In the modern world, stroke occurs in almost every person over 50 years of age. The disease is mainly diagnosed by the degree to which movement of the paralyzed part of the body is reduced. Patients exhibit left- or right-sided numbness of the facial muscles, and swallowing is impaired.
If, after a stroke, symptoms such as distortion of facial features, the inability to raise both arms at the same time, pronounced tremors in the limbs, or difficulty smiling are revealed, then immediately call an ambulance.
Recovery periods
Rehabilitation for stroke patients necessarily takes place in several stages. This is the use of various drugs that help break down growths on the walls of blood vessels and improve blood circulation in the cerebral hemispheres. Also included are various types of exercises used to restore movement and increase sensitivity in the right or left hand.
Physical rehabilitation after a stroke includes the following stages:
- Ask the patient to mentally, with his eyes closed, imagine the state before the illness, try to think about those movements that were previously performed with his hands without problems. The patient will try to move his fingers, then his hand, and learn to bend, straighten and raise his arms.
- Make sure that the victim performs the exercises as accurately as possible.
- The course of exercises can be periodically replaced with more complex ones, depending on the dynamics of improvement in joint mobility. Classes should be designed not only to develop the elbow joint, but also the wrist of the paralyzed hand.
- Exercises during the day should be regular, especially on the paresis side.
- Make sure that the patient tries to work mainly with the hand that does not work well after a stroke. By shifting everything to the healthy hand, he will not learn to move both hands.
Useful exercises for a person who has suffered a stroke include the use of homemade exercise equipment. A hand exercise bike, elastic belts with handrails, and exercises with rubber balls can help get rid of numbness in your arms and legs.
To enhance the effect, together with all physical warm-ups, doctors recommend performing a rubbing massage of the limbs for several minutes every day. Additionally, electrical stimulation, as well as physiotherapeutic procedures, depending on the type of developing consequences.
Signs of a stroke
During a transient ischemic attack, the signs leading to a stroke are periodic, tremors and numbness occur, trembling in the upper and lower extremities, accompanied by severe pain in the head. After a stroke, the duration of symptoms gradually increases.
The following sensations arise:
- Slowly increasing numbness in the arms and legs.
- Speech function disorder.
- Tremor on the side of the paresis.
- Double images, loss of visual fields.
- Excessive sweating, redness of the facial skin.
- Violation of thought processes.
These symptoms may persist even after hospitalization for a month. This is influenced by the depth and extent of the brain stroke focus.
What types of cerebral ischemia cause loss of sensitivity in the limbs?
Numbness of the upper or lower extremities during a cerebrovascular accident is accompanied by motor, visual, and auditory disturbances. The course of a stroke is unpredictable. Symptoms of apoplexy develop depending on the location and extent of damage to the area of the brain. Let us consider the degree of damage in acute cerebrovascular accident (ACVA).
Transient cerebrovascular accident
Symptoms of a transient attack:
- numbness, goosebumps and tingling of the extremities;
- sudden dizziness;
Dizziness with TIA occurs acutely. for no apparent reason
- word pronunciation disorder;
- spots or double vision;
- nausea and vomiting;
- consciousness is preserved, but delirium and loss of orientation are possible.
Transient cerebrovascular accident occurs more often with hypertension, diabetes mellitus and cardiac arrhythmia. After the end of the transient attack, which lasts from 2 minutes to 24 hours, the numbness of the limbs stops.
- numbness of the arms and legs with partial or complete loss of sensation;
- loss or disorder of speech, impaired articulation;
- paresis of an arm or both limbs on one side of the body;
- visual impairment;
- redness and sweating of the face;
- swallowing disorder;
- confused consciousness.
The progression of symptoms after this type of stroke is unpredictable and can persist for up to 21 days. The complex of symptoms depends on the degree and location of the damage. As ischemia progresses, visual and motor disturbances join the symptoms of hand numbness.
The sooner a patient is admitted to the hospital after a brain accident, the more effective the treatment and the fewer consequences.
Reasons for decreased mobility
Sharp tremor and numbness in the body alarm everyone, especially if it concerns loved ones. Such reasons may be associated with the occurrence of a transient ischemic attack or the onset of an ischemic stroke, which the doctor determines by the following signs:
- Atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries.
- Formation of blood clots in the bloodstream of the heart.
- Dilatation of the veins of the lower extremities, there is a possibility of fragmentation; separated growths on the blood vessels can enter the general bloodstream, preventing blood from moving normally along the vascular bed.
- Postoperative intervention in the area of the carotid artery or injuries of the cervical spine, as well as due to osteochondrosis.
- Instability in blood pressure readings.
- High thrombus formation.
Mechanism of sensory impairment in cerebral ischemia
The brain regulates processes occurring in the body through neurohumoral pathways. Each part of the brain is responsible for a specific function: motor, sensory, visual and auditory. After blood flow is disrupted in the corresponding part of the brain, neurons die, and as a result, its function is lost. After damage to the center of the brain responsible for the sensory function of the arms and legs, paresthesia of the limbs appears.
