What diseases can be seen on MRI images?
Such an examination helps to identify all abnormalities of the brain and blood vessels. The procedure is prescribed for the following diseases:
- Malformations of the brain.
- Visual or hearing impairment.
- Malignant and benign neoplasms.
- Infectious diseases, such as meningitis or encephalitis.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Hematomas after injury.
- Stroke.
- Epilepsy.
- Multiple sclerosis and some other diseases of the nervous system.
- Aneurysm, venous thrombosis and other vascular disorders.
- Dementia.
For these diseases, MRI will become the only reliable diagnostic method.
How are the results deciphered?
After the picture is taken, the doctor immediately begins to examine it. At the very end, he draws up a paper conclusion with all the results of his research and gives it to the patient. If desired, the examination result can be recorded on any electronic medium. This will help the patient show the pictures to various doctors and get a more accurate diagnosis.
Interpretation of brain MRI results consists of the following steps:
- The magnetic resonance tomograph transmits the examination results to a special computer. They are displayed as pictures of the brain. Ideally, there should be 4 projections: front, top, left and right.
- All photographs are printed on film.
- The specialist places all the images on a table with internal lighting.
- Consistently, without missing a single detail, the doctor examines all images. It determines normal values and the presence of abnormalities.
- The doctor draws up all his findings in the form of a written report and gives it to the patient.
The results of MRI of the brain in the form of a conclusion contain information about the shape and condition of all tissues examined. A conclusion is made about whether there are deviations from the norm.
The radiologist does not have the right to make an accurate diagnosis and develop a treatment program. This can only be done by the specialist who issued the referral for examination.
What does a healthy person's brain look like in an image?
MRI of the head helps to obtain images in which tissues are indicated by darkening and clearing. Brain tissue is gray in color. Leaking cerebral fluid appears as light gray streams. The black cavities in the image are intracerebral sinuses.
If all areas of the brain are developed correctly, then the intensity of the signal received from the tomograph will be the same. In a healthy person, the ventricular system should have normal dimensions. Any expansion or decrease is considered a deviation. Normally, there should be both perivascular and subarachnoid spaces. Pay attention to the condition of the grooves and convolutions. There should be no deviations in them.
The structure of the brain itself should also be within normal limits. It should not be displaced. The eye sockets, ear canals and sinuses should be of normal size. No diffuse or focal changes should be observed in the brain tissue.
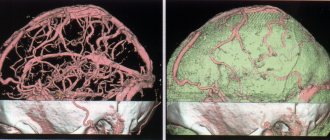
During the procedure with contrast, you can carefully examine the condition of the vessels. They must be properly developed. The contrast agent should fill all vessels evenly.
If the MRI of the brain turns out to be inaccurate, that is, the image does not have sufficient clarity, the doctor decides to repeat the study. People may move during the procedure, which makes the picture blurry.
In some cases, the doctor prescribes a procedure with contrast. In this case, a special chemical is injected into the patient’s blood. Thanks to it you can get a clear, high-quality image. In this case, it is much easier to decipher the MRI of the brain.
The types of brain MRI results and the norm are prescribed in medical reference books. To identify abnormalities, the specialist always compares the patient’s images with samples from a healthy person.
How is a tomogram read?
To make the study as accurate as possible, contrast is used. It will help highlight the brain tissue as clearly as possible. If the tissues have undergone pathological changes, they appear darker during a contrast study. The contrast will help you find out the state of the blood supply to the brain structures.
When analyzing MRI results, the doctor evaluates the following parameters:
- Localization . If a pathological process is detected, the doctor evaluates its location. Localization will help to understand which structures are affected and what this entails. For example, if we compare tumors located in the cerebral cortex with tumors at its base, the latter are much more dangerous.
- Size and shape of the found source . If the tumor has smooth edges, this is most often a sign of its benignity and the presence of a capsule. If there are many foci, this is a sign of the appearance of metastases.
