The procedure during which a special needle is inserted into the subarachnoid space is called a lumbar puncture (spinal, lumbar or spinal puncture, lumbar puncture or spinal puncture). The main purpose of the procedure is to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for further research, which will identify the exact causes of nervous diseases, infections and systemic pathologies. Lumbar puncture is also performed for therapeutic purposes. Before carrying out the procedure, it will be useful to know in what cases it is indicated and when it is prohibited. And when studying the technique of performing a lumbar puncture, the patient will understand that the manipulation is not dangerous to health. However, there is a possibility of some complications after it.
Basic information
Spinal cord puncture is a therapeutic and diagnostic procedure during which cerebrospinal fluid is extracted from the subarachnoid space through a special needle.
There is an opinion that lumbar puncture is dangerous, since during it the spinal cord can be damaged. To understand that this is not so, you need to delve a little deeper into embryology.
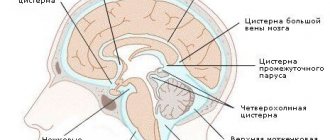
During fetal development, the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, develops from the fetal neural tube. All components of the nervous system (neurons, peripheral nerves, subarachnoid cisterns, cerebrospinal fluid, etc.) have the same origin. Therefore, by the composition of cerebrospinal fluid from the caudal region of the back, the condition of the entire nervous system can be assessed.
The spinal cord ends at the level of the 2nd lumbar vertebra
During fetal development, vertebrae grow faster than nerve tissue. For this reason, the spinal cord ends at the level of the 2nd lumbar vertebra with the conus medullaris. Further, thin threads extend to the junction with the sacrum.
Thanks to this structure, it is safe to puncture the spinal canal in this place. According to doctors, the phrase “spinal cord puncture” is incorrect, since there is no spinal cord at the puncture site, only its membranes and cerebrospinal fluid are located here.
Reference. The volume of cerebrospinal fluid in an adult is approximately 120 ml. It is updated after 5 days.
Not all people understand why they take a spinal cord puncture. Lumbar puncture is done to achieve the following goals:
- Study of biological material in laboratory conditions for glucose, certain cells, proteins and other components.
- Determination of cerebrospinal fluid pressure.
- Removing excess cerebrospinal fluid.
- Introduction of drugs into the nervous system.
Now you know why a cerebrospinal fluid puncture is taken.
The composition of cerebrospinal fluid and the norm of cerebrospinal fluid in adults
Liquor plays an important role in the functioning of both the spinal cord and the brain. It is a mechanical protection, forms a liquid medium necessary for biochemical processes, cell activity and the transmission of nerve impulses.
In an adult, the total volume of cerebrospinal fluid ranges from 140 to 270 ml. About half comes from cerebrospinal fluid.
The fluid is produced by the glandular cells of the choroid plexuses in the ventricles of the brain. It runs throughout the entire space of the central nervous system. The composition of cerebrospinal fluid is close to blood serum, but some components are contained in larger or smaller quantities compared to it. For example, liquor fluid contains more proteins, but about half as much glucose. In a healthy person, the cerebrospinal fluid is colorless, its density is 1005-1009 units.
Cerebrospinal fluid (liquor cerebrospinalis) has a slightly alkaline reaction with a pH range from 7.31 to 7.33. Normally it contains:
- 0.16-0.33 g/l proteins;
- 2.78-3.89 mmol/l glucose;
- 120-128 mmol/l chlorine ions.
Cerebral liquor does not contain large protein molecules. The amount of protein in it varies from person to person and changes with age (adults have more than children). Normally, the cerebrospinal fluid also contains a small amount of carbohydrates, lactic and uric acid, creatinine, cholesterol, and urea. The liquid is involved in water-salt metabolism in the body and maintaining electrolyte balance. It is constantly renewed, flowing through the glandular cells of the choroid plexuses.
Indications for the procedure
As mentioned, a spinal tap may be performed for diagnosis or treatment. In the first case, the procedure is carried out when it is necessary to study the composition of the cerebrospinal fluid, identify pathogens in it, measure the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid, as well as the patency of the subarachnoid (subarachnoid) space.
In the second case, the manipulation is carried out to evacuate excess cerebrospinal fluid and introduce medications (antibiotics or chemotherapy drugs) into the spinal canal.
Indications for lumbar puncture are divided into absolute and relative. In the first case, the procedure is mandatory, and in the second, it is recommended, but the decision is made by the doctor.
Lumbar puncture must be performed in the following cases:
- Infections affecting the central nervous system, for example, meningitis, encephalitis.
- Oncological formations in the membranes or structures of the spinal cord.
- Diagnosis of liquorrhea (leakage of cerebrospinal fluid) using radiocontrast agents.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage (bleeding under the arachnoid membrane).
Relative indications include:
- Multiple sclerosis and other pathologies in which the myelin sheath of neurons is destroyed.