Cerebral ischemia occurs for the following reasons:
- prolonged vascular spasm in atherosclerosis;
- blockage of a cerebral vessel by a thrombus;
- blockage of a cerebral vessel by a thrombus brought with blood flow from the cavity of the heart, aorta or large vessels;
- hemorrhage in the brain or subarachnoid space (secondary ischemia).
In some cases, the atherosclerotic plaque itself blocks the lumen of the vessel, resulting in ischemia with the occurrence of paresthesia of the extremities. In some cases, the formation of a blood clot occurs at the site of an atherosclerotic plaque in the cerebral vessels. With arrhythmia, a blood clot forms in the cavity of the heart, and then travels through the bloodstream into the vessels of the brain and causes a blockage. Blood clots formed in the aorta and carotid artery sometimes break off and enter the brain vessel. If the sensory area of the brain is damaged due to blockage, sensitivity is impaired, numbness of the arms and legs on one side of the body occurs.
Numbness of the limbs often occurs during a hypertensive crisis or diabetes mellitus. In this case, transient cerebral ischemia develops. It lasts from 2 minutes to 24 hours. At the onset of a cerebral stroke, it is clinically impossible to determine what kind of ischemia it is. If ischemia progresses after 24 hours, it is diagnosed as a stroke. Ischemia that stopped before 24 hours is regarded as transient (transitory).
The role of exercise therapy classes
As a result of a stroke, the consequences can be unpredictable. During this very period, not only speech disturbances and decreased mental functions can be observed, but also tremors during movements. There is no likelihood that the patient, without receiving additional help, will be able to independently restore the functions he lost before the illness.
Therefore, during treatment, the use of drugs to reduce coagulation, control blood pressure, including physical exercises that improve the mobility of the joints of the arms and legs, becomes important for many patients. Do not begin exercises without consulting a physical therapist. After all, tremors and numbness in the hands manifest themselves differently in everyone.
After a stroke, the victim may feel his left or right hand shaking for a long time. Including slight numbness in the hands and tremors in the legs when moving.
To reduce paresis on the paralyzed side of the body, exercises are not contraindicated for patients in a coma. They should not be too intense, but take place in a more passive form. Exercise helps eliminate bedsores and atrophy of the lower extremities.
Numbness of the hands after a stroke: causes, treatment. Why does my leg shake after a stroke?
Numbness of the hands (paresthesia) is one of the symptoms of stroke (cerebrovascular accident). Impaired sensitivity of the limbs on one side of the body is accompanied by other focal, cerebral and autonomic symptoms.
The cause of numbness in the hands after a stroke at a young age is inflammation of the vascular wall or blockage by a blood clot. In older age, hand numbness after a stroke is more often associated with atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, abdominal obesity, and smoking.
Risk factors for stroke and hand paresthesia are smoking and alcohol. The genetic background for the development of cerebral ischemia is a predisposition to strokes in relatives.
Urgent Care
What to do with cramps after a stroke - if a muscle spasm occurs, you must:
- Call an ambulance immediately;
- If convulsions are accompanied by loss of consciousness, you need to put the patient on the sofa;
- Open the window and remove tight clothing from the patient to ensure oxygen access;
- Place a pillow or cushion under your head, remove hard or sharp objects that could cause injury;
- Remove food or vomit from the mouth and remove dentures;
- If breathing is impaired and wheezing occurs, the patient should be placed on his side;
- If a seizure continues for a long time, you will have to restrain the patient to prevent accidental injury;
- If the patient is conscious and suffers from strong muscle contractions, it is recommended to prepare a mustard compress with olive oil or gently rub the legs.
Attention!
Basic treatment of seizures after a stroke can only be prescribed by a neurologist after a comprehensive diagnosis.
First aid rules for seizures after a stroke
First aid for seizures after a stroke
In case of a convulsive state in a patient who has suffered a stroke, it is necessary:
- call an emergency medical team;
- if a person experiences fainting with convulsions, it is necessary to ensure that he is in a supine position;
- provide fresh air access to the room, if possible, free the patient from tight clothing;
- the head should be in an elevated position, and it must be ensured that there are no sharp or heavy objects that could injure the patient during loss of consciousness with convulsions;
- check for the presence of food debris, saliva or vomit in the oral cavity, and then remove them; if there are removable dentures, they are removed;
- if the attack is accompanied by wheezing, the patient must be turned on his side and the respiratory function must be monitored;
- in case of convulsions with prolonged seizures, it is necessary to restrain the person at all times to prevent injury;
- if the condition is accompanied by severe muscle spasms, while consciousness is preserved, you can rub the muscles or apply a compress of mustard and olive oil.
You can learn about first aid if stroke symptoms appear here.
The main treatment is prescribed only by a neurologist after the causes have been established.
