Thanks to the work of the brain, the interaction of all organs and systems is carried out smoothly and without interruption. This is due to the functioning of neurons, which, through synaptic connections, supply nerve impulses to tissues. Brain diseases cause disruption of the entire body. Pathologies of this organ are characterized by any anomalies in which its tissues are affected from the inside or outside. As a result, the functioning of neurons is disrupted, which leads to a change in a person’s personality and character, and in severe cases, even death.
Causes
Early, prenatal damage to the central nervous system is always a consequence of pregnancy complications in the expectant mother. Oxygen starvation of the brain negatively affects the intellectual and physical development of the child. Its causes are protracted labor, severe infections suffered by the woman, and premature detachment of the uterine placenta.
Acquired organic brain lesions will have other causes:
- traumatic injuries of the skull, also with penetration into soft tissues, most often transport accidents and domestic injuries;
- infections - bacterial, viral nature, for example, herpetic meningitis, staphylococcal arachnoiditis, less often lesions due to HIV infection;
- various intoxications - abuse of alcohol, tobacco products, damage to the central nervous system due to uncontrolled use of medications, poisoning with mushrooms, metal salts;
- vascular pathologies – up to 2/3 of cases of visits are due to conditions after a stroke of hemorrhagic or severe ischemic origin;
- neoplasms - tumors provoke increased pressure on brain structures, with their deformation and functional impairment;
- demyelinating conditions - the formation of foci without a myelin sheath near the fibers of the central nervous system, often the basis for the development of multiple sclerosis;
- neurodegenerative pathologies - for example, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's syndrome, with a steadily progressing disorder.
Differential diagnosis and identification of causes - infectious lesions have led to organic defects in the central nervous system, or they are the consequences of a penetrating injury to the structures of the skull, the prerogative of the doctor.
Focal symptoms
Let's list the main ones:
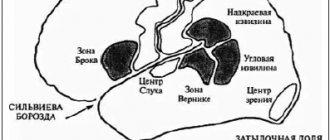
- If the frontal lobe is affected, the eye muscles work poorly, the sense of smell is impaired, and problems with speech appear.
- Parietal lobe. Sensitivity worsens, it is more difficult for the patient to perform meaningful actions, and convulsions often occur.
- Temporal lobe. Taste sensations worsen, hallucinations appear, and emotionality increases.
- Occipital lobe. Vision deteriorates until blindness occurs, and coordination of movements is impaired. The patient becomes delirious, and with such attacks convulsions begin.
Infectious lesions can be eliminated with the use of antibiotics . If the cause is a tumor, it will have to be removed.
Symptoms
It takes a certain period of time for the formation of an organic lesion of the central nervous system. Initially, a person experiences sensations from the disease, which serves as a prerequisite for the development of complications from the central nervous system. Discomfort and pain gradually appear in different parts of the head, dizziness and nausea persist. Against this background, a disorder of consciousness occurs - fainting.
Gradually, CNS depression increases. Symptoms of neurological deficit intensify - a constant feeling of fatigue, passivity, depression. Disturbed sleep and ability to work. When large areas of the central nervous system are involved in the pathological process, signs of disruptions in mental activity appear and memory suffers. Episodes of emotional instability, hysteria, and excessive anxiety appear more and more often.
For example, organic cerebral insufficiency, steadily increasing over decades, leads a person to disability - the inability to self-care. The patient degenerates from mild memory impairment and absent-mindedness to complete dementia and insanity. That is why a preventive medical examination and timely consultation with a neurologist are so important.
Statistical report
In the general group of all intracranial primary tumors, cerebral hemangioblastomas (CHBs) account for 1%-2.5%, and more often (85%) they are diagnosed in the cerebellar hemispheres. The prognosis after complete (!) surgical removal of a tumor with a sporadic occurrence scenario is positive, they do not recur .
But in 25% of cases, the neoplasm is detected as a manifestation of a hereditary disease - Hippel-Lindau disease. Cerebral tumor associated with this disease often has a poor prognosis. In patients with such a genetic pathology, the tumor process can resurface even after complete resection, and not necessarily in the same place; it can appear in any other part of the central nervous system.
The greatest number of cases with HGM is observed in men, who suffer from them 1.5-2 times more often than women. The peak age range when lesions are detected in patients is 40-50 years. For the first time, a neoplasm combined with Hippel-Lindau disease appears in adolescence and young adulthood (up to 30 years).