- Diseases characterized by systemic damage to peripheral nerves.
- Septic vascular embolism.
- Lupus erythematosus and other systemic connective tissue pathologies.
Meningitis is often preceded by an infection, and a lumbar puncture is performed to determine its cause.
During a lumbar puncture, the presence of pathogenic bacteria in the cerebrospinal fluid can be determined.
It is necessary to take cerebrospinal fluid for examination to determine intracranial pressure, the number of neutrophil granulocytes, and the presence of pathogenic bacteria (Haemophilus influenzae, meningococcus, pneumococcus).
A lumbar puncture is done to distinguish a stroke from other pathologies and to determine the cause of its development. A spinal puncture helps determine antibodies in the cerebrospinal fluid, then doctors talk about multiple sclerosis. If tuberculosis is suspected, the cerebrospinal fluid is examined for sugar, neutrophils and lymphocytes. A spinal tap is performed to detect syphilis in asymptomatic cases.
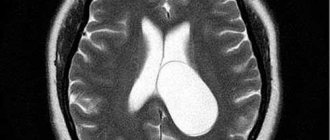
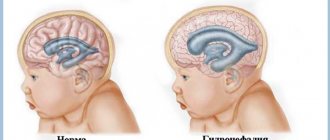
Reference. By measuring cerebrospinal fluid pressure, hydrocephalus (water on the brain) can be detected. When evacuating 50–60 ml of fluid, most patients feel relief.
Lumbar puncture in newborns is performed if meningitis is suspected. The study will help identify the causative agent of infection (viruses or bacteria). The study will also help to identify the level of protein and red blood cells in a child, because their deficiency increases the risk of infectious diseases.
Indications and contraindications
Lumbar puncture is necessary in the following cases:
- if you suspect infectious diseases of the central nervous system (encephalitis or meningitis);
- in case of suspected subarachnoid or intracerebral hemorrhage, if computed tomography cannot be performed or the study gives negative results;
- patients with high intracranial pressure due to hypertensive hydrocephalus, subarachnoid hemorrhage or benign intracranial hypertension;
- for administering medications into the spinal canal (antibiotics for meningitis).
A lumbar puncture of the spine is performed to exclude or confirm the diagnosis of neuroleukemia.
Contraindications to performing a lumbar puncture are infectious skin diseases at the site of the intended puncture, suspicion of the presence of a brain space-occupying lesion (abscess, tumor, subdural hematoma), especially in the posterior cranial fossa, and a marked decrease in the number of platelets in the blood. Repeated lumbar puncture, if indicated, is performed after 5-7 days. Despite the presence of contraindications, lumbar puncture is performed in cases of papilledema (when purulent meningitis is suspected) and in patients with benign intracranial hypertension.
When is spinal tap prohibited?
Before the procedure, you need to know in what cases lumbar puncture is prohibited.
Absolute contraindications:
- Marked swelling and increase in brain volume.
- Sudden increase in intracranial pressure.
- Neoplasms in brain tissue.
- Closed hydrocephalus is a pathology in which cerebrospinal fluid cannot independently enter the subarachnoid space due to obstacles.
If there are such contraindications, a child or adult is prohibited from having a lumbar puncture. Otherwise, the risk of axial herniation of the brain increases - this is a pathology in which part of the brain is displaced into the foramen magnum. Then the work of vital areas is disrupted, which threatens the death of the patient. Herniation can occur if the doctor uses a thick needle and removes a lot of cerebrospinal fluid from the spinal canal.
Carefully! If a lumbar puncture is necessary, and the likelihood of brain herniation is high, then a minimum amount of cerebrospinal fluid should be extracted. When symptoms of pathology appear, you must immediately inject the required volume of cerebrospinal fluid using a needle.
There are other contraindications for spinal puncture:
- Presence of pustules on the lower back.
- Blood clotting disorder.
- Medicines that thin the blood (antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants).
- Blockade of the subarachnoid space.
- Bleeding due to local dilation and rupture of a vessel (aneurysm) in the brain or spinal cord.
- The period of gestation.
In the presence of such conditions, the doctor decides to perform the procedure, taking into account possible complications.
Preparing for a lumbar puncture
Preparation for a planned lumbar puncture includes a comprehensive examination, psychological support, and adjustment of the list of medications taken. Before sending a patient for a lumbar puncture, he is prescribed other examinations, starting with routine blood and urine tests, coagulation tests and ending with visits to specialists, CT scans, MRIs, when necessary. This applies more to outpatients or patients whose lives are not in danger. Otherwise, the doctor will act quickly and based on the patient’s condition.
If the patient’s consciousness is not impaired, then he must inform the anesthesiologist about the medications he is constantly taking, the presence of allergies, and chronic somatic pathology. Women should make sure that there is no pregnancy, especially if they plan to administer radiocontrast agents, toxic antibiotics and cytostatics. All patients must sign written consent to the intervention.
