Recovery after a stroke on the left side of the brain is a long process that requires the involvement of both the patient and his relatives, because their support and assistance is very important for the victim.
The term stroke refers to an acute disruption of blood flow in the vessels supplying the brain. Sometimes it is called apoplexy or acute cerebrovascular accident (ACVA).
As a result, part of the nervous tissue dies, and the patient develops focal and cerebral neurological symptoms. The prognosis depends on the age of the patient, the size of the ischemic focus and its location. Stroke is considered a life-threatening condition and patients should be taken to hospital as quickly as possible where they will receive the necessary treatment and care.
How to recognize a stroke?
The development of the disease depends entirely on which part of the brain is damaged, and works on the principle of “reverse symmetry”. The right hemisphere is responsible for paralysis of the left side of the body, and the left hemisphere is responsible for the condition and performance of the opposite side.
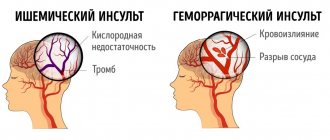
Paralysis of the left side of the body can be a consequence of both hemorrhagic and ischemic types of apoplexy. The latter is characterized by local changes. Diagnosing a stroke of the right hemisphere is much more difficult, since with this anomaly a person’s speech, which is one of the most noticeable symptoms, is not distorted. The phenomenon delays and worsens the patient’s chances of recovery and restoration of the functional abilities of the affected part of the body.
In this case, paralysis may begin with a feeling of slight weakness in the limb - hemiparesis, which over time develops into a complete loss of motor activity - hemiplegia.
To provide first aid to a person at the time of a brain stroke, you need to know its first signs.
The main signs of sudden cerebral hemorrhage include:
- Deformation of the facial muscles of the injured side (the corner of the mouth and eyelids noticeably droop).
- Mimic actions are zero. A person is unable to smile.
- Cannot raise both arms at the same time.
Other indicators of stroke:
- Pathological processes occur in the work of internal organs located on the left side of the body.
- The perception of the affected part of the body is disrupted: the patient does not fully control the limbs and cannot assess the size and distance.
- Manifestation of inexplicable aggression.
- Constant feeling of depression.
- Deformation of color perception.
- Spontaneous dizziness.
- Disorientation in space
- Violation of the vestibular apparatus.
- Problems with vision and hearing: such a patient may have double vision, does not see clear boundaries, and images seem blurry.
- Absent-mindedness.
Comprehensive program “Rehabilitation+”
This stroke rehabilitation program aims to return patients to as full a life as possible.
The main task of the specialists at the “New Hospital” is a separate approach to each patient. We use maximum opportunities to restore lost skills:
- restoration of vision;
- motor activity (recovery of arms and rehabilitation of legs after a stroke, fine motor skills);
- speech restoration;
- learning to tie shoelaces, wash dishes, etc.;
- restoration of driving skills.
As part of the program, our specialists try to restore not only the basic skills that were lost. We try to return the patient to a full life, focusing on the tasks that are necessary for a specific person.
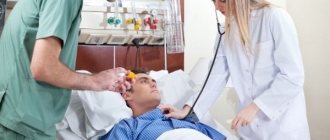
How to provide first aid for a cerebral hemorrhage?
To properly provide first aid to a person with symptoms of apoplexy, it is necessary:
- Notify a specialized team about what happened.
- Lay the patient down; it is recommended to raise the head.
- Make sure to provide fresh air.
- Release the patient from constrictive clothing.
- If the person requiring help is unconscious, turn his head slightly to the side. This is in order to block the passage of saliva, mucus and vomit into the respiratory tract.
- Remove removable dentures from the mouth.
- It is important to apply the cold to the HEALTHY side. Do it with a cold heating pad, ice and cold objects.
- Warm the patient by covering him with a blanket.
- Such a patient needs frequent measurement of blood pressure, scrupulous monitoring of breathing and heart rate.
- In case of clinical death (cessation of heart function, prolonged holding of breath and dilated pupils), perform artificial ventilation and chest compressions.
Providing emergency care for ischemic stroke includes:
- Place the patient on his back so that his head is elevated.
- It is forbidden to revive an unconscious patient with the help of medications, as this can aggravate the person’s condition and contribute to the progression of neurological symptoms.
- Keep your mouth clean and monitor your respiratory tract.
- Provide the patient with the necessary amount of fresh air, freeing him from compressive clothing.
- Rub the damaged part of the body with a semi-alcohol solution or massage.
- The use of pharmacological agents is prohibited.
- Do not feed the patient until examined by a doctor.
Specialized medical care includes:
- Instrumental diagnostics. Its task is to help determine the exact type and location and development of pathological changes in the brain.
- Carrying out monitoring using nanotechnology.
- To regenerate damaged cells, cerebroprotectors (ceraxon, actovegin) are administered.
- Table number 10 is assigned.
- To restore movements, water procedures and therapeutic exercises are prescribed. Exercise machines and massagers are used.
- Preventative measures for bedsores are carried out, care for mucous membranes is carried out, defecation and urination are controlled.
- The patient needs speech therapy sessions.
