective when applied to children aged from one month to seven years.
You can use a form of massage that normalizes muscle tone using a ball. To do this, you need to lie on the ball with your chest and stomach, then make a series of movements in different planes, then change the position of your body and lie on your back on the ball, subsequently repeating the entire listed set of movements. Depending on the muscle tone at the time of the exercise, the duration of the exercise should be determined. On average, this type of massage takes no more than fifteen minutes a day.
Folk remedies
For spasticity of the lower extremities, the following traditional medicine is recommended for use. It is necessary to sew bags according to the shape of the legs and the area of the torso up to the lumbar spine, which are subsequently filled with birch leaves torn from the tree. Immediately before going to bed, the patient should be placed with his feet in these bags and kept in them for some time, while ensuring that the leaves fit the person’s body in a dense layer on all sides as tightly as possible. This is necessary to create the necessary temperature environment in the bags so that the person sweats well. At the same time, your feet sweat just as profusely as they would when using a steam bath. It is recommended to stay in this position all night. In some cases, it may be advisable to replace the leaves around midnight if they become very wet. After completing several such sessions, spastic manifestations in the lower extremities will cease to bother you.
Muscle relaxants
Among the medications used to treat hypertension in patients after a stroke, centrally acting muscle relaxants are used, which effectively relieve muscle tone without affecting their strength. The mechanism of their action is to inhibit pathological impulses that come from spinal motor neurons.
Treatment with muscle relaxants begins with minimal doses. If necessary, they are increased to achieve effect. Expected effects:
- decreased muscle tone;
- improvement of motor functions;
- pain relief;
- prevention of contracture development;
- increasing the effectiveness of therapeutic exercises;
- facilitating patient care.
In our country, the most common muscle relaxants are baclofen, tizanidine, or sirdalud, tolperisone, or mydocalm, diazepam.
Doctors also prescribe muscle relaxants to restore and relax muscles.
The disadvantage of treatment with muscle relaxants is the possibility of developing side effects, the most common of which are:
- drowsiness;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- constipation;
- decrease in blood pressure.
Spasticity of the tongue
Spasticity of the tongue implies a violation of muscle tone not only of the tongue itself, but also of the face, neck, and lips. In this case, the patient’s tongue is pulled back, its back is curved and raised upward, while the tip of the tongue is not pronounced. Sometimes the tongue may be pulled forward.
An increase in the tone of the orbicularis oris muscle leads to a tight closure of the lips, or, on the contrary, the mouth may be slightly open. In the second case, increased salivation is also observed.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital provide medical care to patients of any severity of the disease. The hospital uses modern innovative methods of therapy to smooth out the symptoms of the pathology and, in many cases, completely relieve patients of the disease.
Treatment with botulinum toxin
The use of botulinum toxin for the treatment of hypertonicity is indicated for post-stroke patients with local spasticity.
Main indications for the use of botulinum toxin:
- absence of contractures;
- severe pain syndrome;
- impaired motor function associated with increased muscle tone.
The mechanism of action is to block the transmission of impulses from a nerve cell to a muscle fiber. The clinical effect develops a few days after the injection and lasts for 2–6 months, depending on the individual characteristics of the patient. Due to the production of antibodies, repeated injections do not eliminate hypertension as effectively.
This method is not widely used in the fight against hypertension in patients after a stroke. This is primarily due to the high cost of the drug.
Spasticity: good or bad?
The mechanisms of the formation of spastic syndrome are still not well understood due to their complexity and versatility. Spasticity does not affect everyone. Both its presence and its absence have their pros and cons.
Spasticity keeps muscles toned and promotes good blood supply. Many doctors are very positive about spasticity - it means that the legs or arms can still be restored and the person can walk again. Even despite the pain, many patients are happy to perceive that their legs (or arms) “work,” albeit spontaneously. At least at the first stage of rehabilitation, the role of spasticity is clearly positive. But in the future, the strengthening of spastic syndrome leads to serious difficulties in recovery.
Surgical intervention
To reduce muscle spasticity, it can occur at any of these levels:
- brain;
- dorsal;
- peripheral nerves;
- muscles.
The brain is operated as follows: electrocoagulation of the globus pallidus or cerebellum is turned on. A stimulator is implanted on the surface of the latter.
These operations are quite complex and dangerous. Therefore they are used extremely rarely.
Treatment of the spinal cord can be arranged as follows: the cone is dissected along the longitudinal line. This breaks the reflex arc separating the posterior and anterior horn of this brain.
The operation is performed only in the most extreme cases and with spasticity of the leg muscles. It requires enormous skill of the surgeon and implies a high risk of serious complications.
To eliminate spasticity, peripheral nerves can be cut. Because of this operation, severe pain and dysesthesia develop. After this, orthopedic procedures are carried out. For this reason, it is practically not used today.
And the most common surgical intervention is carried out as follows: the tendon of the muscle is lengthened, or it moves. This reduces the activity of its intrafusal fibers and, as a result, spasticity.
The effect of this method is difficult to predict. In difficult cases, a series of operations is performed. If contracture develops, this method remains the only treatment measure.
Quota stumbling block
In the West, such operations have been performed for more than 20 years. For us, quite recently. One of the pioneers was the Research Clinical Institute of Pediatrics named after Academician Yu. E. Veltishchev. Local surgeons have already installed more than 100 baclofen pumps and performed more than a dozen operations to stimulate deep brain structures and selective dorsal rhizotomy.
Doctors admit: there would be much more such operations if more quotas were allocated for them. It all comes down to expensive devices, which doctors receive in very limited quantities. Experts hope that over time the situation will change for the better. After all, the effect of such operations more than pays for all government expenses: children spend less time in the hospital and need less rehabilitation support. And most importantly, their quality of life improves. What could be more important?
By the way
Abroad, operations to install baclofen pumps are performed on children from 5 years of age. At the Research Institute of Pediatrics, this operation was the first in the world to be performed on very young children – 1.5–2 years old. After all, the sooner a child gets rid of spasticity, the greater success can be achieved in preventing complications of the disease. Patients are taken for selective dorsal rhizotomy from the age of three, and for stimulation of deep brain structures – from the age of eight.
The situation after a stroke or head injury
This is where physical therapy comes to the fore. She gets comfortable from the first days of illness and trains lost movements. The patient begins to stand and walk independently.
The most commonly prescribed medicine is Sirdalud. The doctor correctly determines and develops its dosage to prevent sedation.
When muscle spasticity occurs during a stroke, motor function can be seriously impaired. In this case, botulinum toxin is injected. Optimal results are achieved if its injections are made in the early period (less than a year) of the disease and a modest level of paresis.
Muscle spasticity - what is it?
Muscle spasticity is a syndrome that develops when areas of the upper motor neurons are affected, and there is an increase in tonic reflexes as a result of stretching, combined with an increase in reflexes in the tendon area. The concept of muscle tone means a certain level of tension in muscle groups and resistance that occurs during extension or flexion movements of a limb segment. The normal state is considered to be a feeling of some slight elasticity when palpating the muscles, as well as some muscle tension during leisurely movements. A certain increase in the tone of muscle groups is accompanied by strong resistance during passive movements.
An increase in muscle tone can greatly affect the process of regeneration of previously impaired functions. A high level of muscle spasticity does not allow the implementation of intact functions, as well as the full recovery of impaired ones. At the same time, an increase in muscle tone is a compensating factor for the development of paralysis. This determines the urgent need, immediately after the start of treatment, to clearly determine how necessary and useful it is to reduce the muscle tone of a cramped arm or leg.