Lumbar puncture is performed on an outpatient basis, when the patient himself comes for the procedure, or on an inpatient basis, if the patient is undergoing treatment or examination in a clinic. It is better not to eat or drink 12 hours before the scheduled procedure, and stop taking blood thinners two weeks later.
The puncture for children is carried out by consent and in the presence of the parent, who is simply obliged to support and calm the frightened and confused child. Usually in pediatrics, a puncture is performed under general intravenous anesthesia, which ensures calm and correct positioning of the child.
An important preparatory stage is psychological support for the patient, during which the doctor explains the essence of the procedure and argues in favor of its necessity. Sedatives are used according to indications
It is especially important to work with those people who are allergic to local anesthetics, because for health reasons they will undergo a puncture without pain relief.
Technique for performing spinal cord puncture
The technique of performing a lumbar puncture is simple, but requires caution and knowledge of anatomy, so it is performed by an experienced doctor with the help of a nurse.
To perform a lumbar puncture, a special needle with a mandrel is used
First, the assistant prepares the kit for the procedure:
- gloves, mask;
- antiseptic solution that contains iodine;
- cotton wool;
- sterile underwear with a hole for the puncture site;
- Beer puncture needle with mandrin (rod for closing the lumen of the needle);
- test tubes with caps;
- adhesive plaster.
The nurse prepares the patient for the procedure and provides care after it.
Important. The main thing during a lumbar puncture is to correctly determine the puncture site. In some pathologies of the spinal column, it is impossible to pierce the spinal canal.
First, the doctor explains all the details of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection procedure to the patient. In addition, before the manipulation it is necessary to empty the bladder and intestines.
Lumbar puncture in the lateral position
In the ward, the patient must take a lying or sitting position. In the first case, the patient lies on the couch on his side, arching his back and pulling his knees towards his stomach (fetal position). In this position it is easiest to feel all the vertebrae, processes and even the distance between them.
In the second case, the patient sits on the couch and bends his torso forward to make it easier for the doctor to determine the puncture site in the lumbar spine.
Technique for performing lumbar puncture:
Symptoms and prognosis for spinal cord tumor
- The puncture point is determined, which is located between L3 – L4 (third and fourth lumbar vertebrae) or L4 – L5.
- The puncture area is wiped with an antiseptic three times, starting from the intervertebral area and continuing to increase the circumference.
- After the antiseptic has dried, the back is covered with sterile linen with a hole.
- An anesthetic injection is given; as a rule, Novocaine, Lidocaine or Ultracaine are used for this.
- The puncture needle is inserted into the previously determined space between the spinous processes at an angle, trying to adhere to the midline.
- The doctor punctures all layers in turn (for example, the yellow ligament, dura mater) until he penetrates the spinal canal. After passing through all the structures, the needle seems to fall into the spinal canal. If there is no such sensation, then you need to remove the mandrin; if the liquid leaks, then this indicates that the needle is already inside the canal. If the doctor has inserted the needle correctly, but the cerebrospinal fluid does not flow out, the patient is asked to cough or sit up to increase fluid pressure.
- Next, the liquid is collected in different test tubes of approximately 1 ml. The liquid should drain passively; do not extract it with a syringe.
- Then you need to measure the pressure, which is normally 100 - 150 mm Hg. Art. To get accurate results, you need to relax as much as possible. The pressure can be determined approximately: 60 drops of CSF is the norm. During inflammatory processes, the volume of cerebrospinal fluid increases.
- The needle is carefully removed, the puncture site is treated with an antiseptic and a sterile bandage is applied.
During a lumbar puncture, the needle is inserted between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae at a slightly inclined angle.
The procedure lasts approximately 30 minutes.
Lumbar puncture in newborns has its own characteristics:
- The child is held in a position on his side or sitting so that the lumbar region is flexed. In this case, you need to ensure that the cervical segment does not bend, because then the patency of the upper respiratory tract worsens.
- In very low birth weight premature babies, the puncture is made in the area between the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebrae to avoid damaging the spinal cord.
- The depth of needle insertion is up to 1 – 1.5 cm.
Reference. With numerous lumbar punctures, adhesions appear, due to which the fluid may not flow out. Then the puncture is performed in an area slightly higher or lower.
The spinal puncture protocol is recorded in the medical history.
How is cerebrospinal fluid collected?
The technique of performing a spinal puncture is as complex as it is elementary. In the skillful hands of a qualified doctor, the manipulation takes no more than half an hour.
How is the patient prepared?
The very first and most important stage is preparing the patient for the procedure.
To begin with, the doctor conducts a survey on:
- taking medications. It is mandatory to list absolutely all medications taken in the near future. It is mainly necessary to exclude groups of anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The appropriateness of other drugs (including the Vital and Essential Drugs group) is determined by the attending physician,
- history of allergic status. All possible drugs and substances that give a nonspecific histamine response of the body are carefully identified,
- pregnancy _ Women should definitely inform their doctor about this fact.
