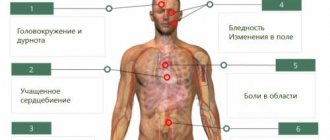
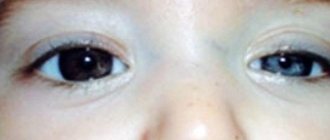
What are the causes of blepharospasm
The exact pathophysiology underlying the development of blepharospasm is still unknown, but it is thought to be multifactorial, with a likely genetic component and environmental triggers.
It has been suggested that it is associated with abnormalities in the basal ganglia and dopaminergic system of the brain. Etiology:
- Parkinson's disease;
- Regular use of antipsychotic and other medications;
- Trichiasis;
- Supranuclear palsy;
- Entry of a foreign body;
- Dry eye syndrome;
- Neoplasms;
- Cortical epilepsy;
- Inflammation of the sinuses, teeth, nasopharynx;
- Blepharitis.
Provoking factors:
- Hypo- and vitamin deficiency;
- Long work at the computer;
- Stress;
- Sleep disorders;
- Physical and mental fatigue.
Benign essential blepharospasm is associated with a family history of dystonia, head or facial trauma, and other neurological movement disorders (eg, Tourette's syndrome).
Secondary pathology manifests against the background of focal lesions in several areas of the brain or develops in patients with tardive dyskinesia. Finally, secondary blepharospasm often occurs as a result of conditions associated with eyelid weakness, such as facial palsy and myasthenia gravis.
Diagnostics
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to find out the root cause of the disease. Diagnosis is based on an analysis of the patient’s complaints and additional research methods, for example:
- Examination of the eyes using a slit lamp. In this way, it is possible to identify ophthalmological disorders - keratitis, conjunctivitis, glaucoma.
- Examination by a neurologist. The examination helps to identify pathologies of the nervous system (paresis, involuntary muscle contractions).
- CT, EEG and MRI. Detect disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system (including benign and malignant brain tumors).
- Consultation with a psychiatrist. A specialist will help identify signs of mental disorders and epilepsy.
- Electromyography (a research method that evaluates the bioelectrical activity of muscles). This diagnostic method is used to identify diseases of the muscles and peripheral nervous system.
For an expanded analysis of the patient's condition, differential diagnosis is performed.
Symptoms of blepharospasm
Symptoms are characterized by stereotypical, bilateral and synchronous spasms of the orbicularis oculi muscles. The spasms can be brief or long lasting and can cause the eyelids to narrow or close.
Focal dystonia, manifested by involuntary closure of the eyelid, has two stages:
- Tonic;
- Clonic.
The clonic form is characterized by frequent involuntary blinking. The problem usually begins on one side and then moves to the second organ.
| It should be noted that unilateral lesions practically never occur. |
Over time, the duration and intensity of the clonic spasm gradually increases. In this case, the patient closes his eyes tightly and for a long time against his will. In this case, the nosology moved to another stage - tonic. In severe cases of the disease, mechanical blindness develops in 70% of patients. A person loses visual function because he cannot open his eyelids. Young girls suffering from hysterical seizures experience bilateral squinting that lasts for several hours.
A distinctive feature of hysteria is that when pressing on the exit points of the branches of the trigeminal nerve, the spasmodic state of the periocular muscles is stopped.
Main manifestations:
- Intense twitching of the eyelids;
- Frequent blinking;
- Excessive tearing;
- Photophobia, burning and itching;
- Involuntary squinting;
- Areas of maceration on the skin of the eyelids;
- Impaired outflow of tear fluid.
Psychiatric changes include depression, anxiety, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. If the pathological process proceeds for a long time and is painful, then it becomes difficult for the individual to fulfill his professional duties, take care of himself at home, interpersonal interaction and emotional balance are disrupted.
| Sudden attacks interfere with driving and provoke emergency situations on the road. |
Treatment measures
Note that in youth, a disease can arise for no reason and then disappear. There are also many cases where the symptoms of the disease go away if you press on a certain point on the face.
Therapy should be aimed at the main disease that is causing the irritation of the facial nerves.
Reflex tonic blepharospasm is treated by an ophthalmologist or dentist. Essential tonic or clonic - psychiatrist or neurologist.
Please note - the cause of a burst vessel in the eye. How should it be treated?
In the news (more details) analogues of solcoseryl gel.
Treatment for eye blepharitis!
Drug therapy
Basic treatments:
- psychotropic,
- sedatives,
- correcting metabolism,
- affecting microcirculation in the central nervous system,
- reflexology.
Muscle relaxants (muscle relaxers), auto-training, and psychotherapy give good results.
A sufficient effect in the treatment of blepharospasm is achieved by using anticholinergic drugs, for example, benzexol.
Scheme for its administration:
- on the first day 1 mg,
- increasing the dose to 5 mg every 8 hours.