- Activating movements through simple actions.
Interesting fact! A stroke spares no one and can target a person of any age category as a victim. A brain stroke occurs suddenly. Therefore, in order to save your life or the life of “your neighbor,” it is important for every person to know the basic symptoms of cerebral hemorrhage and the algorithm of actions for providing first aid.
Causes
All causes of left-sided stroke must be divided into two main groups. This is explained by the form of the disease. For hemorrhagic left-sided stroke there are:
- Hypertension or the appearance of a hypertensive crisis.
- Chronic forms of vasculitis.
- Consequences of long-term use of anticoagulants or other drugs that thin the blood.
- Poisoning with toxic chemicals.
- Diseases associated with insufficient blood clotting, for example, hemophilia, thrombocytopathy.
- Violation of the integrity of the vascular wall.
- Consequences of strong physical exertion.
- Consequences of traumatic brain injury.
In ischemic pathologies, the causes are:
- Atherosclerotic lesion of the vascular wall.
- The manifestation of varicose veins of the lower extremities, which is complicated by the formation of blood clots.
- Blood clots formed in the atria due to abnormal heart rhythms, for example, the result of atrial fibrillation.
- Excess body weight.
- Increased blood clotting.
- Abrupt increase in blood pressure.
- Having bad habits such as smoking, drinking alcohol, or overeating foods with high calorie content and excess cholesterol.
Left-sided hemiparesis after stroke
Hemiparesis means wasting of the muscles on one side, while the other part of the body retains full functionality and remains in its normal state. The severity of the process is determined by symptoms, which depend on individual nuances. These include:
- Age.
- General state.
- Factors contributing to the occurrence of an anomalous phenomenon.
Main signs of hemiparesis:
- Frequent migraines.
- Lack of appetite.
- Unbearable joint pain.
- Weight loss is obvious.
- Accelerated fatigue.
Depending on the location, hemiparesis is divided into two types:
- On the left side – one of the forms of cerebral palsy; complete muscle paralysis is possible.
- Right-sided - observed in adults. The right side suffers (disturbances in movements occur).
The primary reasons for the immediate appearance of right-sided hemiparesis include:
- Stroke.
- Neoplasms in the brain.
- Traumatic injuries.
- Encephalitis.
- Frequent, prolonged headaches.
- Manifestations of multiple sclerosis.
- Development of diabetic encephalopathy.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures include:
- Examination of the injured arm/leg.
- Assessment of the performance of the oppressed party.
- Determining the root cause.
- Studies using electromyography, CT and MRI.
Treatment for left-sided hemiparesis includes:
- Exercise therapy and therapeutic gymnastics.
- Physiotherapy (as prescribed by a doctor, for each patient personally).
- Hippotherapy (use of horse movements).
- Reflexology.
- Massage of an injured limb.
- Water procedures include: swimming, dousing, hardening, Charcot's shower.
In more severe cases, drug therapy is prescribed.
After a stroke, the left side is paralyzed. Forecast.
Making a prognosis for a patient who has suffered a stroke is very difficult, since it depends on the stage of development of the disease, the size of the affected area, and the attitude towards the health of the patient and his family. For a favorable prognosis, it is important to begin treatment of a stroke patient as soon as possible, using medication and rehabilitation measures.
Recovery of the left side after a stroke in a hospital includes:
- Correction of movement disorders. Depending on the general condition of the patient and the severity of the disease, the rehabilitation doctor selects an individual course of exercises.
- Prevention of contracture.
- Application of basic therapy.
- Depending on the type of disease, specific treatment is prescribed.
- Restoration of speech thanks to sessions with a speech therapist.
Even after recovering from a stroke, such a person needs continued treatment.
Treatment of left-sided stroke at home has its own characteristics and includes:
- Maintaining bed rest. Moreover, due to damage to the left eye, the patient’s bed and objects in the room should be on the right side.
- Using breathing exercises.
- Regular physical therapy classes, which increase in duration and physical activity over time.
- Alternating position from vertical to horizontal. This can be done thanks to the handrails and straps that the patient’s bed should be equipped with.
- Using actions that help develop a paralyzed limb.
- Constantly communicate with the post-stroke patient. The questions asked should be: simple, concise, understandable.
- Massage the injured part of the body. This will help normalize blood flow, eliminate pain and restore muscle tone, eliminate limb spasms and prevent bedsores.
Recovery course
The rehabilitation program includes many methods of influencing paralyzed limbs, learning to walk, eat, maintain personal hygiene, and self-care. It includes areas such as kinesiotherapy (movement therapy), speech and memory training, dietary nutrition, medication, physical therapy, and massage.
Watch the video about recovery after a stroke:
Motor program
You need to start moving as early as possible. At first, this may include flexion and extension of the fingers, hands and feet of the healthy side of the body. This speeds up the recovery of brain cells in the affected area. Subsequently, usually simultaneously with the massage, the physical therapy instructor performs gentle flexion, extension, and sequential rotation in all joints of the arm and leg.