Dangerous complications
Lack of adequate treatment for seizures after stroke can cause complications. Such patients are at risk:
- Repeated stroke, which not everyone manages to survive;
- Comatose state - attacks of muscle spasms lead first to a short-term and then to a longer loss of consciousness. With frequently recurring seizures, the patient falls into a coma;
- Loss of ability to work - the regular occurrence of seizures that do not disappear when taking standard medications indicates necrotization of large areas of the brain. Rehabilitation of such a patient is not effective, the person becomes disabled;
- Fatal outcome - constant relapses of convulsive attacks, the lack of positive dynamics during treatment indicates the likelihood of internal bleeding. It is practically impossible to eliminate this condition. Therefore the patient dies.
To prevent the development of dangerous consequences of seizures during a stroke, you should immediately seek medical help, undergo a comprehensive examination and begin treatment.
What are the dangers of post-stroke seizures?
Treatment of seizures after a stroke is necessary in 8% of cases of the total number of victims of cerebral hemorrhage. The development of complications is facilitated by the occurrence of hemorrhagic or ischemic lesions in an acute form, complicating an already severe form of the disease.
The consequences of brain disorders are:
- Recurrent stroke - repeated convulsive seizures during the recovery period of a stroke indicate the ineffectiveness of the prescribed therapy. If treatment adjustments are not made in a timely manner, recurrent brain damage can be expected to develop. Particularly dangerous is a generalized seizure after a stroke, indicating that internal bleeding has already begun.
- Fatal outcome - the frequency of seizures after a stroke may be a clear indication that drug therapy has failed to stop internal bleeding or ischemic damage to brain tissue. Constantly increasing intracranial pressure leads to a deterioration in the patient’s well-being, the development of coma, as well as neurotic manifestations. Repeated convulsions with constantly increasing intensity indicate extensive damage to brain tissue, often incompatible with life.
- Coma - post-stroke convulsions lead to short-term and long-term loss of consciousness. Intense convulsive phenomena cause the development of coma.
- Disability – involuntary spasms in the arms and other limbs, accompanied by chaotic movements. The patient is unable to control his actions and often causes harm to his body: he may get hurt, bite off the tip of his tongue, etc.
It is necessary to combat limb cramps. A gradual decrease in the intensity of manifestations indicates that drug therapy was chosen correctly, and restoration of lost brain functions is observed.
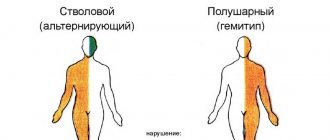
Alternating Benedict's syndrome
Benedict's syndrome belongs to a group of alternating syndromes that affect the structures of the brain stem.
Similar syndromes include Wallenberg syndrome, which affects the posterior inferior cerebellar artery, medial Dejerine syndrome, ventrocaudal pontine syndrome, or Foville syndrome.
All these diseases are due to ischemia, thrombosis of the cerebral arteries, or hemorrhage, and are very difficult, since bilateral (and even extensive unilateral damage to the bridge) is incompatible with life.
Source: https://probol.info/nevralgiya/onemenie-ruk-posle-insulta-prichiny-lechenie-pochemu-tryasetsya-noga-posle-insulta.html
Rehabilitation
A person after a stroke needs constant help from the medical team and loved ones.
Knowing the characteristics of the course of a stroke, start with the simplest and most uncomplicated activities. For example, flexion and extension of the arms and legs at the joints up, down, counterclockwise, and in the opposite direction.
It is worth considering that if there is excessive numbness of the hands, accompanied by pain when moving, then physical exercise should be reduced or changed to less active ones.
It is necessary to constantly praise the victim for the task he performed, even minor movements of the fingers. After restoring some movements, one should not assume that the patient will independently perform the exercises indicated to him. Therefore, in order for the numbness of the hands to begin to be felt in a less pronounced form, the patient must perform any exercises within his power every day during the subsequent years of rehabilitation.
Traditional medicine
Numbness after a stroke leads to periodic tremors. If pathology is detected on the left side of the head, then the right leg and arm are paralyzed. And vice versa.
To save the patient, the doctor prescribes anticonvulsants, for example, Finlepsin or Carbamazepine 200 mg per day.
It is important to be careful: you should not allow the dose of Finlepsin to increase; there is a danger of causing bone fragility due to leaching of calcium from the body. The drug Carbamazepine is addictive, if there is little benefit and the doctor may write a prescription for Topiramate, Levitaratsitam or Gabapentin instead of this medicine.
Read also: Right hemisphere stroke consequences
Traditional methods
No treatment method can lead to a 100% guarantee that paresis will be cured and subsequently recur. Therefore, it is worth remembering that there will always be consequences.
First of all, when prescribing medications, doctors may recommend rubbing an infusion of 2 tbsp to increase sensitivity. l laurel with vegetable oil. Tremor and numbness in the body, arms and legs after such a procedure are expressed to a lesser extent.
If you drink linden tincture before eating, you can prevent paresis and increase the restoration of movements in the arms and legs.
A mixture of medicinal herbs Adonis vernacular, Cinquefoil anserina and common thyme helps reduce paresis and help restore blood flow in the affected limbs.
Unrefined oil and garlic infused with an oil base, when taken three times a day, 10 ml of the drug within 24 hours, helps eliminate many of the consequences of a stroke. It is also useful for restoring movements due to the cleansing properties of garlic cloves.