This is followed by the appointment of general clinical laboratory tests (blood for general and biochemical tests). If there are indications, an MRI or CT scan of the head is prescribed to exclude tumor formations that can cause negative consequences and complications after spinal cord puncture.
more about what facet rhizotomy is here.
The final stage of preparation is the day before the study. On the last day, you must take a 12-hour fast and refrain from drinking liquids for 4 hours before the procedure.
The collection process itself
The manipulation algorithm for lumbar puncture consists of several stages:
- The patient wears a special surgical shirt with a wrap around the back.
- The patient lies on the couch on his side in the “cocoon” position - legs bent at the knees and brought as close as possible to the chest, chin to the jugular notch.
- The puncture site is disinfected first with alcohol, then with iodine.
- Local infiltration anesthesia is performed (“ Novocaine”, “Ultracaine”, “Lidocaine” ).
- After palpating the required point, a special needle for spinal puncture is inserted to a depth of approximately 5 cm. The direction angle is sagittal and upward. At the specified depth, a feeling of an obstacle should appear. After some pressure, the needle should “fall” into the subarachnoid space.
- Then the mandrel is removed from the needle, and passive outflow of cerebrospinal fluid occurs.
- After collecting the required amount of biomaterial, the puncture is covered with a bandage.
After the manipulation, complete 3-4 hours of rest is recommended, lying on your back or side.
Feelings during the procedure
Many patients are interested in the question of whether it is painful to perform a lumbar puncture. If the procedure is performed correctly, the patient does not feel any significant discomfort or pain. He can feel the needle passing through the hard membranes, but there is no painful reaction. Unpleasant symptoms do not appear, since the doctor administers an anesthetic solution before the puncture.
You may feel an electric shock if the needle hits a spinal nerve. Some patients experience headaches during the procedure.
How to carry out the procedure
Why the procedure is being done has been determined, now you need to understand the methods for carrying it out. They are different and directly depend on the area where the liquid is taken.
Anterior horn of the lateral ventricle
The ventricular procedure for this area is performed as follows:
- The patient lies on his back when a tumor in the brain is to be identified. Usually the patient lies down on the healthy side to make it more convenient for the doctor to perform a puncture on the injured side.
- The head is slightly tilted towards the chest.
- The puncture site is thoroughly disinfected and coated with iodine twice.
- Draw a puncture line, which should be guided by the arrow-shaped seam, passing the Kocher point. It is covered with a layer of brilliant green solution.
- The head is covered with a sterile sheet.
- Any local anesthetic to which the patient is not allergic is used to numb the puncture area, most often it is Novocain.
- Using a scalpel, an incision is made along the intended line.
- A cut is made on the trepanation window on the exposed skull.
- The neurosurgeon makes a cross-shaped incision on the dura mater. Wax is rubbed in or electrocoagulation is performed. For what? To stop bleeding, the latter method being the most effective.
- The cannula is inserted into the brain tissue to a depth of no more than 5-6 cm so that it runs parallel to the incision line. When puncturing the wall of the lateral ventricle, the doctor will feel a slight dip.
- Yellowish cerebrospinal fluid will begin to flow through the submerged cannula. Having penetrated the cavity of the ventricle, the doctor fixes the needle and, using a mandrel, regulates the volume and speed of the withdrawn fluid.
Important! Rapid collection of cerebrospinal fluid is strictly prohibited. This must be done drop by drop.
Often there is high pressure in the ventricular cavity, and if it is not controlled, the fluid will flow out in a stream. This will lead to the patient developing neuralgic problems.
The permissible volume of fluid intake is in the range of 3-5 ml. It is important to note that in parallel with the preparation of the room for the puncture, the operating room is also prepared, since there is a high risk that air may enter the area being examined, or the depth of the puncture will be excessive, which may cause injury to the blood vessel. In these cases, the patient will be urgently operated on.
In cases of puncture, children use the methods of collecting cerebrospinal fluid according to Dogliotti and Geimanovich:
- In the first case, the puncture is carried out through the orbit.
- In the second - through the lower part of the temporal bone.
Both of these options have a significant difference from the traditional procedure - they can be repeated as often as necessary. For infants, this procedure is carried out through an open fontanel, simply by cutting the skin above it. In this case, there is a serious danger that the baby will develop a fistula.
Posterior horn of the brain
The technology for collecting cerebrospinal fluid from the area is carried out in the following order:
- The patient lies on his stomach. His head is tightly fixed so that the sagittal suture is strictly in the middle cavity.
- The preparatory process is identical to the above procedure.
- The incision of the skull tissue is carried out parallel to the sagittal suture, but so that it passes through the Dandy point, which should be strictly in its middle.