Restoring finger movement after a stroke
To restore the function of the upper limb, a towel is hung over the bed, and the patient grabs it and moves back and forth, sideways, up and down. After mastering these exercises, the towel is hung higher.
Also, a rubber bandage is used as a training device; it is tied into a ring (the length of the strip is approximately 80 cm) and fixed on a stationary object or between the arms, legs, arm and leg. During training you need to stretch the ring.
The lower limbs in bed can be developed with passive movements in the ankle, knee and hip joints, and then the patient is asked to slide his heel along the bed . To eliminate the spasm, you need to place a hard cushion under the knee.
Exercises in bed
The next stage of training is training while sitting on the bed, and then standing on the floor. The following exercises may be included in the rehabilitation complex:
- pick up a box of matches from the table and then from the floor;
- stand on your toes with your arms raised above your head;
- expander compression;
- body bends;
- scissor-type hand movements;
- squats.
Special simulators for recovery after a stroke significantly speed up the rehabilitation process and can be used from the first days
Speech training
Speech is restored later than movements in the limbs; it may even take several years. To restore the ability to speak, it is important that the patient constantly hears the conversation addressed to him, even if he is not yet able to respond. Even the perception of someone else's speech activates the corresponding centers of the brain, which contributes to their disinhibition. If speech is completely absent, then the following techniques can be used for training:
- the patient finishes the word (the part without the last letter or syllable is pronounced to him), then the sentence;
- repetition of simple phrases;
- well-known poems;
- Tongue Twisters;
- singing together.
Advice from a speech therapist for speech restoration
In order to force the muscles involved in articulation to develop, the patient is asked to move his lower jaw daily, stick his tongue forward, lick his lips in different directions, and curl them into a tube.
Memory recovery
Against the background of drug therapy (nootropic drugs), special exercises are also carried out to develop memory:
- repeating a number sequence with your eyes closed;
- learning proverbs, sayings, poems;
- retelling a text read or a song heard;
- Board games.
Board games for memory restoration
The best results can be obtained if classes are combined with the patient’s previous hobbies so that the training process is accompanied by positive emotions.
Nutrition
It is most difficult to feed patients with impaired swallowing and sensitivity in one half of the oral cavity. They have to learn to eat again. To do this, you can use exercises to restore lost abilities:
- the patient imitates coughing, swallowing and yawning;
- puffs out cheeks;
- rinses your mouth and throat.
Exercise “Puffing up the cheeks”
When organizing nutrition for patients with impaired chewing and swallowing functions, the following features must be taken into account:
- food should only be warm and smell appetizing;
- exclude viscous and hard foods - rice, dry cottage cheese, dried bread, crackers;
- the side dish should have the consistency of thick puree, and soup or juice can be added to meat and fish;
- eating takes at least 40 minutes, the patient should not be rushed;
- it is necessary to feed in such a way that the food gets to the healthy side;
- For drinks and water, it is convenient to use a sippy cup or a cocktail straw.
The easiest foods for stroke patients with eating problems to swallow are:
- boiled carrots, potatoes, mashed or diced;
- cauliflower, broccoli;
- minced meat;
- baked flounder, sardines;
- omelette;
- avocado, banana;
- soft pear cubes;
- baked or pureed apples;
- jelly, pudding;
- soft cheese;
- porridge made from flakes or grains (thoroughly boiled).
Puree soups from vegetables, meat, fish.
It is unacceptable to include fatty meat, broths, fried and spicy foods, alcoholic and caffeinated drinks in the diet.
Drugs
The choice of medications for rehabilitation is carried out exclusively by a neurologist. The following groups of drugs are used:
| Groups | Medicines |
| Vasodilators (with caution, under pressure control) | Cavinton, Sermion, Instenon; |
| Neuroprotectors | Somazina, Semax, Cerebrolysin, Encephabol; |
| Antioxidants | Mexidol, Tanakan; |
| Nootropic | Lucetam, Phenotropil. |
If indicated, antiplatelet agents (Tiklid, Aspirin) and cholesterol-lowering drugs (Atokor, Vasilip) are used.
Physiotherapy
The appointment of procedures can be no earlier than 1 - 2 months from the onset of the stroke. The following techniques are indicated during the recovery period:
- electrophoresis on the collar area;
- sulfide baths on hands;
- magnetic therapy on the neck area;
- general baths with sea salt, pine extract, carbon dioxide and pearl;
- ozokerite or paraffin, mud or galvanic mud on the affected limbs;
- reflexology – acupressure or acupuncture;
- electrical stimulation with sinusoidally modulated currents;
- Darsonvalization of limbs.
Massage
Indicated from the first week of illness daily, starting from 10 minutes to half an hour. All movements are slow and low-intensity, especially if there is muscle spasm. On the healthy side, the technique of massage movements can be classic. Massaging sequence:
- Scapular region.
- Shoulder.
- Forearm and hand.
- Pelvic, femoral area.
- Shin and foot.
The course requires from 30 to 50 sessions, after which a break is needed for a month, then for maintenance therapy, massage can be performed in 10 sessions 3 - 4 times a year.
Watch the video about massage and exercise therapy after a stroke: