About the benefits of exercise therapy
Physical exercise after a stroke speeds up the recovery process. Daily exercise improves blood circulation, prevents blood from stagnating, helps restore muscle memory, reduces muscle tone, prevents the development of contractures, bedsores, atrophy and spasms, and eliminates involuntary movements of the limb.
Physical activity leads to positive changes in the body:
- the functioning of the cardiovascular system improves;
- breathing is normalized;
- metabolic processes are stimulated;
- the patient's emotional state improves.
Exercise therapy after a stroke includes compensatory mechanisms to restore function. Repeated repetitions of exercises contribute to the emergence of new conditioned reflex connections.
Contraindications to exercise therapy
Physiotherapy exercises are not prescribed for the following conditions:
- being in a coma;
- recurrent stroke in older people;
- epileptic seizures;
- mental disorders and aggressive behavior;
- the presence of diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis, malignant tumors.
For hemorrhagic stroke, exercise therapy is prescribed when the patient’s symptoms stop increasing and the functioning of the vascular system and internal organs improves. In the first 3 days from the start of classes, breathing exercises and superficial massage are recommended. Physical therapy is contraindicated if blood pressure exceeds 180/105 mmHg. Art.
Preparatory activities
Preparation for exercise therapy consists of the following stages:
- Changing the patient's body position to prevent blood stagnation.
- Passive loads for different joints and muscle groups by medical staff: circular movements and abduction of the limbs, flexion and extension.
- Breathing exercises to improve lung function.
- Mental gymnastics to restore muscle memory.
- Massage to normalize blood circulation and prepare the body for more active activities.
Passive loads
When the patient regains consciousness, passive exercises are prescribed. In the early period, correction is carried out by position. Light stroking is used on affected muscles with increased tone. For other muscles, deeper massage techniques are used: gentle rubbing and kneading.
Gymnastics for bedridden patients is carried out carefully, the patient’s breathing should be free. In case of stiffness, classes begin with large joints, in the absence of contractures and increased muscle tone - with the distal parts of the arms and legs.
To regain muscle memory, use mental gymnastics. To restore memory, you need to perform mental exercises every day, during which the patient himself or his relative voices what movement he is making. For example: “I move my hand to the side.”
A person who has suffered a stroke is depressed, feels disabled, and does not believe in his own strength, so he needs to be encouraged and praised.
Paralysis often leads to speech impairment. It is important to do articulation exercises every day and not stop practicing. In order for the function to recover faster, you need to talk to the patient, he must hear speech. Classes begin with the reproduction of individual sounds, then gradually move on to syllables and words.
Passive exercises should be done 2-3 times a day, 10-15 repetitions for each joint. It is important to monitor the patient's reaction. Holding your breath, causing pain and increasing muscle tone should not be allowed.
Physical therapy after a stroke: examples of exercises and rules of execution
After a stroke, nerve cells die and 80% of patients experience movement disorders. To restore functions, rehabilitation measures are necessary, including physical therapy.
Exercise therapy is an individually selected set of exercises taking into account the characteristics of the disease, its degree and stage of development, and the patient’s well-being. Dosed daily loads are indicated, starting 2-3 days after the attack.
About the benefits of exercise therapy
Physical exercise after a stroke speeds up the recovery process. Daily exercise improves blood circulation, prevents blood from stagnating, helps restore muscle memory, reduces muscle tone, prevents the development of contractures, bedsores, atrophy and spasms, and eliminates involuntary movements of the limb.
Physical activity leads to positive changes in the body:
- the functioning of the cardiovascular system improves;
- breathing is normalized;
- metabolic processes are stimulated;
- the patient's emotional state improves.
Exercise therapy after a stroke includes compensatory mechanisms to restore function. Repeated repetitions of exercises contribute to the emergence of new conditioned reflex connections.
Contraindications to exercise therapy
Physiotherapy exercises are not prescribed for the following conditions:
- being in a coma;
- recurrent stroke in older people;
- epileptic seizures;
- mental disorders and aggressive behavior;
- the presence of diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis, malignant tumors.
For hemorrhagic stroke, exercise therapy is prescribed when the patient’s symptoms stop increasing and the functioning of the vascular system and internal organs improves. In the first 3 days from the start of classes, breathing exercises and superficial massage are recommended. Physical therapy is contraindicated if blood pressure exceeds 180/105 mmHg. Art.
