What is the danger of the disease
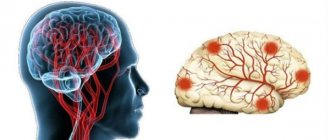
This pathology causes many complications. Vascular diseases occupy one of the leading places in mortality in all countries. Lost tissues and structures in the brain cannot be restored. The consequences of an advanced disease can be:
- Ischemic stroke (cerebral infarction), accompanied by nausea, dizziness, tinnitus, vomiting due to cessation of blood supply to one of the parts of the brain. Speech, motor, emotional and volitional functions suffer and the functioning of internal organs is disrupted.
- Hemorrhagic stroke (hemorrhoidal), is provoked by blood thrown into the brain cavity from ruptured vessels. Pressure increases, the brain contracts, the structures of the foramen magnum are damaged, and blood circulation in the brain is disrupted. In terms of mortality, hemorrhoidal stroke occupies a leading place.
- Transistor ischemic attack, characterized by paralysis of the limbs, drowsiness, damage to motor, visual, and speech functions. Blood circulation is restored with medications that improve brain function.
Problems with peripheral blood flow lead to chronic poor circulation. The patient is diagnosed with intellectual retardation and dulling of mental abilities. The patient becomes irritable, sometimes aggressive, restless, and has absent-mindedness.
Causes
The main causes of the occurrence and development of cerebrovascular accidents are:
- Hypertension. Consistently high blood pressure leads to decreased elasticity, spasms of vessel walls and increased resistance to blood flow.
- Atherosclerosis. As a result of impaired fat metabolism, plaques form on the vascular walls, preventing normal blood circulation.
- Thromboembolism. A detached blood clot leads to blockage of the vessel.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. The disease leads to vasospasms. According to statistics, this particular pathology causes oxygen starvation in a quarter of patients.
- Operations and injuries in the head. These phenomena are associated with large blood loss, leading to damage to brain tissue and hematomas.
- Disturbances of venous outflow. Pathologies of this type lead to the formation of stagnation and the release of toxins.
- Hypoxia during pregnancy and childbirth. Blood circulation disorders are diagnosed in children.
Factors that lead to impaired cerebral circulation include states of strong psycho-emotional stress, stress, alcohol, smoking, age after 40 years, and lack of sufficient movement.
PNMK - how dangerous is it?
The brain is a complex autonomous system with its own laws and rules, but as practice shows, any rule can be violated as a result of a negligent attitude, in this case, a person’s way of life.
The blood supply to the brain is designed in such a way that if one part of the brain is overactive, blood is redistributed from less busy areas for productive work. But the circulatory system suggests, and a person does as he wants, and not as he needs.
In the process of life, the human body receives a huge amount of harmful substances, which (for example, cholesterol) can be deposited on the walls of blood vessels, causing them to narrow. Gradually, cholesterol fillings form on the walls of the vessels; as they grow, they come off and float freely through the circulatory system, getting into the arteries narrowed by cholesterol deposits and blocking the flow of blood, which ultimately results in a micro-stroke.
Among other things, the older a person is, the greater the likelihood of artery blockage, not only due to cholesterol fillings, but also as a result of blocking the blood flow with emboli or small pieces of blood clots.
Transient cerebrovascular accidents can also occur against the background of improper distribution of blood between areas of the brain. In such a situation, its most active parts do not receive a sufficient amount of blood due to poor vascular patency, and the result is the same - PNMK.
Mechanism of occurrence of PNMK
Cerebral circulatory disorders, called transient, are usually of the following types:
- Microstroke (transient ischemic attack) - characterized by a short duration, on average from a few seconds to 1-2 hours. Symptoms vary depending on the area of the brain affected.
- Hypertensive crisis - can occur as a result of a sudden change (jump) in blood pressure. As a rule, it aggravates the general condition of the brain.
- Short-term paroxysm is one of the rare forms of PNMC, causing fainting in the patient.
- PNMK against the background of a sharp turn of the head - as a result of compression of the vertebral artery, this disorder occurs.