- Hue . An experienced doctor, armed with knowledge of pathological anatomy, can draw a conclusion from the shade of the lesion and its structure which pathological process is running. A changed gray tint, for example, may indicate new growth or softening of the tissue.
There are also indirect indicators that help the doctor make the correct diagnosis. For example, a tomogram of the vessels of the neck and head will help determine the cause of stroke or ischemia.
If the outflow of blood is disrupted, neurological symptoms may also appear, for example, increased intracranial pressure. This leads to compression syndrome.
Differential diagnosis of brain lesions on MRI using algorithms - interpretation of images with explanations:
What do the diseases look like in the pictures?
Deciphering an MRI of the brain is a complex and lengthy process. Even the patient himself can identify some serious diseases in the images. They are clearly visible in the image. These include:
Stroke
This disease is accompanied by cerebral oxygen starvation. The area where hypoxia is particularly severe is indicated by a light spot on the image. If the procedure was carried out with contrast, you can notice how reduced the blood supply is in this area.
Vascular ruptures help decipher the presence of a hemorrhagic stroke. Such places are displayed as dark cavities, which will have ring-shaped stripes along the periphery. Over time, the thickness of such rings will decrease, therefore, the sooner the patient is examined, the more accurately the diagnosis will be made.
What can be detected with MRI?
We have already talked about the safety of this method, but not about its effectiveness. The fact is that there are a large number of diagnostic options, but almost each of them cannot even be compared in effectiveness with the option under consideration. The fact is that during brain tomography it is possible to identify a large number of diseases, among which it is worth highlighting the most dangerous ones, here is a list of them:
- various injuries affecting the cerebral cortex;
- significant disturbances associated with blood circulation;
- problems with cerebrospinal fluid functions;
- brain cyst;
- tumors;
- epilepsy;
- Alzheimer's disease at various stages;
- identifying various consequences of stroke;
- finding pathologies related to the brain;
- degree of brain damage in various head injuries.
And all this can be learned using a non-invasive method, which has absolutely no effect on the functioning of brain structures, therefore, as mentioned earlier, the patient will not feel pain, and everything will be safe for him. As for the comparison with radiography, which is often carried out, it is worth mentioning a more modern method. The fact is that x-rays imply the presence of special rays, which are based on small, but still radiation radiation. Yes, the procedure is relatively safe, given modern equipment, but during an MRI, a magnetic method is used, that is, the device uses a special electromagnetic field, which must be adjusted to a certain power. It is important to understand that, fortunately, it does not affect brain activity in any way.
Note! To obtain accurate information about brain structures, specialists rarely set the strength of this field to more than 3 Tesla. This is quite enough for the image to be clear, if, of course, the procedure is carried out according to all the rules.
MRI of the brain helps to see the surface of the brain and its entire thickness.
Multiple sclerosis
This disease is accompanied by the appearance of nerve fibers that have lost their myelin layer. Such anomalies will be visible on the image as focal formations. During a procedure with contrast, they will have different shades, since they accumulate chemicals in different quantities.
Such lesions can be located in various areas of the white matter. At the initial stage of the disease, as a rule, one or two lesions are detected. As the disease progresses, the number of lesions can number in the dozens.
Changes in tumors
Neoplasms are most easily identified using MRI. In the pictures they all look different, depending on the type of tumor:
- Astrocytoma. This malignant neoplasm is most often diagnosed in the temporal or frontal region. It does not have clear boundaries, and its density is lower than that of tissues not affected by pathology. Such formations do not “absorb” the contrast agent.
In the picture, glioblastoma looks like this:
- Oligodendroglioma. Develops in the frontal part or near the crown. The neoplasm has clear contours. Its density is lower than that of normal tissue.
- Ependymoma. Often formed in the ventricles. This is a malignant formation that develops rather slowly. In the photographs it is determined as a dense, rounded area. Has clear contours.
- Glioblastoma. A malignant tumor with negative consequences. This is a round formation with clear contours.