Preparatory activities
Preparation for exercise therapy consists of the following stages:
- Changing the patient's body position to prevent blood stagnation.
- Passive loads for different joints and muscle groups by medical staff: circular movements and abduction of the limbs, flexion and extension.
- Breathing exercises to improve lung function.
- Mental gymnastics to restore muscle memory.
- Massage to normalize blood circulation and prepare the body for more active activities.
Passive loads
When the patient regains consciousness, passive exercises are prescribed. In the early period, correction is carried out by position. Light stroking is used on affected muscles with increased tone. For other muscles, deeper massage techniques are used: gentle rubbing and kneading.
Gymnastics for bedridden patients is carried out carefully, the patient’s breathing should be free. In case of stiffness, classes begin with large joints, in the absence of contractures and increased muscle tone - with the distal parts of the arms and legs.
To regain muscle memory, use mental gymnastics. To restore memory, you need to perform mental exercises every day, during which the patient himself or his relative voices what movement he is making. For example: “I move my hand to the side.”
A person who has suffered a stroke is depressed, feels disabled, and does not believe in his own strength, so he needs to be encouraged and praised.
Paralysis often leads to speech impairment. It is important to do articulation exercises every day and not stop practicing. In order for the function to recover faster, you need to talk to the patient, he must hear speech. Classes begin with the reproduction of individual sounds, then gradually move on to syllables and words.
Passive exercises should be done 2-3 times a day, 10-15 repetitions for each joint. It is important to monitor the patient's reaction. Holding your breath, causing pain and increasing muscle tone should not be allowed.
Active physical activity
Active loads are aimed at restoring old and forming new conditioned reflexes. The exercises include 2 phases - static and dynamic. Performed by a physical therapy methodologist. The first phase causes muscle tension and develops the ability to hold an arm or leg in the desired position. The second phase is the movement itself.
The purpose of active exercises is to achieve isolated movements in the patient by providing light resistance.
When a person is paralyzed, fine motor skills are impaired. Its recovery depends on the degree of loss of motor function. If the hand does not move at all, passive loads are needed. Then they move on to exercises in turning over cards, collecting scattered coins, writing letters, etc.
Patients are shown exercise on a stationary bike to train the cardiovascular system and restore motor skills of the lower extremities.
For urinary incontinence, it is recommended to perform Kegel exercises.
If there are no contraindications during the recovery period, you can use the yoga method, but not earlier than 6 months after the stroke.
Exercises while lying down
Gymnastics in bed is started in the early period of rehabilitation. Exercises after a stroke are performed in a lying position on your back, stomach, or healthy side.
Exercise 1 . The patient lies on his back. You need to clasp his ankles with your hands and bend his knees so that his feet slide on the bed (imitation of walking).
Exercise 2 . Hang the affected arm of the paralyzed person on a towel and rotate it in a circle. Exercise for up to 30 minutes with breaks of 2-3 minutes.
Exercise 3 . To restore the swallowing reflex, you need to perform the following exercises:
- strain your mouth, pretending to whistle without sound;
- cough;
- to yawn;
- snore;
- when pushing, pronounce “a” and “e”.
You can do exercises for your eyes and hands while lying down.
Gymnastics while lying down is preparation for the next stage, when the patient will be able to perform sitting and standing exercises for the vestibular system, restore coordination of movements and begin to learn to walk.
Complexes from a sitting position
When the acute period ends and the patient can sit down, they move on to sitting exercises.
Exercise 1 . Lean your back against the pillow, stretch your legs, hold the edges of the bed with your hands. While inhaling, bend forward slightly, and as you exhale, return to the starting position. Repeat 5 times.
Exercise 2 . Sit on the bed, keep your back straight, arms out to the sides. Bring your shoulder blades together. Repeat 5 times.
Exercise 3 . While sitting, hold onto the edge of the bed with your hands. Raise your left and right legs alternately. Perform 4 times with each leg.
Complexes from a standing position
Exercise 1 . Feet shoulder-width apart, hands on the waist. While inhaling, turn to the left, while exhaling, turn to the right. Perform slowly 5 times in each direction.
Exercise 2 . Feet shoulder-width apart, arms down along the body. Raise your arms up, stretch slightly, inhale; lower your hands down, describe a circle with them, exhale. Repeat 5 times.
Exercise 3 . Stand on your toes, raise your arms up and stretch as if trying to reach the ceiling.
Exercise 4 . Walk in place for 30 seconds.