How does PNMK occur?
People at risk include:
- smoking or drinking alcohol
- those suffering from osteochondrosis of the cervical spine (possible compression of blood vessels)
- suffered traumatic brain injuries
- those who have undergone injury or surgery with heavy blood loss
- susceptible to weather conditions
- suffering from diabetes
- working or engaged in activities associated with severe psycho-emotional overload
Much less frequently, the cause of a disorder of cerebral blood supply, called transient, can be:
- lupus erythematosus
- syphilis
- heart diseases
- heart attack
- infectious vasculitis
- various vascular lesions
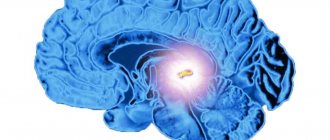
With prolonged oxygen starvation, ischemic strokes can develop in some areas of the brain. This is the main danger of PNMK, because with such a pathology, disturbances in the blood supply are observed, which leads to pathological changes and disturbances in the functioning of individual areas and the organ as a whole.
If after a stroke a long recovery and complex rehabilitation are required, then with PNMK the negative consequences are quickly eliminated. The treatment is short and usually very effective. Even the attack of PNMK usually passes within a few minutes, only in some cases it can last up to an hour.
A transient cerebrovascular accident requires immediate medical attention when the first symptoms are detected. The consequences of neglected pathology can be very serious and even deadly.
Basic treatment methods
After receiving the results of a comprehensive examination, an individual treatment regimen is selected for the patient. As a rule, he is prescribed a certain course of medications that help stabilize blood circulation in the brain.
It is very important to determine the form and stage of cerebrovascular accident; the effectiveness of therapy directly depends on this.
Drug therapy
In case of acute hemorrhagic cerebrovascular accident, the patient is prescribed drugs to lower blood pressure, stop bleeding and reduce swelling in the brain. The following medications are used for this:
- Arfonad, Pentamin , etc. - help stabilize blood pressure;
- ascorbic acid, calcium gluconate – increase the permeability of the walls of blood vessels, improving the function of blood clotting;
- Kaviton, Cinnarzin , etc. - improve the rheological properties of blood;
- Lasix – helps relieve swelling.
In most cases, drugs are administered intravenously or intramuscularly. If intracranial pressure is elevated, the patient undergoes a puncture.
For ischemic stroke, drugs are used to stabilize the functioning of the cardiovascular system (Strophanthin, Cardiamin, etc.), and a course of intracranial pressure stabilizers is also prescribed.
If chronic cerebral circulatory failure is diagnosed, antioxidants, ventotonics, neuroprotectors, and agents that improve blood circulation are used. Since this condition often develops against the background of severe nervous shock, the patient is prescribed mild sedatives and vitamin complexes. The course of treatment and dosage is selected by the attending physician individually.
If cerebrovascular accident is caused by atherosclerosis, then medications are used that help break down cholesterol plaques (Vabarbine, Simartin, etc.). If there is multiple blockage of blood vessels, surgery may be required.
ethnoscience
You can improve cerebral circulation using folk remedies. The most commonly used infusions or decoctions are based on medicinal plants: ginseng and Chinese lemongrass, hawthorn, chamomile, motherwort, etc.
These drugs must be used in combination with the main treatment regimen, otherwise the risk of complications increases. Before using traditional medicine, you should consult your doctor.
Proper nutrition
A balanced diet plays a big role in the treatment of circulatory dysfunction. People prone to obesity should avoid fatty, spicy, smoked foods. It is better to eat fresh fruits and vegetables in season, healthy cereals, fish, seafood and lean meats.
Dietary nutrition will help avoid the development of atherosclerosis and other diseases that cause impaired blood circulation in the vessels of the brain.
Drug therapy allows you to stop the progression of the disease, but does not return the patient to lost abilities (restoration of speech, movements, etc.). Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner, since the sooner changes are recorded, the easier they are to treat and have fewer negative consequences for the patient.