Agonists provide effective assistance, in particular:
- bromocriptine,
- dopamine,
- L-add.
Effective procedure
The modern method of treating the disease includes botulinum toxin type A. The very minimum of this drug is injected into the orbicularis oculi muscle, which allows temporary flaccid paralysis of the muscle to occur. The toxin binds to peripheral nerves, stopping the release of acetylcholine. This procedure sometimes restores vision.
This potent drug does not cause serious complications. If used correctly, it does not harm either the eye muscle or the entire body.
The effectiveness of the procedure is several times higher than that of antipsychotics and anticonvulsants, achieving almost 100% results. The drug lasts from three to six months. Then, if necessary, the injection is repeated.
Help from traditional medicine
Medicinal plants can be used to support therapeutic measures and prevent attacks of spasmodic blinking in the following composition:
1. Treatment of chronic trigeminal neuralgia. Take infusions twice a day, a third of a glass, an hour after meals.
First collection: wormwood (1 part), cinquefoil herb (2 parts), medicinal valerian root (2).
Second collection: common motherwort herb (1), heart-shaped linden flowers (1), white mistletoe herb (2), fragrant rue herb.
2. In case of functional disorders of the central nervous system, infusions are taken according to the same scheme:
First collection: in equal parts medicinal valerian root, common yarrow herb, common oregano herb, common pine buds.
Second collection: equal quantities of peppermint leaves, five-lobed motherwort herb, medicinal valerian root, common hop cones.
3. For insomnia and neurotic conditions, take 0.5 cups of infusion of peppermint leaves (1), common heather grass (2), medicinal lemon balm leaves (2), valerian root (4) three times a day.
Treatment of blepharospasm
Treatment of the disease depends on its cause and predisposing factors.
If dry eye syndrome is detected, the doctor prescribes “artificial tears” in the form of drops with a moisturizing effect. If a foreign body enters the organ of vision, the ophthalmologist very carefully removes it and prescribes anti-inflammatory and absorbable medications. If, after a comprehensive examination, it is not possible to determine the exact etiology of the closure of the palpebral fissure, then several microdoses of botulinum toxin are injected into the periocular muscles. Botox causes paralysis of muscle fibers, and thus eliminates blepharospasm. Side effects such as transient ptosis, blurred vision or diplopia are relatively rare and usually disappear spontaneously after a few weeks.
Symptom resolution from botulinum toxin injections is considered temporary and requires repeated injections every three months for the remainder of the patient's life. Many affected individuals develop a more severe form and/or clinical resistance to botulinum toxin.
If the injections do not lead to positive and lasting results, the spasm still persists, then surgical intervention is indicated. During the operation, the surgeon completely or partially removes defective muscles in the area of the eyebrows and eyelids.
Electromyographic studies help determine the best injection sites for optimal response and differentiate patients who require limited or complete myectomy.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is a method of research that excludes other diseases with a similar set of symptoms, as a result of which the patient is given the only correct diagnosis. Diagnostics are carried out using special computer programs (DiagnosisPro, QMR). Thus, blepharospasm is differentiated from the following diseases:
- Hemifacial spasm (facial hemispasm, characterized by involuntary contractions of the facial muscles).
- Parkinson's syndrome (apraxia of eyelid opening).
- Tourette's syndrome (a genetic disorder of the central nervous system manifested by multiple motor tics).
Attention! Differential diagnosis is required in cases where there are no ophthalmological symptoms of the disease (photophobia, cutting pain, lacrimation).
Prevention of blepharospasm
In modern medicine there are no specific ways to prevent blepharospasm. If the pathology has developed secondary, then it is necessary to avoid irritating factors as much as possible. Wear dark sunglasses in bright light. It is recommended to treat blepharitis and dry eyes with medication, eliminate stress if possible and reduce the dosage of the provoking drug. Ophthalmologists recommend excluding drinks that provoke stimulation of the central nervous system (coffee and strong tea). After working at the computer for a long time, it is better to do eye exercises.
If you notice that for some reason the frequency of blinking is increasing or you need to make an effort to close your eyelids, you should seek help from a neurologist or ophthalmologist.
At the Fedorov Clinic in Moscow, doctors will help diagnose the disease in a timely manner and prescribe treatment. Making an appointment Today: 17 registered
What is blepharospasm of the upper eyelids?
Blepharospasm is a progressive disease accompanied by involuntary tonic spastic contractions of the orbicularis muscles around the eyes. The duration of the attack is from several seconds to several minutes. Happens:
- clonic, rapid and increased blinking;
- tonic contraction (spasm), leading to a narrowing of the eye fissure, and over the years to its complete closure.
The disease usually occurs in people over 50 years of age and is often associated with Parkinson's disease. Women get sick three times more often. There may be unilateral or bilateral spasm of the upper eyelids, combined with spasm of the muscles of the face, arms, and legs. The cause of the development of the disease is assumed to be a central genesis of damage to the nervous system.