Eye complex
Motor function of the eyes is restored after a stroke using the following exercises:
- Forcefully squeeze and unclench your eyelids 15 times.
- Move your eyeballs up and down, right and left with your eyes open and closed.
- Fix your gaze at one point.
- Blink frequently.
- Rotate your eyes clockwise and counterclockwise.
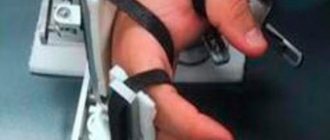
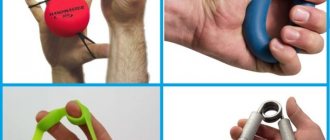
Hand loads
If the hand is affected, bend and straighten the fingers in any convenient position 10 times.
To strengthen the shoulder joint, perform the exercise while lying on your healthy side. The methodologist fixes the shoulder joint with his right hand and slowly and smoothly moves the affected limb away from the body with his left hand. The methodologist holds the patient’s elbow with the forearm in a state of pronation, and the hand in an extended position, then raises his arm up, moves it to the side, then back.
In the supine position, the methodologist extends the patient’s arm at the elbow and abducts it to the side.
When minimal voluntary movements appear in the paralyzed arm, they proceed to the exercise of raising and lowering the affected limb using a blocking device and a healthy arm.
Leg loads
To restore movement in the joints and muscles of the legs, use the following exercises:
- Hip abduction and adduction.
- Rotation in the hip joint.
- Passive flexion and extension of the knee joints.
- Passive knee extension while lying on your side with the hip extended.
- Raising your leg with your healthy arm and using a pulley with a cord...
- Passive movements in the ankle.
Exercises begin with healthy limbs, then alternate them with exercises for the paralyzed in combination with massage and muscle relaxation.
Active movements are done slowly, avoiding painful exercises.
Articulation complex
When cerebral circulation is impaired during a stroke, the facial muscles are paralyzed and the person loses the ability to pronounce sounds. The following complex helps restore articulation:
- Roll your lips into a tube and stretch them out.
- Stick out your tongue as much as possible.
- Spread your lips wide, as if to pronounce “y”.
- Bite your upper and lower lips alternately.
Daily exercises make it possible to quickly return to intelligible speech.
Breathing exercises
Exercises should be started when the patient regains consciousness and can control the facial muscles. The simplest action is to exhale through closed lips.
Gymnastics after a stroke consists of taking a deep breath, holding your breath for a few seconds and exhaling slowly.
The patient must see the result and believe that function will be restored. When he gets better, he will be able to inflate a balloon or blow into a tube lowered into water. So he sees how the ball increases in size, or hears how the water gurgles.
Breathing exercises are performed often with rest breaks. You should not strain while holding your breath to avoid dizziness or headaches.
Exercise equipment
Exercising on exercise equipment, such as:
- The verticalizer gives the human body a vertical position.
- Rehabilitation exercise bike with electric or mechanical drive.
- The lokomat is intended for people who are learning to walk.
- Exercise machines for legs and arms. "Bud" develops his fingers. “Shagong” imitates walking and can be used for bedridden patients.
In order for the patient to recover faster, an integrated approach is needed. Drug therapy without exercise therapy will not give the desired result.
Source: https://mozgmozg.com/reabilitacia/lfk-posle-insulta
Active physical activity
Active loads are aimed at restoring old and forming new conditioned reflexes. The exercises include 2 phases - static and dynamic. Performed by a physical therapy methodologist. The first phase causes muscle tension and develops the ability to hold an arm or leg in the desired position. The second phase is the movement itself.
The purpose of active exercises is to achieve isolated movements in the patient by providing light resistance.
When a person is paralyzed, fine motor skills are impaired. Its recovery depends on the degree of loss of motor function. If the hand does not move at all, passive loads are needed. Then they move on to exercises in turning over cards, collecting scattered coins, writing letters, etc.
Patients are shown exercise on a stationary bike to train the cardiovascular system and restore motor skills of the lower extremities.
For urinary incontinence, it is recommended to perform Kegel exercises.
If there are no contraindications during the recovery period, you can use the yoga method, but not earlier than 6 months after the stroke.
Exercises while lying down
Gymnastics in bed is started in the early period of rehabilitation. Exercises after a stroke are performed in a lying position on your back, stomach, or healthy side.