- Take a needle number 18, which is used strictly for this type of puncture.
- It is inserted at an angle, directing the needle tip into the outer upper edge of the orbit to a depth of no more than 7 cm. If the procedure is performed on a child, the puncture depth should not exceed 3 cm.
WE RECOMMEND WATCHING: Why the left side of your head may hurt
inferior horn of the brain
The principle of the procedure is similar to the previous two:
- the patient should lie on his side, since the surgical field will be the side of the head and the auricle;
- the incision line will go 3.5 cm from the external auditory canal and 3 cm above it;
- part of the bone in this area will be removed;
- an incision will be made in the dura mater of the brain;
- insert a puncture needle 4 cm, directing it to the top of the auricle;
- cerebrospinal fluid will be collected.
Rules of conduct after puncture
It is recommended to lie on your stomach for 3 hours after a lumbar puncture. It is also prohibited to lift heavy objects or subject yourself to physical stress. If these rules are followed, the patient will be able to avoid leakage of cerebrospinal fluid from the hole.
If medications are administered into the subarachnoid space, the patient must remain in bed for at least 3 days.
Carefully. If there is an increase in temperature, numbness or fluid discharge from the hole after the puncture, you should visit a doctor.
Types of puncture in gynecology
There are several types of punctures that are used for the diagnosis and treatment of female diseases:
- Breast puncture. It is prescribed in the presence of nodules, ulcers or any seals, changes in skin tone, or strange discharge from the nipples. The procedure allows you to determine the presence of tumors of different etiologies and diagnose their nature. Some preliminary preparation is required. For example, a week before the puncture you should not take Aspirin or any other medications that help reduce blood clotting. After the puncture, a woman may feel slight discomfort, which goes away after a few days.
- Retrieval of eggs for artificial insemination. The procedure should be carried out 35 hours after the injection of human chorionic gonadotropin. The puncture is performed transvaginally. A special needle is also required. The entire process is controlled by ultrasound. This procedure requires certain skills, so you need to look for an experienced specialist for this. In general, it is considered practically painless, but in order to avoid complications after the puncture, the woman is given anesthesia.
- Cardocentesis. This procedure is important for determining congenital pathologies or infectious lesions of the fetus. To do this, blood is taken from the umbilical cord. It is allowed from the 16th week, but in order not to harm the baby and to get a more accurate result, a puncture is prescribed from 22 to 24 weeks. A puncture is made through the pregnant woman's abdomen into the umbilical cord vessel. All devices must be sterile. For puncture, a special needle with an attached syringe is taken. This method of determining infection or developmental abnormalities is considered the most accurate, but is used only if other diagnostic methods are ineffective.
- Ovarian cyst puncture. This procedure is used for diagnostic as well as therapeutic purposes. The procedure requires general anesthesia, which is administered intravenously. The instruments are inserted through the vagina. The needle enters through a special sensor. An aspirator is attached to it. The instrument is used to suction fluid from the cyst cavity. The biomaterial is sent to the laboratory for cytological and histological analysis. After there is no more fluid left in the cyst, a small amount of alcohol is injected into it, gluing the walls of the formation. In most cases, this procedure allows you to completely get rid of the cyst, although in rare cases relapses are possible. After the puncture, the woman returns home on the second day. In general, the manipulation does not cause pain, however, the patient must be completely motionless, so anesthesia is necessary.
- Abdominal puncture. It is carried out through its wall or posterior vaginal fornix. The procedure is used to diagnose gynecological pathologies, as well as to prepare for surgery. Since such a puncture is very painful, it must be performed with anesthesia. Moreover, anesthesia can be local or general. Before the puncture is performed, the intestines and bladder must be empty.
All of these types of punctures are used in gynecology in difficult cases when diagnosis or treatment by other methods does not give a positive result.
Research results
As a rule, CSF is collected in 3 containers, which are then sent for general, biochemical and microbiological analysis.
Doctors pay attention to the color of the cerebrospinal fluid:
- Bloody - an admixture of blood in the fluid may indicate blood leaking into the cavity between the arachnoid and pia mater.
- The yellowish color of the CSF indicates long-term development of hemorrhagic processes, for example, subdural hematoma (accumulation of blood between the brain and membranes), metastases in the meninges, blockage of the cerebrospinal fluid pathways.
- Grayish-green – neoplasms in the brain.
- Transparent – the person is healthy.
The ventricular mass is carefully examined, doctors measure pressure, determine the amount of protein, glucose, etc.
Normal results of a cerebrospinal fluid test look like this:
- liquid color – transparent;
- protein level – from 150 to 450 mg/l;
- glucose concentration – from 4 to 60% of the blood level;
- there are no atypical cells;
- leukocytes – up to 5 in 1 mm³ of blood;
- neutrophils and red blood cells are absent;
- pressure – from 150 to 200 mm Hg. Art.