Classification
The form of development of the disease allows us to distinguish acute and chronic course. Acute is characterized by transient cerebrovascular accidents and stroke. Its main features are the rapid development and rapid onset of symptoms.
A chronic course is characteristic of various types of discirculatory encephalopathy. Signs of the disease appear gradually and increase over several years. The pathology causes many small foci of necrosis, which negatively affect the functioning of the brain. At the first stages, the symptoms are invisible and are usually attributed to overwork, the consequences of acute respiratory viral infection or other causes.
Prevention methods
Prevention of cerebrovascular accidents includes a healthy lifestyle and nutrition, walks in the fresh air, and minimizing strong physical and emotional stress. If you have a genetic predisposition to this disease, you should undergo regular examinations with a doctor.
To improve blood circulation, doctors recommend visiting saunas or baths 1-2 times a week (in the absence of direct contraindications). This will help open clogged blood vessels and enrich the brain with the necessary amount of blood. In addition, it is recommended to regularly take complexes of vitamins and microelements, which help strengthen the walls of blood vessels.
Problems with blood circulation in the brain are quite common. They appear for various reasons and must be treated immediately. Otherwise, the risk of developing irreversible consequences for the patient increases (speech and movement disorders, memory loss, etc.). For therapy, special medications are used, which are selected by the doctor, depending on the form and severity of the disease. Self-medication with such a diagnosis is unacceptable.
Symptoms of PNMK
The symptoms of short-term disruption of cerebral blood supply can be very different. This significantly complicates the definition of the disease and its detection in the early stages. Typically, the disease develops acutely, occurs suddenly, and symptoms disappear quickly.
Symptomatic manifestations are divided into several groups:
- General cerebral manifestations of the disease may be as follows:
- headaches of various nature and localization;
- nausea and vomiting;
- weakness throughout the body;
- feeling of lack of air;
- blurred vision;
- vasomotor reactions;
- disorders of consciousness that quickly pass.
- Focal (regional) manifestations of the disease are reduced to the following manifestations:
- numbness or tingling sensation in the face, arms or legs;
- musculoskeletal disorders;
- paretic phenomena in the area of the hand, individual fingers or feet;
- hemiplegia;
- Jacksonian epilepsy is a rare disorder;
- blindness of one eye;
- systemic dizziness indicates PNMK in the vertebrobasilar region;
- impaired swallowing ability;
- seizures of temporal lobe epilepsy;
- memory impairments indicate ischemic disorders in the medial-basal region.
Transient disturbances in cerebral blood flow can cause a variety of symptoms, each of which requires attention. You cannot ignore the messages that come from the body. They may have good reason to worry.
Symptoms
Signs of the disorder are approximately the same in all three cases. With minor differences, and adjusted for the volume of the deficit.
Transitory violation
A microstroke gives a typical clinical picture of necrosis of cerebral structures. General cerebral and focal signs appear.
Among the first:
- Headache. Initial manifestations are neurological. The discomfort is pronounced and strong. Localization cannot always be determined. These are the temples, the occipital region, and the crown of the head, which are most common.
The diffuse (spread) nature of the unpleasant sensation is often detected. Type of syndrome - baling, shooting. Pulsates in time with the beat of the heart.
The intensity of discomfort can be extremely high. Therefore, the patient takes a forced lying position in order to somehow reduce the severity of the pain.
- Dizziness is a characteristic sign of cerebrovascular accident, also called vertigo. Accompanied by impaired coordination of movements and orientation in space. The vestibular apparatus is affected.
- Nausea, vomiting. They develop due to disturbances in the trophism (nutrition) of special brain centers. They are responsible for removing toxins from the body.
As part of poisoning, they are stimulated by the toxic substances themselves. And in this case, a paradoxical reflex reaction arises. Vomiting is usually one-time. The symptom does not last long. No more than a sixth of the entire acute condition.
- Loss of consciousness. Fainting. A bad sign indicating a significant hemodynamic impairment.
- Front sights, fog in the field of view. Double vision is also possible.