Hemangioblastomas are characterized by slow growth and benign biological behavior. However, sometimes (rarely) they are complicated by spontaneous significant hemorrhages in the posterior cranial fossa. Massive hemorrhages usually occur with large tumor sizes (more than 1.5 cm).
Any hemangioblastoma in the brain is a serious problem that requires timely detection and treatment. In every patient, the tumor becomes the cause of progressive neurological deficit and a non-stop decline in quality of life. Mortality is not excluded. Unfortunately, this diagnosis cannot be treated conservatively. The only chance for the patient to survive and recover is purely neurosurgical intervention.
Classification
In direct dependence on the mechanism and etiology of the formations, specialists divide organic lesions of the central nervous system in adult patients and children into the following types:
By time of appearance:
- congenital – formed in the baby during the woman’s pregnancy;
- acquired - after the birth of a person.
By etiology:
- hypoxic-ischemic lesions of the central nervous system - due to poor blood supply to the brain, foci are created in tissues with oxygen deficiency;
- post-traumatic – consequences of birth or domestic traumatic brain injury;
- residual organic lesions of the central nervous system - residual defects of brain structures, for example, after drug poisoning or chronic malnutrition;
- hypoxic lesions of the central nervous system - of vascular origin, for example, due to aneurysms or atherosclerotic plaques in the bloodstream, blood flow is disrupted and organ structures do not receive the required amount of nutrients;
- brain tumor – even with a benign formation, pressure is observed on the cells of neighboring tissues, which leads to their trauma and disruption of functioning.
By age criterion:
- organic brain damage in children - due to disturbances in intrauterine formation or suffered negative influences in infancy;
- CNS lesions in adults – vascular, metabolic, post-traumatic.
The specialist’s diagnosis will indicate both the cause that led to structural damage to the brain and its consequences - disorders in the intellectual/cognitive sphere.
Development of alcoholic encephalopathy
Against the background of alcohol withdrawal (hangover), especially at the time of alcoholic psychosis (delirium), alcoholic encephalopathy develops especially rapidly. Changes in a person can be observed within a few hours. Therefore, we often encounter a situation where people around us are surprised to observe a sharp change in the behavior and condition of the patient.
Alcoholic encephalopathy Wernicke-Korsokov can develop simultaneously in a severe and acute form. However, most often ophthalmoplegia and ataxia precede the onset of the disease several days, sometimes 10 or 20 days, before the onset of the main symptoms.
Alcoholic encephalopathy Wernicke-Korsokov is very often accompanied by other diseases. Most often this is due to the toxic effects of alcohol not only on the brain, but on the entire body as a whole. For example, in one variation or another, patients suffer from polyneuropathy, impaired liver function, heart disease, genital diseases, gastrointestinal diseases, endocrine and other disorders. The clinical picture may be supplemented by the manifestation of spastic spinal ataxia.
Consequences of alcoholic encephalopathy
In the chronic stage of the disease, a person ceases to recognize odors. This is due to toxic damage to the diencephalic region of the brain.
Cardiovascular changes occur, tachycardia, shortness of breath on exertion, and postural hypotension appear. However, only minor changes may occur on the ECG. Quite often such people die suddenly. The cause of their death is often determined to be cardiovascular collapse. However, having become more fully acquainted with its history, such a judgment will be fundamentally incorrect. The true cause of such deaths is the sudden development of alcoholic encephalopathy, a disorder of brain tissue. The tissue of the area of the brain that is responsible for regulating cardiovascular functions is damaged.
It has been proven that with Wernicke-Korsokov alcoholic encephalopathy, a fairly high cardiac output occurs, which does not correspond to the volume of oxygen consumed. Fainting and motor impairment may occur. This is a consequence of an imbalance in the functions of the peripheral nervous system, which are usually more specific to a defect in sensory regulation.
Can encephalopathy be prevented?
Yes, alcoholic encephalopathy is preventable. First of all, it is necessary to avoid excessive alcohol consumption or eliminate it altogether. In this case, we recommend undergoing special anti-alcohol therapy. You should also exclude from use the main toxic substances that cause the formation of toxic encephalopathy.
Toxic substances causing toxic encephalopathy include:
- Drugs,
- IQOS,
- Various types of hallucinogens,
- Other psychoactive substances.
A healthy lifestyle will significantly reduce risk factors for brain diseases.
Prognosis for the treatment of alcoholic and toxic encephalopathy
The prognosis depends on the cause and extent of the disease. Most cases are reversible and can be cured. However, one should take into account the fact that any encephalopathy can be fatal. Therefore, treatment of alcoholic and toxic encephalopathy is mandatory.