Important. If the cerebrospinal fluid pressure is higher than normal, then decongestant therapy should be performed. If this indicator is underestimated, then this indicates brain pathologies.
Red blood cells, neutrophils and pus indicate blood diseases. Atypical cells are found in brain tumors, and sugar levels decrease in bacterial meningitis.
Lumbar puncture will allow timely identification of many dangerous diseases and treatment.
Evaluation of the result of spinal puncture
The result of a cytological analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid is ready on the day of the study, and if bacteriological culture and assessment of the sensitivity of microbes to antibiotics is necessary, the wait for an answer can last up to a week. This time is necessary for microbial cells to begin to multiply in nutrient media and show their response to specific drugs.
An admixture of blood in the cerebrospinal fluid indicates hemorrhage under the membranes of the brain or injury to the vessel during the procedure. To distinguish between these two reasons, the liquid is taken into three containers: in case of hemorrhage, it is colored homogeneously red in all three samples, and in case of damage to the vessel, it becomes lighter from the 1st to the 3rd tube.
The density of cerebrospinal fluid also changes with pathology. So, in the case of an inflammatory reaction, it increases due to the cellularity and protein component, and in case of excess fluid (hydrocephalus) it decreases. Paralysis, brain damage from syphilis, and epilepsy are accompanied by an increase in pH, and with meningitis and encephalitis it falls.
The cerebrospinal fluid may darken with jaundice or metastases of melanoma, it turns yellow with an increase in the content of protein and bilirubin, after a previous hemorrhage under the membranes of the brain.
Cloudiness of the cerebrospinal fluid is a very alarming symptom that may indicate leukocytosis due to bacterial infection (meningitis). An increase in the number of lymphocytes is typical for viral infections, eosinophils for parasitic infestations, and erythrocytes for hemorrhages. The protein content increases with inflammation, tumors, hydrocephalus, infectious damage to the brain and its membranes.
The biochemical composition of the cerebrospinal fluid also indicates pathology. Sugar levels decrease with meningitis and increase with strokes, lactic acid and its derivatives increase in the case of meningococcal lesions, abscesses of brain tissue, ischemic changes, and viral inflammation, on the contrary, leads to a decrease in lactate. Chlorides increase with neoplasms and abscess formation, and decrease with meningitis and syphilis.
According to reviews from patients who have undergone a spinal puncture, the procedure does not cause significant discomfort, especially if it is performed by a highly qualified specialist. Negative consequences are extremely rare, and patients experience the main concern at the stage of preparation for the procedure, while the puncture itself, performed under local anesthesia, is painless. After a month after the diagnostic puncture, the patient can return to his usual lifestyle, unless the result of the study requires otherwise.
Complication of spinal cord puncture
Consequences of puncture are rare (in 1–5 patients out of 1000):
- displacement and herniation of brain tissue;
- the appearance of symptoms of meningitis due to irritation of the meninges;
- neuroinfections as a result of violation of antiseptic rules by doctors;
- severe headache may be associated with impaired CSF circulation;
- severe pain along a certain nerve when the spinal cord roots are damaged;
- hemorrhages due to bleeding disorders or taking medications that thin the blood;
- epidermoid cyst;
- meningeal reaction - changes in CSF parameters after the administration of medications or contrast solutions.
These are the main complications that can occur after a lumbar puncture.
Postoperative period and possible complications
After taking the cerebrospinal fluid, the patient is not lifted, but is taken in a supine position to the ward, where he lies on his stomach for at least two hours without a pillow under his head. Babies up to one year old are placed on their backs with a pillow under their buttocks and legs. In some cases, the head end of the bed is lowered, which reduces the risk of dislocation of brain structures.
For the first few hours, the patient is under careful medical supervision; specialists monitor his condition every quarter of an hour, since the flow of cerebrospinal fluid from the puncture hole can continue for up to 6 hours. If signs of edema and dislocation of the brain regions appear, urgent measures are taken.
After a spinal tap, strict bed rest is required. If the cerebrospinal fluid levels are normal, then after 2-3 days you can get up. In case of abnormal changes in the punctate, the patient remains on bed rest for up to two weeks.
A decrease in fluid volume and a slight decrease in intracranial pressure after a spinal tap can trigger headache attacks that can last about a week. It can be relieved with analgesics, but in any case, if such a symptom occurs, you should talk to your doctor.