- Muscle weakness. Accompanied by the inability to stand on your feet. You have to sit or lie down to avoid falling.
- Paresis, paralysis. Movement disorders. Not always. They relate rather to focal symptoms (with damage to the frontal lobe of the brain).
A classic sign known to many - facial distortion - is not always encountered, which can lead others to the wrong path and prevent them from reacting.
The key differences between transient cerebrovascular accidents and acute and chronic ones are the temporary nature of the condition and its pronounced severity.
The usual duration of PNMK is 1-12 hours. Ends with complete regression of the clinical picture. Everything returns to normal.
At the same time, only a doctor can conduct a differential diagnosis and distinguish between a transient disorder of cerebral blood flow and full-blown necrosis. And not right away.
Focal symptoms
Depends on the specific area of the brain deprived of nutrition.
- Occipital lobe.
Visual deviations. Up to complete blindness. There are also photopsia (lightning flashes in the form of dots, lines, geometric shapes), simple visual hallucinations, metamorphopsia (the inability to determine the size of objects, the distance to them), fog, double vision. Loss of part of vision (scotoma).
- Frontal lobe.
Accompanied by disturbances in behavior and motor activity (paralysis, paresis), a return to childhood is possible (rapid personality regression).
Severe epileptic partial seizures with tonic-clonic convulsions are detected (covering all the muscles of the body at once).
Intellectual activity also decreases to critical levels. A person cannot think normally, much less perform actions that require tension.
- Parietal lobe.
Tactile functions are impaired. A person loses the ability to recognize objects by touch and feels physical hallucinations (touching, crawling under the skin).
The ability to read, write, and perform simple arithmetic operations is also lost.
- Temporal lobe.
Manifestations are mainly auditory. Tinnitus, voices (pseudohallucinations), hearing loss, inability to understand speech in one's native language, loss of consciousness, epileptic seizures.
Aphasia is a speech disorder.
- Limbic system.
Learning abilities suffer, the sense of smell is completely lost. But this is a temporary violation. A person does not have time to notice the first symptom due to the short-term duration of the dysfunction.
- Extrapyramidal system (cerebellum).
Responsible for coordination, voluntary movements, normal orientation in space. Symptoms of cerebellar cerebellar circulatory disorders are nystagmus (rotation of the eyeballs to the right and left), vertigo, muscle weakness.
The patient cannot walk in a straight line. Basic reflexes are impaired (detected during routine neurological examination).
- Brain stem. The only case where a transient circulatory disorder can lead to the death of the patient. Vital centers are located here.
Disorders of breathing, cardiac activity, and body temperature occur (uncontrolled jumps within 41 degrees and even higher).
Motor disorders and speech dysfunction are possible. Patients need to be urgently transferred to a hospital setting.
Signs of acute disorder
Acute-type NMC is accompanied by mental and neurological disorders. The initial symptoms are identical, but develop within minutes.
The clinical picture is completely identical (taking into account the localization of the ischemic or hemorrhagic focus).
The key difference is the persistence of violations. They don't go away on their own. At the end of the destructive process, a neurological deficit remains. What kind depends again on the location of the violation.
Manifestations of chronic urinary tract
The sluggish type of cerebrovascular insufficiency does not provoke pronounced focal symptoms.
CNMK gives a weak clinical picture and does not allow timely detection of the pathological process. In 70% of cases, the patient does not have time to react (statistics for Russia and the states of the former Union).
In more developed countries, the percentage hardly exceeds 15%, which is due to the quality of the early screening program and the high medical culture of the population.
Chronic circulatory disorder of the first degree is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Headache. Regular, but not constant. Medium in intensity. They intensify after a night's rest, prolonged stay in one, often uncomfortable position, or physical activity.
Patients do not associate discomfort with hemodynamic disturbances, which puts an end to early diagnosis.
- Dizziness. Vertigo. Also temporary, paroxysmal. Insignificant in strength.
- Weakness, fatigue, constant weakness. Since the brain does not receive enough nutrients, the body strives to compensate for the functions. Puts the body into “standby” mode. Because cerebral structures consume the greatest amount of energy.