Classification
Hemiparesis is classified based on several criteria. It looks like this:
- Symptoms can be congenital or acquired.
- Both left and right limbs can be affected.
- According to the severity of muscle strength, mild hemiparesis is distinguished (strength 3.5-4 points), moderate (2-3.5 points), severe (up to 2 points). The assessment is carried out during a neurological examination of the patient.
- There are central hemiparesis, which develops as a result of impaired cerebral and spinal circulation, and peripheral hemiparesis. The latter is a consequence of dysfunction of peripheral nerve fibers (for example, with intervertebral hernias).
It is important to note that paresis can be spastic and flaccid. This sign depends on the tone of the muscles of the limbs. With increased tone, spastic paresis is exhibited, and with decreased tone, flaccid paresis is observed.
The first type is often accompanied by shortening of the limbs and is more often a consequence of damage to the central nervous system, while the second type is the result of pathologies of the peripheral nerves.
Exercise equipment
Exercising on exercise equipment, such as:
- The verticalizer gives the human body a vertical position.
- Rehabilitation exercise bike with electric or mechanical drive.
- The lokomat is intended for people who are learning to walk.
- Exercise machines for legs and arms. "Bud" develops his fingers. “Shagong” imitates walking and can be used for bedridden patients.
In order for the patient to recover faster, an integrated approach is needed. Drug therapy without exercise therapy will not give the desired result.
source
Therapeutic exercise in case of hemiparesis
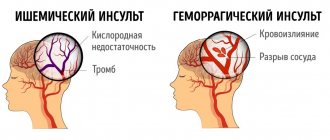
Hemiparesis is partial paralysis of any side of the body. The cause may be abnormalities in intrauterine development, trauma, or the presence of certain diseases. Often, paresis is caused by tumors of the brain or spinal cord, which can be benign or malignant. Since there are many causes of hemiparesis, the main task is to identify and eliminate the underlying disease and its consequences.
Exercise therapy for hemiparesis is part of a set of measures and is of great importance, since it allows you to improve the motor functions of the affected limbs, avoid the occurrence of contractures, and, as a result, improve the patient’s life, his ability to move and self-care.
Symptoms
The main symptom of hemiparesis is muscle weakness in the limbs. Other symptoms depend on the underlying disease. Strokes may affect speech, swallowing, vision, consciousness, and the functions of the pelvic organs.
If compression of the nerve root occurs, there is pain in the spine, which intensifies with movement and static tension. Often patients complain of numbness in the extremities and coldness in them. Patients with tumors report significant weight loss.
If there is an inflammatory process of the meninges, headaches, nausea and vomiting, and increased body temperature are diagnosed. In some cases, specific meningeal signs are detected.
The functions of memory and attention, writing and speech are often impaired. Disturbances in gait and coordination are also quite common.
Features of hemiparesis
When the disease occurs, the facial muscles usually suffer and the motor functions of the limbs are impaired. There is weakness and pain in the affected parts of the body. The level of limitation of movement depends on the degree of the disease.
In severe cases, the arms are bent at the elbows and the fingers are clenched into a fist. The movements are disproportionate, the person cannot move quickly and dexterously, and there is no smoothness characteristic of a healthy person. In some patients, the legs become entangled, the person is unable to maintain balance and sways from side to side.
There are right-sided and left-sided hemiparesis, depending on which half of the body movements are limited. You should know that the right side of the brain is responsible for the actions of the left side of the body and vice versa.
Right-sided hemiparesis is typical for adult patients and occurs as a result of injury or disease. Right-sided hemiparesis, with the help of a complex of exercise therapy and other procedures, is often eliminated with virtually no consequences. Diseases that can lead to hemiparesis:
- stroke;
- encephalitis;
- diabetes;
- traumatic brain injuries (bruises, concussions);
- complications of epilepsy;
- multiple sclerosis.
Left-sided hemiparesis occurs more often in children; it can be caused by pathologies of intrauterine development, birth injuries, or the cause may be prematurity of the baby.
If the left side of the brain is damaged, disturbances are observed:
- speeches;
- ability to analyze;
- perform operations with numbers;
- logic and linear representations.
When the function of the right side is impaired, the speech of adult patients usually does not suffer, unless, of course, the person is left-handed. In children, speech problems can occur if any part of the brain is affected.
When the right side of the brain is damaged, the following is disrupted:
- the ability to dream;
- sense of rhythm;
- ability for holistic and three-dimensional perception;
- the ability to imagine and perceive colors.