Collecting cerebrospinal fluid for research may be associated with certain risks, and if the puncture algorithm is violated, the indications and contraindications are not carefully assessed, or the patient’s general condition is severe, the likelihood of complications increases. The most likely, although rare, complications of a spinal puncture are:
- Displacement of the brain due to the outflow of a large volume of cerebrospinal fluid with dislocation and wedging of the brainstem and cerebellum into the occipital foramen of the skull;
- Pain in the lower back, legs, sensory disturbances due to spinal cord root injury;
- Post-puncture cholesteatoma, when epithelial cells enter the spinal cord canal (using low-quality instruments, lack of a mandrel in the needles);
- Hemorrhage due to injury to the venous plexus, including subarachnoid;
- Infection followed by inflammation of the soft membranes of the spinal cord or brain;
- If antibacterial drugs or radiopaque substances enter the intrathecal space, symptoms of meningism with severe headache, nausea, and vomiting occur.
Consequences after a properly performed spinal tap are rare. This procedure makes it possible to diagnose and effectively treat, and in case of hydrocephalus it is itself one of the stages in the fight against pathology. Danger during puncture may be associated with a puncture, which can lead to infection, damage to blood vessels and bleeding, as well as dysfunction of the brain or spinal cord. Thus, spinal puncture cannot be considered harmful or dangerous if the indications and risks are correctly assessed and the procedure algorithm is followed.
Cost of the procedure
Prices for spinal puncture depend on the level of the clinic, the complexity and nature of the procedure.
In Moscow, the cost of lumbar puncture differs depending on the medical institution:
- Clinic "El. En." — 5400 rubles.
- "PENTA-CLINIC" - 3350 rubles.
- Medical - 2300 rubles.
- Central Clinical Hospital No. 2 of JSC Russian Railways - 1,700 rubles.
- Clinical Hospital No. 119 – 1500 rubles.
- Children's Clinical Hospital named after Semashko - 1450 rubles.
The higher the qualifications of the doctors, the better the equipment of the medical facility and the more complex the procedure, the more you will have to pay for it.
Reviews
Almost all patients respond positively to lumbar puncture. The procedure does not cause significant discomfort or pain, but provokes mental stress. In most cases, there are no complications after a lumbar puncture, although it all depends on the skill level of the doctor.
Irina, 45 years old: “I was treated several times in an inpatient setting for meningitis, and then a lumbar puncture was prescribed. It was scary the first time, but then I realized that there was nothing wrong with it. I felt a slight pain only during the anesthetic injection, then there was a sensation of interference in the lower back, but it became numb. The main thing is to find an experienced doctor, because you can remain disabled if you catch a nerve.”
Ekaterina, 34 years old: “I had a lumbar puncture twice for suspected meningitis. There were no serious complications after the procedure, although after the first time I had a headache. The second time I asked the doctor to make a puncture with a smaller needle, then I didn’t feel anything at all, and there was no headache.”
Igor, 44 years old: “I had to do a spinal tap 3 times. During the procedure, pain is not felt, only movement in the lumbar region was heard, this causes psychological discomfort. I tried to distract myself and stopped paying attention to it. There were never any complications after the study.”
Decoding the results
Normally, cerebrospinal fluid has moderate viscosity, a transparent and colorless structure. Even before the analysis, the doctor evaluates the appearance of the cerebrospinal fluid, the presence of impurities in it (for example, blood), the consistency of the liquid and the rate of its flow. Normally, cerebrospinal fluid should be released at a rate of 20 to 60 drops per minute. Deviation from these indicators may indicate inflammatory processes, tumor diseases or metabolic disorders (for example, leukodystrophy).
Normal indicators for studying the composition of cerebrospinal fluid
Normal cerebrospinal fluid values and possible abnormalities
| Parameter | Norm | The indicator is increased (possible reasons) | The indicator is lowered (possible reasons) |
| Cerebrospinal fluid density | 1,005-1,008 | Any inflammatory (including infectious and purulent) diseases of the spinal cord | Excess fluid (possible signs of hydrocephalus) |
| pH level (acidity) | 7,3-7,8 | Neurogenic syphilis, epilepsy, organic lesions of the nervous system | Inflammation of the brain and its membranes |
| Protein | 0.44 g/l | Neuroinfections, inflammation of the meninges and various structures of the brain and spinal cord, hydrocephalus, malignant tumors | Neuropathy |
| Glucose | 2.3-4.0 mmol/l | Strokes | Meningitis and meningoencephalitis |
| Lactic acid salts | 1.0-2.5 mmol/l | Inflammation of the brain and its membranes due to infection with pathogenic bacteria and any inflammatory pathologies of the central nervous system | Viral cerebrospinal meningitis |
| Hydrochloric acid salts | 115-135 mmol/l | Neoplasms and accumulation of pus in the cranial cavity | Inflammation of the soft membranes of the brain, neurogenic syphilis, brucellosis |
Cloudiness of the cerebrospinal fluid indicates increased infiltration of leukocyte cells, and a dark yellow color indicates possible metastases from skin cancer.