- Insomnia. Frequent awakenings at night, after a formally good sleep. Leads to aggravation of other symptoms and disturbances in well-being.
Other signs are much less common. Therefore, it is this complex that is evaluated first.
At stage 2 of CNMK, another symptom is added - loss of consciousness and fainting. Possible unsteadiness of gait, tremors (trembling in the limbs, chin).
The third degree of CNMK is accompanied by a critical impairment of intellectual activity. Complete personality degradation and early dementia occur.
It is not difficult to diagnose the pathological process if you consult a doctor in time.
Types of disorders
Acute cerebrovascular accident (ACVA) develops extremely quickly. Sometimes a few hours or minutes are enough for a serious attack to occur. ONMC are divided into:
- Hemorrhagic stroke.
- Ischemic stroke.
- Local disorders that do not affect vital organs and systems.
Chronic brain disorder (dyscirculatory encephalopathy) progresses slowly, over many years. Due to the pathology, many small necroses of tissues and brain structures develop, which have a detrimental effect on its functioning. In the initial stage, the symptoms of the disease are almost invisible. Later, with the steady development of the disease, they become pronounced.
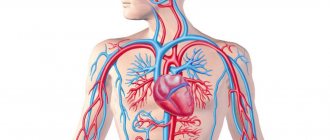
Chronic heart failure
Chronic heart failure sometimes develops over many years. Over time, the efficiency of the heart as a pump gradually decreases.
The most common signs of chronic heart failure are:
- edema - caused by the accumulation of excess fluid in extracellular spaces and body cavities; they are the main sign of heart failure; the most typical is a tumor located on the lower extremities - after pressing on the swollen skin with a finger, it does not quickly return to its previous form; swelling may also occur between the shoulder blades or in the lumbar region;
- shortness of breath - difficulty inhaling air; this is the second symptom (besides swelling) that may indicate heart failure; difficulty breathing occurs due to the accumulation of fluid in the lungs, which makes it difficult to transfer oxygen to the blood; the development of cardiovascular failure causes an increase in shortness of breath. In some patients (at an early stage), this symptom appears only during physical activity. For example, when the patient climbs the stairs.
- grayish skin color;
- persistent cough with sputum and mucus production,
- decreased urination during the day,
- increased need to urinate at night,
- fatigue,
- drowsiness.
Diagnosis and treatment of chronic circulatory disorders
Additional tests used in diagnosing the disease:
- general urine analysis,
- X-ray examination of the chest,
- ECG,
- echo of the heart,
- Magnetic resonance,
- angiography,
- A blood test designed to evaluate: ion concentrations, cardiac markers, liver and kidney tests and morphology.
Diagnostic methods
We will study methods for diagnosing the disease a little later, but for now let’s turn to the international classification system ICD10 and find the code that is assigned to PNMK. This will be G45, this is the designation for this disease accepted by international medicine, and it is indicated on the medical history.
If PNMK manifests itself in the form of transistor ischemic attacks, then the essence of diagnosis comes down to excluding stenotic lesions of extra- and intracranial arteries. This is especially true for repeated manifestations of the disease. For these purposes, the following methods are used:
- Ultrasound G;
- MR angiography;
- contrast angiography;
- study of microcirculation disorders;
- the ability of the circulatory system to clot is assessed;
- CT and MRI can exclude a hemorrhagic process.
In the presence of a hypertensive crisis, the essence of diagnosis comes down to the exclusion or confirmation of secondary hypertension. In the case of meningeal syndrome, it is necessary to exclude subarachnoid hemorrhage. It is imperative to diagnose disturbances in the functioning of other organs and systems that have arisen as a result of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Diagnostics
You cannot independently compare the symptoms and take treatment at your own discretion, since in this case there is a high risk of developing complications, including life-threatening ones. At the first symptoms, you should immediately seek emergency medical help.