The therapeutic effect in our clinic is achieved by introducing the latest technologies of restorative medicine. Treatment of brain diseases will improve your condition and improve your quality of life.
Diagnostics
Recognizing an organic lesion in the central nervous system is not easy. After all, this is not the presence of some kind of formation in the tissues - for example, a focus of cancer. Changes, as a rule, affect the entire organ or a significant part of it - the primary disease gives its complications. Specialists establish the relationship between the patient’s complaints and the objective changes they obtained using neuroimaging methods.
Magnetic resonance imaging has proven itself to be excellent - in pictures in different projections you can carefully examine lesions of the brain parenchyma, choroid plexuses, as well as cranial nerves and skull bones. However, a more accessible study is computed tomography.
There are different options for examining vascular lesions - angiography, rheoencephalography, or ultrasound. As needed, contrast solutions are introduced into the vein, which make the image on the monitor screen clearer - to understand the nature and area of the organic lesion.
Laboratory tests help to understand the nature of disorders in the central nervous system - blood tests for biochemical parameters, hemoglobin and red blood cell concentration, as well as tumor markers and hormonal levels. It is in the totality of information - a neuralgic examination and examination results that the doctor will be able to carry out a differential diagnosis of damage to the central nervous system in the patient.
Treatment tactics
Doctors will, of course, place the main emphasis of therapy for organic brain damage on the pathology that is at the root of the disorder. All large tumors and consequences of brain injuries are subject to surgical correction.
Medications:
- to improve blood flow;
- antioxidants;
- statins;
- antiplatelet agents;
- vitamins;
- sedatives;
- anticonvulsant medications.
Complexes of physiotherapeutic procedures and physical therapy are relevant, especially with residual damage to the central nervous system, as well as proper nutrition and giving up bad habits. The diet should be dominated by dishes with fresh vegetables and fruits, herbs and healthy microelements.
During the rehabilitation period, psychosocial treatment is important - working with a psychotherapist not only for the patient himself, but also for his family members. In case of severe organic brain damage, the solution seems to be to send the victim to a specialized institution with round-the-clock medical supervision.
Prevention
Since, as such, there is no single cause for an organic disease of the nervous system, its occurrence can only be prevented by maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Therefore, experts include the following among measures to prevent central nervous system disorders:
- avoid severe psycho-emotional shocks and intellectual stress;
- prevention of traumatic brain injuries;
- timely treatment of cardiovascular pathologies;
- for chronic diseases of brain structures - courses of vascular and nootropic drugs;
- refusal to abuse tobacco and alcohol products.
Compliance with the National Calendar of Preventive Vaccinations in children, as well as in adults, is also a specific measure of protection against neuroinfections, as a provocateur of damage to the central nervous system.
Of course, diet therapy for health is an essential condition. It is better to give preference to freshly prepared dishes from vegetables, lean meat and fish, fruits and dairy products. They contain a huge amount of vitamins and microelements for the functioning of the central nervous system.
Features of brain diseases
Human brain diseases include a fairly large group, which are often associated with damage to the nervous system. Depending on the source of development, these ailments are divided into:
- infectious;
- immune;
- parasitic;
- genetic pathologies;
- vascular;
- injuries;
- neoplasms.
The first include tuberculoma with neurosyphilis and meningitis. Immune pathologies include multiple sclerosis. A disease caused by parasites is cysticercosis. Recklinghausen's disease is a genetic disorder. Vascular diseases of the brain include aneurysm and stroke as a consequence. Injuries can be of different types: bruises with blows, bullet wounds. Neoplasms can be benign or malignant.
Consequences and prognosis
Since damage to the central nervous system can have varying degrees of severity, specialists will give a prognosis taking this factor into account. Thus, residual phenomena are always long-term consequences of external influences on the brain, so it will be possible to judge the depth of changes in intelligence only after a comprehensive medical examination and drug rehabilitation.
For example, in the case of ischemic damage to the central nervous system, recovery can be achieved in 2/3 of cases - by introducing modern medications in the form of injections and tablets. Whereas doctors will fight mental disorders with training, antipsychotics, and hypnosis.
People with decreased intelligence due to demyelinating damage to the central nervous system require daily outside help - multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer's disease are difficult to correct and are steadily progressing. As well as the consequences of injuries and neuroinfections such as epilepsy. For social support and rehabilitation, improving the quality of life with dementia, people are assigned a disability group with financial assistance from the state.