Video - Spinal tap
Spinal cord puncture is an effective therapeutic and diagnostic neurosurgical procedure that has a high degree of reliability and information content in cases of suspected various diseases of the central nervous system. Today, sufficient practical experience has been accumulated in carrying out such manipulations, and the risk of possible complications is minimized, so you should not be afraid of a lumbar puncture. All actions are performed under local anesthesia, and the patient does not feel pain during the procedure, except for the initial discomfort from the injection itself.
Main conclusions
As you can see, lumbar puncture is an important and also informative diagnostic and treatment procedure. Most often it is prescribed for neuroinfections, suspected subarachnoid bleeding, malignant process, autoimmune pathologies of the nervous system. It is contraindicated in cases of severe cerebral edema, a sharp increase in intracranial pressure, the presence of a large tumor in the brain, etc. There are some features of performing a lumbar puncture for children and adults. To ensure that the procedure goes without complications, you need to contact an experienced specialist. After a lumbar puncture, the cerebrospinal fluid is sent for research, during which dangerous diseases of the nervous system can be identified and treated. Most patients who have had a lumbar puncture are satisfied with its results; they claim that there is no discomfort or pain during it.
When is a lumbar puncture necessary and why should you not do it?
lumbar puncture
Lumbar puncture is performed both for diagnostic purposes and for therapy, but always with the consent of the patient, except in cases where the latter, due to his serious condition, cannot contact the staff.
For diagnosis, a spinal puncture is performed if it is necessary to examine the composition of the cerebrospinal fluid, determine the presence of microorganisms, fluid pressure and patency of the subarachnoid space.
Therapeutic puncture is needed to evacuate excess cerebrospinal fluid or introduce antibiotics and chemotherapy drugs into the intrathecal space in case of neuroinfection or oncopathology.
The reasons for lumbar puncture are mandatory and relative, when the decision is made by the doctor based on a specific clinical situation. Absolute indications include:
- Neuroinfections - meningitis, syphilitic lesions, brucellosis, encephalitis, arachnoiditis;
- Malignant tumors of the brain and its membranes, leukemia, when CT or MRI cannot make an accurate diagnosis;
- The need to clarify the causes of liquorrhea with the introduction of contrast or special dyes;
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage in cases where non-invasive diagnosis is not possible;
- Hydrocephalus and intracranial hypertension - to remove excess fluid;
- Diseases requiring the administration of antibiotics and antitumor agents directly under the membranes of the brain.
Among the relative ones are pathology of the nervous system with demyelination (multiple sclerosis, for example), polyneuropathy, sepsis, unidentified fever in young children, rheumatic and autoimmune diseases (lupus erythematosus), paraneoplastic syndrome. A special place is occupied by lumbar puncture in anesthesiology, where it serves as a method of delivering an anesthetic to the nerve roots to provide fairly deep anesthesia while maintaining the patient’s consciousness.
If there is reason to suspect a neuroinfection, then the cerebrospinal fluid obtained by puncture of the intrathecal space will be examined by bacteriologists, who will establish the nature of the microflora and its sensitivity to antibacterial agents. Targeted treatment significantly increases the patient's chances of recovery.
With hydrocephalus, the only way to remove excess fluid from the subarachnoid spaces and the ventricular system is puncture, and often patients feel relief almost immediately as soon as cerebrospinal fluid begins to flow through the needle.
If tumor cells are detected in the resulting liquid, the doctor has the opportunity to accurately determine the nature of the growing tumor, its sensitivity to cytostatics, and subsequent repeated punctures can become a way to administer drugs directly to the area of tumor growth.
Lumbar puncture may not be performed on all patients. If there is a risk of harm to health or danger to life, then the manipulation will have to be abandoned. Thus, the following are considered contraindications for puncture:
- Cerebral edema with risk or signs of herniation of brain stem structures or cerebellum;
- High intracranial hypertension, when removal of fluid can provoke dislocation and wedging of the brain stem;
- Malignant neoplasms and other space-occupying processes in the cranial cavity, intracerebral abscesses;
- Occlusive hydrocephalus;
- Suspicion of dislocation of stem structures.
The conditions listed above are fraught with the descent of the stem structures to the foramen magnum with their wedging, compression of vital nerve centers, coma and death of the patient. The wider the needle and the more fluid removed, the higher the risk of life-threatening complications. If the puncture cannot be delayed, then the minimum possible volume of cerebrospinal fluid is removed, but if wedging occurs, a certain amount of liquid is reintroduced.
If the patient has suffered a severe traumatic brain injury, massive blood loss, has extensive injuries, or is in a state of shock, it is dangerous to perform a lumbar puncture.
Other obstacles to the procedure may include:
- Inflammatory pustular, eczematous skin changes at the point of the planned puncture;
- Pathology of hemostasis with increased bleeding;
- Taking anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents;
- Aneurysm of cerebral vessels with rupture and bleeding;
- Pregnancy.
These contraindications are considered relative, increasing the risk of complications, but in cases where puncture is vitally necessary, they can be neglected if maximum caution is observed.