To clarify the etiology and make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes the following laboratory and instrumental examination methods, if the patient’s condition allows them:
- general blood analysis;
- lipid profile;
- blood sampling for glucose testing;
- coagulogram;
- duplex scanning to identify affected vessels;
- neuropsychological testing using the MMSE scale;
- MRI of the head;
- CT.
In some cases, the diagnostic program may include genetic studies if a hereditary factor is suspected.
Method for diagnosing initial manifestations of cerebrovascular accident
Only a doctor can tell how to treat this disorder, after an accurate diagnosis and identification of the etiology.
Development mechanism
The mechanism of development depends on the reasons that caused the pathology. So, when blood pressure jumps, protein metabolism is disrupted; they leave the blood, remain on the walls of blood vessels and form dense masses similar to cartilage tissue. The blood vessels lose elasticity and density and can no longer control blood pressure.
The mechanism of development of cerebral circulatory disorders caused by atherosclerosis is somewhat different. A fatty plaque forms on the wall of any vessel, to which calcium deposits grow. The formation grows to such a size that the vascular cavities narrow and natural hemodynamics are disrupted.
Over time, a plaque located in a large vessel may come off. Then it enters the blood stream and clogs the smaller one. This is found when a blood clot breaks off. In each of these situations, brain nutrition is stopped and, as a result, an ischemic stroke or micro-stroke occurs.
These processes are often associated with stress. Adrenaline produced during acute mental stress leads to increased heart rate and constriction of blood vessels.
The factors have been partially named. Poor circulation is caused by arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis.
These are the two most common points. In combination, they lead to a rapid increase in the risk of stroke.
Rare causes - malformations, aneurysms, congenital abnormalities of the vascular structures of the brain, tumors, heart pathologies (coronary artery disease, defects, previous heart attack, coronary insufficiency), blood clots.
The reasons are determined without fail. Without identifying the etiology, it is not possible to prescribe quality treatment.
Treatment
Treatment will depend on the underlying factor - depending on this, basic therapy is selected. In general, drug therapy may include the following drugs:
- sedatives;
- neuroprotectors;
- multivitamins;
- venotonics;
- vasodilators;
- antioxidants.
All drug therapy, regardless of etiology, is aimed at protecting brain neurons from damage. All funds are selected only individually. During drug therapy, the patient should constantly monitor blood pressure, as there is a high risk of stroke and heart attack.
In addition to drug treatment, the doctor may prescribe a course of physical therapy. In some cases, such activities are used for rehabilitation. The standard program includes the following:
- a set of “balance” exercises, which is aimed at restoring coordination of movements;
- a set of reflex exercises according to Feldenkrais;
- microkinesitherapy;
- exercises according to the Voight system.
The recovery program also includes therapeutic massage and a course of treatment with a chiropractor.
Signs
- Modern life moves at such a crazy pace that an ordinary person has to speed up his actions more and more, sleep less, work seven days a week, and stress has long become an integral part of our existence.
- And in this rush, we sometimes have no time to look back and listen to the complaints of loved ones about poor health or to think about our own.
- Therefore, is it any wonder that today the mortality rate associated with damage to the blood vessels of the brain has increased significantly, and it is already diagnosed in those who are not even 40 years old.
Cerebrovascular accident
The process when blood moves through the vessels of the spinal cord and brain is called cerebral circulation.
Disruption of proper blood flow can occur, for example, in the following situations:
The patient has some kind of cerebral vascular pathology.
Such changes can occur if in the vessels:
- An inflection has occurred.
- A blood clot has formed;
- The clearance has decreased;
A sick citizen has a disruption of blood flow in the main and cerebral arteries.
Any disturbance in the proper movement of blood through the vessels of the brain is explained by the fact that there is a discrepancy between the amount of blood that is necessary for the proper functioning of the brain and the amount of blood that actually enters the brain.
If a patient has a cerebrovascular accident, he must seek advice and examination from the doctors listed below:
- Neurologist;
- Therapist;
- Angiosurgeon, that is, a surgeon who examines blood circulation in the brain;
- Cardiologist;
- Reanimatologist.