- Meningioma. Can occur in any area of the meninges. Its characteristic manifestation is severe swelling, which can be even greater than the neoplasm itself.
A qualified doctor can easily distinguish these types of tumors in photographs.
Ependymoma on MRI
Neoplasms
When describing MRI of the brain, it is easiest to detect the presence of tumors. They look like light spots that have an asymmetrical shape and uneven edges.
The neoplasm can impair the functioning of surrounding tissues. If the tumor grows quickly enough, the formation of new blood vessels is observed in this area. If cancer is suspected, experts recommend conducting a contrast study. This will help more accurately identify the location of the tumor and the possibility of surgical removal.
Other pathologies
- Vascular atherosclerosis. Determination of diseases of the vascular system is carried out only during studies with contrast. With atherosclerosis, the images will clearly show a decrease in the lumen of blood vessels and the presence of atherosclerotic plaques.
- Aneurysm. The image will show that the walls of the vessels have become thin and expanded.
- Hypertensive angiopathy. The images will show small round cavities located in close proximity to the vessels.
- Malformation. An MRI will show radially arranged vessels that connect closer to the center.
- Hydrocephalus. The ventricular cavities are significantly expanded. The perivascular and subarachnoid spaces are changed.
- Congenital anomalies. Determined by comparing patient images with reference images. If the detected anomalies do not pose a threat to human health, then treatment will not be required.
Deviations from the norm in photographs may appear differently in different people. Therefore, deciphering the results should be trusted only to a practicing specialist with extensive experience.
Brain diseases detected on MRI
What other diagnoses can be confirmed or made for the first time based on MRI results?
Tumor
In photographs, it will differ in color from healthy tissue; most often it appears as a lighter area with uneven contours. Such a formation can displace other brain structures. If a tumor is detected, additional studies may be required to determine its nature and monitor its growth. In particular, additional MRGs of the brain may be needed to monitor the dynamics of its growth.
Stroke
During a stroke, some areas of the brain suffer from hypoxia, that is, from a lack of oxygen. Because during an attack, the vessels of the head spasm, oxygen-rich blood stops flowing. Depending on the duration of the attack, the degree of hypoxia will vary. In the most severe cases, some areas of the brain may die.
The area of the brain affected by hypoxia will appear lighter in the image than healthy areas of the brain. It can be visually distinguished from a tumor, because this zone corresponds to the innervation of one of the affected cerebral arteries.
If a vessel ruptures during a stroke, a hematoma will be visible on the image. In the photographs, its shade is darker than the healthy area.
Multiple sclerosis
This is a disease in which some nerve fibers lose their outer layer. Because of this, the conduction of impulses through them from the brain to all limbs and internal organs deteriorates. Therefore, with multiple sclerosis, it is difficult for a person to control his body.
Foci of the disease appear on photographs as light areas. They can be found in any part of the brain. Their number can be anything from one to several dozen. If there is only one formation, it can be confused with a neoplasm. But unlike a tumor, the affected areas in multiple sclerosis do not compress or deform other parts of the brain.
Hydrocephalus
This disease is also called dropsy. This is an expansion of the cavities of the ventricles of the brain. Since their volume is larger than normal, they will compress the brain, interfering with its normal functioning. If the patient's condition is not controlled, subsequent brain injuries can be fatal.
Brain gliosis
Brain gliosis (as doctors more often say) is not a disease, but rather a condition of the brain, which is characterized by disruption of the central nervous system. With gliosis, brain neurons die. This condition is a consequence of prolonged hypoxia or stroke. In this case, scars are visible in the photographs.
Anomalies of brain structure and development
If the patient has congenital pathologies, they will be visible in the photographs. Their severity and impact on the patient’s health will be judged by the attending physician. In many cases, such anomalies are either corrected surgically or do not affect the patient’s well-being.
Various vascular diseases
These diseases are confirmed by the results of vascular MRI performed with the introduction of a contrast agent.
Vascular atherosclerosis
In the photographs, this disease looks like a narrowing of the vessel, as if it was pinched. There is less contrast penetration in this area, so this area appears lighter on the image.