It follows from this that the left hemisphere is responsible for the ability to think logically and draw conclusions, and the right hemisphere helps to navigate in space.
With left-sided hemiparesis, the exercise therapy complex and treatment in general are more complex, since its consequences are much more difficult to correct.
What is hemiparesis
This condition is quite common in neurology and is a consequence of many pathologies of both the central and peripheral nervous systems.
It is important to determine the difference between hemiparesis and hemiplegia. With paresis, muscle strength in the limbs is reduced. With plegia, strength is completely lost, the patient is unable to move the affected arm and leg. The second name is paralysis.
The assessment is based on an examination by a neurologist, who is able to assess the degree of impairment of motor function and strength. Thus, hemiplegia and hemiparesis are distinguished.
Treatment methods
Successful treatment requires a set of measures to help identify and eliminate the causes of the pathology. Surgery may be necessary if there is, for example, a tumor or inflammation of the brain or spinal cord. Drugs that improve cerebral circulation are used.
To restore motor functions the following is prescribed:
- drugs that reduce muscle spasticity;
- courses of various physiotherapeutic procedures;
- massage and exercise therapy.
The importance of exercise therapy in this case is especially great; in combination with massage, physical therapy allows you to expand, and sometimes almost completely restore, the ability to move normally.
Diagnostic methods
To diagnose hemiparesis, an examination by a neurologist is necessary. The specialist will conduct a study of cranial nerves, reflexes, and muscle strength. The doctor also examines for the presence of pathological signs of both central and peripheral origin. After this, patients are prescribed the following studies:
- General clinical tests - general blood and urine tests.
- Biochemistry of blood.
- Study of hormonal status.
- Computer or magnetic resonance imaging.
- Electroneuromyography.
- Myelography.
- Electroencephalography.
In some cases, ultrasound examination of the vessels of the cervical spine and radiography of the skull may be prescribed. These techniques allow us to identify the cause of hemiparesis and prescribe the correct treatment.
Organization of exercise therapy for hemiparesis in children
It should be remembered that a complex of exercise therapy for hemiparesis in children is not only training with a specialist in the gym; in the case of cerebral palsy, this diagnosis is the main one for hemiparesis in children; swimming brings invaluable benefits.
Exercising in the pool is a great way to help cope with the problem; now the opportunity to not just swim, but communicate with dolphins has become popular. If available, take your baby to the sea. Swimming in sea water is excellent for strengthening, and walking on warm sand or smooth small pebbles is, among other things, an excellent massage. Hypotherapy (horse riding) brings results. At the same time, the child gains a friend, which is very important. Exercises using a large ball (fitball) are valuable.
How does exercise therapy affect hemiparesis?
Treatment is carried out with complex therapy, which includes: drug treatment, exercise therapy for hemiparesis, massage, and in some cases acupuncture is prescribed.
Exercise therapy for hemiparesis in the later stages of the disease is also not excluded, but on the contrary is considered an effective method.
On topic: Left arm hurts where the muscles are
Daily exercise therapy for hemiparesis allows you to strengthen and improve motor functions, develop coordination, and also improve the patient’s condition. With the help of exercise therapy for hemiparesis, re-education of the neuromuscular system is observed; exercises help develop the patient’s ability to both tense and relax muscles; develop differentiated movements of the paretic arm and leg.
The complex of exercise therapy for hemiparesis includes exercises: exercises using a chair for flexion and extension of the joints of the upper and lower extremities, both healthy and paretic limbs; exercises for hemiparesis standing at the gymnastic wall in combination with breathing elements and walking with obstacles; exercises while sitting on a chair to flex and extend the hand and fingers in combination with breathing exercises, as well as developing hand relaxation skills.
Exercise sets
If hemiparesis occurs after an injury or illness in an adult, a complex of physical therapy helps to recover more quickly. It should be done after a massage, this allows you to prepare the muscles for physical activity and improve blood flow. The massage is done from hand to shoulder and from foot to thigh.
Complexes of exercise therapy for hemiparesis vary significantly, depending on the degree of damage.
Complex No. 1
If the patient is still weak, the exercises are done while lying in bed.
- The patient tries to bend his leg at the knee, slowly moving it along the bed.
- It is necessary to straighten the leg bent at the knee. If the patient at first cannot bend his leg at the knee on his own, he is helped by a person under whose supervision the exercises are performed.