Cerebral circulation may be impaired in a patient for a number of reasons:
- High blood pressure (hypertension).
- Special plaques that form in the blood vessels of the brain. Such formations prevent blood from moving properly through these vessels.
If such plaques increase over time, they form a blood clot and then blood can no longer circulate through the affected vessel. And as a result of such blockage, a person may have a stroke. This damage to the blood vessels of the brain is called atherosclerosis in medicine.
- Various head injuries (bruises, concussions).
- Constant (chronic) fatigue.
Read a similar article about brain changes.
In adults
In adults, cerebral blood flow may be impaired in situations such as:
- The presence of osteochondrosis, in which compression of the vessels responsible for the proper functioning of the brain occurs.
- There are blood clots in the cerebral arteries that could appear after injury or surgery.
- The person has tumors in the neck or head.
In the elderly
In people of retirement age, the correct movement of blood through the vessels of the brain can most often be disrupted if they have a history of:
- Disease of the blood or organs that are responsible for the movement of blood;
- Heart problems;
- Inflammatory processes in blood vessels.
Prevention of the disease
This disease is much easier to prevent than to cure, especially if there are complications and concomitant diseases. Preventive measures are especially important for people who are at risk. The essence of preventive measures comes down to the following points:
- regular monitoring of blood pressure indicators;
- periodic monitoring of changes in blood composition;
- complete and categorical cessation of smoking;
- giving up or at least reducing alcohol consumption.
Maintaining these preventive measures is also extremely important for people who have already been diagnosed with PMN.
You need to be very careful about your health and not ignore the signals that your body sends. Any deviation from the norm requires medical consultation and detailed study if there are appropriate indications.
Features of cephalgia with impaired MV
In the initial stages of discirculatory encephalopathy, pain in the head is periodic. After a hard day at work, stress, physical exertion, a dull, minor headache appears. As the disease progresses, the discomfort in the head is accompanied by tinnitus, dizziness, and nausea.
In acute attacks of cerebral circulatory disorders, the symptoms of cephalgia are of a different nature. Pain syndrome occurs unexpectedly. Accompanied by tinnitus, dizziness, loss of coordination. Sometimes nausea appears, circles or zigzags float in the eyes. The patient experiences depression, disorientation in space, or, conversely, becomes emotionally excited.
A severe attack of cephalgia can result in fainting, convulsions, and paralysis of the limbs. When the patient regains consciousness, he falls into a deep sleep. In the following days he feels weakened and completely defeated. At first, such attacks occur rarely. Then the condition worsens, unpleasant attacks are repeated systematically.
Stages
The development of CNMK goes through 3 stages. At the initial stage, tissue damage is insignificant, the lesions are small in size. Properly selected treatment will correct the resulting pathology. Violations are found mainly in the emotional sphere and are usually attributed to overwork and excessive nervous tension.
A person quickly gets tired, becomes apathetic, irritable, absent-minded, whiny, impulsive, and forgetful. There is a decrease in performance, difficulties with the perception and processing of new information. Headache occurs periodically. After a good rest, all these signs disappear.
At the second stage, the symptoms worsen and become more vivid. The patient loses interest in work, in what previously fascinated him. A decrease in motivation leads to unproductive, monotonous useless work, the purpose of which cannot be explained by the patient himself. Memory and intelligence decrease. Bouts of inexplicable aggression appear. The patient experiences uncontrolled mouth movements, problems with fine motor skills, and slows down movements.
How to help during an attack
Poor blood circulation in the brain can lead to a stroke. During an exacerbation, it is important to competently provide assistance. This will avoid serious consequences and alleviate the suffering of the patient.
During an attack, it is necessary to measure blood pressure and count the pulse. If your heart function worsens, your blood pressure is high or very low, you need to call an ambulance. Offering any medications if they have not been prescribed by the attending doctor is strictly prohibited. It is not recommended to exceed the dosage of previously prescribed medications - this will not improve the situation, and can cause great harm.