Hypertensive angiopathy
This is an expansion of the perivascular spaces, that is, the appearance of edema. In the image you can see round or oval areas with a clear border next to the vessels.
Aneurysm
This is the thinning of the vessel wall due to its expansion. An aneurysm can rupture at any time. Therefore, such conditions are extremely dangerous and require immediate consideration at a consultation.
Malformation
This is a pathology of the vascular bed, it refers to congenital pathologies. The images show that the vessels, which are located radially, converge towards the center.
What can make deciphering an MRI difficult?
The results of MRI of the brain in most cases are accurate and reliable. The contrast procedure always helps to get a clear picture. Therefore, in the absence of any contraindications, it is better to carry it out.
A deteriorated image is obtained in patients with endoprostheses. The presence of metal in them distorts the image. In addition, any metal object left in a pocket may invalidate the test results. Therefore, before the procedure, it is extremely important to remove all jewelry and check the contents of your pockets.
Metal particles may be contained in the ink used to apply tattoos. Therefore, the presence of drawings on the body becomes a contraindication to MRI. They not only worsen the results, but also cause pain during the examination.
The presence of braces can also ruin the picture. In this regard, it is imperative to notify the radiologist about them. If possible, it is better to remove them during the study.
What does an MRI show?
Tumors, hydrocephalus (another name is dropsy) and much more - this is exactly what can be detected using MRI. But in the photographs everything does not look so simple, because not everyone will be able to distinguish the brain of a healthy person from the brain affected by some dangerous pathology. The various sections that are captured in the photographs are expressed only in shades of two colors - black and white, that is, different places are emphasized using varying contrast, which completely depends on the degree of vibration of the hydrogen protons contained in the tissues. It is this (impulses from such vibrations) that the MRI machine captures.
As for the images themselves, you can see the ventricles containing intracerebral fluid, as well as gray matter and white matter; their condition can already tell a specialist a lot, but this data is not yet enough to make a competent, and most importantly, correct diagnosis . For this reason, it is necessary to analyze other brain structures in the images, for example, subcortical centers, as well as various formations that are responsible for the functions of the body. But, in addition to the listed structures, there are other parts, the importance of which is often forgotten. We are talking about the meninges, as well as the space that is between them, about the eye sockets, about the nasal sinuses, about the various bones of the skull and ear canals. Yes, these parts do not belong to the brain, but they can also provide a specialist with useful information.
Is it possible to interpret MRI results yourself?
The conclusion of MRI of the brain should be made only by a specialist with extensive experience. In order to correctly determine the presence of anomalies, it is not enough to have samples; it is necessary to have an excellent understanding of the anatomy of the human body. In addition, the doctor must not only analyze the images themselves, but also correlate them with the results of the preliminary examination and tests performed. This is the only way to get a complete picture of the disease and subsequently develop the correct treatment method.
If the deciphered MRI of the brain gives you doubts, you can always get the pictures in hand. The radiologist will give them to you in printed form and record them on any electronic media. You can then ask another specialist to analyze them.
Today it is possible to receive online consultations with specialists. All you have to do is post your photos on a specialized resource. You will receive not only a transcript of the results, but also an explanation of them in simple accessible language. But such consultations should not be taken as final. It is necessary to gather all opinions and consult a doctor you trust.
Remember that you need to do an MRI of the brain and get a transcript only from a specialist with extensive experience in practice. He will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and select an effective treatment program.
Who treats brain diseases?
The attending physician for a patient with brain pathology may be a neurologist or neurosurgeon. As a rule, doctors in this specialty can independently interpret tomograms. A neurologist or neurosurgeon, having performed an independent analysis of tomograms, may not agree with the description and conclusion of the radiologist, since in addition to MRI images, he also analyzes the results of examination and other examinations of the patient.
If the doctor has doubts and disagreements with the radiologist, as a rule, a medical consultation is held, and a repeat study is performed.