- The hand clenches into a fist and unclenches. This exercise can be performed using a small rubber ball or punching bag. Exercises with a special massage ball give an excellent effect.
- The arm is bent at the elbow, brought to the shoulder, then straightened and lowered. First, you can help yourself with your healthy hand.
- The foot stretches towards itself, then relaxes.
- The leg is placed on a rubber band or bandage stretched over the bed in several layers, and the patient performs circular movements with the foot.
- The patient pulls on the ends of the rubber band, trying to stretch it.
Complex No. 2
This exercise therapy complex for hemiparesis is performed when the patient is already stronger and can sit on a chair and stand against a support.
- Sitting straight on a chair, lower your head, pulling or pressing your chin to your chest.
- The head tilts alternately to the right and left shoulders. The exercise is performed slowly and carefully so as not to provoke dizziness.
- Sitting on a chair, lower your arms along your body and perform rotational movements with your hands.
- Hands are raised to shoulder level and slowly and smoothly lowered.
- You should try to touch your shoulders with your fingers.
- Sitting on a chair, rest your foot on your heel and press an imaginary pedal, placing your foot on the entire foot, and then returning it to its original position.
- Perform rotational movements of the feet.
- Holding the back of the chair, rise onto your toes.
- Holding the back of a chair, legs together. The leg is moved to the side, returned to its original position, then back and returned to its original position.
- Lying on your back, bend and straighten your knees.
- Lying on your back, try to slightly raise one or the other sore leg.
Treatment
Therapy is always determined individually. Treatment tactics for spastic and other types of hemiparesis in adults and children directly depend on the provoking disease.
All available methods are used: medications, therapeutic exercises, massage, mechanotherapy, physiotherapy. It is the combination of these techniques that can lead to a positive result.
It is important to note that the treatment of tumors requires surgery followed by chemotherapy. If a patient is diagnosed with encephalitis or encephalomyelitis, therapy is prescribed based on the sensitivity and nature of the pathogen.
Therapeutic exercises are the main method of getting rid of hemiparesis and are recommended on an ongoing basis. Patient training is carried out by experienced instructors who, at the initial stages, monitor the correct execution of the exercises. You can do the following complex:
- Flexion and extension at the knee and hip joints while lying on your back.
- In the same position, you need to pull your foot towards you and away from you.
- The next exercise requires you to stretch the band between the supports. Afterwards, the affected leg is placed on it and the foot is made in a circular motion.
- Patients are recommended to rise on their toes and stand on their heels, while holding onto support. As you improve, you need to switch to walking in this position without support.
- As for the arms, patients are recommended to do flexion, extension and rotation in the wrist and shoulder joints.
- Another exercise is to clench and unclench your hand into a fist (use of an expander is allowed).
- With your hands behind your back, you need to connect them together.
Patients are also recommended mechanotherapy (gymnastics on special simulators), regular swimming and Nordic walking.
As for massage for hemiparesis, it helps improve metabolism and blood flow, normalize muscle tone and limb function. The procedure is carried out by a specialist, it begins with light circular movements, the intensity of which gradually increases. For hemiparesis, any type of massage is useful - general health, segmental, acupressure.
As for other methods, physiotherapy (electrical stimulation, paraffin wraps) and acupuncture have a good effect.
Rules for performing exercises
Gymnastics is done with the help and under the supervision of healthy assistants. Any exercises are performed at a comfortable pace; there is no need to rush or strain too much.
Classes are held daily; consistency in this case is the key to recovery.
During the process, you can take short (no more than 5 minutes) breaks between 2-3 series of exercises. At first, each exercise should be done no more than 5 times; once you get used to the exercises, you can increase the load to 10 repetitions.
Additional recommendations and useful tips
Both children and adults with hemiparesis should definitely develop fine motor skills. You can string beads or make mosaics, lace or fasten things. Play catch with the patient. Just use a tennis ball.
If possible, organize exercises for your patient in the pool. Such procedures have a beneficial effect on muscles and train the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. If a person is strong enough to walk, walk a short distance every day, gradually increasing the load.
Of course, recovering from serious neurological diseases is very difficult, and requires the guidance of experienced medical professionals and the support of loved ones. But hemiparesis is still much easier than tetraparesis, when all limbs are affected, or paralysis, when movements are completely absent. That is why the likelihood of an almost complete recovery is much higher. Study, don’t waste time and energy on it. And be healthy.
source